Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover Image
- First Published: 25 June 2024

Cover caption: The cover image is based on the Research Article Root nodules of red alder (Alnus rubra) and Sitka alder (Alnus viridis ssp. sinuata) are inhabited by taxonomically diverse cultivable microbial endophytes by Robyn Dove et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/mbo3.1422.
Image credit to Felisha Pooler.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Utilizing novel Escherichia coli-specific conserved signature proteins for enhanced monitoring of recreational water quality
- First Published: 29 April 2024
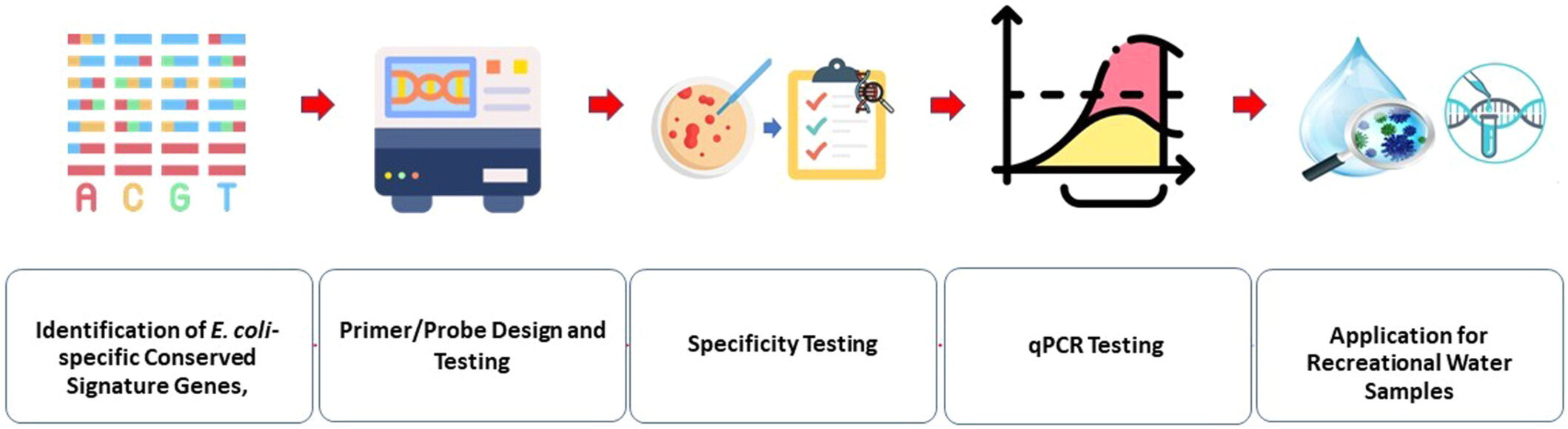
This paper explores the application of a novel DNA sequence type, specifically conserved signature genes encoding conserved signature proteins (CSPs), for bacterial identification. Although our focus is on the identification of Escherichia coli, the same principle can be extended to identify other taxa using their respective CSPs.
