Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Nomograms forecasting long-term overall and cancer-specific survival of patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 943-952
- First Published: 07 March 2018
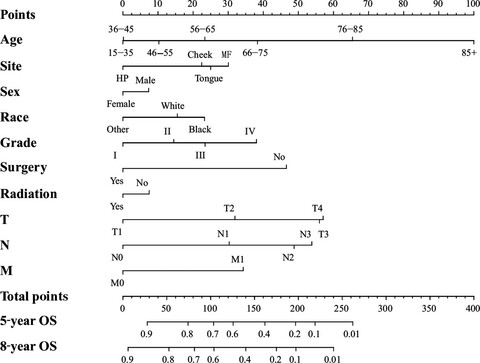
We successfully established two nomograms predicting overall survival(OS) and cancer-specific survival(CSS) of OSCC patients collected from SEER database. The validation results of the nomograms through the concordance index (C-index) and calibration curves showed that the model were credible, which can assist surgeons in developing a more effective therapeutic regimen and conducting personalized prognostic evaluations.
The role of primary lymph node sites in survival and mortality prediction in Hodgkin lymphoma: a SEER population-based retrospective study
- Pages: 953-965
- First Published: 09 March 2018
Little is known about the role of primary lymph node sites in survival in Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). This study uses a huge population-based cohort using the SEER database. It was found that intra-abdominal LN sites predict the worst survival in HL patients and that pelvic LN sites were the most aggressive in predicting HL-specific 1-year mortality, and hence, we recommend that primary LN sites be added to future international prognostic scores for HL.
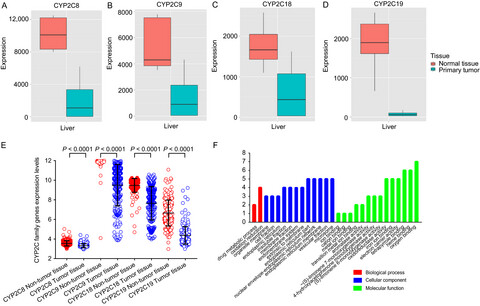
The prognostic value of CYP2C subfamily genes in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 966-980
- First Published: 26 February 2018
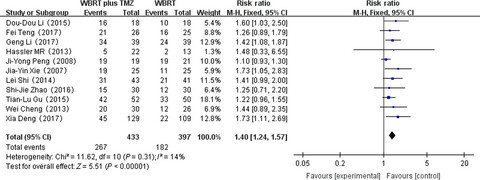
Meta-analysis of whole-brain radiotherapy plus temozolomide compared with whole-brain radiotherapy for the treatment of brain metastases from non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 981-990
- First Published: 07 March 2018
Higher than reported adolescent and young adult clinical trial enrollment during the “Golden Age” of melanoma clinical trials
- Pages: 991-996
- First Published: 25 February 2018
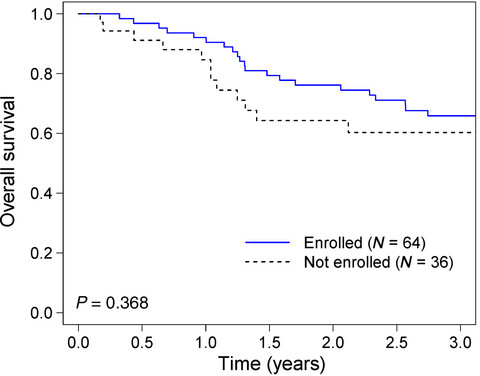
Adolescents and young adult (AYA) patients have had lower clinical trial accruals over the past few decades and this has led to fewer survival benefits when comparing these patients to children and older adults with cancer. Here we report nearly 1 out of 5 AYA melanoma patients enrolled on trials during the past decade when these trials improved survival substantially.
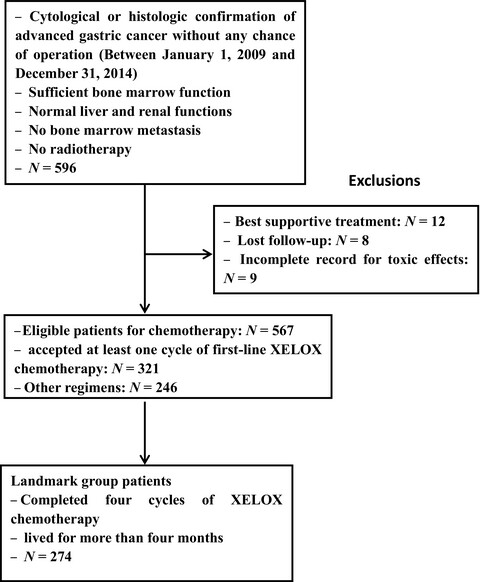
Timing of chemotherapy-induced neutropenia is a prognostic factor in patients with advanced gastric cancer undergoing first-line chemotherapy with oxaliplatin and capecitabine: a retrospective study
- Pages: 997-1005
- First Published: 13 March 2018
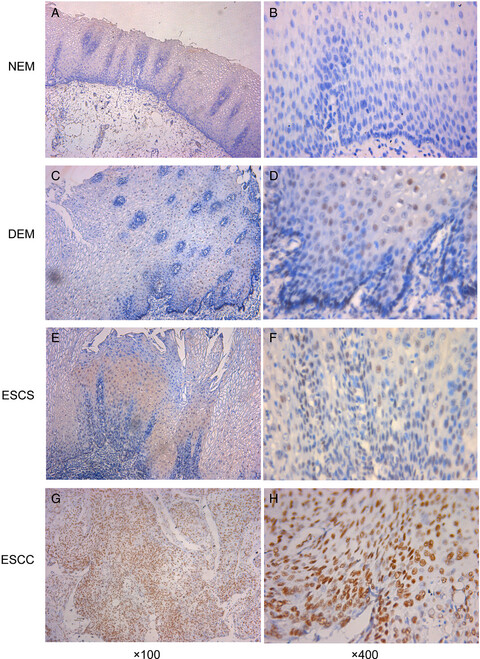
Clinical values of Ku80 upregulation in superficial esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1006-1018
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Integrative analysis of competing endogenous RNA network focusing on long noncoding RNA associated with progression of cutaneous melanoma
- Pages: 1019-1029
- First Published: 09 March 2018
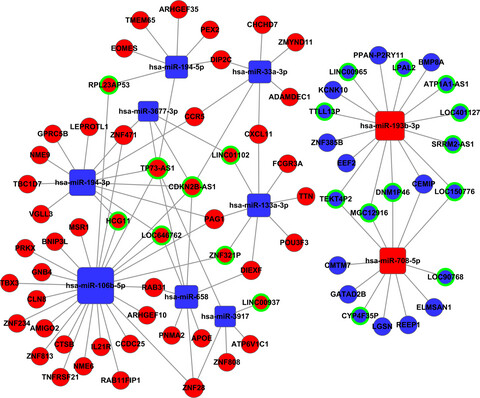
Twenty lncRNAs, 10 miRNAs, and 54 mRNAs, which are associated with the prognosis of CM, were conducted the competing endogenous network based on their regulation relationship. Squares represent miRNAs, balls represent mRNAs, and balls with a green circle around represent lncRNAs. Red means upregulated genes, while blue means downregulated genes.
