Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
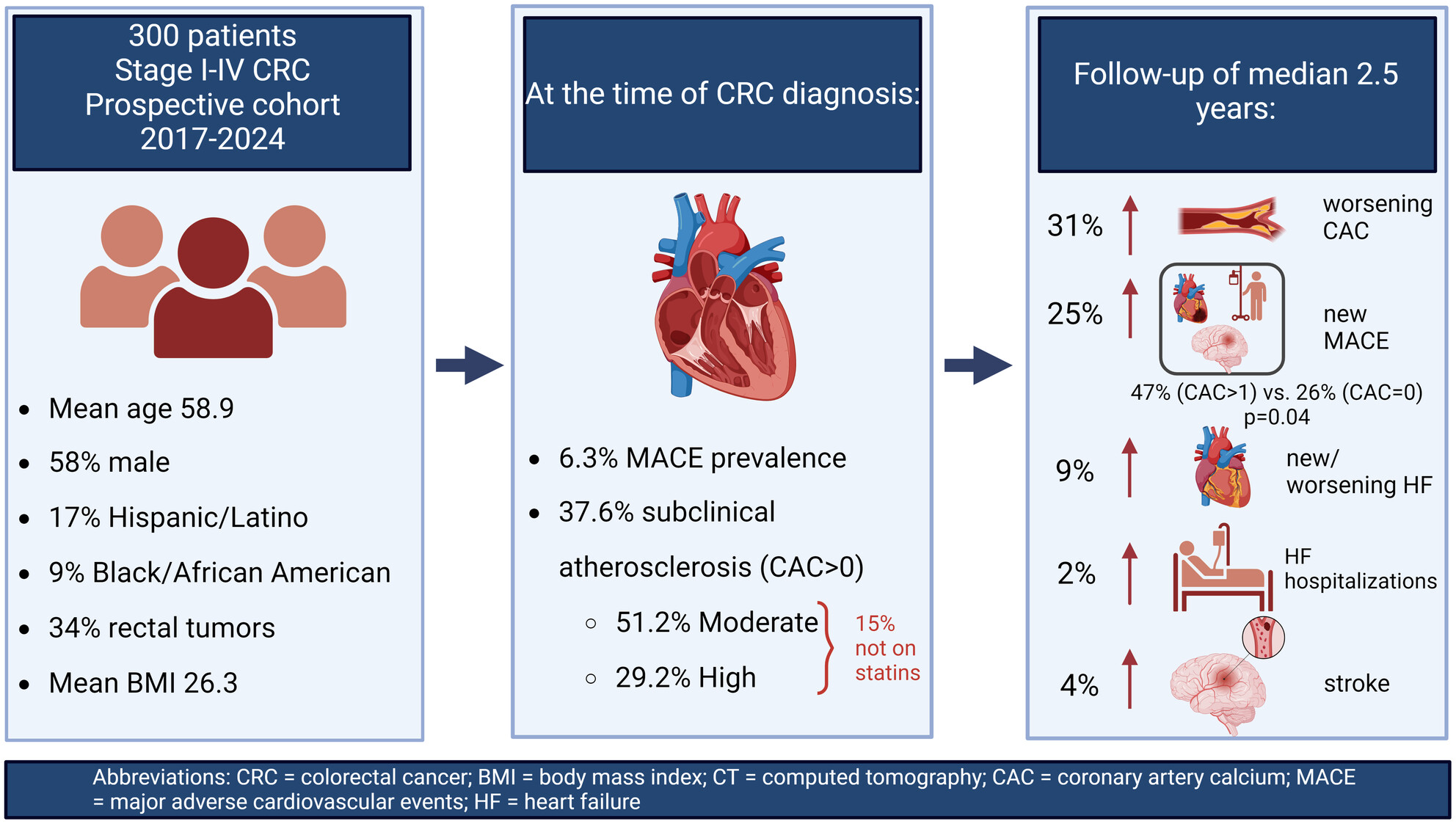
Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Events Among Patients With Colorectal Cancer
- First Published: 14 May 2025
EIF2S1 in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles as a Novel Diagnostic Marker for Bladder Cancer
- First Published: 14 May 2025
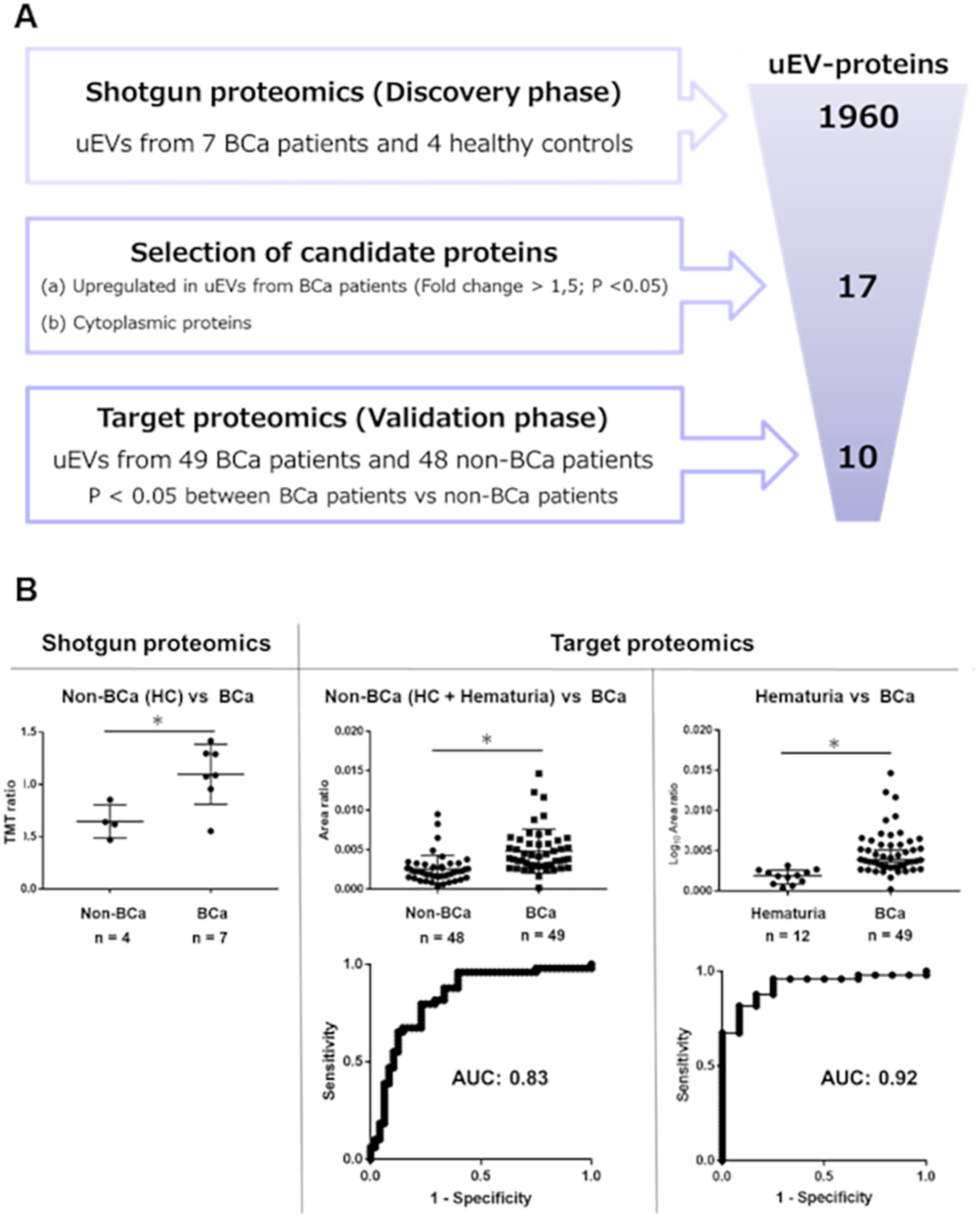
We conducted a proteomic analysis of urinary extracellular vesicles (uEVs) to identify and validate new diagnostic markers for bladder cancer. Focusing on cytoplasmic EV proteins, we discovered EV-EIF2S1 as a novel marker and demonstrated its crucial role in the growth and survival of bladder cancer.
REVIEW
Advances in the Study of Metabolic Reprogramming in Gastric Cancer
- First Published: 14 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Early Detection and Longitudinal Follow-Up of Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: First Results of the BEAL-Study