Turbidimetric bioassays: A solution to antimicrobial activity detection in asymptomatic bacteriuria isolates against uropathogenic Escherichia coli
- First Published: 06 May 2024
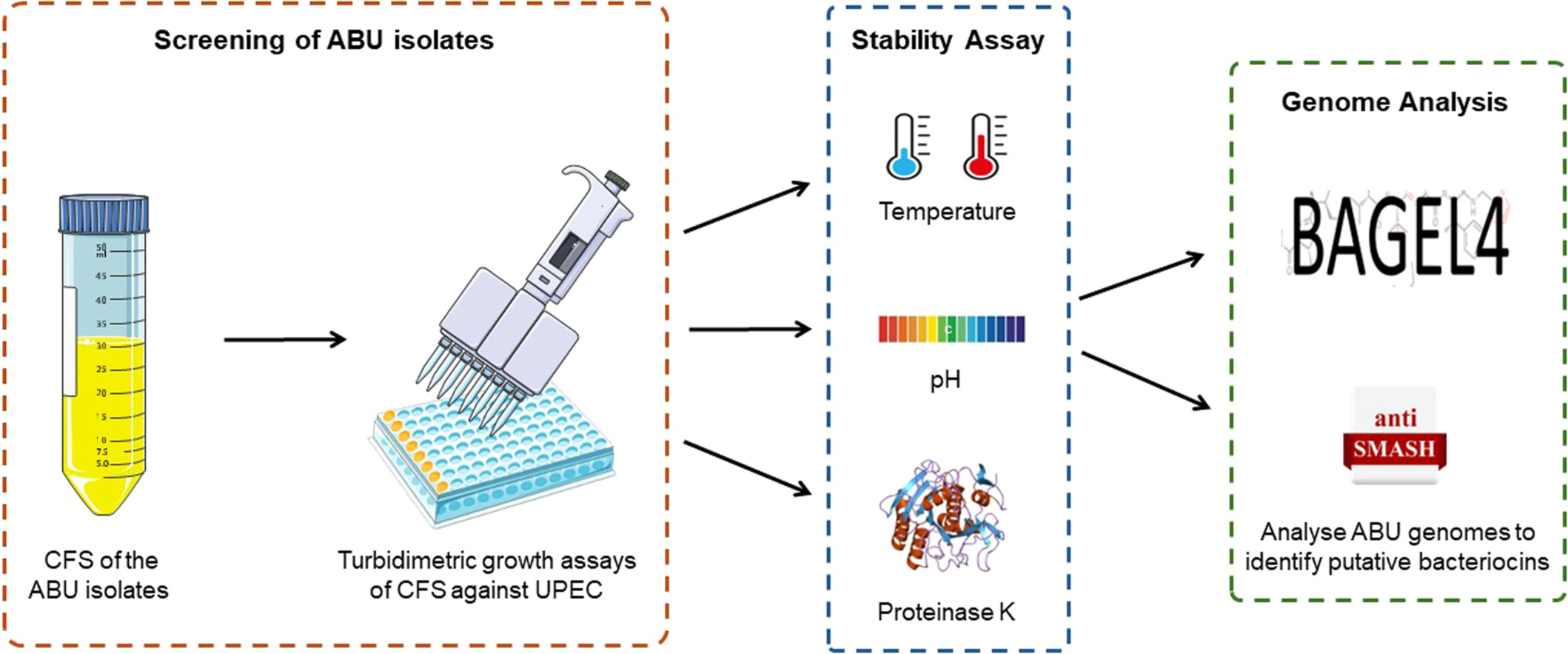
This study uses turbidimetric bioassays to detect antimicrobial activity in asymptomatic bacteriuria (ABU) isolates against uropathogenic E. coli (UPEC). The cell-free supernatant (CFS) from eight ABU isolates showed promising results. Notably, E. coli PUTS 58 and SK-106-1 demonstrated enhanced activity in artificial urine medium. The findings suggest a potential use of ABU bacteriocin-producers as prophylactics and therapeutics amidst rising antibiotic resistance.
