Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Biofilm Formation on Endotracheal and Tracheostomy Tubing: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Culture Data and Sampling Method
- First Published: 07 July 2025
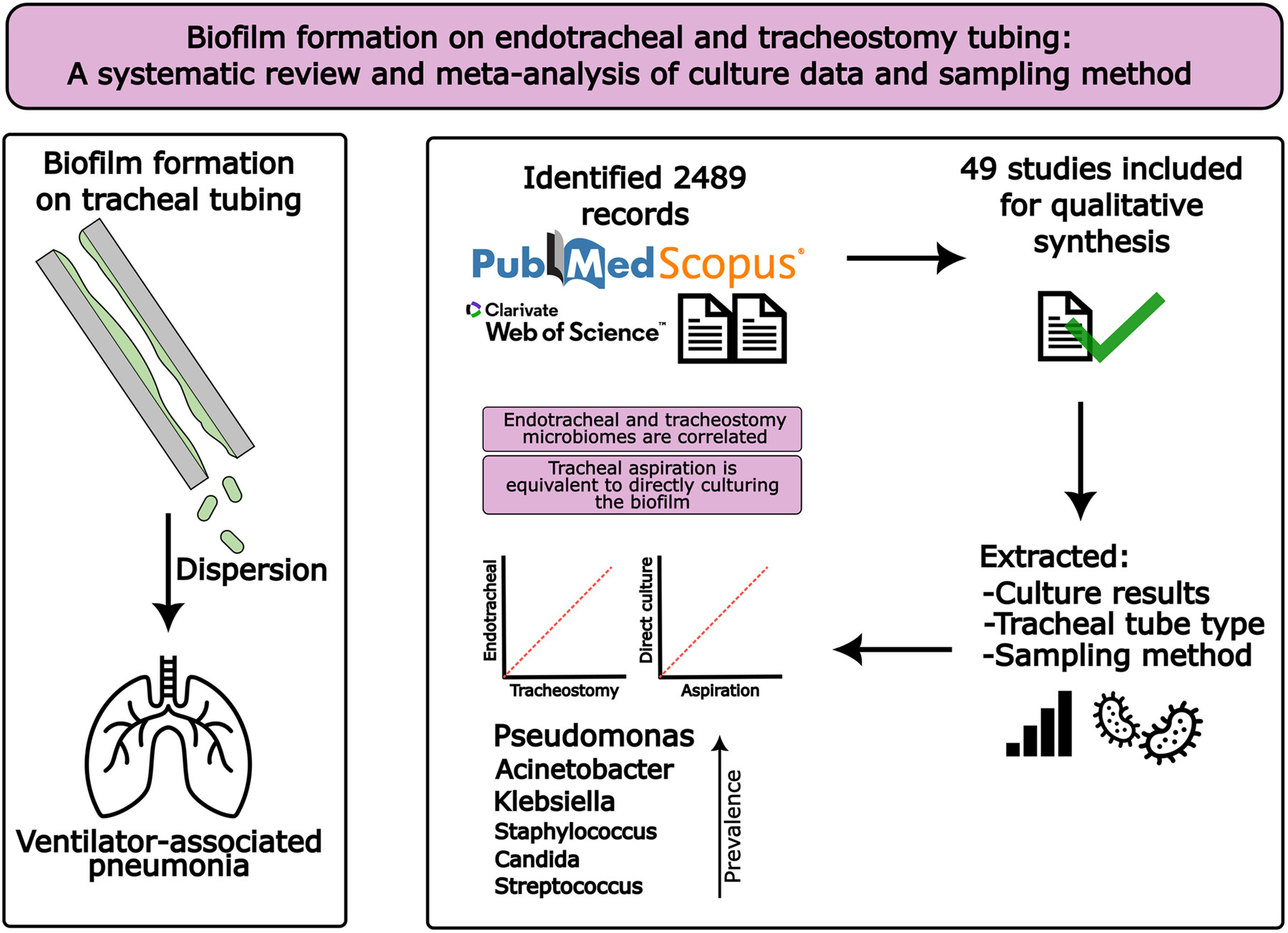
This systematic review provides an up-to-date profile of tracheostomy and endotracheal tube microbiomes, with Pseudomonas emerging as the most prevalent genus overall. Microbial profiles were equivalent whether identified by tracheal aspiration or direct culture, supporting aspiration as a reliable, noninvasive approach for biofilm assessment without requiring extubation.
REVIEW
Analyzing the Challenges and Opportunities Associated With Harnessing New Antibiotics From the Fungal Microbiome