Prognostic factors in breast phyllodes tumors: a nomogram based on a retrospective cohort study of 404 patients
- Pages: 1030-1042
- First Published: 26 February 2018
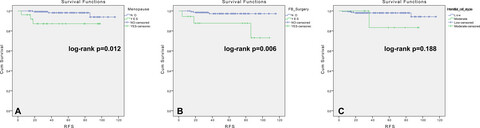
Stromal cell atypia was an independent prognostic factor for recurrence-free survival (RFS) in the low-risk breast phyllodes tumors. Surgical approach and tumor border were independent prognostic factors for RFS in the high-risk breast phyllodes tumors. We made a nomogram based on comprehensive consideration of the histological type, tumor border, tumor residue, mitotic activity, and degree of stromal cell hyperplasia and atypia. It could well predict the RFS probability of breast phyllodes tumors patients.
Ibrutinib versus rituximab in relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: a randomized, open-label phase 3 study
- Pages: 1043-1055
- First Published: 13 March 2018
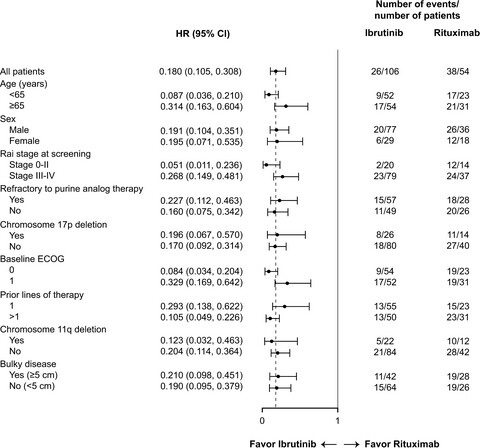
To our knowledge, this report is the first study of ibrutinib in a predominantly Asian population of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL/SLL and the first to compare ibrutinib with rituximab. Our results show that ibrutinib significantly improved progression-free survival, overall response rate, and overall survival compared with rituximab. Ibrutinib displayed a manageable safety profile with no new or unexpected events reported. These findings are consistent with previous studies of single-agent ibrutinib and demonstrate the efficacy and safety of ibrutinib in a predominantly Asian population of patients.
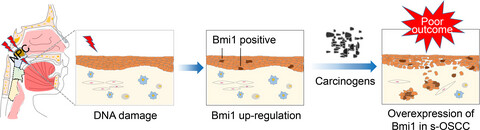
The poor outcome of second primary oral squamous cell carcinoma is attributed to Bmi1 upregulation
- Pages: 1056-1069
- First Published: 26 February 2018
Pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 1070-1080
- First Published: 24 February 2018
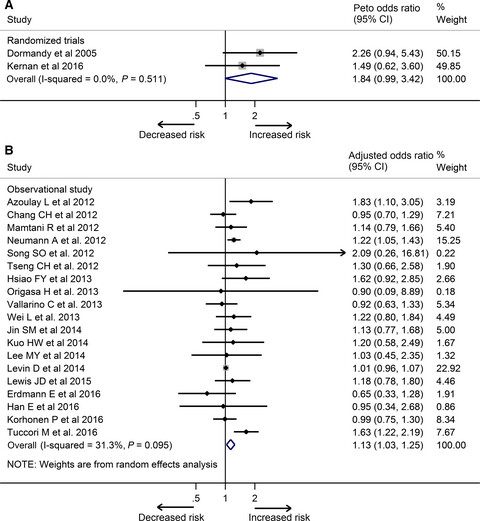
Current evidence about the association between pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk remains inconsistent. This meta-analysis of two randomized controlled trials and 20 observational studies showed that use of pioglitazone might increase risk of bladder cancer. Our findings suggest a close monitoring of bladder cancer in patients with long-term and high-dose exposure to pioglitazone.
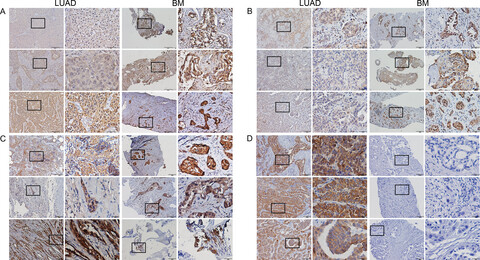
Differentially expressed and survival-related proteins of lung adenocarcinoma with bone metastasis
- Pages: 1081-1092
- First Published: 09 March 2018
The impact of comorbidity on overall survival in elderly nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients: a National Cancer Data Base analysis
- Pages: 1093-1101
- First Published: 01 March 2018
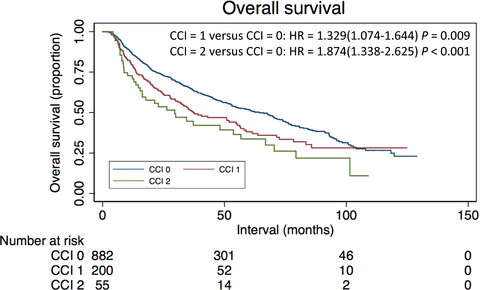
Elderly nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients with Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) score of 0 had significantly higher 5-year overall survival (OS) than patients with a CCI score of 1 or >2 (53.1% vs. 42.2% vs. 32.9%, P < 0.0001). In multivariate analysis, comorbidity was a statistically significant independent prognostic factor for OS in the elderly NPC patients.
Determinants of malignant pleural mesothelioma survival and burden of disease in France: a national cohort analysis
- Pages: 1102-1109
- First Published: 26 February 2018

The analysis of a national hospital database allowed the analysis of 1890 incident malignant pleural mesothelioma managed in France in 2011 and 2012. One- and 2-year survival rates were 64% and 48%, respectively. Median survival was 14.9 months. The mean cost per patient was 27,624 ± 17,263 euros After adjusting to age, sex, and co-morbidities, social deprivation index was not significantly associated with survival but living in Rural/semi-rural area was associated with better 2-year survival (HR: 0.83 [95% CI: 0.73–0.94]; P < 0.01).
Dynamic changes in plasma Epstein–Barr virus DNA load during treatment have prognostic value in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a retrospective study
- Pages: 1110-1117
- First Published: 01 March 2018
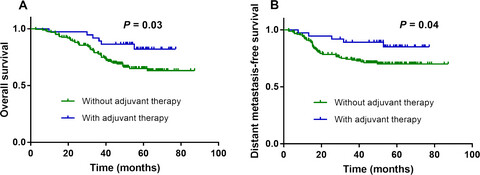
EBV DNA represents a dynamic biomarker for monitoring treatment and predicting survival in NPC. Assessing plasma EBV DNA before, during, and after chemoradiotherapy could be clinically valuable and enable selection of patients most likely to benefit from additional therapy and improve assessment of treatment response and disease surveillance.