Root nodules of red alder (Alnus rubra) and Sitka alder (Alnus viridis ssp. sinuata) are inhabited by taxonomically diverse cultivable microbial endophytes
- First Published: 07 June 2024
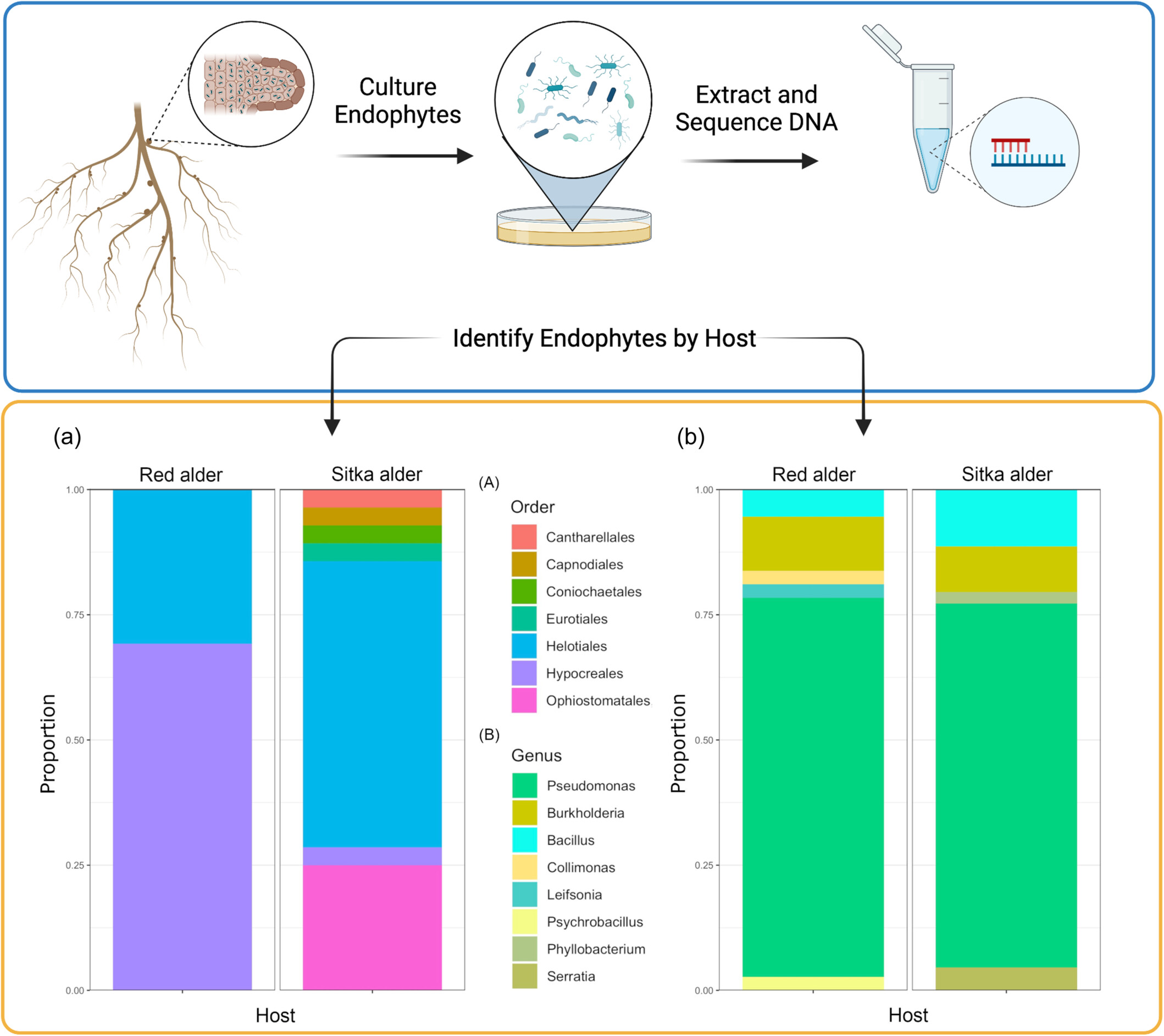
Plants that host nitrogen-fixing symbionts in their root nodules play a significant role in both ecology and economy. However, the secondary members of these root nodule microbiomes have not been thoroughly studied. Our field survey conducted on Mount St. Helens revealed that both red Alder and Sitka Alder host a diverse range of cultivable microorganisms in their root nodules.
Distinct biogeographical patterns in snail gastrointestinal tract bacterial communities compared with sediment and water
- First Published: 02 June 2024

This study investigates the biogeographical patterns of bacterial communities in the gastrointestinal tract of Ampullaceana balthica snails compared with those in sediment and water. The findings indicate that substrate type significantly influences bacterial community composition, with distinct patterns observed in snail gastrointestinal tract communities. The research highlights the role of local water bacterial communities in colonizing the gastrointestinal tract, contributing to our understanding of host-associated bacterial biogeography.