- First Published: 14 May 2025
CORRECTION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Rising Threat: Long-Term Trends in the Incidence and Mortality of Thymic Epithelial Tumor
- First Published: 15 May 2025
NOP2-Mediated m5C Methylation Modification of LMNB2 mRNA Facilitates Colorectal Cancer Progression
- First Published: 14 May 2025
REVIEW
Clinical Implications of Mismatch Repair Deficiency in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma
- First Published: 14 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Mapping of Functional Metabolic Phenotypes in Acute Myeloid Leukemia
- First Published: 19 May 2025
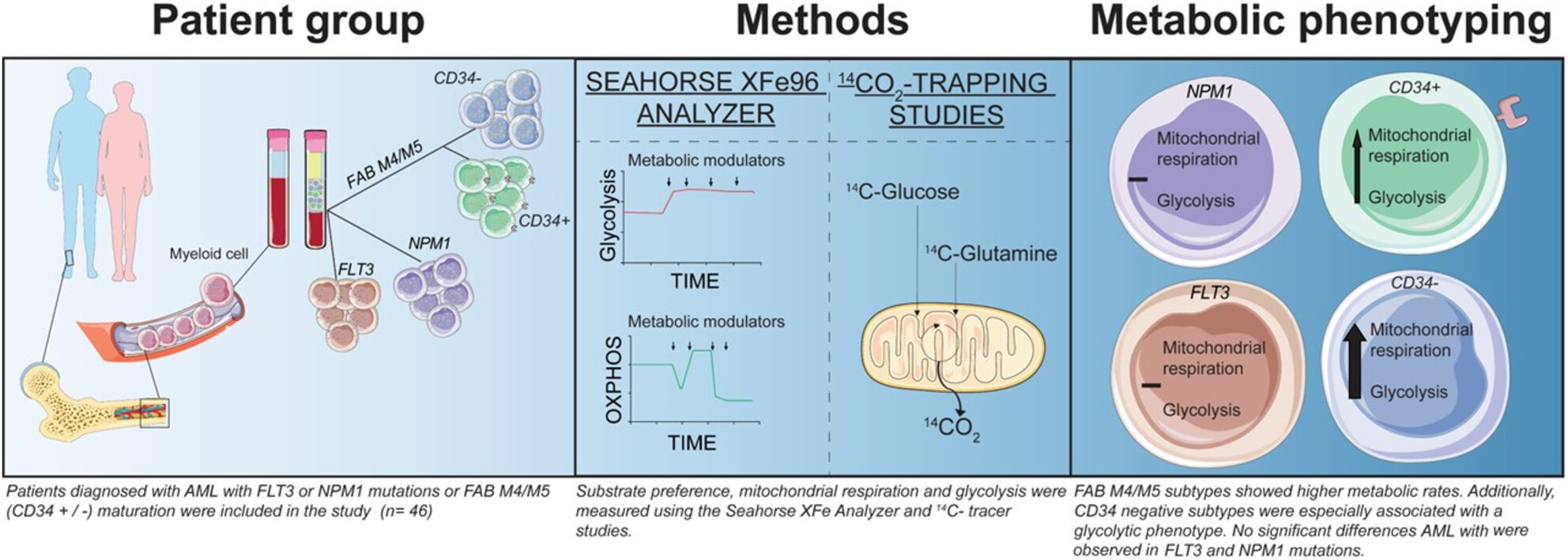
Analysis of primary AML cells from 46 patients shows significant variability in metabolic activity, highlighting diverse metabolic phenotypes within the disease. AML cells classified as FAB