Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Characterizing arginine, ornithine, and putrescine pathways in enteric pathobionts
- First Published: 01 April 2024
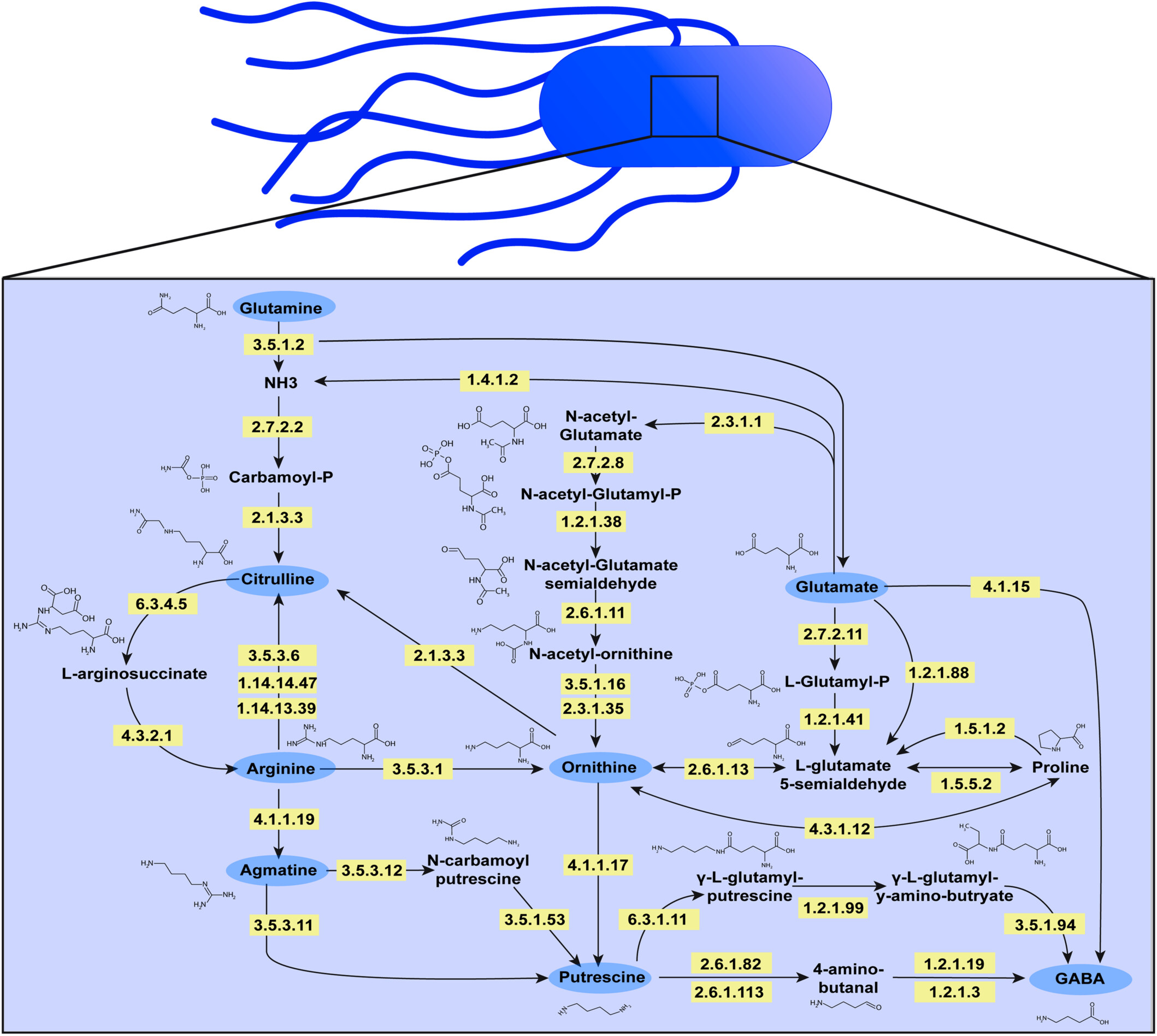
The amino acid L-arginine is converted by bacteria into a variety of downstream metabolites, including citrulline, agmatine, ornithine, putrescine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Our study shows that both Gram-negative bacteria (Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella aerogenes, Pseudomonas fluorescens, and Acinetobacter baumannii) and Gram-positive bacteria (Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus aureus, and Enterococcus faecalis) consume arginine, glutamine, and glutamate, and generate citrulline, ornithine, and GABA. This suggests that these pathways are conserved and essential within gut bacteria. We also found that Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Klebsiella aerogenes, and Pseudomonas fluorescens generate the arginine intermediate agmatine and produce the polyamine putrescine. These findings indicate that arginine is a crucial amino acid for gut bacteria.