Exploring solute binding proteins in Pseudomonas aeruginosa that bind to γ-aminobutyrate and 5-aminovalerate and their role in activating sensor kinases
- First Published: 23 May 2024
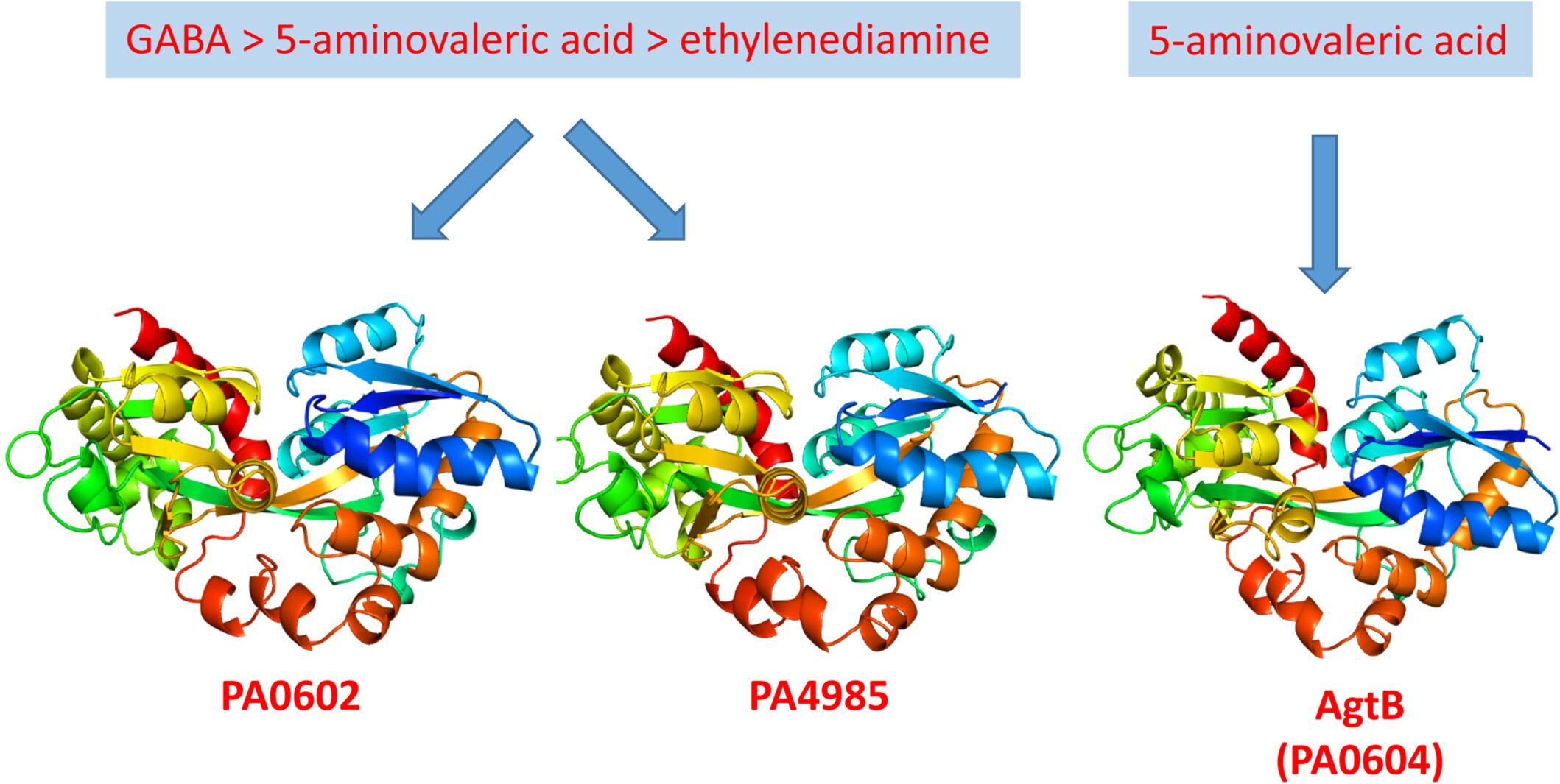
The protein AgtB has a specific affinity for 5-aminovalerate. In contrast, both PA0602 and PA4985 show a strong preference for GABA, with secondary affinities for 5-aminovalerate and ethylenediamine. Despite these findings, there is no evidence to suggest that these solute-binding proteins—PA0602, PA4985, and AgtB—have any role in activating the AgtS and AruS sensor histidine kinases.
