Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Combining culture and culture-independent methods reveals new microbial composition of halitosis patients' tongue biofilm
- First Published: 14 November 2019

Oral malodor is a discomforting condition deriving from the presence of volatile sulfur compounds in the expired air. The study characterized and compared the microbial composition of tongue biofilm in volunteers suffering from halitosis and healthy volunteers by means of both the culture method and culture-independent cloning technique, revealing a distinct bacterial composition of halitosis-associated biofilms compared with the health-associated biofilms and a high bacterial diversity within the halitosis-associated biofilms.
Co-dynamics of Symbiodiniaceae and bacterial populations during the first year of symbiosis with Acropora tenuis juveniles
- First Published: 31 October 2019
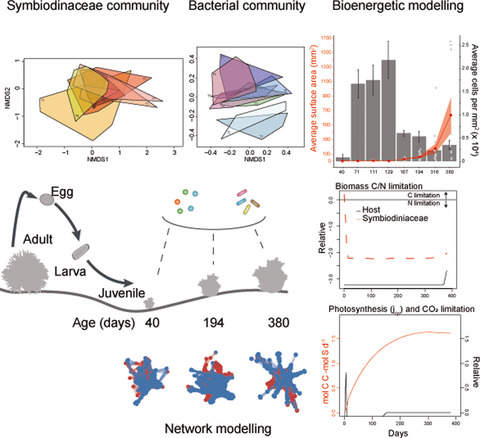
We characterized the establishment and maintenance of bacterial and Symbiodiniaceae communities in the coral Acropora tenuis across the first year of juvenile ontogeny, identifying potentially key co-occurrence patterns using network modeling. Bioenergetic modeling combined with physiological measurements of coral juveniles (surface area and Symbiodiniaceae cell densities) identified periods of carbon limitation and nitrogen assimilation, potentially coinciding with shifts in microbial community composition. These dynamic communities vary in tandem with important fitness effects on host juvenile corals.
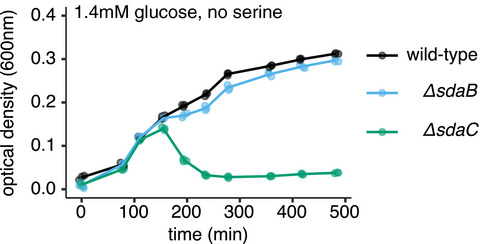
The serine transporter SdaC prevents cell lysis upon glucose depletion in Escherichia coli
- First Published: 03 November 2019
Bacterial communities in the solid, liquid, dorsal, and ventral epithelium fractions of yak (Bos grunniens) rumen
- First Published: 07 November 2019
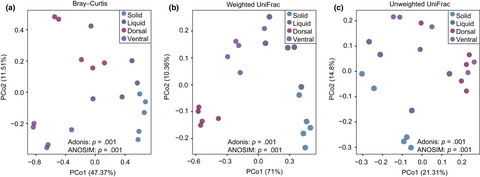
In this present study, we explored microbiota in the solid, liquid, and epithelium (dorsal and ventral) fractions of yak rumen, and compared functional profiles of microbiota of the four fractions, and also compared microbiota of the ventral epithelium between yak and cattle. Our results indicated the significant differences in bacterial communities between the liquid, solid, and epithelium fractions, and between dorsal and ventral epithelium fractions. Moreover, comparison of functional profiles among the solid, liquid, and dorsal and ventral epithelium fractions also revealed significant differences. Finally, we found that the microbial composition and functional profile in the ventral epithelium between yak and cattle significantly differed, suggesting the specific role of microbiota in the ventral epithelium of yak rumen.