Biosynthetic potential of the sediment microbial subcommunities of an unexplored karst ecosystem and its ecological implications
- First Published: 09 April 2024
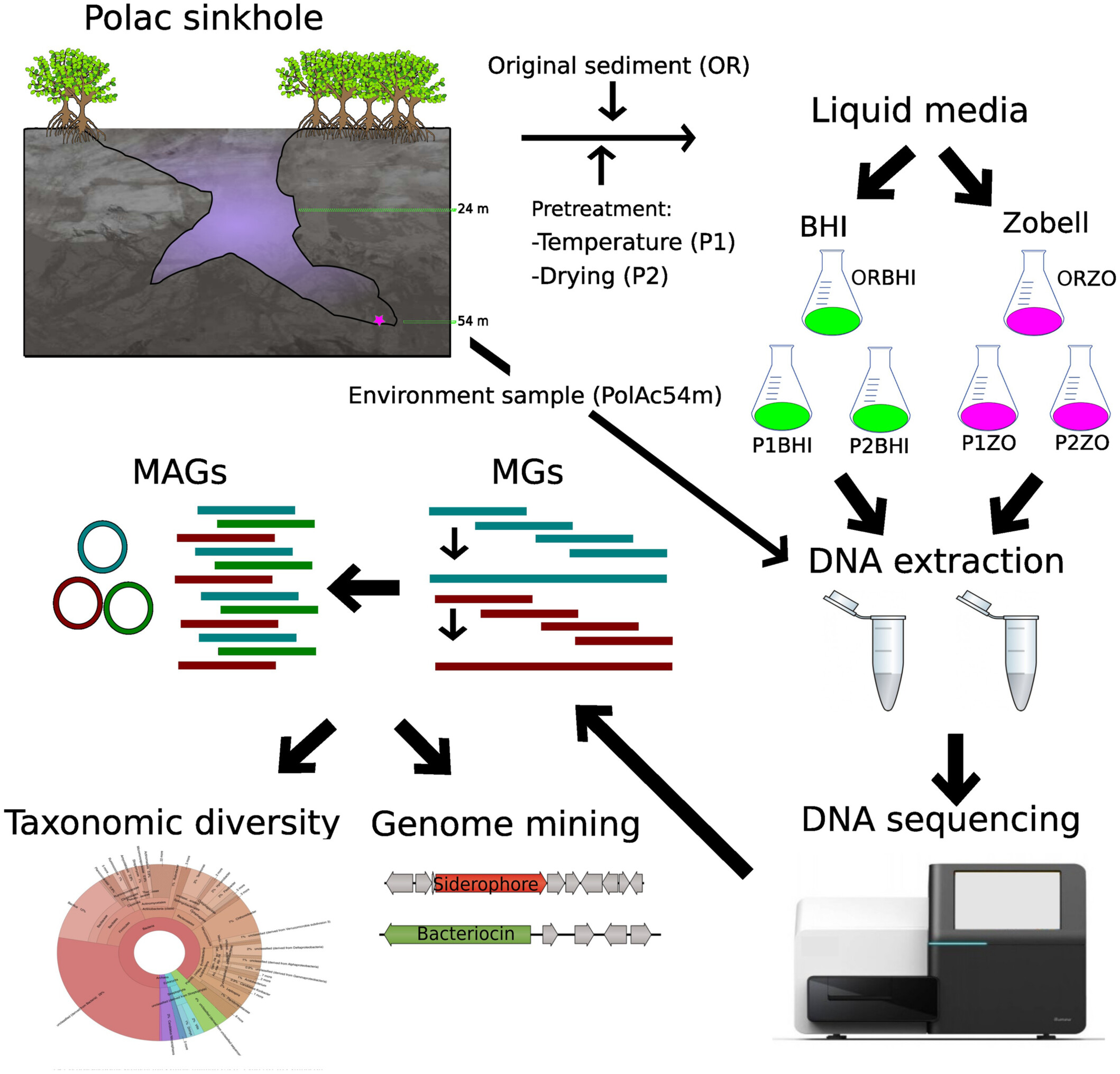
This study employed an enrichment method and genome mining tools to uncover novel bacterial genomes and explore their biosynthetic potential. The research focused on microbial communities residing in the sediments of an uncharted karst environment, specifically the Polac sinkhole, located on the Yucatán Peninsula.