Multidrug-resistant Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in residential aged care facilities: An emerging threat
- First Published: 29 April 2024
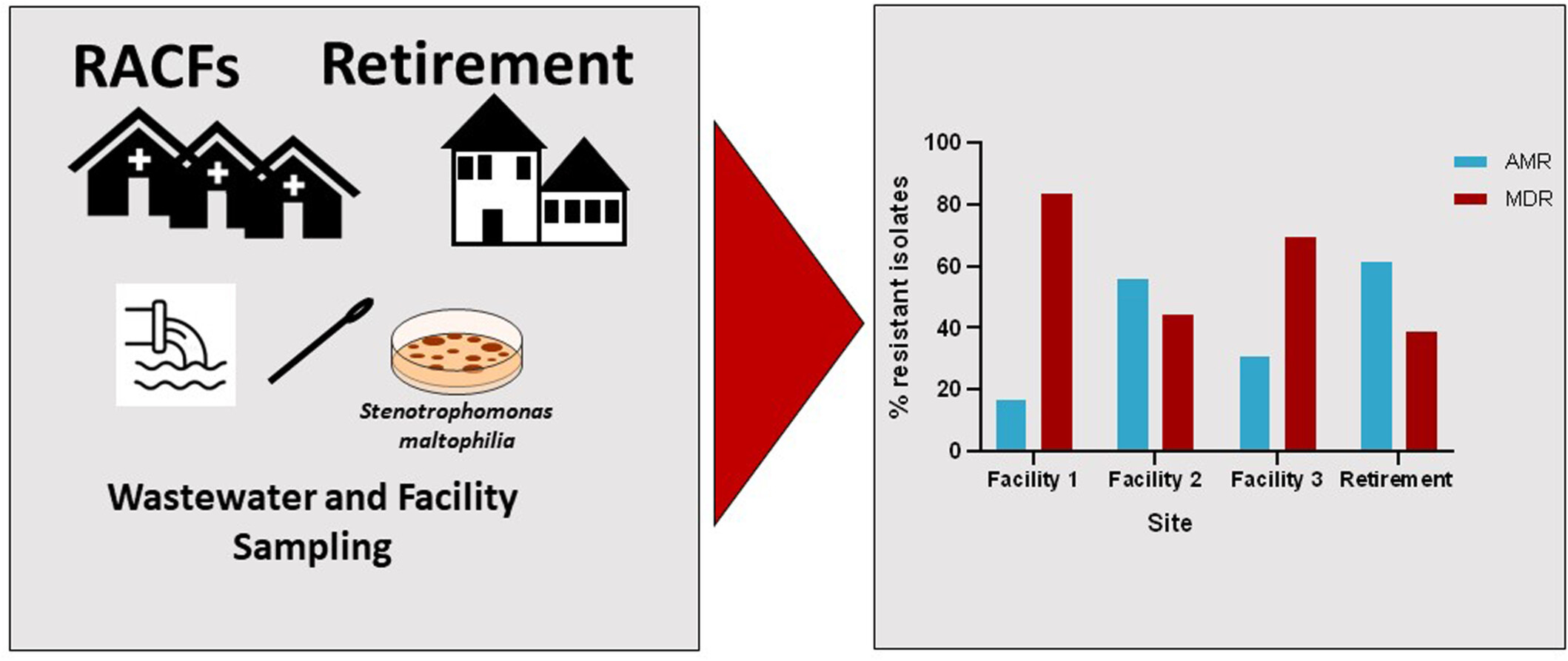
This study marks the first assessment of the prevalence, resistome, and genomic characteristics of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in residential aged care facilities. MDR S. maltophilia were found in all sampled facilities, with colistin non-wild type and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole resistant isolates recovered. Many isolates also exhibited high tolerance to triclosan and benzalkonium chloride. Notably, our findings indicate the continued emergence of S. maltophilia, with lineages not previously identified in Australia observed in this study. This underscores the urgent need for comprehensive surveillance and effective control measures.
