Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
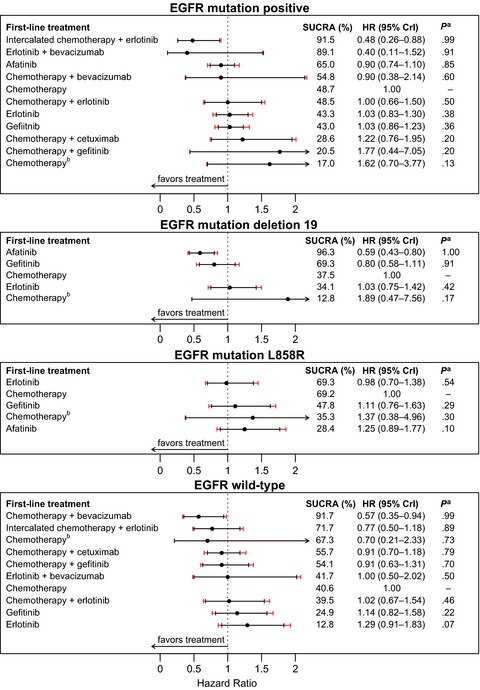
Meta-analysis of first-line therapies with maintenance regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) in molecularly and clinically selected populations
- Pages: 1847-1860
- First Published: 03 July 2017
Identification of patients with cancer with a high risk to develop delirium
- Pages: 1861-1870
- First Published: 07 July 2017
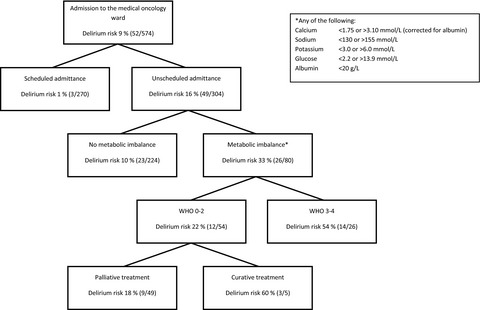
The predisposing factors of an unscheduled admittance and a metabolic imbalance accurately predict the development of delirium in patients with cancer (delirium risk 1:3). This prediction algorithm for delirium that can be easily implemented in daily clinical practice should be evaluated for the potential benefit of preventive treatment of patients with cancer who are prone to develop delirium.
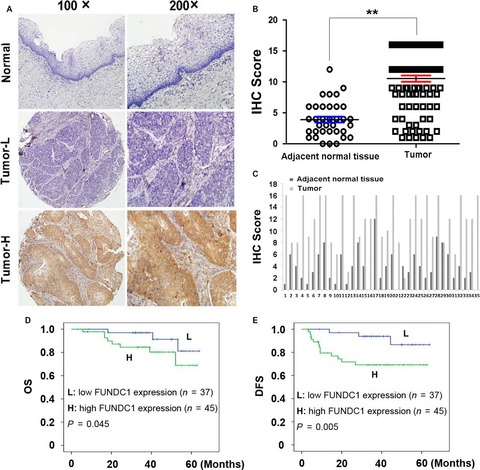
High expression of FUNDC1 predicts poor prognostic outcomes and is a promising target to improve chemoradiotherapy effects in patients with cervical cancer
- Pages: 1871-1881
- First Published: 18 July 2017
Time-dependent and nonlinear effects of prognostic factors in nonmetastatic colorectal cancer
- Pages: 1882-1892
- First Published: 14 July 2017
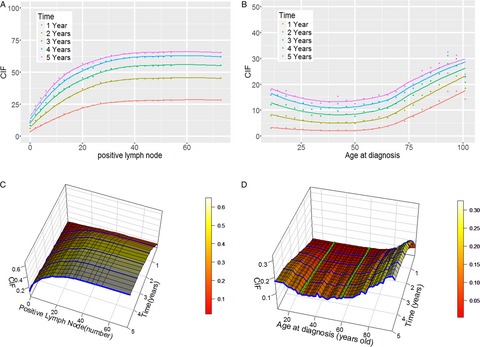
Time-dependent effects on survival indicated that prognostic factors of colorectal cancer had changeable risks as time progressed. Nonlinear modeling detected nonlinear effects and provided more prognosis information. Three-dimensional cumulative incidence curves were used to identify the change points of the risk trends.