Multidrug-resistant Enterococcus faecium strains enter the Norwegian marine environment through treated sewage
- First Published: 05 March 2024
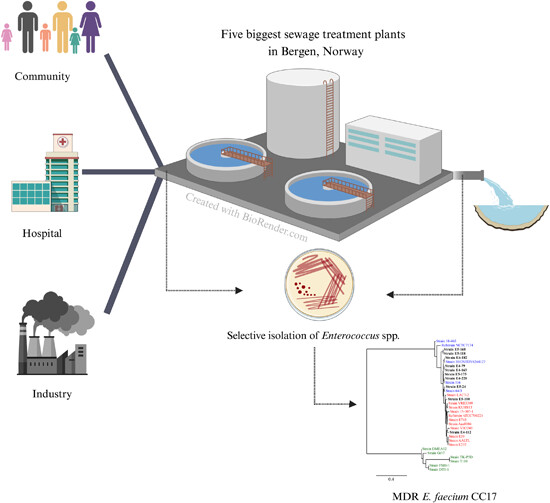
This study investigated the prevalence of antibiotic resistance in Enterococcus spp. from raw and treated sewage in Bergen, Norway. We analyzed 307 Enterococcus faecium isolates from raw sewage and 185 E. faecium isolates from treated sewage for antibiotic sensitivity and sequenced selected isolates (n = 25). This study found that multidrug-resistant E. faecium clones from clonal complex 17 are entering the marine environment through treated sewage.
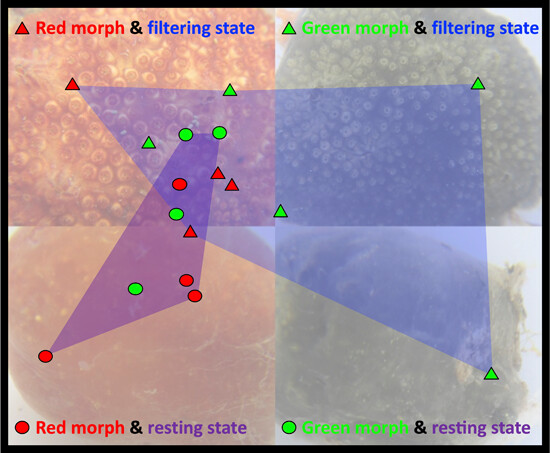
Effects of color variation and physiological state on ascidian microbiomes
- First Published: 13 March 2024
Using meta-analysis to understand the impacts of dietary protein and fat content on the composition of fecal microbiota of domestic dogs (Canis lupus familiaris): A pilot study
- First Published: 21 March 2024
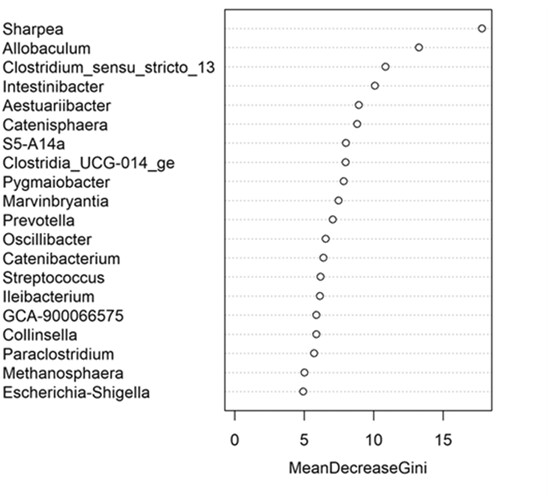
This meta-analysis investigates the impact of dietary crude protein and fat on the fecal microbiota composition in healthy dogs. While overall community changes were minimal, individual taxonomic alterations were observed with increasing levels of protein and fat. The study highlights the role of low-abundant genera like Sharpea in differentiating the microbiome based on dietary intake, suggesting a need for further research into their functional roles.
REVIEWS
What is the role of microbial biotechnology and genetic engineering in medicine?