Characterization and discrimination of microbial community and co-occurrence patterns in fresh and strong flavor style flue-cured tobacco leaves
- First Published: 05 December 2019
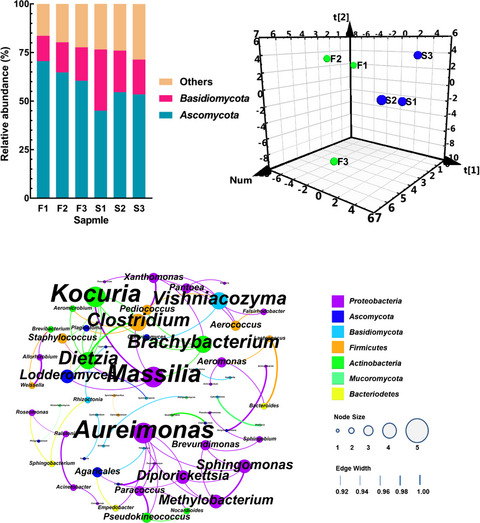
In this study, we use 16S and 18S rRNA Illumina MiSeq sequencing data to characterize and compare the microbiota associated with fresh and strong flavor style flue-cured tobacco leaves and reveal correlations between the microbial taxa within them. Flue-cured tobacco leaf microbiota are correlated with flavor style, and species present at low numbers within the microbial communities can be used as microbial markers to discriminate between samples of different flavor styles and to stabilize flue-cured tobacco leaf microbial communities.
Physiological and genomic features of Paraoceanicella profunda gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel piezophile isolated from deep seawater of the Mariana Trench
- First Published: 19 November 2019
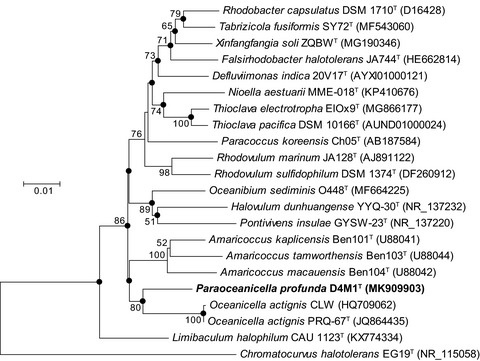
A novel piezophilic alphaproteobacterium, strain D4M1T, was isolated from deep seawater of the Mariana Trench. The combined evidence shows that it represents a novel species of a novel genus in the family Rhodobacteraceae, for which the name Paraoceanicella profunda gen. nov., sp. nov. is proposed. The complete genome contained 5,468,583-bp with a G + C content of 70.2 mol% and contained 4,855 protein-coding genes and 78 RNA genes. Genomic analysis revealed abundant clues on bacterial high-pressure adaptation and piezophilic lifestyle.
Effect of Streptomyces probiotics on the gut microbiota of Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus
- First Published: 18 November 2019
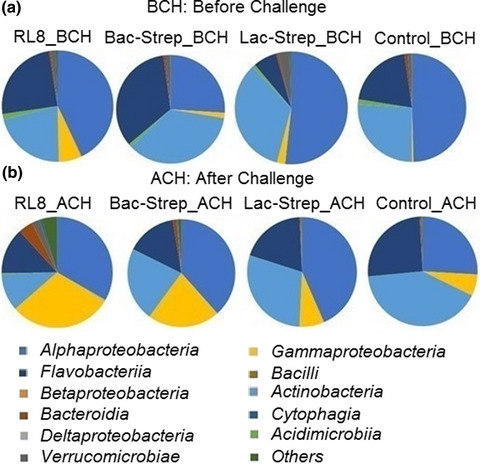
-
We have shown the modulating effect of Streptomyces sp. RL8 alone and combined with Bacillus, but not with Lactobacillus, over the gut microbiota of the white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei challenged with Vibrio parahaemolyticus. This effect was characterized by a higher bacterial diversity, as well as a significant stimulation of the predatory Bacteriovorax population and other antimicrobial producing genera that protected shrimp from infection.