Towards bioprocess engineering of cable bacteria: Establishment of a synthetic sediment
- First Published: 06 May 2024
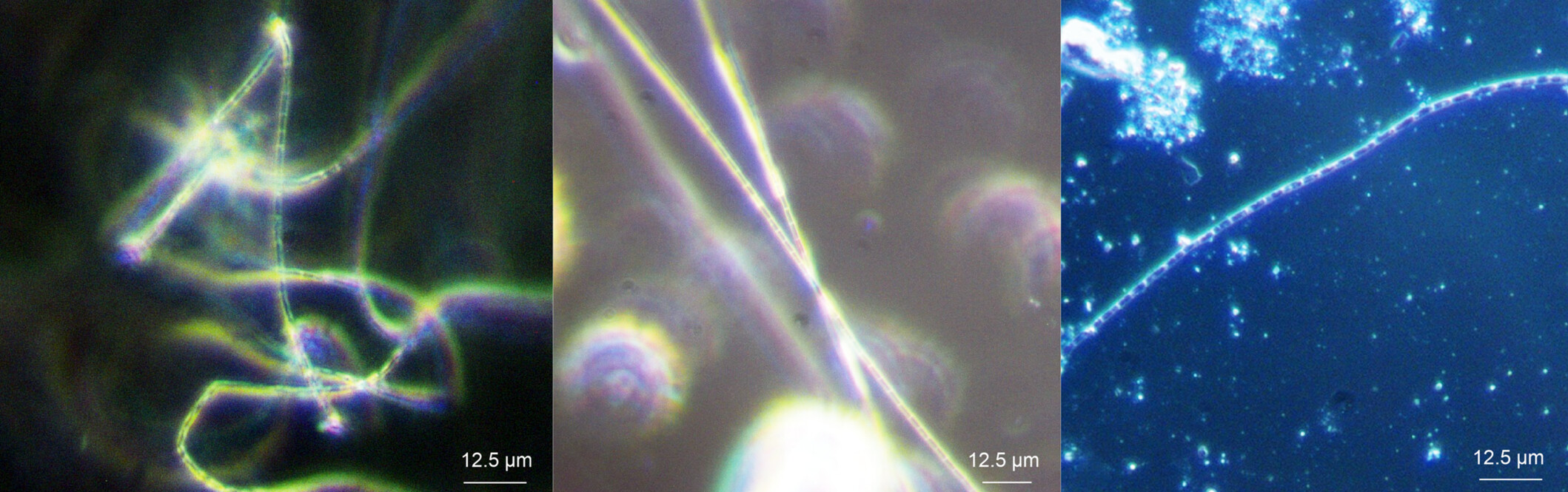
In this study, we successfully cultivated the cable bacteria strain Electronema aureum GS on a newly developed synthetic sediment, marking the first instance of such cultivation on synthetic rather than natural sediment. The combination of this synthetic sediment and a specially designed sediment bioreactor enables reproducible cultivation of cable bacteria. This advancement paves the way for future investigations into the potential application of cable bacteria in bioprocess engineering.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor agonist G-1 decreases ADAM10 levels and NLRP3-inflammasome component activation in response to Staphylococcus aureus alpha-hemolysin