- First Published: 31 March 2024
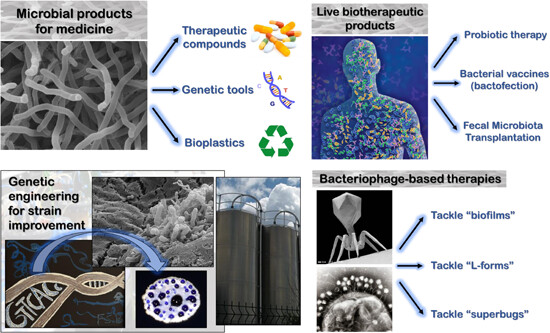
Microbial biotechnology, the technological application of microorganisms, has been instrumental in producing significant natural bioactive products. These include antibiotics, antifungals, anticancer drugs, antiparasitics, antivirals, immunosuppressants, toxoid vaccines, and therapeutic enzymes. Certain microbial components have proven invaluable in the creation of genetic tools, such as CRISPR-Cas systems and thermostable DNA polymerase enzymes. These tools are essential for the development of genetic engineering strategies. Genetic engineering, as a discipline, plays a crucial role in the rational and precise advancement of microbial biotechnology. Consequently, these two conceptual themes—microbial biotechnology and genetic engineering—exhibit a positive interplay. This review presents major advancements in microbial biotechnology, with a particular emphasis on gene-based technologies within the medical field.
COMMENTARY
Complete nucleotide sequence and comparative genomic analysis of microcin B17 plasmid pMccB17
- First Published: 05 March 2024
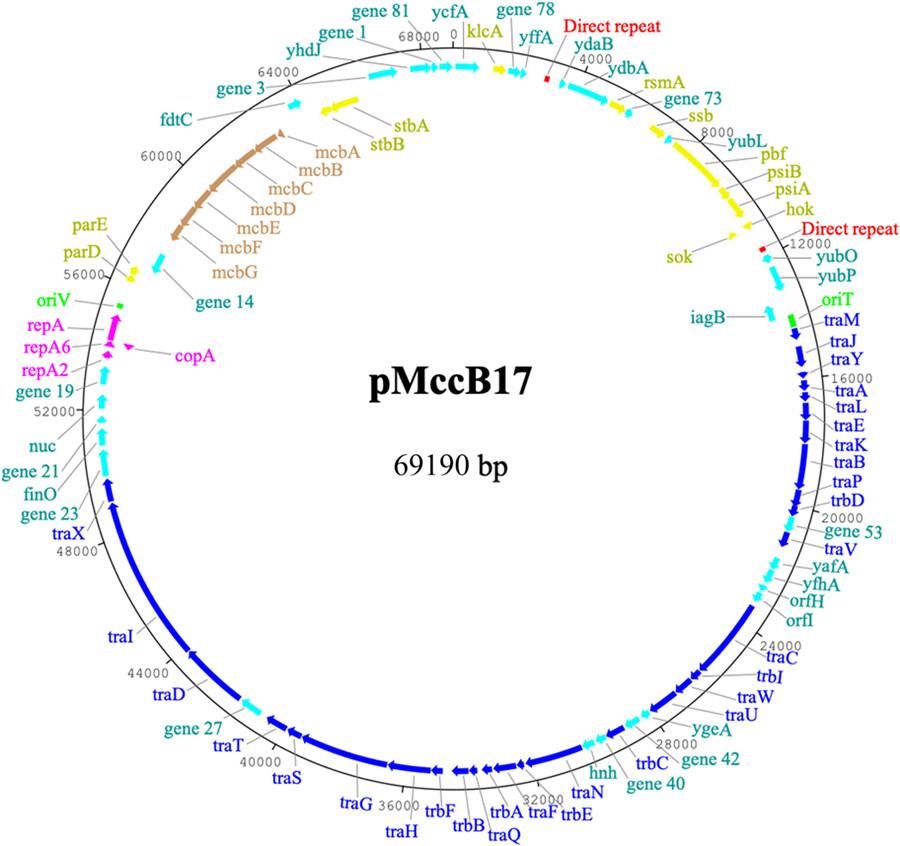
We have determined the complete sequence of plasmid pMccB17 (isolated in 1977), which carries the prototypical microcin operon mcb. The plasmid is 69,190 bp and assigned to the IncFII group of F2:A-:B- replicon type with a conjugation system from the MOBF12 group. While the mcb operon is the major noteworthy feature, pMccB17 is unlike many contemporary IncFII plasmids in that it lacks transposable elements and antibiotic resistance genes.