- First Published: 23 July 2025
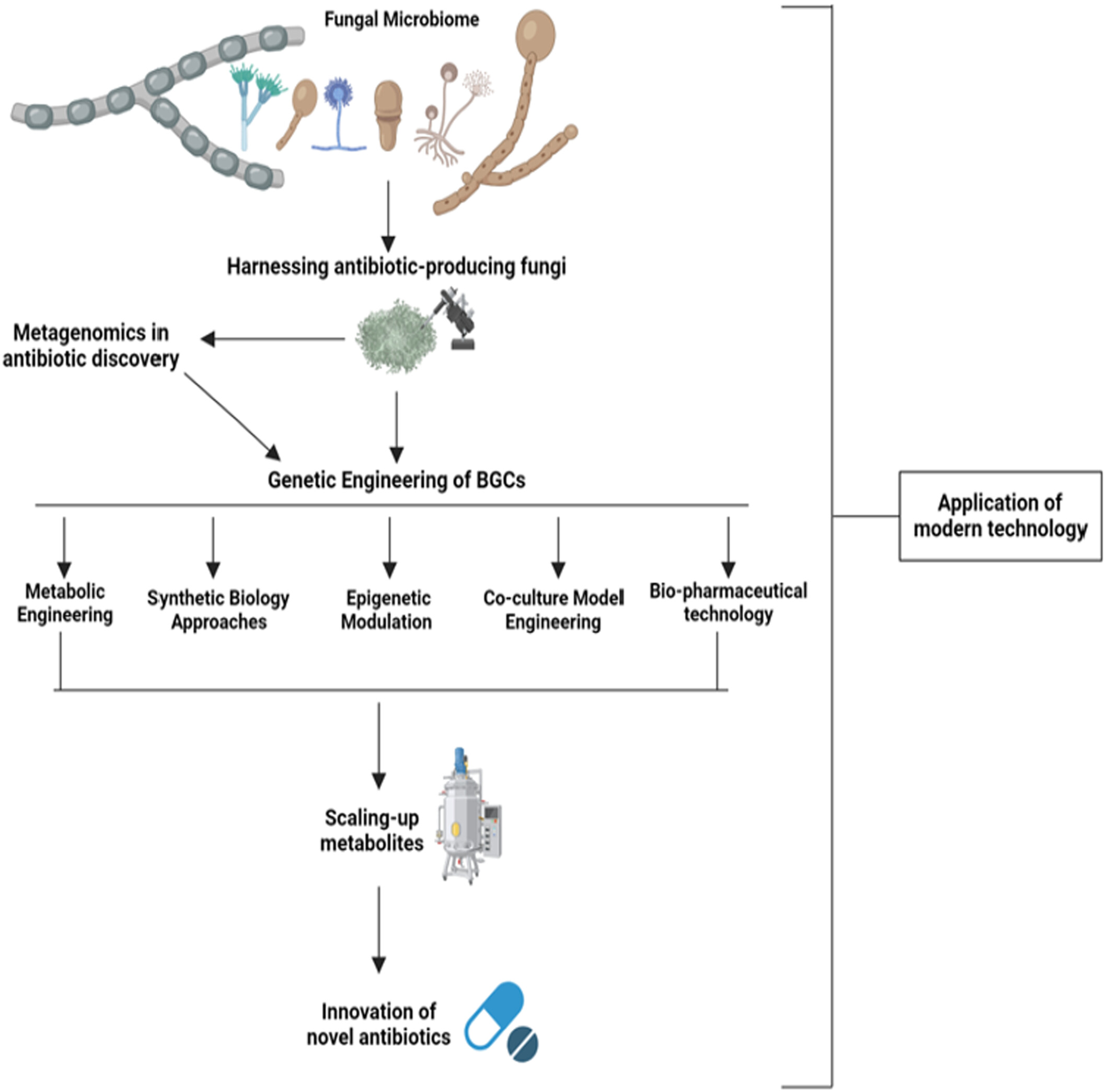
Graphical abstract illustrating the multifaceted approach to harnessing fungal microbiome diversity for antibiotic discovery. Key elements include historical insights, modern genomic tools, and innovative biotechnological strategies for isolating and enhancing fungal antibiotic production. Highlighted are fungal communication networks and advanced fermentation techniques aimed at scaling up production and improving antibiotic yields.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
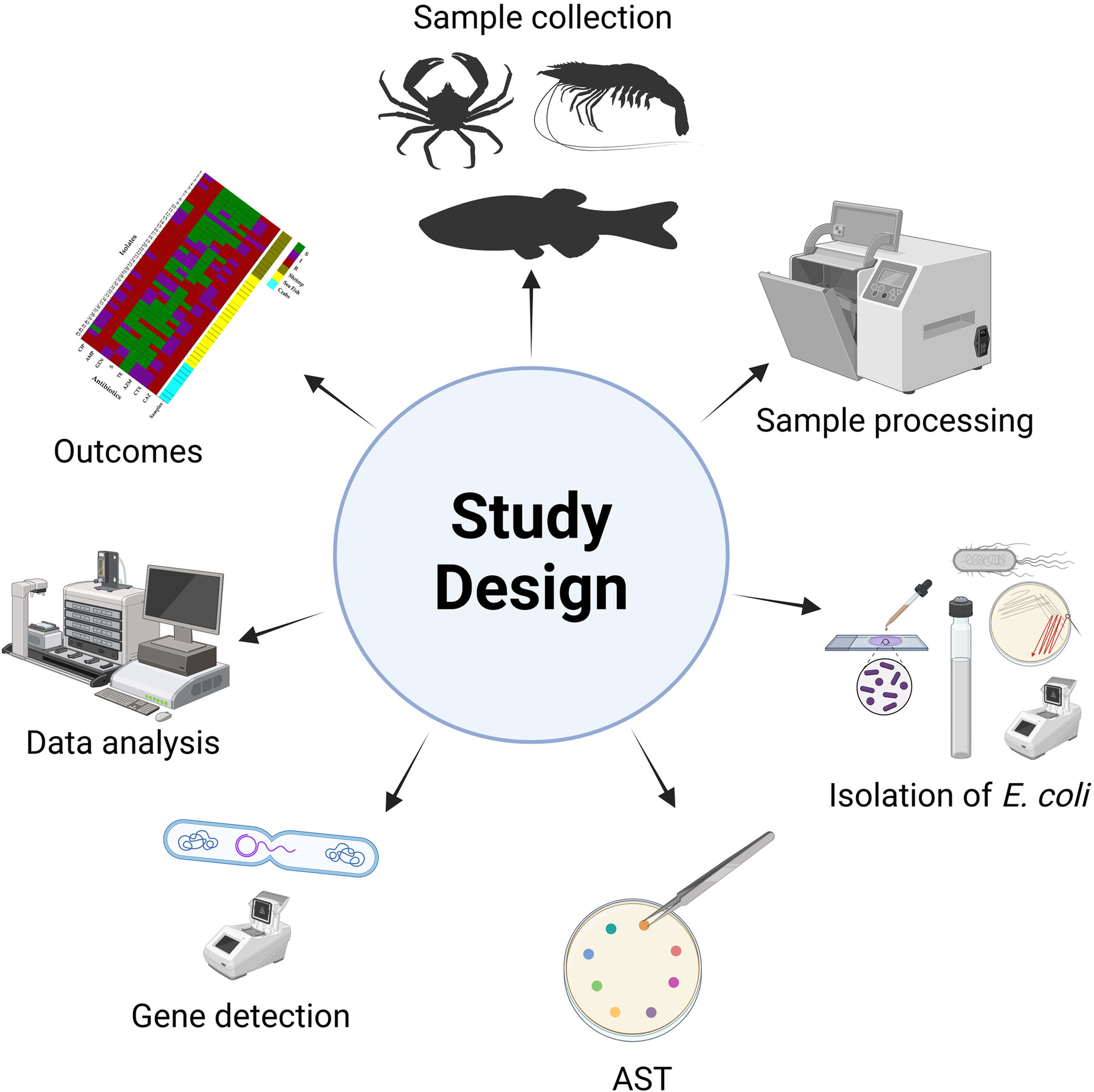
Detection and Characterization of Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli in Raw Seafood From the Coastal Area of Bangladesh
- First Published: 27 June 2025