M4/M5 exhibited higher metabolic rates compared to less mature phenotypes. The findings underscore the potential for targeted therapeutic strategies based on specific metabolic profiles.
Transcutaneous Imiquimod Combined With Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Monoclonal Antibody Extends the Survival of Mice Bearing Renal Cell Carcinoma
- First Published: 15 May 2025
In Silico Network Toxicology, Molecular Docking, and Multi-Level Bioinformatics Reveal Methyl Eugenol-Induced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Mechanisms in Humans
- First Published: 15 May 2025
Residual Volume and Total Lung Capacity at Diagnosis Predict Overall Survival in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
- First Published: 15 May 2025
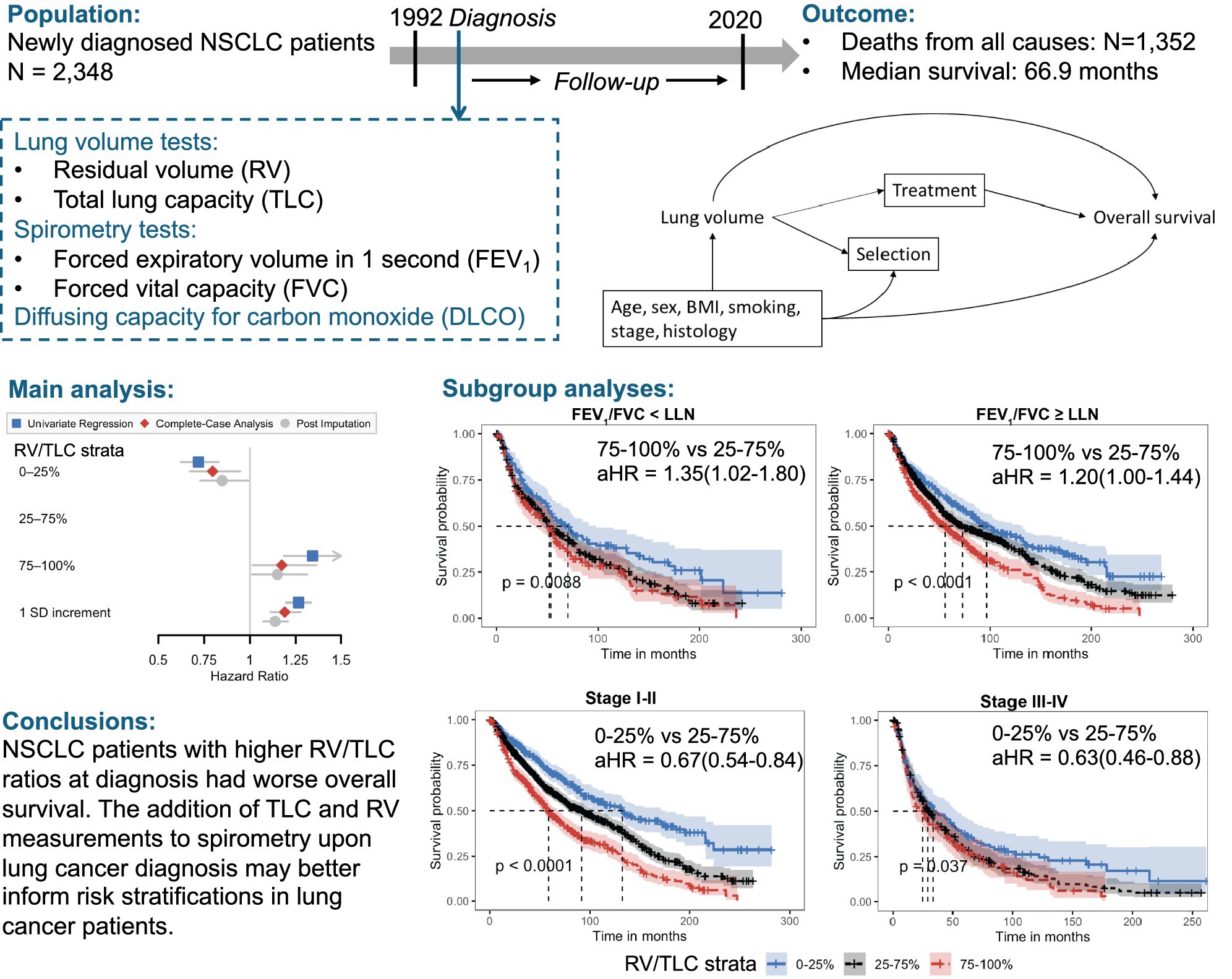