Genomic characterization of extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli from urban wastewater in Australia
- First Published: 15 March 2024
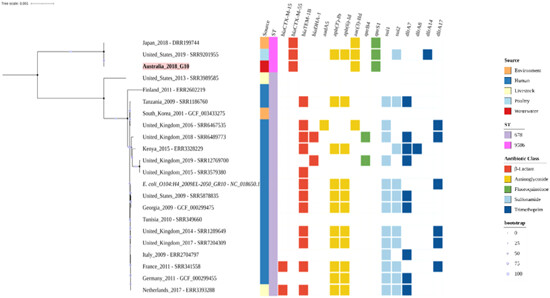
This study investigates extended-spectrum beta-lactamase-producing and carbapenem-resistant Escherichia coli isolates from Sydney's wastewater. These isolates exhibit resistance to critical antibiotics and harbor novel resistance mechanisms. The findings highlight the importance of wastewater-based surveillance in monitoring resistance beyond the clinical setting.
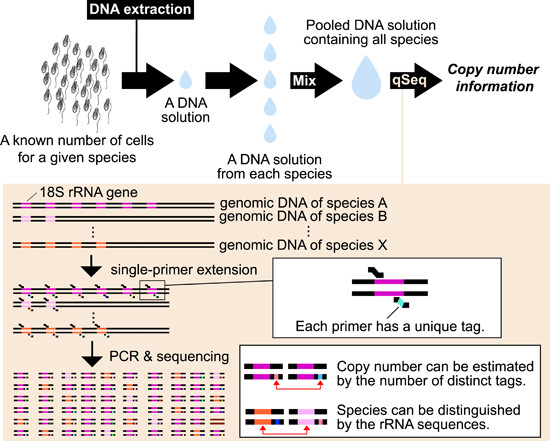
The copy number of the eukaryotic rRNA gene can be counted comprehensively
- First Published: 04 March 2024
Ultrastructural and glycoproteomic characterization of Prevotella intermedia: Insights into O-glycosylation and outer membrane vesicles
- First Published: 26 February 2024
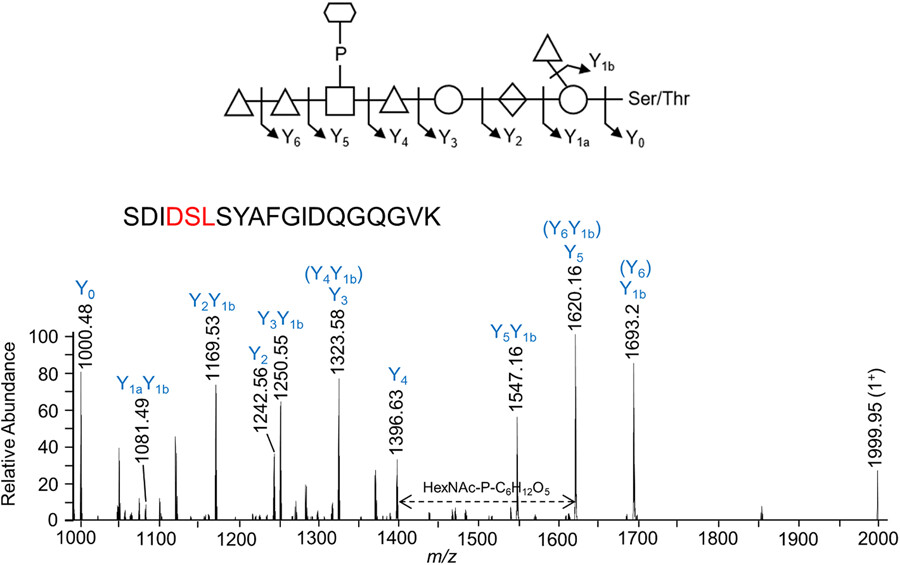
Electron cryotomography analysis revealed ultrastructural details of Prevotella intermedia, revealing an electron-dense surface layer surrounding both cells and outer membrane vesicles (OMVs). Mass spectrometry analysis enabled the identification of a single major O-glycan [dHex-dHex-HexNAc(HPO3-C6H12O5)-dHex-Hex-HexA-Hex(dHex)] found in 443 unique sites within 224 glycoproteins. Bioinformatic analyses of O-glycoprotein localization predicted 73 periplasmic proteins, 53 inner membrane proteins, 52 lipoproteins, 26 outer membrane proteins, and 14 proteins secreted by the type IX secretion system.