Evaluating Effects of Antibiotics Across Preclinical Models of the Human Gastrointestinal Microbiota
- First Published: 16 July 2025
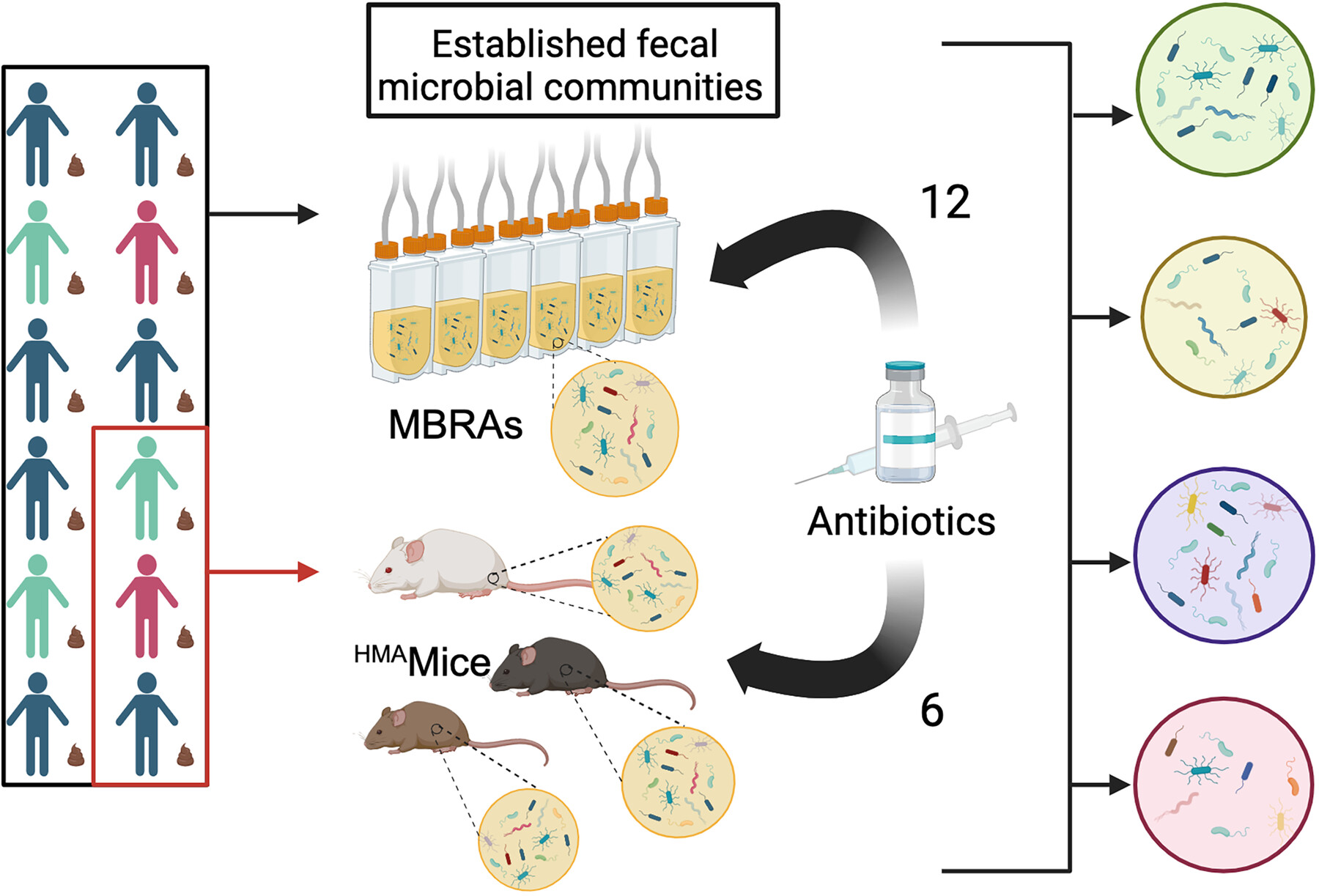
We compared microbiota changes following antibiotic treatment in two preclinical models of the human GI microbiota, minibioreactor arrays (MBRAs) and human microbiota associated mice (HMAmice). MBRAs and HMAmice were colonized with feces from 12 or 3 healthy humans, respectively, before treatment with each of 12 or 6 antibiotics.
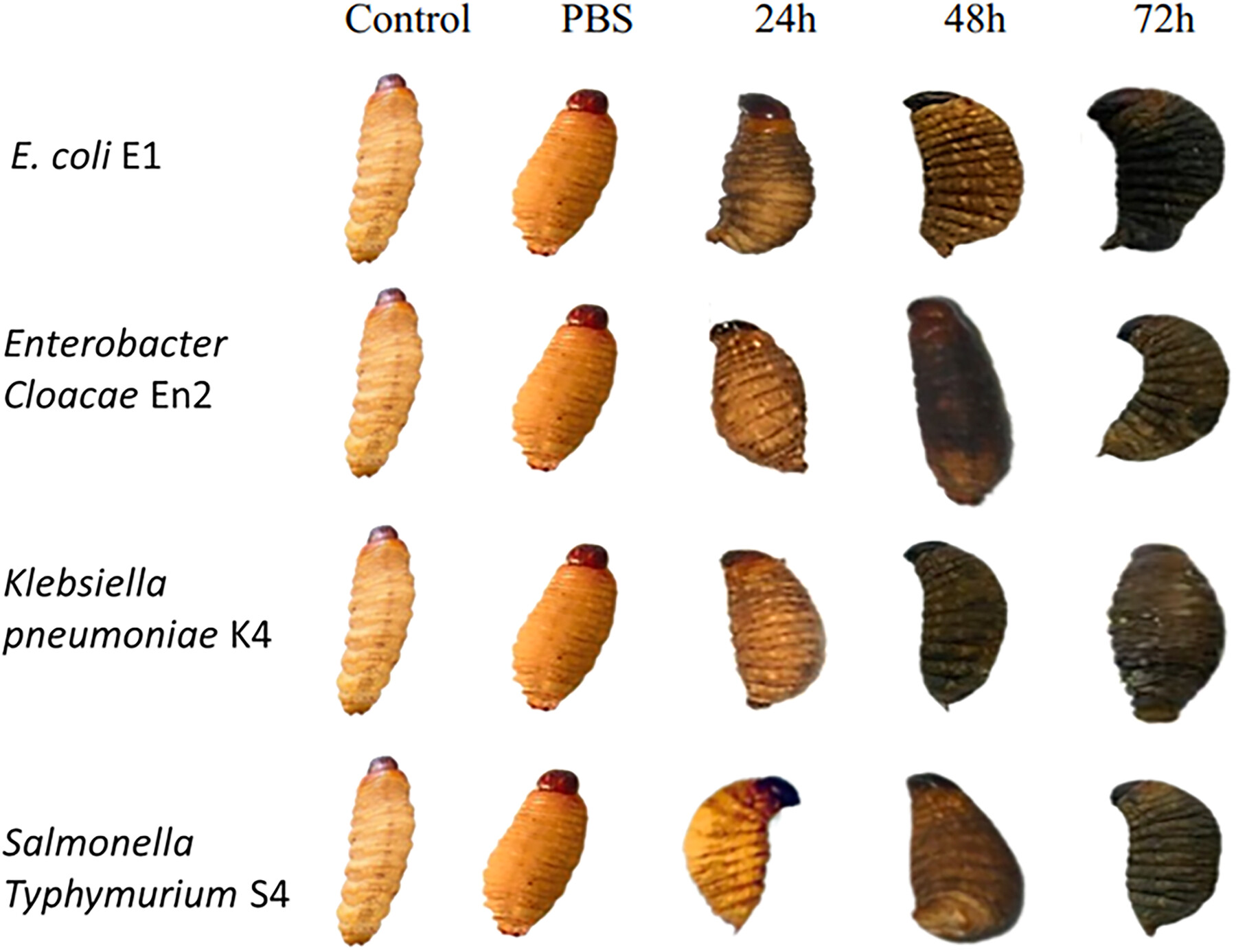
Novel Animal Model of Enterobacteria Pathogenicity, Virulence, and Amoxicillin—Biosurfactant Synergic Using Nsombé (Rhynchophorus phoenicis Larvae)
- First Published: 30 June 2025