Adult nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: treatment modality utilization and survival
- Pages: 1118-1126
- First Published: 26 February 2018
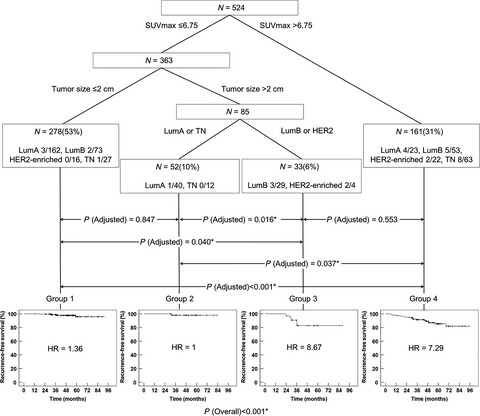
A hierarchical prognostic model for risk stratification in patients with early breast cancer according to 18F-fludeoxyglucose uptake and clinicopathological parameters
- Pages: 1127-1134
- First Published: 26 February 2018
Development and validation of an individualized diagnostic signature in thyroid cancer
- Pages: 1135-1140
- First Published: 09 March 2018
Comparison of survival between right-sided and left-sided colon cancer in different situations
- Pages: 1141-1150
- First Published: 13 March 2018
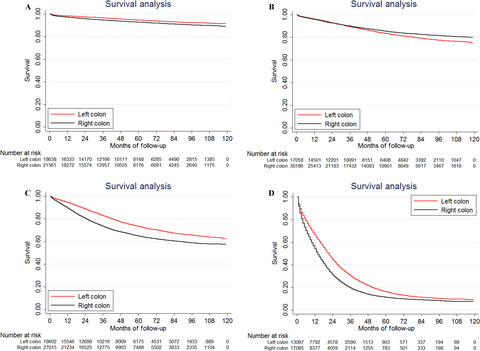
The relationship between survival and tumor location in colon cancer was not straightforward. There is a need for further subdivisions when analyzing the survival difference between right-sided colon cancer (RSCC) and left-sided colon cancer (LSCC). We found that RSCC patients had better prognosis than LSCC in stage II disease or mucinous adenocarcinoma/signet ring cell carcinoma patients.
National cancer database analysis of outcomes in pediatric glioblastoma
- Pages: 1151-1159
- First Published: 13 March 2018
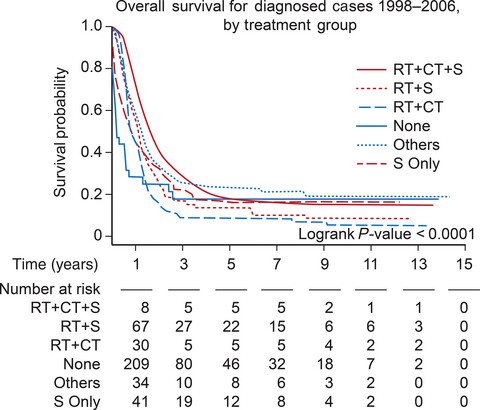
This is the largest demographics and patterns of care study of pediatric glioblastoma. We found age and tumor location related differences in outcomes that reflect variances in tumor biology and of treatment receipt. Our findings demonstrated improved survival was associated with the use of multimodality treatment, particularly the combination of surgery, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Differences in clinicopathological characteristics and computed tomography findings between signet ring cell carcinoma and nonsignet ring cell carcinoma in early and advanced gastric cancer
- Pages: 1160-1169
- First Published: 13 March 2018
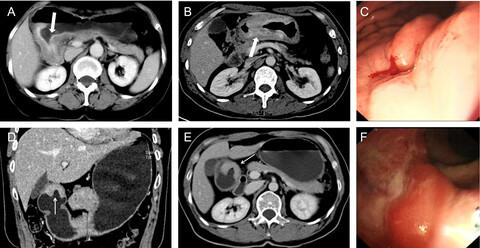
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of advanced gastric carcinoma. (A, B) Two contrast enhanced CT images in different patients with advanced SRC. Contrast enhanced CT scan shows diffuse gastric wall thickening with strongly enhancement. The layered and heterogeneous-enhancement pattern is shown. (C) Endoscopic image (same patient in B) of the lesion shows a diffusely infiltrating lesion. (D–F) Fifty-five-year-old man with NSRC. Contrast enhanced CT scan and coronal reconstruction show focal gastric wall thickening mainly of the enhancing thickened inner layer (arrow). The homogeneous-enhancement pattern is shown. Endoscopic image of the lesion shows an ulcer lesion located in the gastric antrum.
Comparison and validation of the prognostic value of preoperative systemic immune cells in hepatocellular carcinoma after curative hepatectomy
- Pages: 1170-1182
- First Published: 13 March 2018
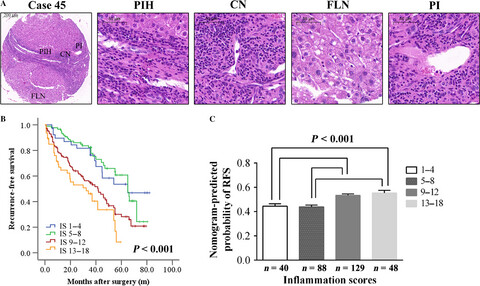
In this study, we developed two nomograms to predict postoperative recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS), respectively, after comparisons of the systemic inflammatory/immune cells prognostic scores. The nomogram-predicted probability of RFS was associated with peritumoral necroinflammatory activity scores. The proposed nomograms included NMLR had accurate prognostic prediction in patients with HCC after curative hepatectomy.
Racial/ethnic disparities in de novo metastases sites and survival outcomes for patients with primary breast, colorectal, and prostate cancer
- Pages: 1183-1193
- First Published: 26 February 2018
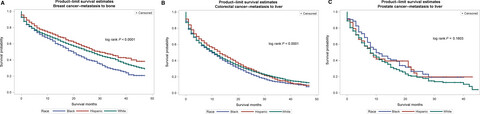
Racial disparities in cancer mortality still exist despite improvements in treatment strategies leading to improved survival for many cancer types. Data from SEER 2010–2014 were utilized to assess racial/ethnic differences in site of de novo metastasis and relative survival associated with de novo metastasis by race/ethnicity. In conclusion, de novo metastasis is a major contributor to cancer mortality among patients with cancer in the USA.
Polymorphism rs2682818 in miR-618 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility in a Han Chinese population
- Pages: 1194-1200
- First Published: 13 March 2018
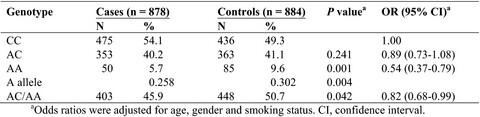
We found that individuals carrying the AA or AC/AA genotype had a decreased CRC susceptibility compared with the CC genotypes(OR = 0.54, 95% CI = 0.37–0.79 for AA vs. CC, in co-dominant model; OR = 0.82, 95% CI = 0.68–0.99 for AC/AA vs. CC, in dominant model). It is the first study to investigate the association between rs2682818 and CRC susceptibility and this finding could be a meaningful hint for further relevant studies.
Excessive risk of second primary cancers in young-onset colorectal cancer survivors
- Pages: 1201-1210
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Population-based differences in the outcome and presentation of lung cancer patients based upon racial, histologic, and economic factors in all lung patients and those with metastatic disease
- Pages: 1211-1220
- First Published: 13 March 2018
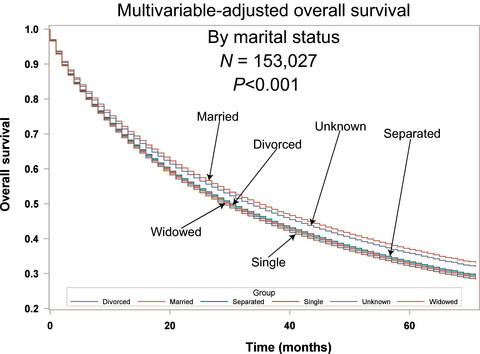
Our comprehensive study investigates ethnicity (nine different groups), marital status, treatment factors, standard histopathologic prognostic variables, and economic factors to see whether ethnicity is related to presentation or outcomes in lung cancer. We demonstrate that disparities in income, marriage, and insurance rather than ethnicity affect the survival of patients with lung cancer.