Lung volume as a part of pulmonary function test is often underrepresented in prognostic lung cancer research. In this longitudinal lung cancer patient cohort, higher residual volume to total lung capacity (RV/TLC) ratio upon diagnosis was associated with worse overall survival regardless of spirometry results or cancer stage. The findings provide first-line evidence for the prognostic value of lung volume measurements and lay the groundwork for future studies to clarify their role in lung cancer prognosis.
Physical Activity Patterns According to Demographic, Social, and Clinical Correlates Among Breast Cancer Survivors
- First Published: 20 May 2025
REVIEW
Reactive Oxygen Species: From Tumorigenesis to Therapeutic Strategies in Cancer
- First Published: 16 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
FUT8 Is a Critical Driver of Prostate Tumour Growth and Can Be Targeted Using Fucosylation Inhibitors
- First Published: 19 May 2025
Changes in Breast and Cervical Cancer Incidence by Stage at Diagnosis During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Utah
- First Published: 19 May 2025
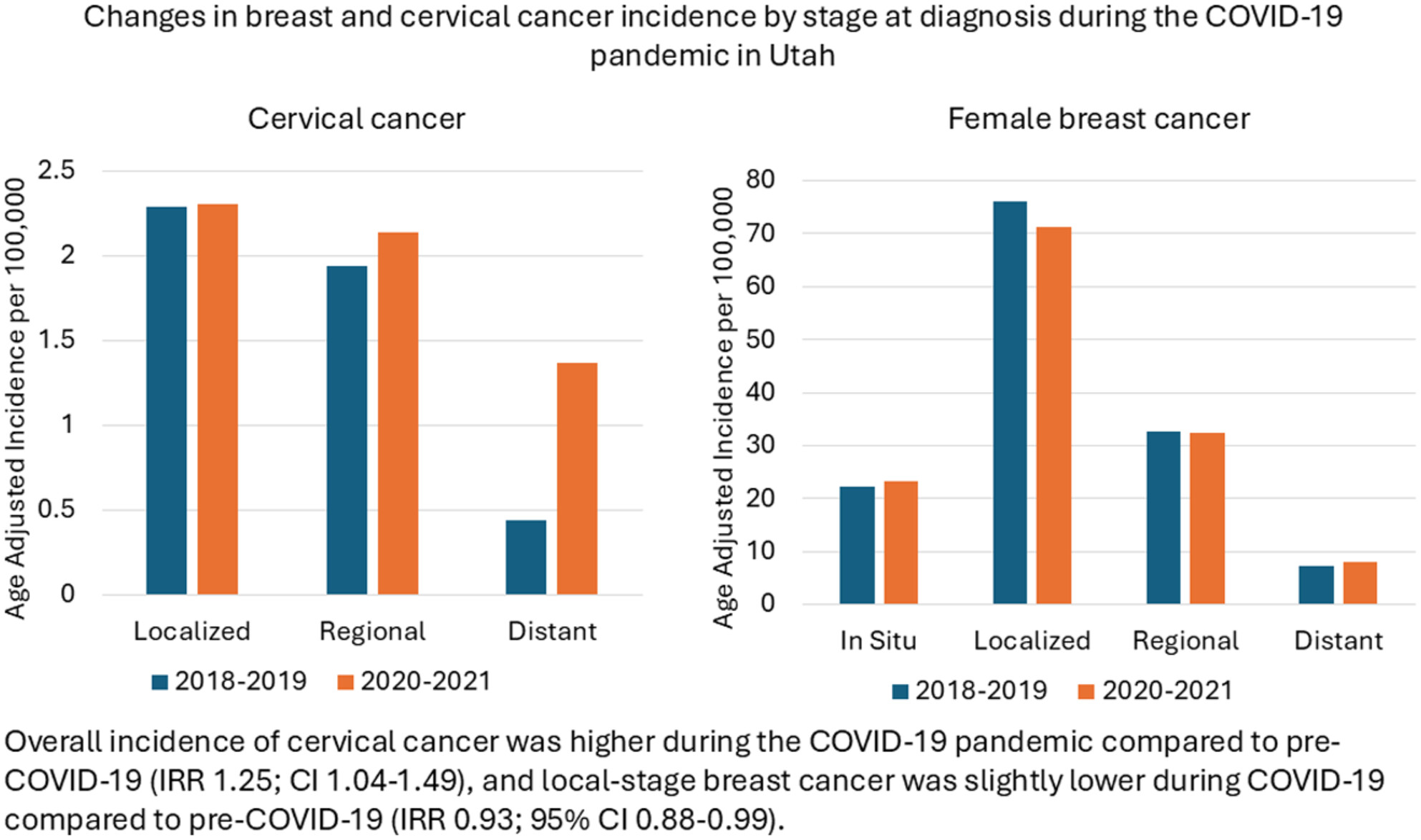
This study examined whether there were changes in the stage of diagnosis for breast and cervical cancers diagnosed among Utah women during the pandemic (January 2020–December 2021) compared to years prior to the pandemic (January 2018–December 2019). We saw a significant increase in the incidence of late-stage cervical cancer during the pandemic compared with pre-pandemic. Conversely, while local-stage breast cancer incidence was slightly lower during COVID-19 compared with pre-COVID-19, no difference was observed among all other stages.
Peripheral Blood T-Cell Receptor Repertoire Diversity as a Potential Biomarker in the Diagnosis and Treatment Evaluation of Colorectal and Lung Cancers: A Prospective Observational Study
- First Published: 19 May 2025