Pseudomonas syringae Lipopolysaccharide Synthesis Gene wbpL Displays Heterogeneous Expression Within In Vitro and In Planta Populations
- First Published: 22 July 2025
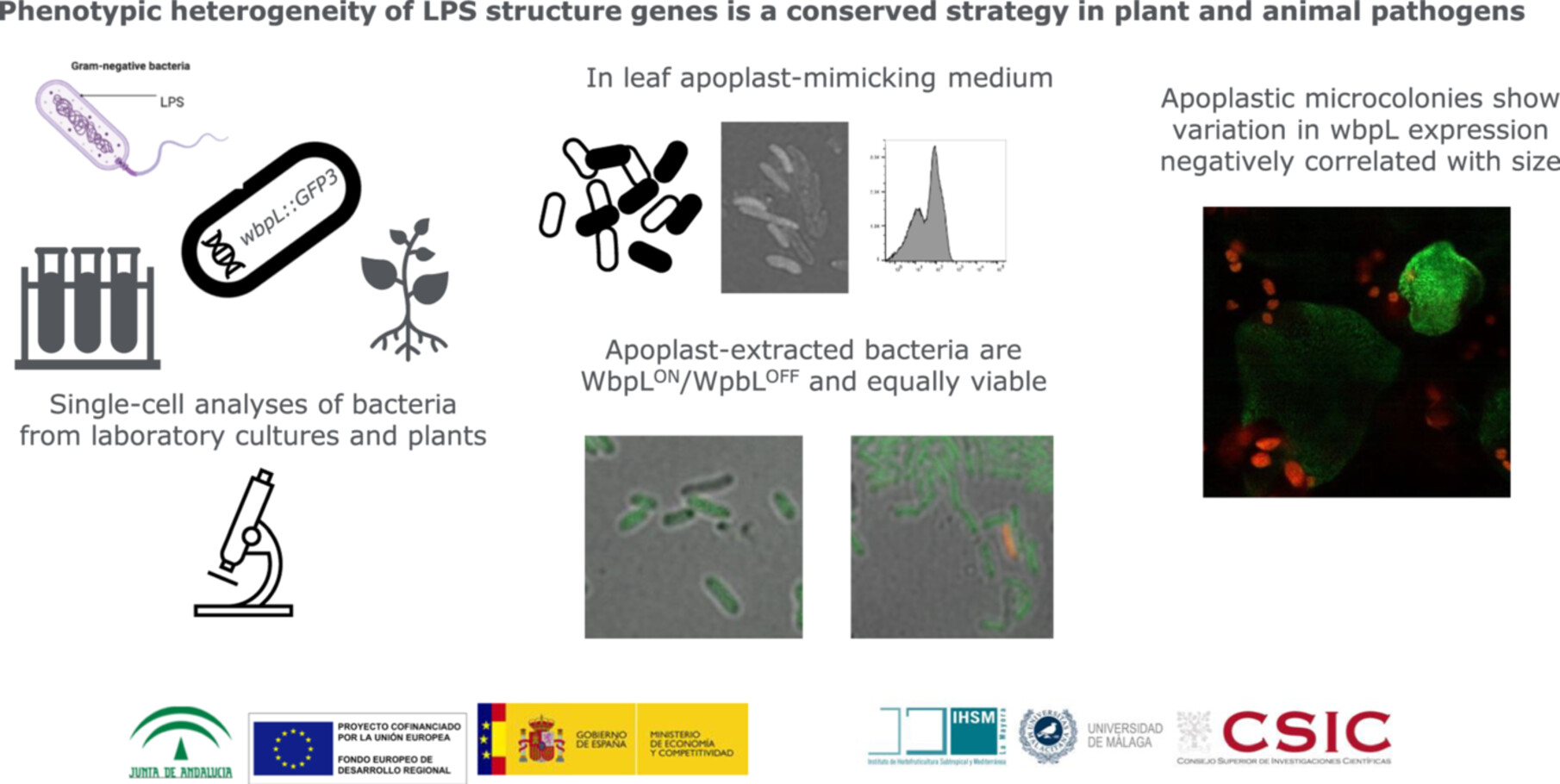
Genetically identical bacteria in the same environment sometimes behave differently. This happens for the expression of wbpL, a gene of plant pathogenic Pseudomonas syringae that shapes the bacterial surface and is important for infection and immunity. whose expression varies among individual bacteria, with ON/OFF bacteria coexisting with similar viability. In planta, the smaller size of microcolonies with higher wbpL expression suggests wbpL expression might slow growth or trigger stronger defenses. Phenotypic heterogeneity of lipopolysaccharide genes is a common strategy for plant and animal pathogens.