Albumin-to-fibrinogen ratio as a promising biomarker to predict clinical outcome of non-small cell lung cancer individuals
- Pages: 1221-1231
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Cancer Biology
Review
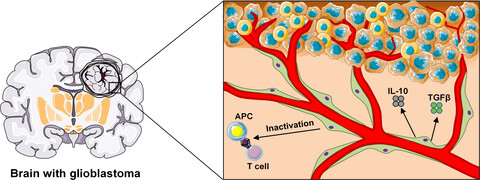
Glioblastoma-activated pericytes support tumor growth via immunosuppression
- Pages: 1232-1239
- First Published: 25 February 2018
Original Research
Mitochondrial Acetyl-CoA Synthetase 3 is Biosignature of Gastric Cancer Progression
- Pages: 1240-1252
- First Published: 01 March 2018
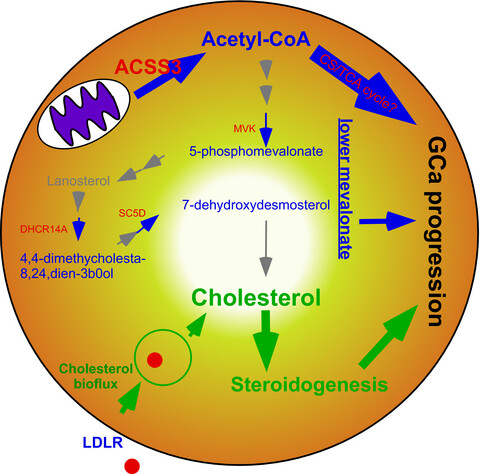
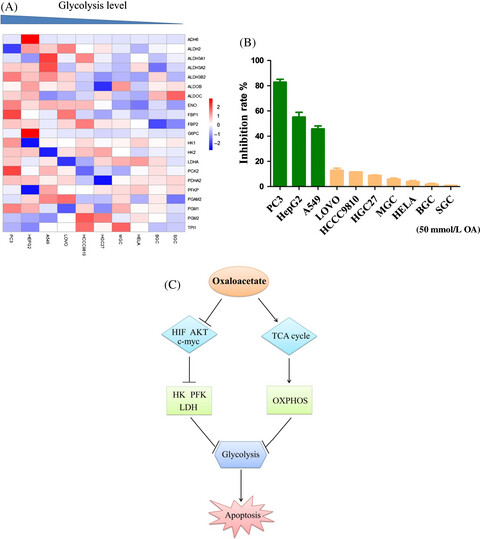
The cholesterogenic committing step enzyme (HMGCR) is not important in GCa patients, which explain the failure of statins in GCa clinical trials. However, the mitochondrial acetyl-CoA producer (ACSS3), and lower-mevalonate lipidomes are biosignatures for GCa progression. Interfering ACSS3 expression could almost abolished GCa cell growth under starvation stress. This study suggesting a targeting value of ACSS3 for GCa therapy.
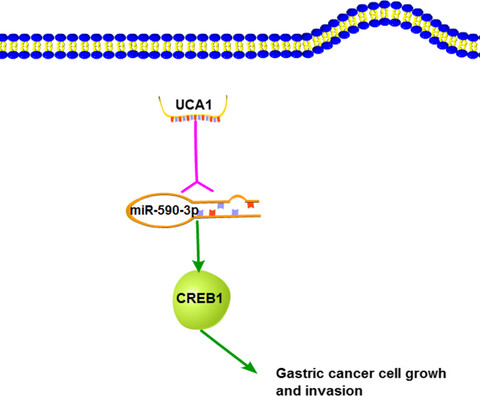
UCA1 promotes cell proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer by targeting CREB1 sponging to miR-590-3p
- Pages: 1253-1263
- First Published: 08 March 2018
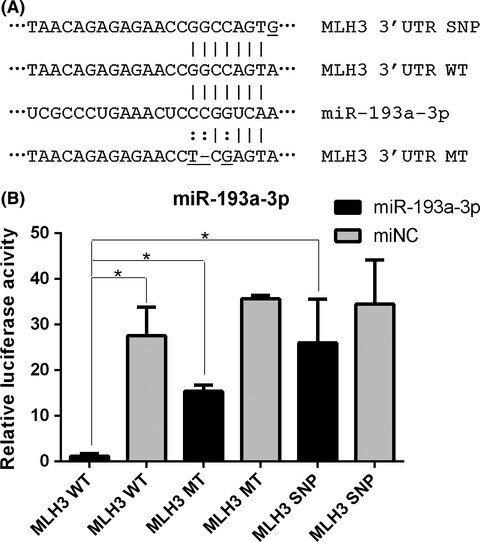
The polymorphisms of miRNA-binding site in MLH3 and ERCC1 were linked to the risk of colorectal cancer in a case–control study
- Pages: 1264-1274
- First Published: 08 March 2018
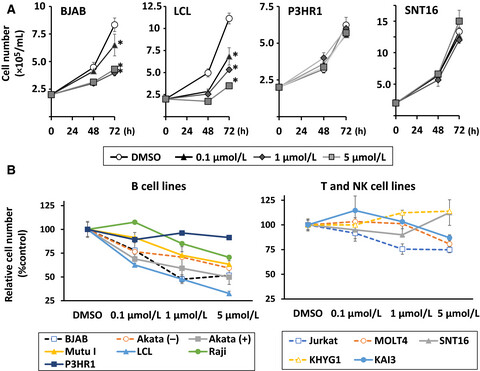
Antitumor effects of duvelisib on Epstein–Barr virus-associated lymphoma cells
- Pages: 1275-1284
- First Published: 09 March 2018
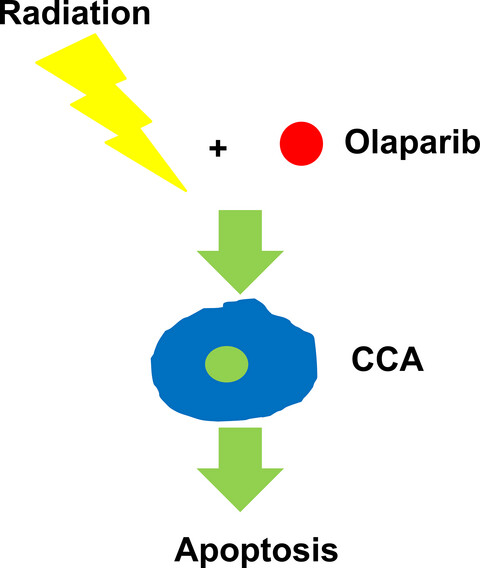
PARP inhibitor olaparib sensitizes cholangiocarcinoma cells to radiation
- Pages: 1285-1296
- First Published: 26 February 2018
Clofarabine exerts antileukemic activity against cytarabine-resistant B-cell precursor acute lymphoblastic leukemia with low deoxycytidine kinase expression
- Pages: 1297-1316
- First Published: 23 February 2018
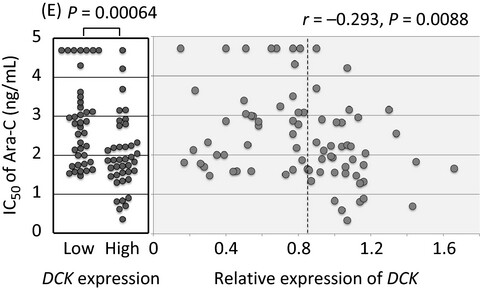
We demonstrated that DCK knockout by genome editing with a CRISPR-Cas9 system in an Ara-C-sensitive-ALL cell line induced resistance to Ara-C and clofarabine, a second-generation deoxyadenosine analog, and that higher DCK expression was associated with higher AraC sensitivity in a series of B-cell precursor ALL (BCP–ALL) cell lines. In contrast, sensitivity to clofarabine was only marginally associated with DCK gene expression level, suggesting the high antileukemic potential of clofarabine may overcome low DCK expression in Ara-C-resistant BCP–ALL.