Trends in Practice Patterns and Clinical Outcomes for Desmoid Tumors: A Large Single-Institutional Australian Cohort
- First Published: 19 May 2025
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Optimization of Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields) Frequency and Treatment Duration in Colorectal Cancer Cells
- First Published: 19 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
REVIEW
Centromere Protein F in Tumor Biology: Cancer's Achilles Heel
- First Published: 19 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Risk of Second Primary Neoplasms Among Cancer Survivors: A Population-Based, Cohort Study in Golestan Province, Northern Iran, 2004–2019
- First Published: 20 May 2025
REVIEW
Lipid Metabolism in Gastrointestinal Malignancies: Exploring Dysregulation, Biomarkers, and Treatment Strategies
- First Published: 20 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
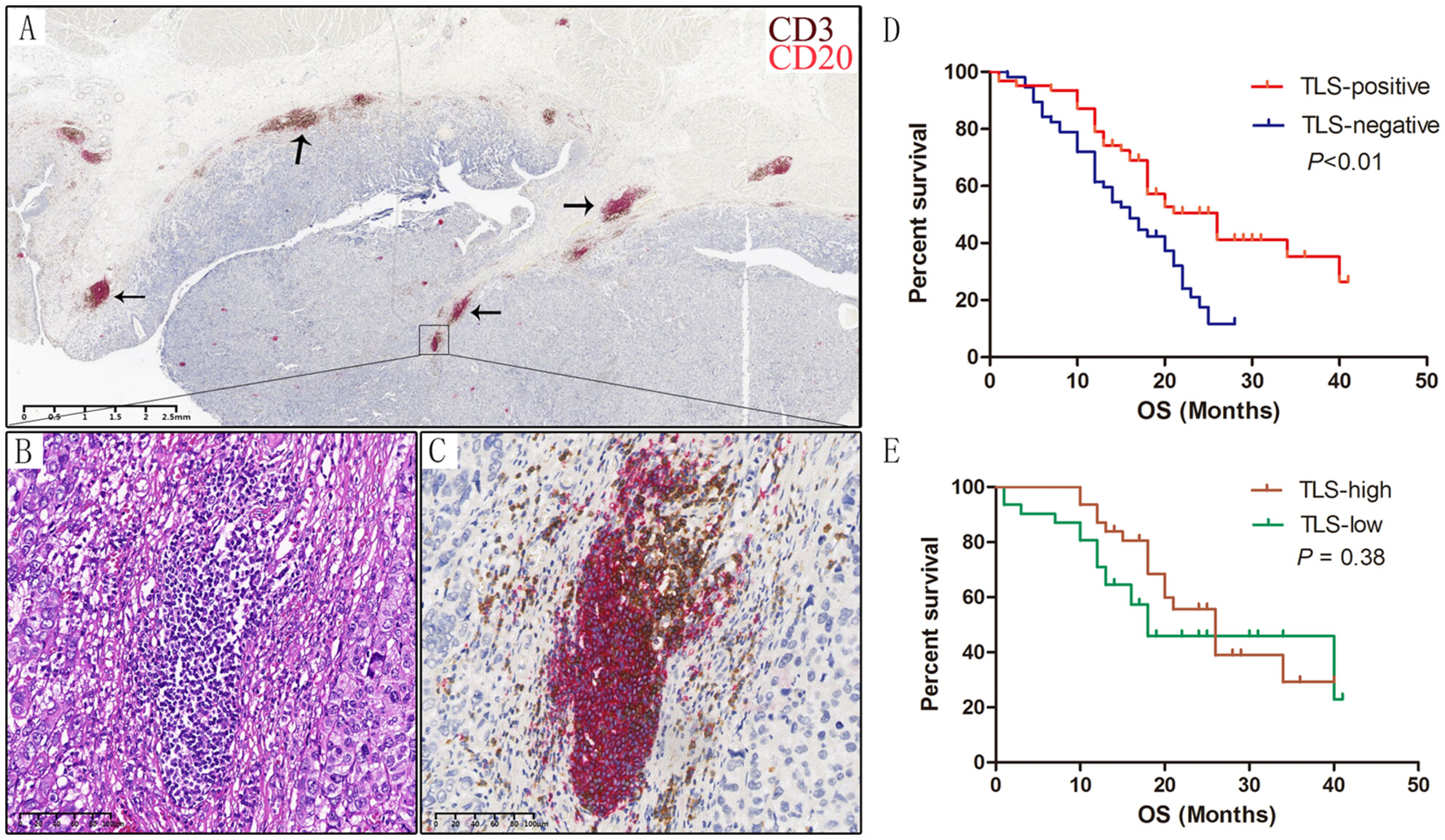