Genotypic Analysis of Candida tropicalis Clinical Isolates From Korea via Multilocus Sequence Typing
- First Published: 29 June 2025
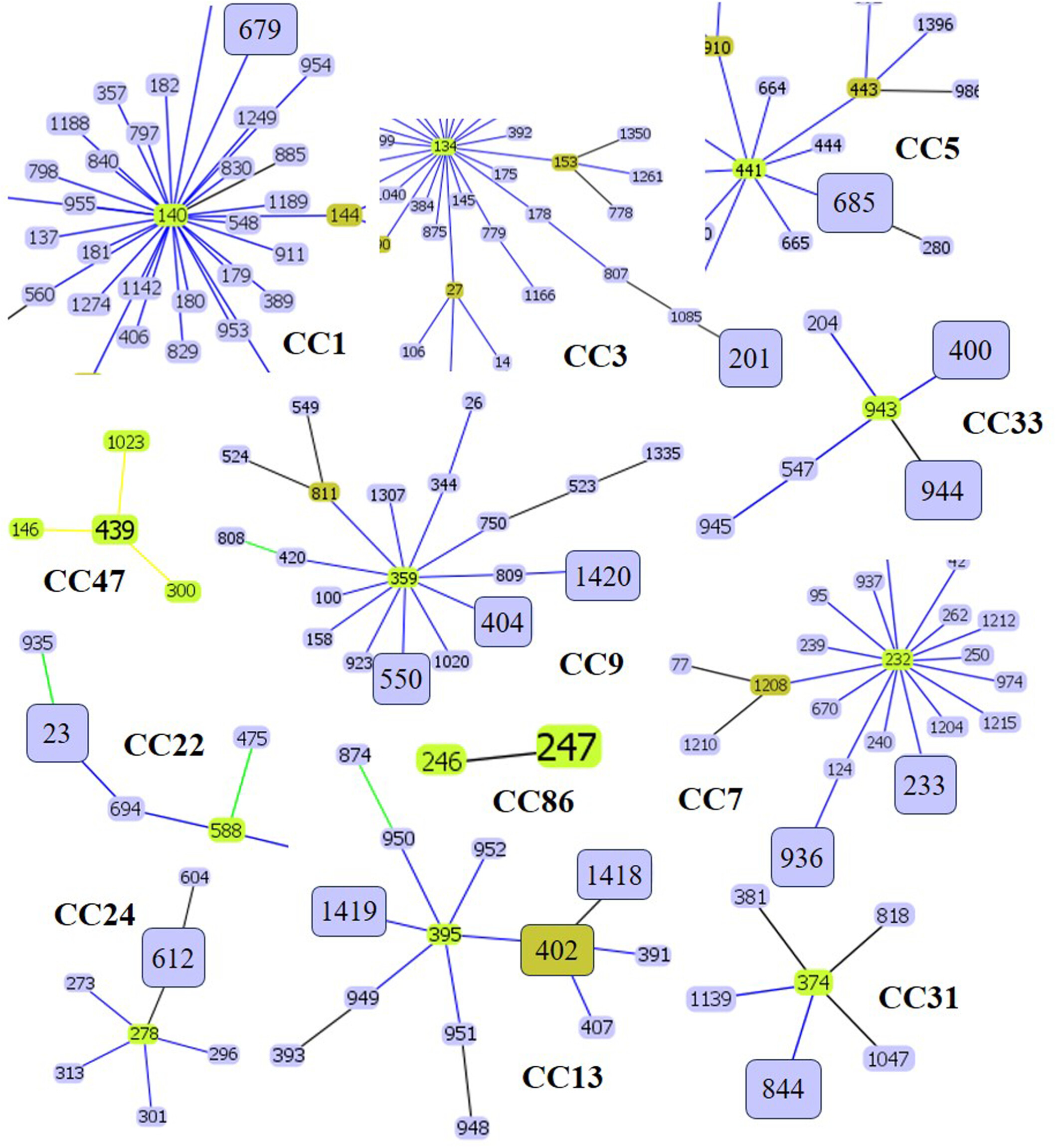
Multilocus sequence typing of 34 Candida tropicalis clinical isolates from Korea revealed three novel sequence types and evidence of genetic recombination. These findings highlight the ongoing genetic diversification and underscore the need for integrated genomic surveillance of emerging antifungal-resistant strains.
Evaluation of Six Commercial and Noncommercial Colistin Resistance Diagnostics
- First Published: 29 June 2025
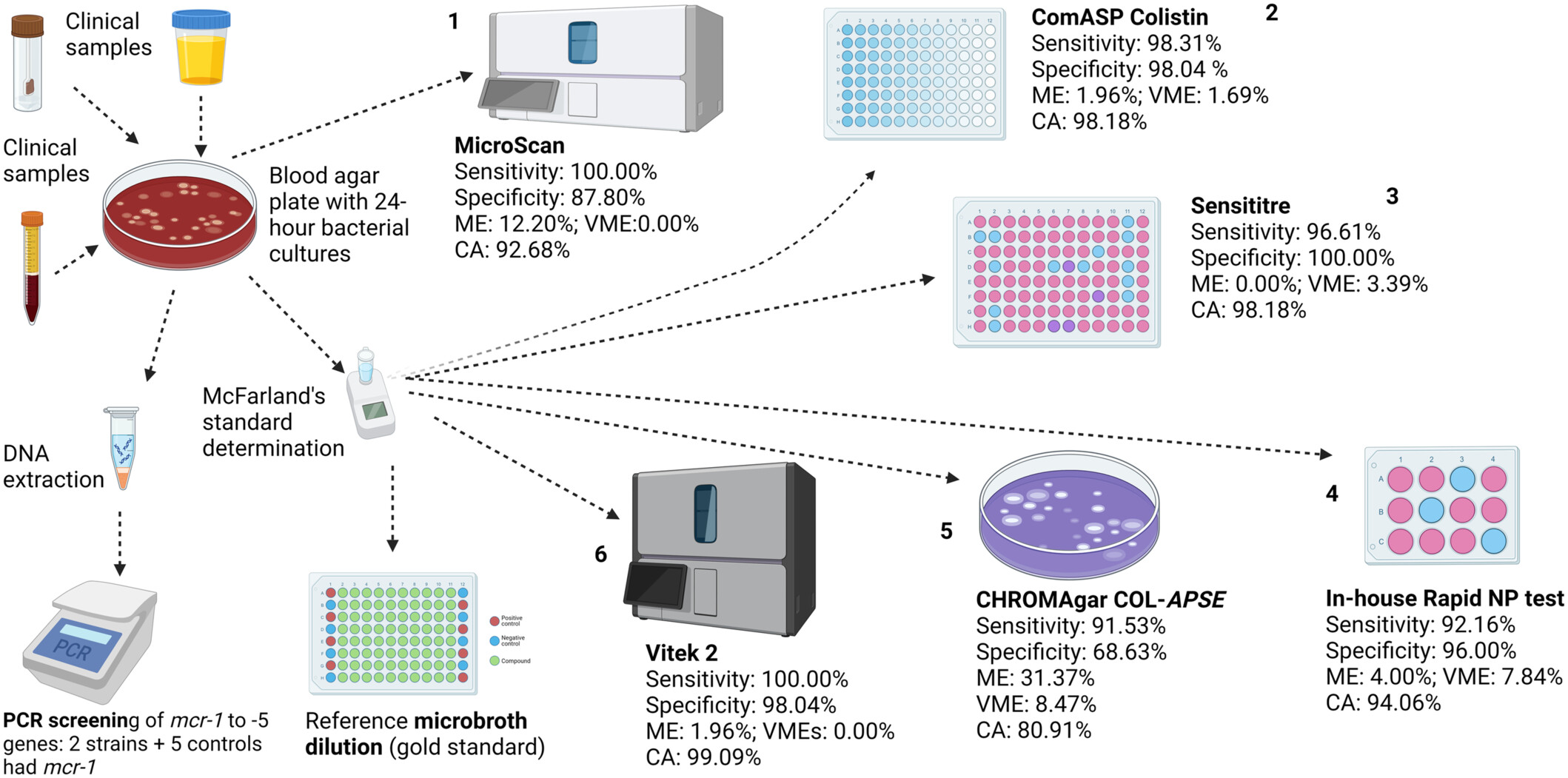