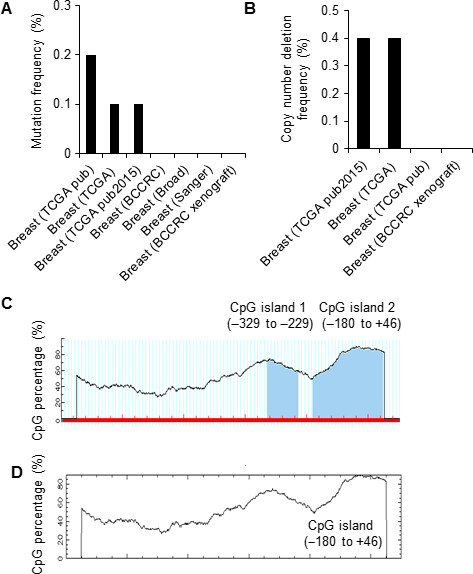
Epigenetic silencing of RNF144A expression in breast cancer cells through promoter hypermethylation and MBD4
- Pages: 1317-1325
- First Published: 23 February 2018
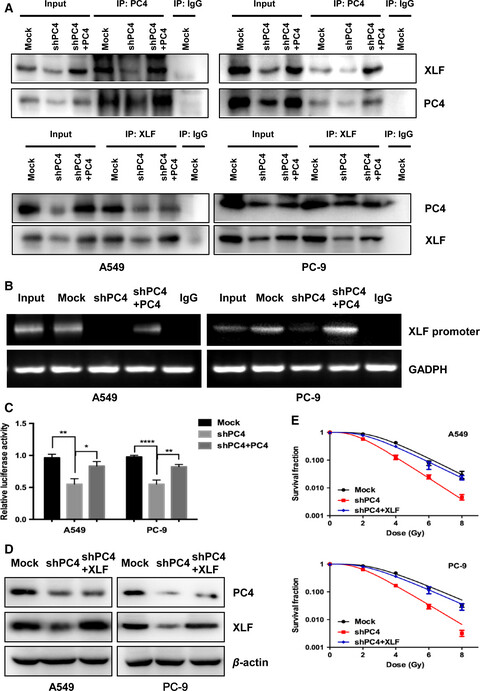
Inhibition of PC4 radiosensitizes non-small cell lung cancer by transcriptionally suppressing XLF
- Pages: 1326-1337
- First Published: 09 March 2018
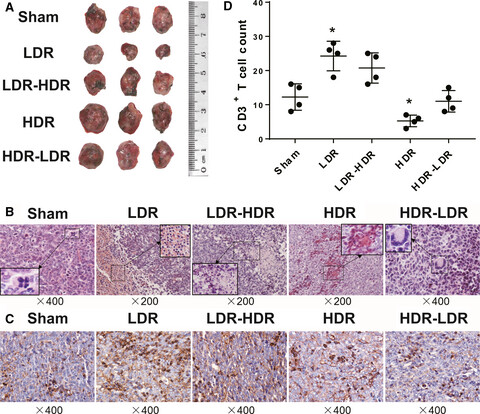
Validating the pivotal role of the immune system in low-dose radiation-induced tumor inhibition in Lewis lung cancer-bearing mice
- Pages: 1338-1348
- First Published: 25 February 2018
Gene panel testing of 5589 BRCA1/2-negative index patients with breast cancer in a routine diagnostic setting: results of the German Consortium for Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer
- Pages: 1349-1358
- First Published: 09 March 2018

In this case-control study of well-characterized breast cancer patients, we confirm ATM, CHEK2, PALB2, CDH1, and TP53 as BC risk genes, no association was observed for NBN. We demonstrate a significant association of deleterious variants in the CHEK2, PALB2, and TP53 genes with bilateral BC and both, ATM and CHEK2, were negatively associated with TNBC and (ER)-negative tumor phenotypes. Our study confirmed the benefit of multi-gene testing for risk assessment in BC families while clinical phenotypes associated with non-BRCA1/2 gene mutations remain to be determined.
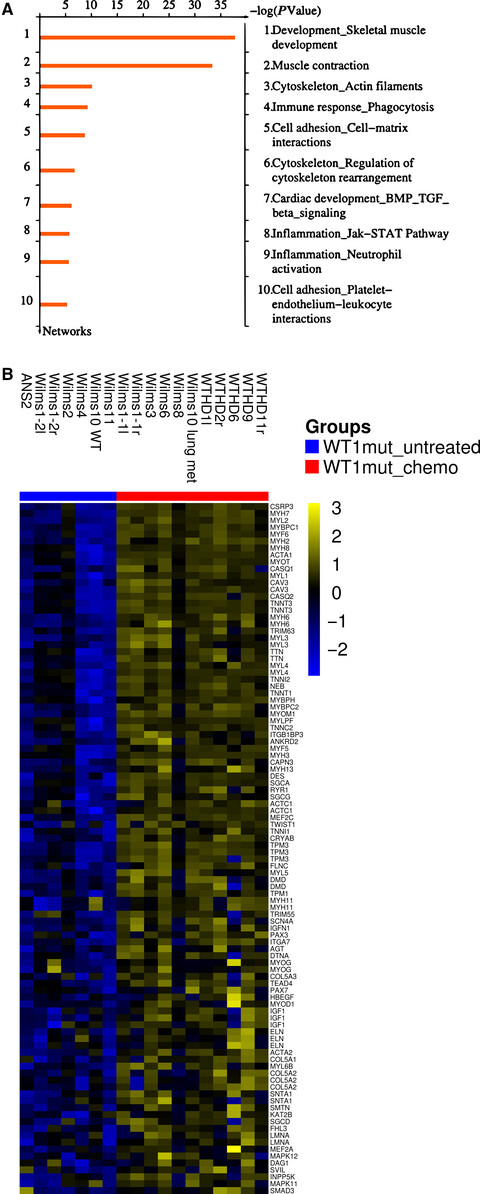
Chemotherapy and terminal skeletal muscle differentiation in WT1-mutant Wilms tumors
- Pages: 1359-1368
- First Published: 15 March 2018
Apoptin-derived peptide reverses cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer through the PI3K–AKT signaling pathway
- Pages: 1369-1383
- First Published: 09 March 2018
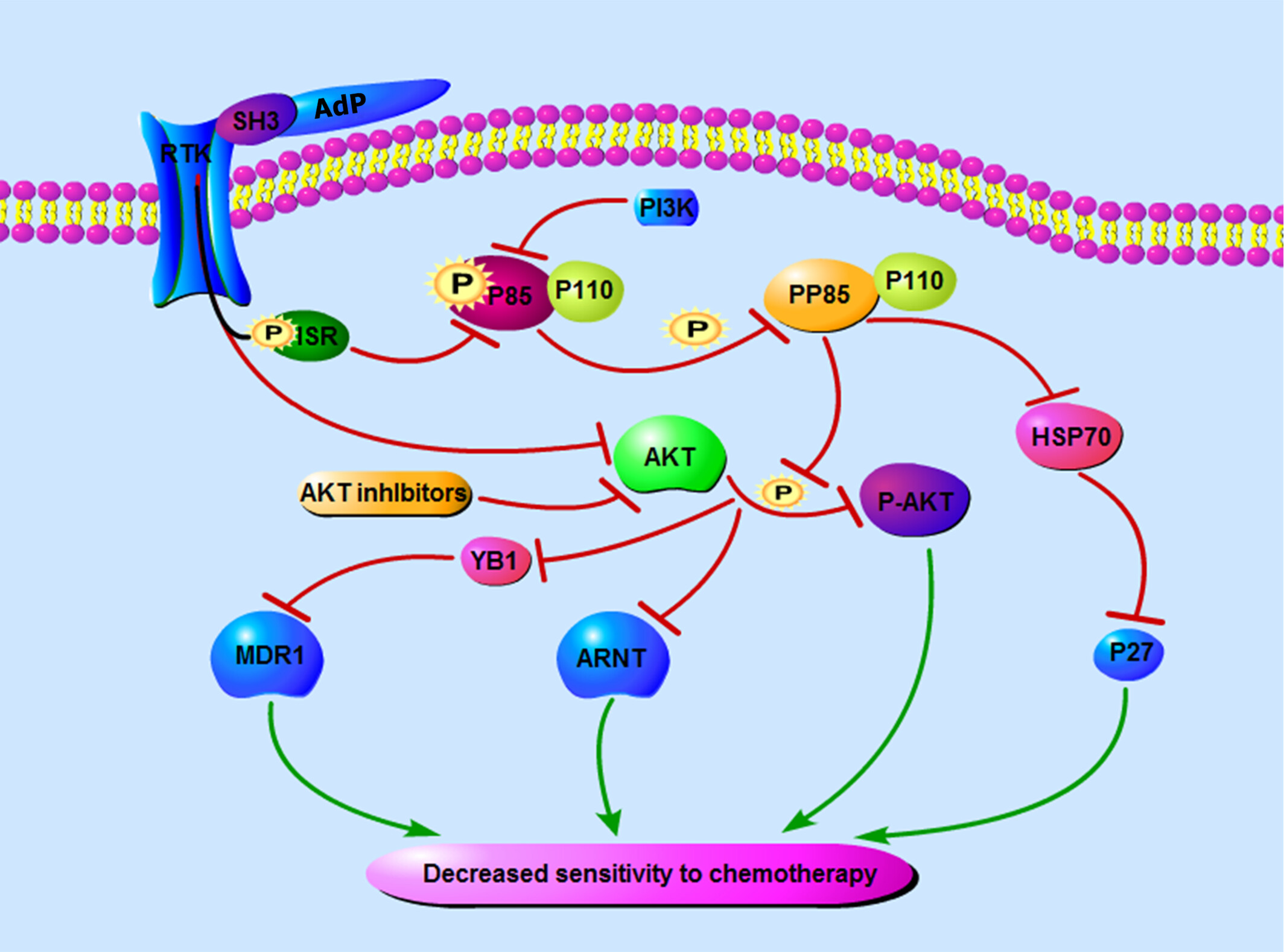