Experimental evolution for niche breadth in bacteriophage T4 highlights the importance of structural genes
- First Published: 28 November 2019
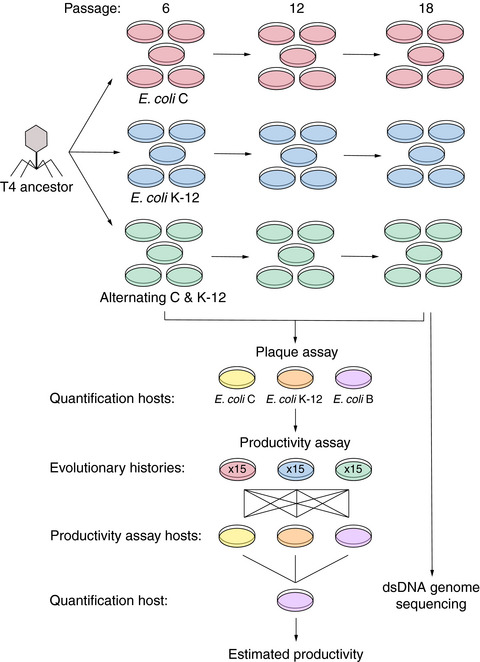
Microbial ecologists have long asked how microbes expand their niche breadth. Our study uses experimental evolution in bacteriophage T4 to inquire about the genes that change in response to expanded host niche breadth. We find that structural genes—those that provide morphological and biophysical integrity to a virus—are central determinants in bacteriophage niche breadth.
Lysosome assembly and disassembly changes endocytosis rate through the Leishmania cell cycle
- First Published: 19 November 2019
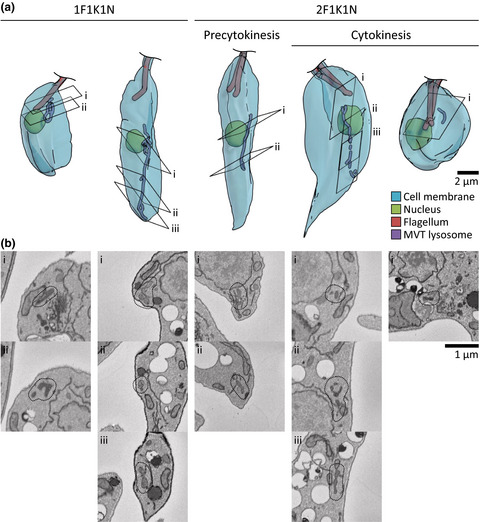
The Leishmania lysosome has an atypical structure, consisting of a vesicle-filled tubule called the multivesicular tubule (MVT) lysosome. We examined the dynamics of this structure through the cell cycle using mNeonGreen tagged protein markers; the MVT lysosome elongated during the cell cycle and then disassembled before cytokinesis. The disassembly of the MVT lysosome coincided with a reduction in endocytosis rate.
The adaptive response to iron involves changes in energetic strategies in the pathogen Candida albicans
- First Published: 01 December 2019
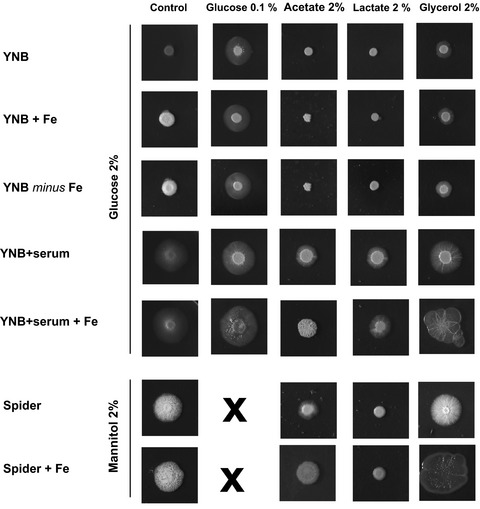
We analyze here the adaptive response of Candida albicans cells to changes in the iron content of the culture environment. This response includes changes in intracellular redox status and the reorientation of metabolic pathways, as shown by label-free analyses and biochemical measurements. We found that iron deficiency stimulated the TCA cycle, mitochondrial respiratory chain, and ATP production, to compensate for cellular stress, to maintain normal levels of ATP, and to ensure cell survival. Conversely, an increase of iron is associated with biosynthetic needs, especially in filamentous forms.