Colistin-resistance diagnostics that are efficient, affordable, easy to use, with quicker turnaround times are important for surveillance and control of resistance. The in-house Rapid NP test has very major errors but is both affordable and fast, with 92.16% sensitivity and 96.00% specificity. In descending order, the Vitek 2, ComASP colistin, Sensititre, and MicroScan had high efficiencies and a turnaround time of 18–24 h. CHROMAgar COL-APSE was more efficient in A. baumannii than Enterobacterales, with significant rates of major and very major errors.
REVIEW
Shaping Plant Growth Beneath the Soil: A Theoretical Exploration of Fungal Endophyte's Role as Plant Growth-Promoting Agents
- First Published: 02 July 2025
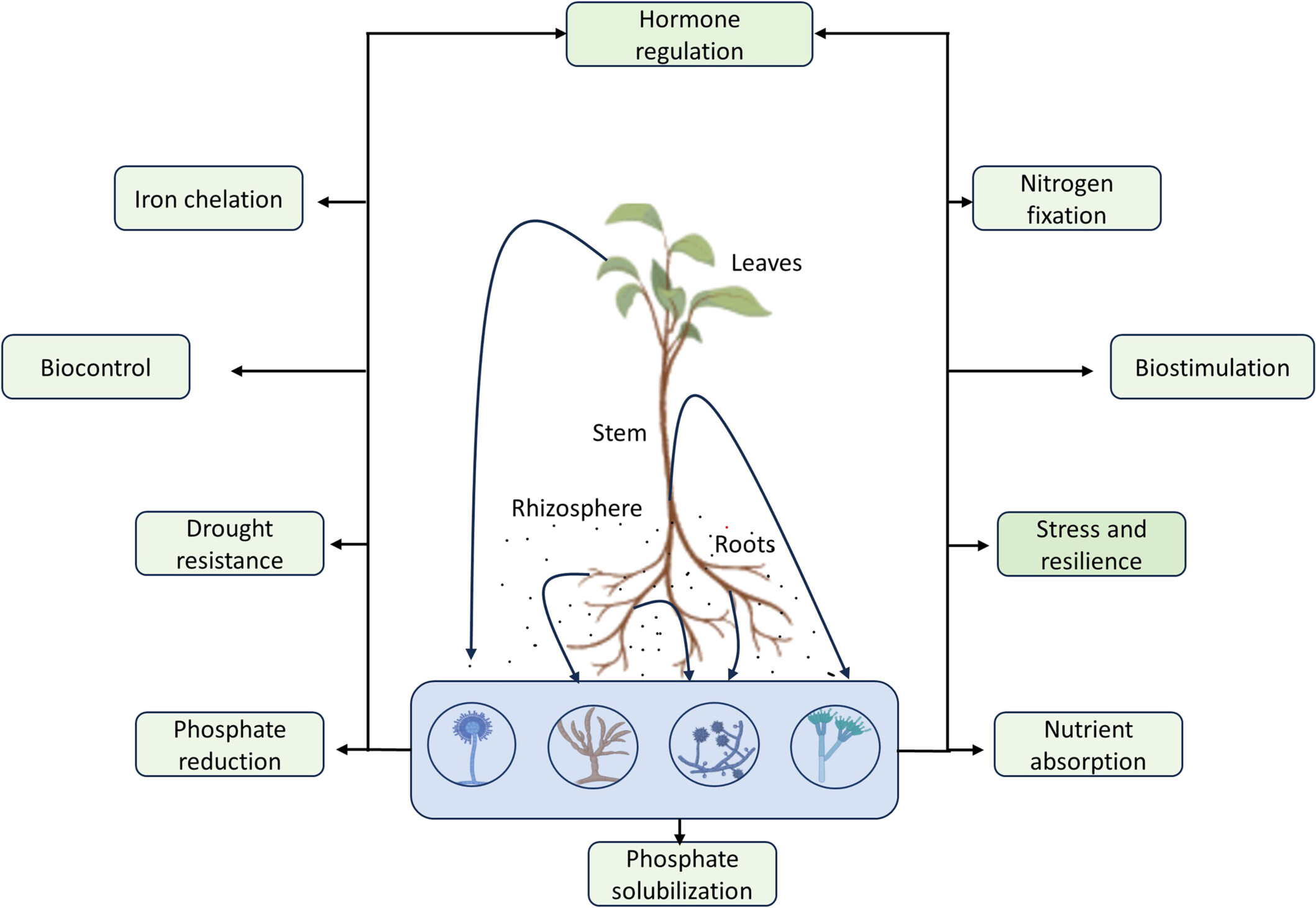
A schematic representation depicting various mechanisms of plant growth promotion by fungal endophytes present in different parts of the plant. Fungal endophytes are present in various parts of the plant, including leaves, stems, and most abundantly in roots. In each of these niches, they promote plant growth through several mechanisms, such as nutrient absorption, hormonal stimulation, nitrogen fixation, iron uptake, and phosphate solubilization. Additionally, they aid in biostimulation and biocontrol mechanisms.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
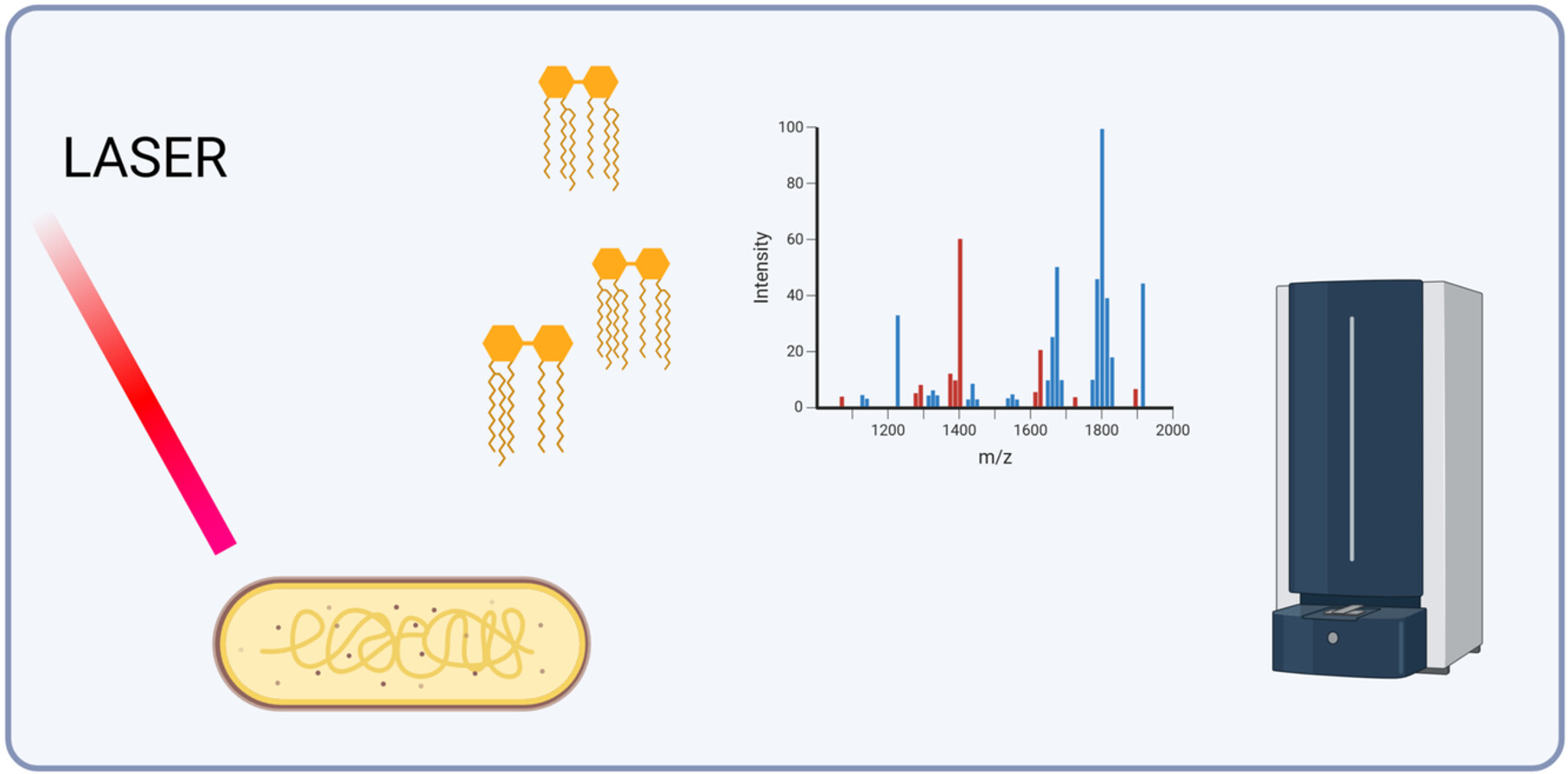