Apoptin-derived peptide (AdP) is an antitumor polypeptide constructed in our laboratory that has been used to combat cisplatin (CDDP) resistance in GC cells. AdP exerted a specific cytotoxic effect on GC cells and CDDP-resistant GC cells, and suppressed invasion and migration. AdP inhibited the expression of p85, AKT, p-p85, p-AKT, multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1), and aryl hydrocarbon nuclear translocator (ARNT) within the PI3K/AKT/ARNT signaling pathway.
Genomic complexity in pediatric synovial sarcomas (Synobio study): the European pediatric soft tissue sarcoma group (EpSSG) experience
- Pages: 1384-1393
- First Published: 13 March 2018
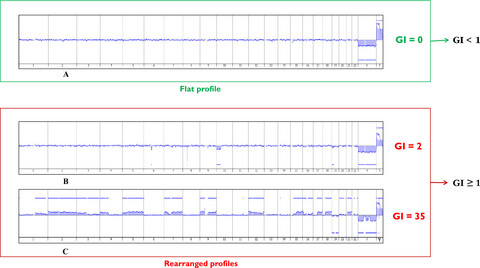
This study analyzes 61 pediatric/adolescent/young adults (<25 years) with localized synovial sarcoma prospectively enrolled in the European EpSSG-NRSTS05 protocol to demonstrate that somatic genomic index (GI) analyzed using comparative genomic hybridization had a high prognostic value in pediatric synovial sarcoma as an independent prognostic factors. It demonstrates that patients with tumor harboring high GI had worse five-year event-free and metastatic-free survivals comparing to ones with no genomic instability, and that therefore GI could be used to stratify more accurately patients in the future.
Increased expression of miR-641 contributes to erlotinib resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer cells by targeting NF1
- Pages: 1394-1403
- First Published: 01 March 2018
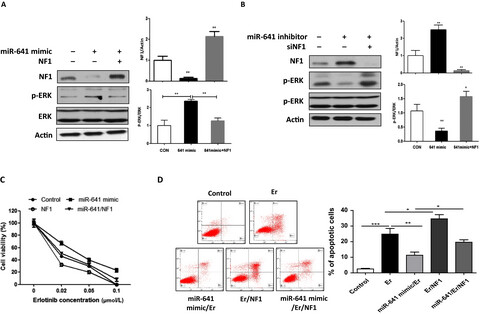
We first time determined the role of miR-641 on the erlotinib resistance development in NSCLC cells. Our findings suggest that upregulated expression of miR-641 was significantly associated with erlotinib resistance development in NSCLC cells. Our findings may also aid in the development of potential therapeutics for the treatment of erlotinib-resistant NSCLC.