Tertiary Lymphoid Structures as Independent Predictors of Favorable Prognosis in Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer
- First Published: 21 May 2025
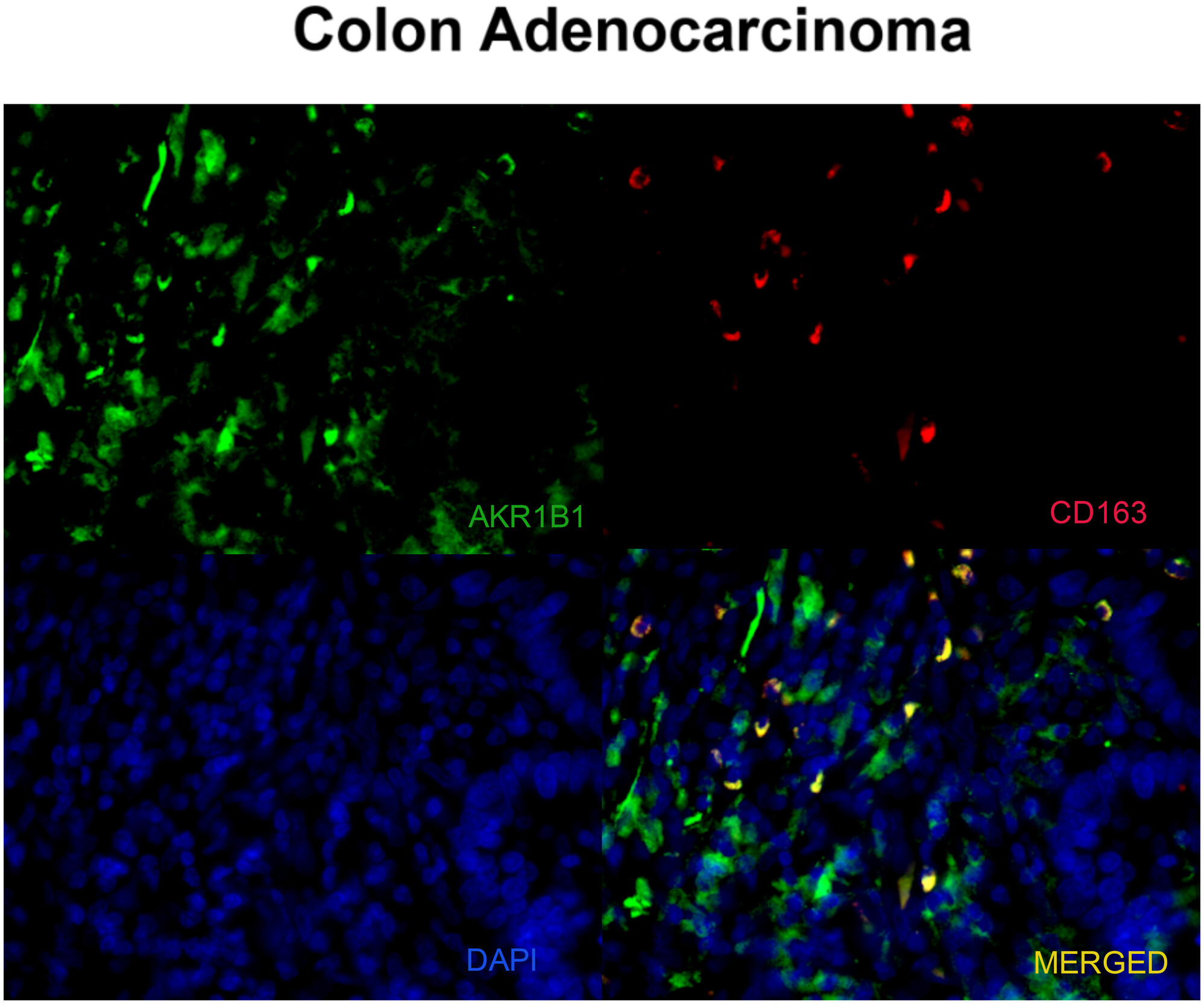
AKR1B1 Expression in the Colorectal Tumor Microenvironment Contributes Towards Its Prognostic Significance
- First Published: 21 May 2025
NSD2 and miRNAs as Key Regulators of Melanoma Response to Romidepsin and Interferon-α2b Treatment
- First Published: 19 May 2025
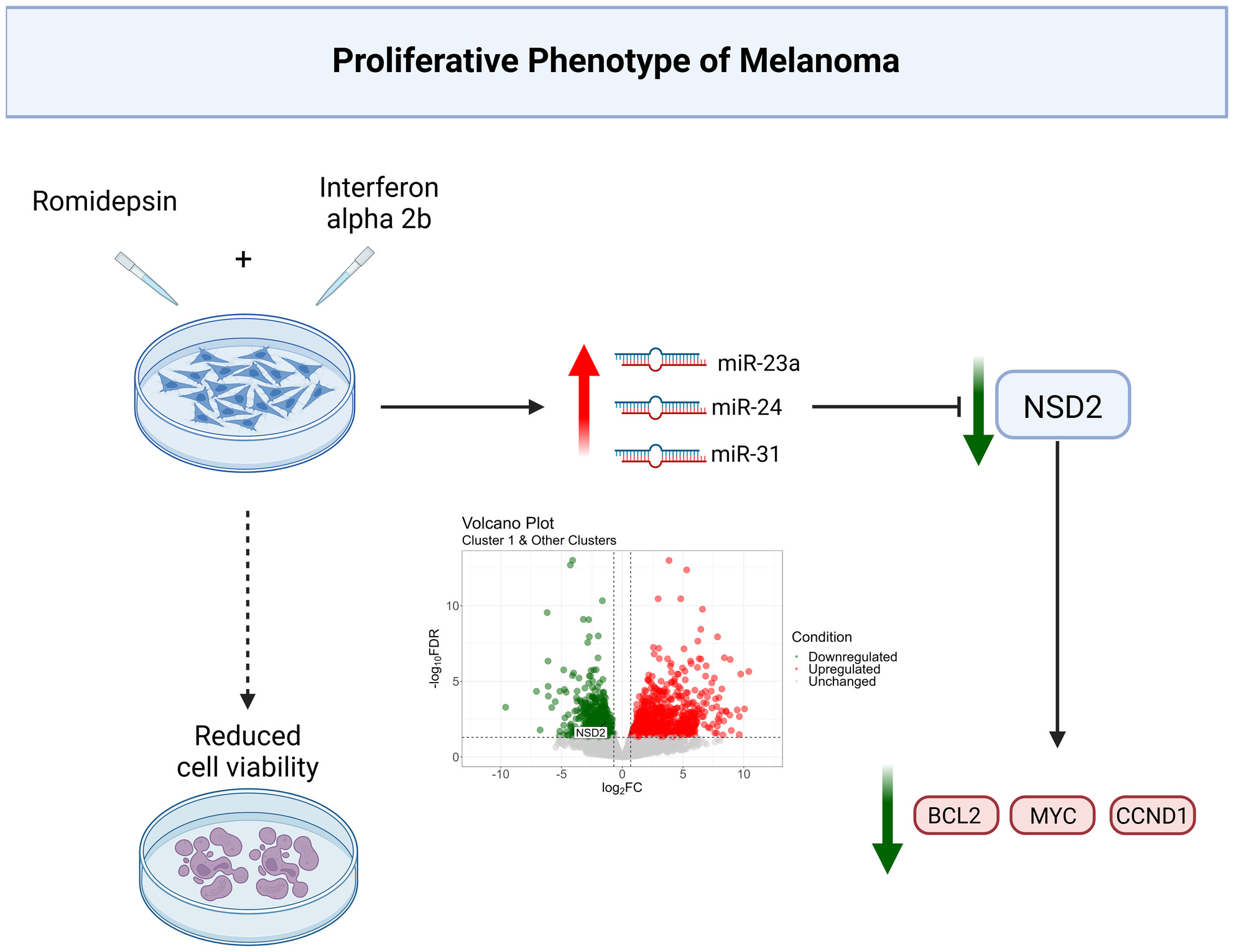
This figure illustrates the proposed mechanism of NSD2 regulation in melanoma following romidepsin and interferon-α2b (RI) treatment. RI induces a de-differentiation process, particularly in proliferative melanoma cells, leading to NSD2 downregulation. This effect is mediated by the upregulation of specific miRNAs (miR-23a, miR-24, and miR-31), which target NSD2 and influence downstream oncogenic pathways involving CCND1, MYC, and BCL2.