Discrimination of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Klebsiella quasipneumoniae by MALDI-TOF Mass Spectrometry Coupled With Machine Learning
- First Published: 15 July 2025
REVIEW
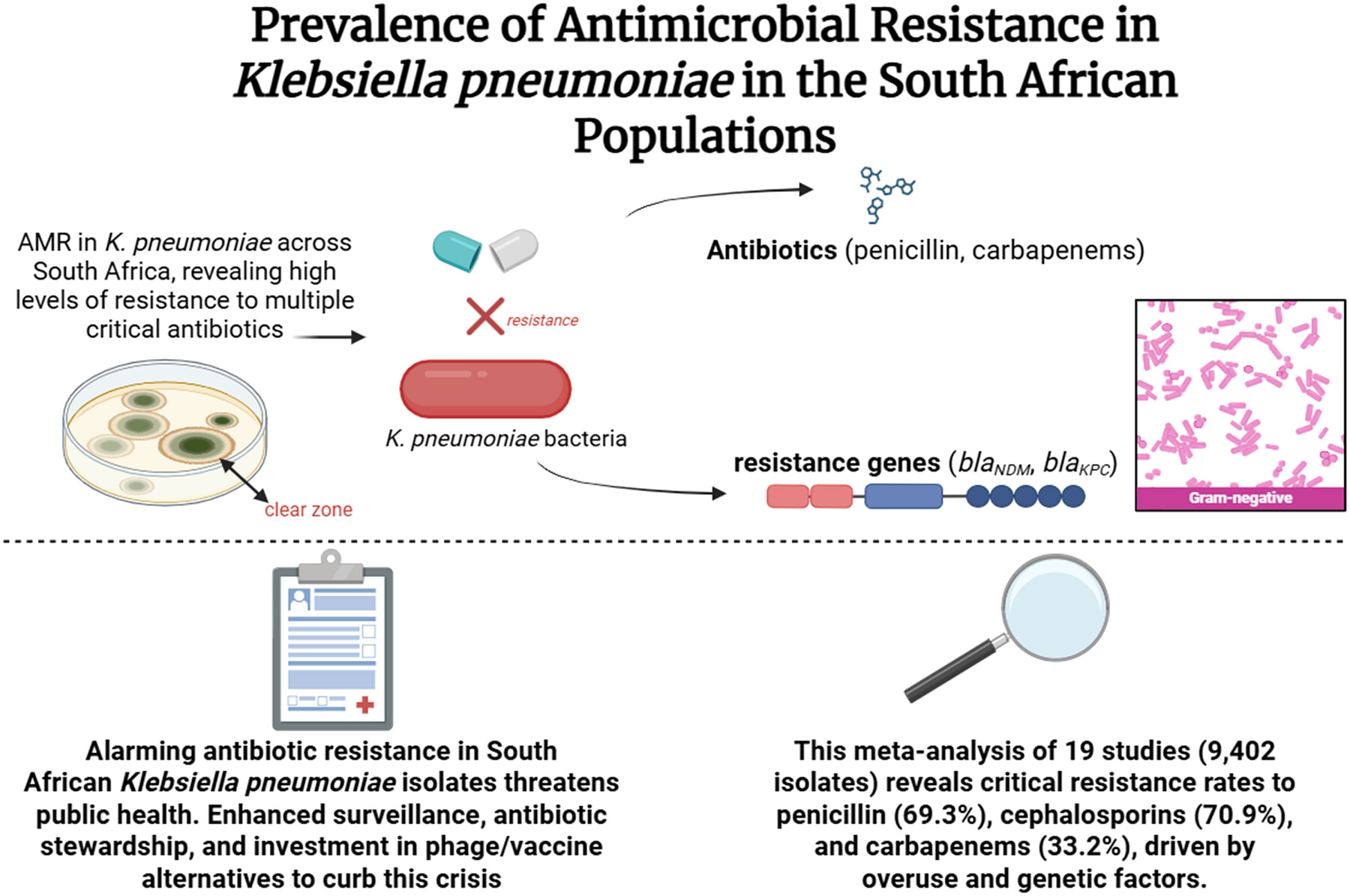
Prevalence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Klebsiella pneumoniae in the South African Populations: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Surveillance Studies
- First Published: 24 July 2025
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
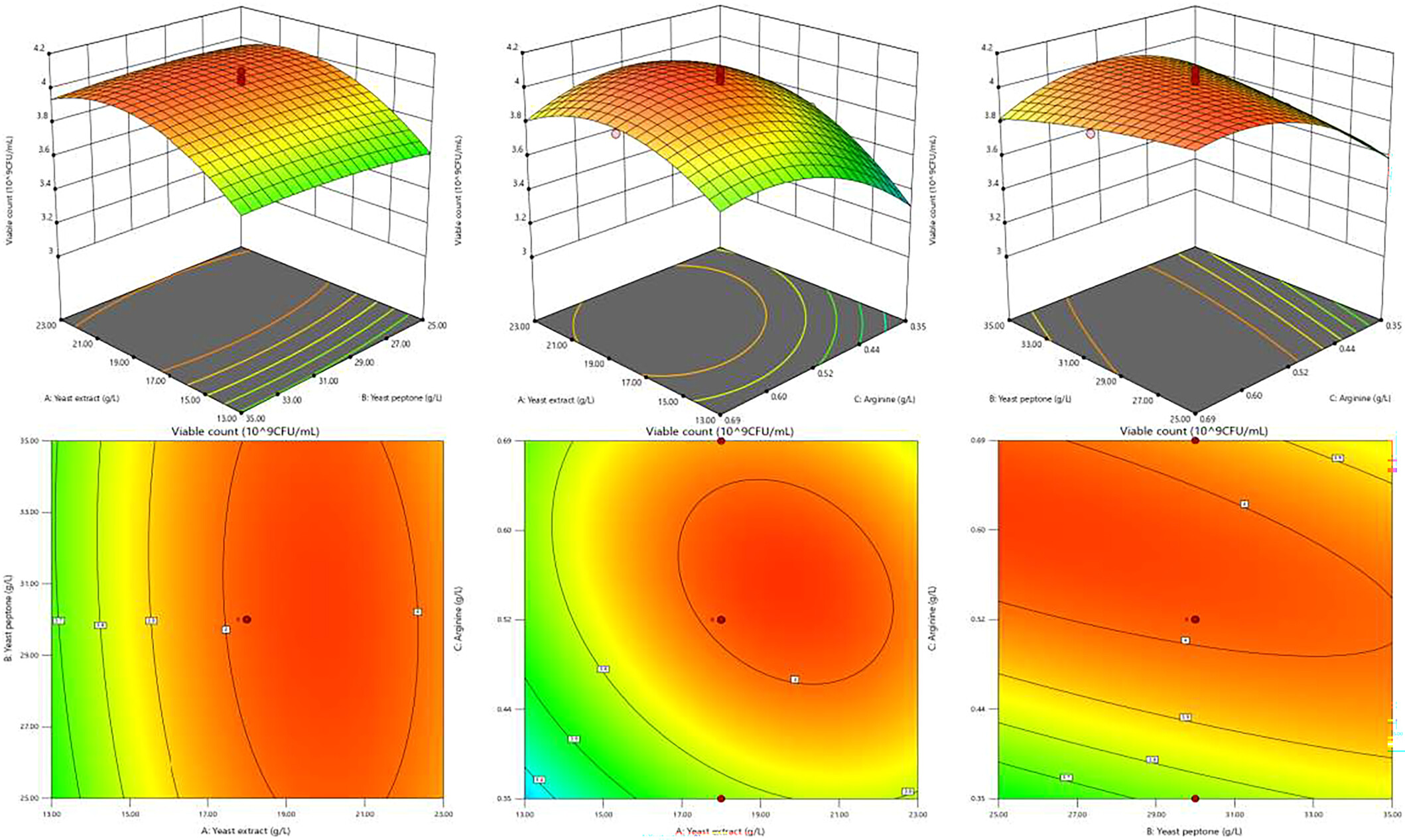
Optimization of Medium Composition for High Cell Density Culture of Bifidobacterium longum HSBL001 Using Response Surface Methodology
- First Published: 02 July 2025