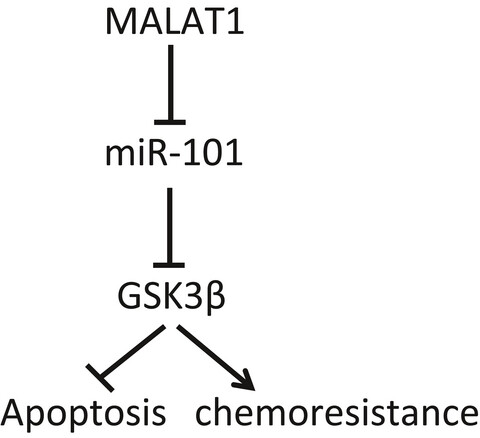
Long noncoding RNA MALAT1 knockdown reverses chemoresistance to temozolomide via promoting microRNA-101 in glioblastoma
- Pages: 1404-1415
- First Published: 26 February 2018
Oxaloacetate induces apoptosis in HepG2 cells via inhibition of glycolysis
- Pages: 1416-1429
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
YL143, a novel mutant selective irreversible EGFR inhibitor, overcomes EGFRL858R, T790M-mutant resistance in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 1430-1439
- First Published: 13 March 2018
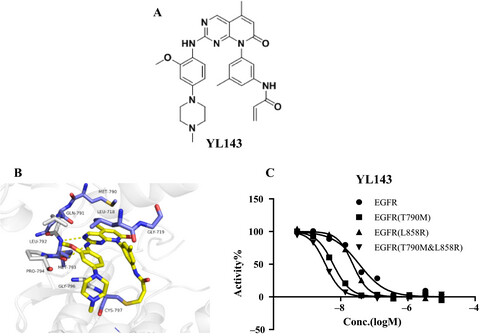
We have developed a novel EGFR inhibitor YL143, which displayed highly potent, specific EGFRT790M inhibition and improved the oral bioavailability. YL143 also exhibited antiproliferative effect in H1975 cells and animal xenografts. YL143 may serve as a new promising lead compound for drug discovery overcoming the acquired resistance of patients with NSCLC without adverse toxicities.
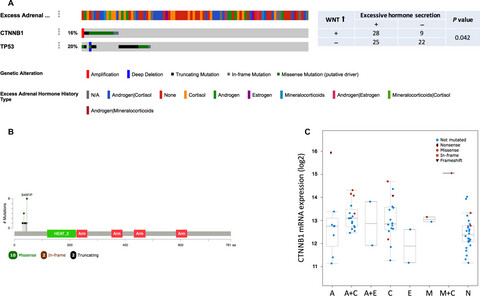
Nutlin-3a as a novel anticancer agent for adrenocortical carcinoma with CTNNB1 mutation
- Pages: 1440-1449
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Physical activity across the lifespan and liver cancer incidence in the NIH-AARP Diet and Health Study cohort
- Pages: 1450-1457
- First Published: 13 March 2018
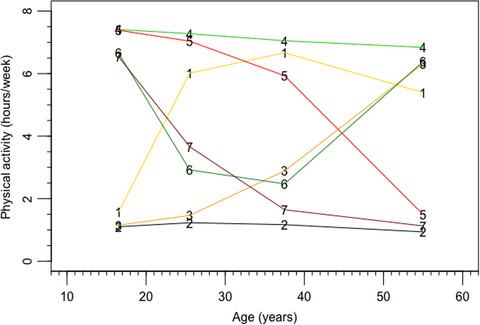
While physical activity has been associated with lower risk of developing liver cancer, most studies assess physical activity only at a single point in time, often in midlife. Our findings that, compared to individuals who reported little activity over the life course, only sustained physical activity was associated with lower liver cancer risk, offer support for federal recommendations to maintain physical activity both as a young and as an older adult.
Establishment and validation of a two-step screening scheme for improved performance of serological screening of nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 1458-1467
- First Published: 25 February 2018
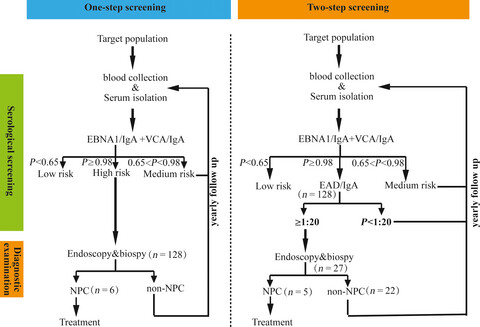
A simple two-step screening scheme was established to improve the PPV of the screening, with the combination of EBNA1/IgA and VCA/IgA in the first step of screening and anti-EAs in the second step. The PPV could be increased from 4.69% in the first step of screening to 18.52% after the second step of screening. With this two-step serological screening, more people could be benefited from the screening program.
Prostate cancer surveillance by occupation and industry: the Canadian Census Health and Environment Cohort (CanCHEC)
- Pages: 1468-1478
- First Published: 01 March 2018
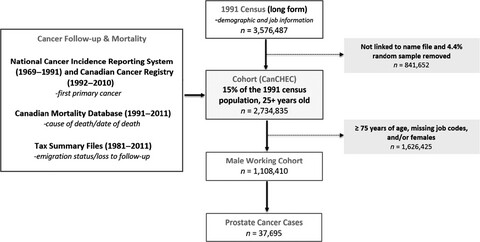
We examined occupation, industry, prostate cancer, and patterns of prostate cancer rates using a large Canadian worker cohort. Increased risks were observed in white-collar, agriculture, and protective services occupations, and decreased risks were observed in construction and transportation occupations across men aged 25–74 years. These findings emphasize the need for further study of job-related exposures and the potential influence of non-occupational factors such as screening behaviours.
International trends in lung cancer incidence from 1973 to 2007
- Pages: 1479-1489
- First Published: 14 March 2018
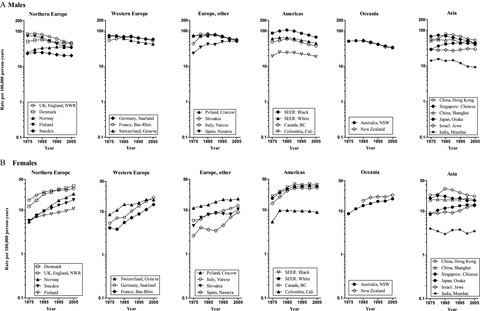
The international trends between 1973 and 2007 showed that ASRs of lung cancer among males were declining in 13 of 18 selected Americas, Oceania, and Europe populations, with AAPC from −0.7% to −2.9%. Whereas the rates among females in 18 selected populations were increasing, with AAPC from 1.3% to 5.0%. The increasing and decreasing trends of ASRs of lung cancer in Asia have an geographic variation but no gender differences.
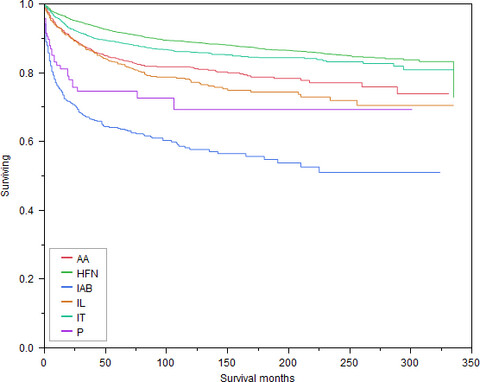
Disparities in cancer survival and incidence by metropolitan versus rural residence in Utah
- Pages: 1490-1497
- First Published: 13 March 2018
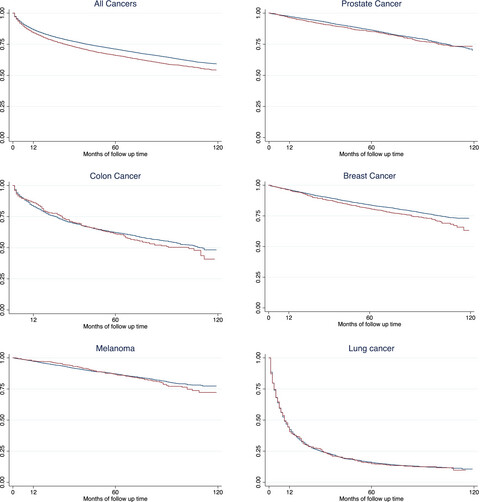
Cancer disparities in rural and frontier communities are an important issue in Utah because much of Utah is sparsely populated. Patients with cancer from rural counties in Utah were more likely to be older, American Indian/Alaskan Native, non-Hispanic, male, and diagnosed at higher stage. Rural residents had a five-year relative survival that was 5.2% lower than metropolitan residents and a 10% increase in risk of death (HR = 1.10, 95% CI = 1.03, 1.18) after adjustment for multiple factors.