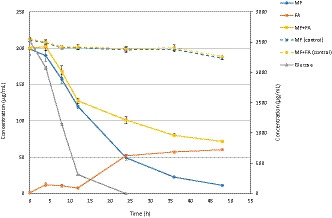
Does glucose affect the de-esterification of methyl ferulate by Lactobacillus buchneri?
- First Published: 29 November 2019
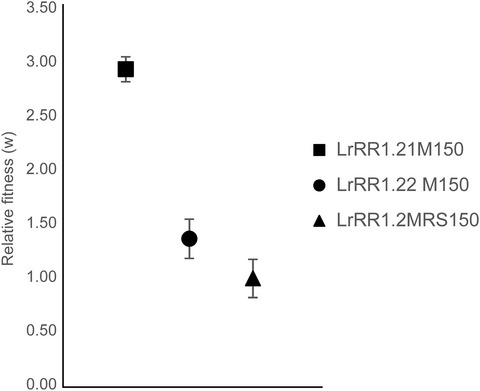
Evolutionary changes of an intestinal Lactobacillus reuteri during probiotic manufacture
- First Published: 19 November 2019
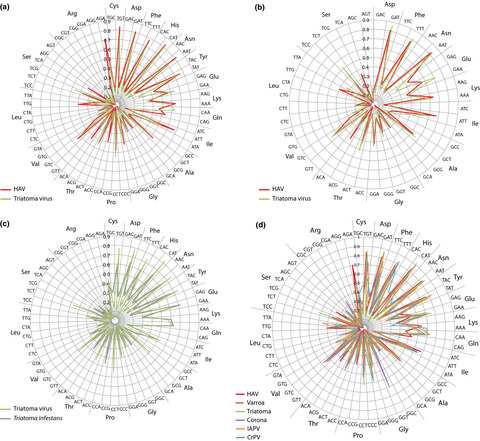
Comparative genomics of hepatitis A virus, hepatitis C virus, and hepatitis E virus provides insights into the evolutionary history of Hepatovirus species
- First Published: 19 November 2019
Whole-genome comparison between the type strain of Halobacterium salinarum (DSM 3754T) and the laboratory strains R1 and NRC-1
- First Published: 03 December 2019

The genome of the Halobacterium salinarum type strain (91-R6, DSM 3754) was compared at the DNA and protein levels to the genomes of two well-studied laboratory strains, NRC-1 and R1. The chromosomes and portions of the plasmids were very closely related. However, distinct homologs for proteins involved in motility and N-glycosylation were encountered.
COMMENTARY
Putting an end to the Pseudomonas aeruginosa IQS controversy
- First Published: 30 October 2019
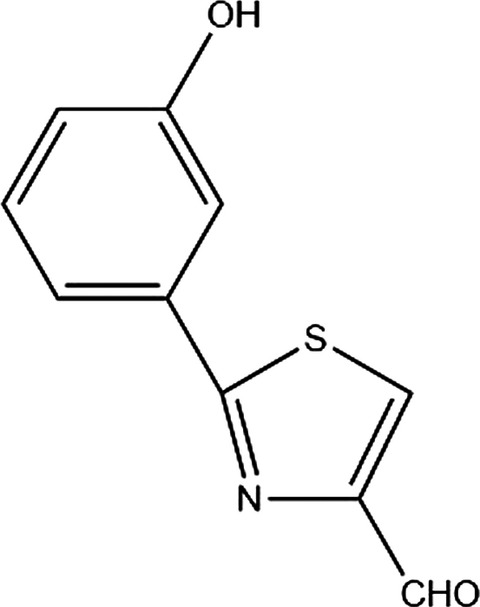
Despite published evidence that IQS (2-(2-hydroxylphenyl)-thiazole-4-carbaldehyde) is in fact aeruginaldehyde, a by-product of the siderophore pyochelin biosynthesis or degradation and that the ambABCDE genes are not responsible for IQS synthesis, several authors, including in top review journals, perpetuate the wrong information. I hope that this short comment will clarify the situation once and for all.