- First Published: 12 June 2024
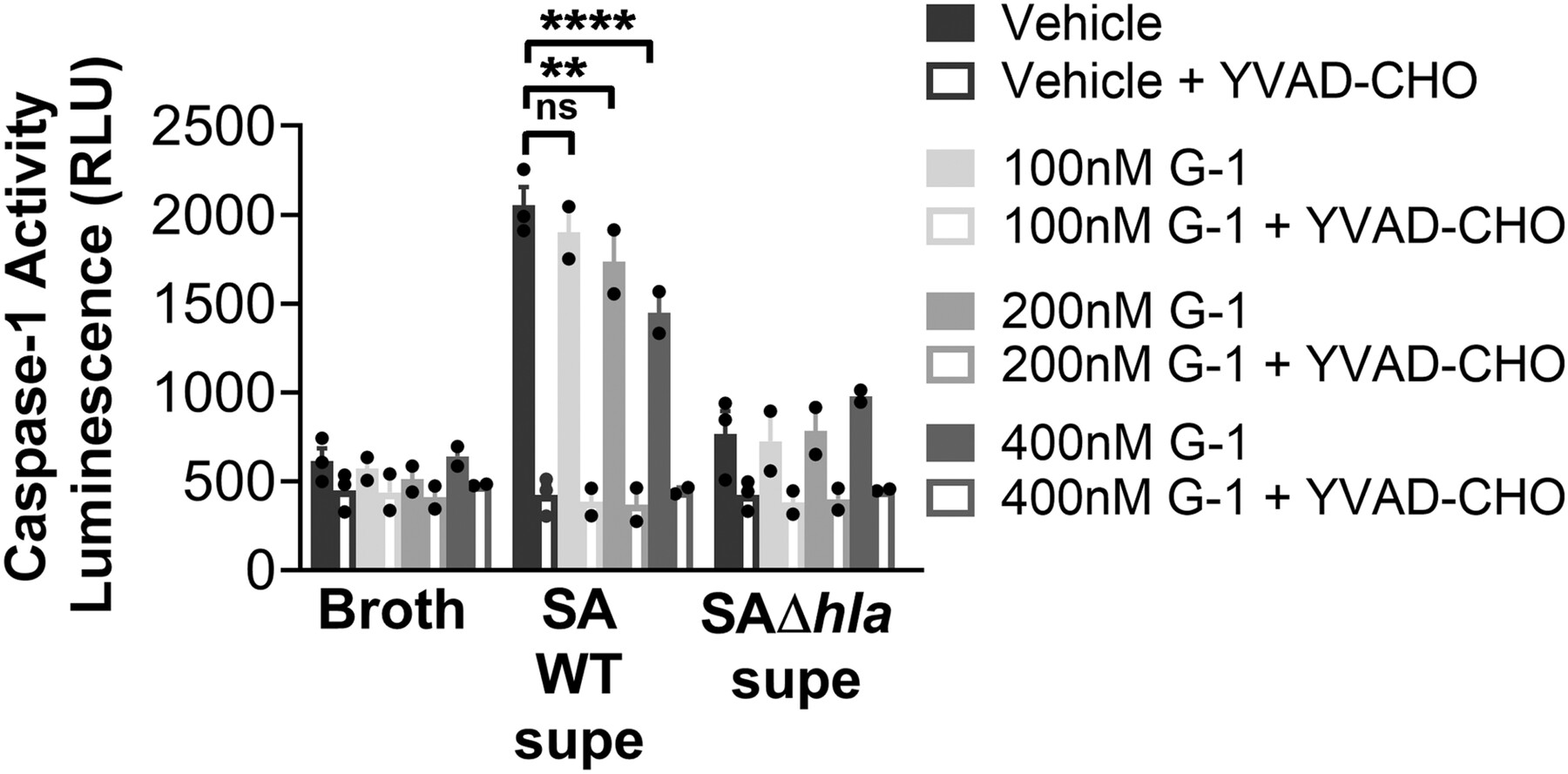
G-1, a selective agonist of the G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), mitigates the pathogenesis mediated by alpha-hemolysin, a toxin produced by Staphylococcus aureus. It achieves this by reducing the surface display of the toxin's receptor, ADAM10. Our study, conducted on macrophage-like differentiated THP-1 cells, reveals that treatment with G-1 leads to a decrease in ATP release, a reduction in the activity of the caspase-1 enzyme, and a decrease in cell death following exposure to alpha-hemolysin.
CORRIGENDUM
Correction to “Staphylococcus argenteus from rabbits in Thailand”
- First Published: 15 May 2024