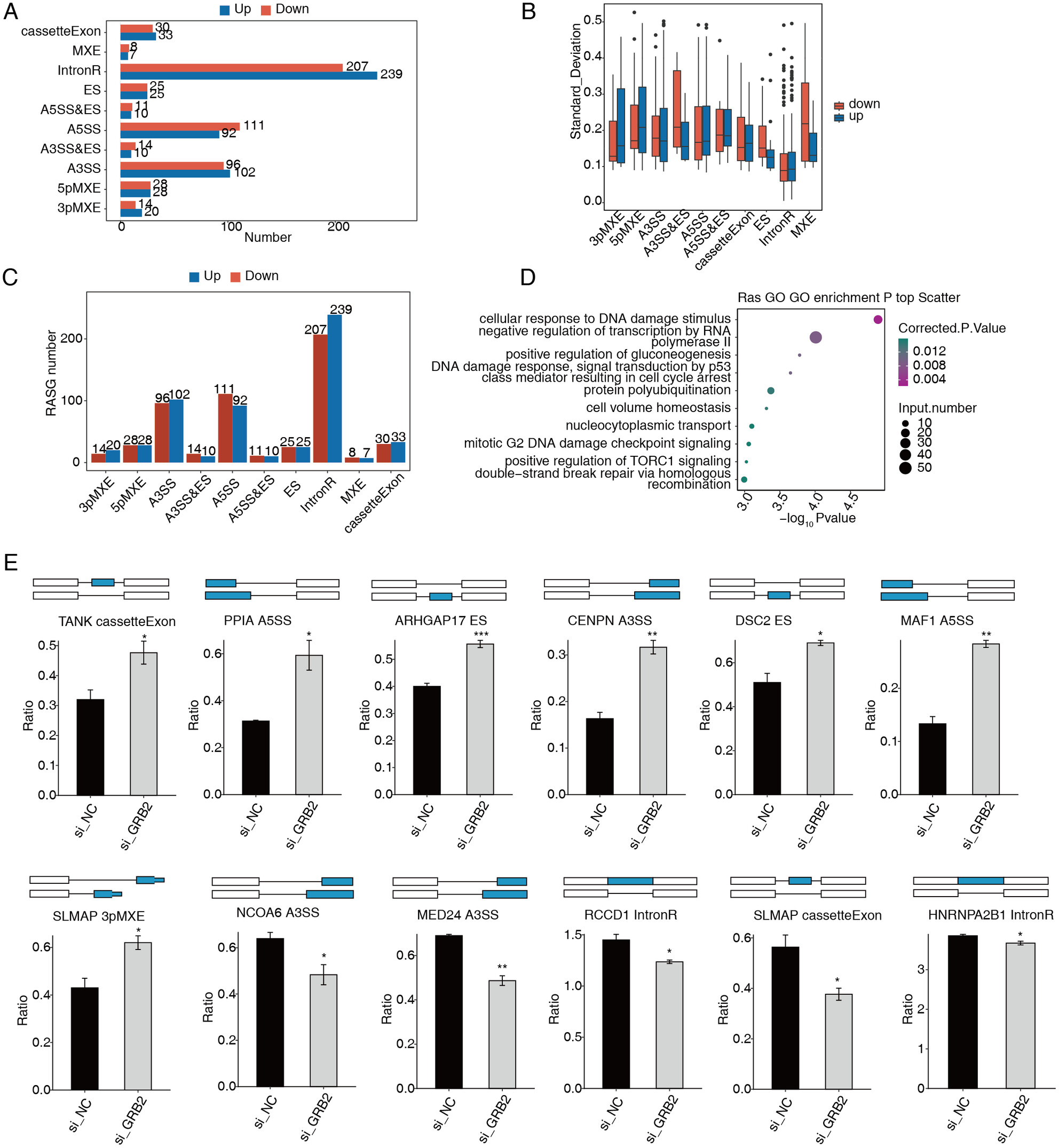
GRB2 Promotes Malignant Behaviors of Breast Cancer by Modulating the Global Expression and Alternative Splicing Profiles in SK-BR-3 Cells Through Binding mRNA
- First Published: 19 May 2025
Is Diet Perceived as a Cancer Risk Factor? Lay Perceptions in a Representative French Sample
- First Published: 15 May 2025