Socioeconomic and demographic inequalities in stage at diagnosis and survival among colorectal cancer patients: evidence from a Swiss population-based study
- Pages: 1498-1510
- First Published: 26 February 2018
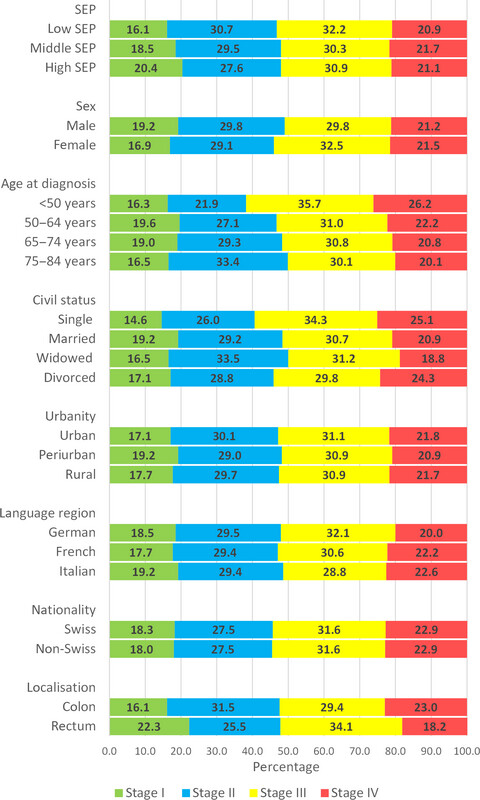
This is the first population-based study in Switzerland investigating socioeconomic and demographic inequalities in stage at diagnosis and survival among patients with colorectal cancer (CRC). This study describes high-risk groups for later stage CRC diagnosis (patients with low SEP) and poorer disease-specific survival (non-Swiss and patients living in nonurban areas). Swiss public health strategies should facilitate equal access to CRC screening and optimal CRC care for all social groups and in all regions of Switzerland.
Being present: oncologists' role in promoting advanced cancer patients' illness understanding
- Pages: 1511-1518
- First Published: 26 February 2018
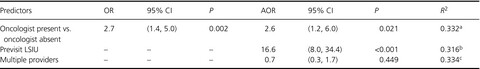
In this longitudinal cohort study that included 209 patients with late-stage cancers, patients were over two-and-a-half times as likely to report that their disease was late-stage if an oncologist was present versus not present for their scan results discussion in clinic. Our findings suggest that it is important for oncologists to be present during clinic visits in which scan results are discussed for patients to understand their cancer is at a late-stage.
Association between preoperative serum insulin levels and lymph node metastasis in endometrial cancer—a prospective cohort study
- Pages: 1519-1527
- First Published: 13 March 2018

Our novel findings are that (1) WHR, lesion diameter >2 cm, myometrial invasion ≥50%, pathological grade, and insulin levels were significant predictors of LNM risk in both premenopausal and postmenopausal women, (2) insulin level with a cut-off of 10.48 μIU/mL was predictive of LNM risk when adjusted for BMI (OR: 3.51, 1.42–5.98; P < 0.05) or WHR (OR: 1.87, 1.08–2.66; P < 0.05) in premenopausal women, and (3) insulin with a similar cut-off of 10.15 μIU/mL was predictive of LNM risk when adjusted for BMI (3.07, 1.26–5.40; P < 0.05, respectively) or WHR (OR: 1.61, 1.04–2.35; P < 0.05).
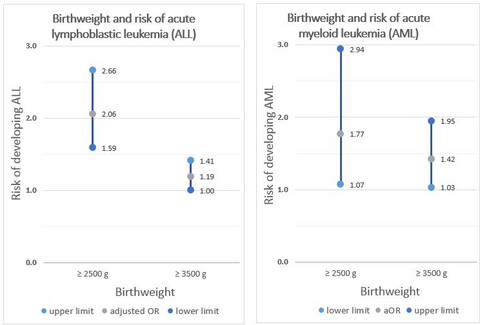
A greater birthweight increases the risk of acute leukemias in Mexican children—experience from the Mexican Interinstitutional Group for the Identification of the Causes of Childhood Leukemia (MIGICCL)
- Pages: 1528-1536
- First Published: 13 March 2018
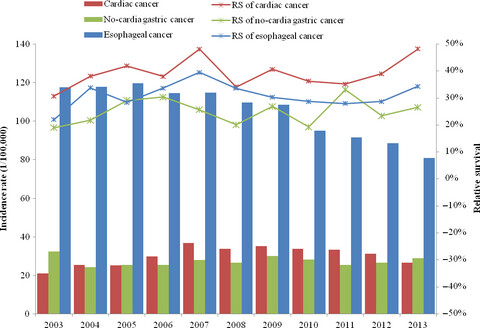
Cancer survival in Cixian of China, 2003–2013: a population-based study
- Pages: 1537-1545
- First Published: 13 March 2018
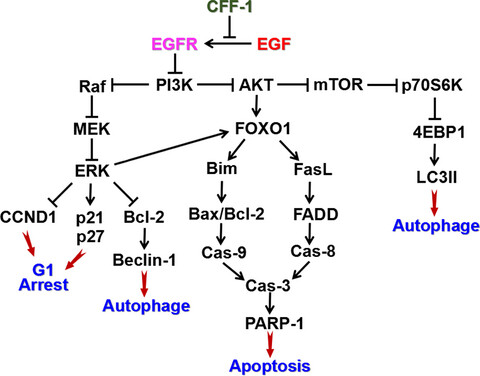
Traditional Chinese Medicine CFF-1 induced cell growth inhibition, autophagy, and apoptosis via inhibiting EGFR-related pathways in prostate cancer
- Pages: 1546-1559
- First Published: 13 March 2018
Clinical outcomes of radio-hyperthermo-chemotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma compared to a soft tissue sarcoma registry in Japan: a retrospective matched-pair cohort study
- Pages: 1560-1571
- First Published: 26 February 2018
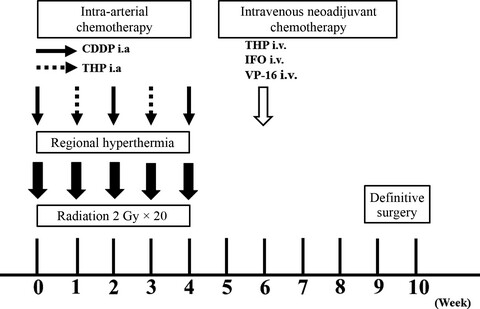
The efficacy of concomitant radiotherapy, hyperthermia, and chemotherapy (RHC) for neoadjuvant treatment of malignant soft tissue sarcoma was confirmed by comparing to the Bone and Soft Tissue Tumor Registry in Japan (BSTT). RHC resulted in a high local control at 5 years compared to the BSTT group, and the difference in overall survival was not significant between groups.