Clinical value of integrated-signature miRNAs in esophageal cancer
- Pages: 1893-1903
- First Published: 14 July 2017
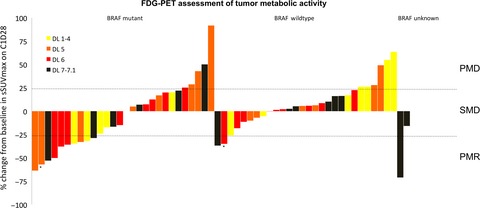
A first-in-human phase I, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study of the oral RAF/VEGFR-2 inhibitor (RAF265) in locally advanced or metastatic melanoma independent from BRAF mutation status
- Pages: 1904-1914
- First Published: 18 July 2017
Identification of sentinel lymph nodes by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with Sonazoid in patients with breast cancer: a feasibility study in three hospitals
- Pages: 1915-1922
- First Published: 01 August 2017
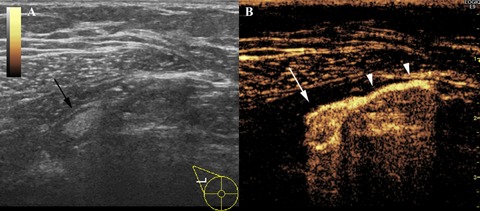
Patients (n = 100) received periareolar injection of Sonazoid followed by ultrasonography of the axilla for identification of contrast-enhanced sentinel lymph node (SLN). This method is technically simple with a high success rate (98%) and comparable to the conventional method using blue dye and/or radiocolloid.
Review
Endocrine toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors: essential crosstalk between endocrinologists and oncologists
- Pages: 1923-1929
- First Published: 18 July 2017
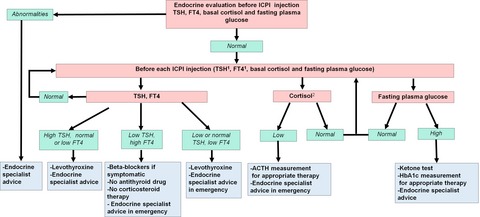
The rational data on endocrine toxicity of immune checkpoint inhibitors are scarce. It seemed important to us to indicate and discuss some pre- or misconceptions about thyroid dysfunction, hypophysitis, and diabetes induced by immune checkpoint inhibitors, in order to improve the management of patients.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Telomerase reverse transcriptase germline mutations and hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 1930-1940
- First Published: 04 July 2017
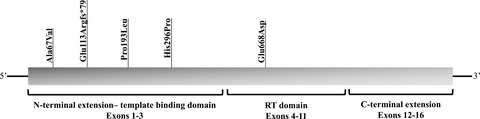
Telomere length was reduced in individuals who developed hepatocellular carcinoma in nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFLD-HCC) versus those with cirrhosis and healthy controls, independently of age and sex. We detected an enrichment of hTERT mutations in NAFLD patients affected by primary liver cancer, predominantly in females and specifically in the N-terminal template-binding domain. In conclusion, shorter telomeres and enrichment of hTERT rare germline mutations are associated with NAFLD-HCC.
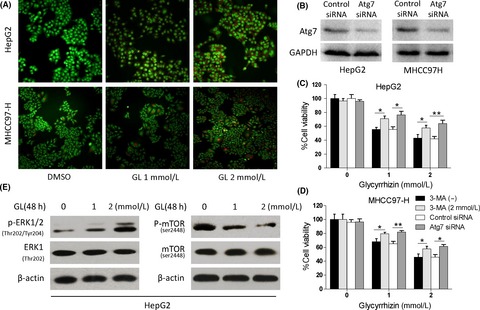
The mTOR inhibition in concurrence with ERK1/2 activation is involved in excessive autophagy induced by glycyrrhizin in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 1941-1951
- First Published: 03 July 2017
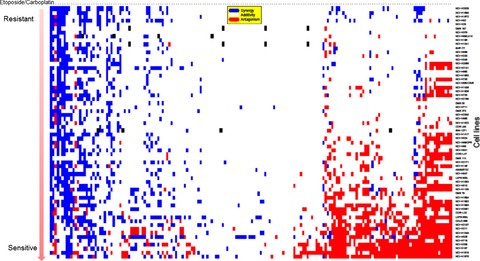
Small cell lung carcinoma cell line screen of etoposide/carboplatin plus a third agent
- Pages: 1952-1964
- First Published: 01 August 2017
Metformin synergistic pemetrexed suppresses non-small-cell lung cancer cell proliferation and invasion in vitro
- Pages: 1965-1975
- First Published: 18 July 2017
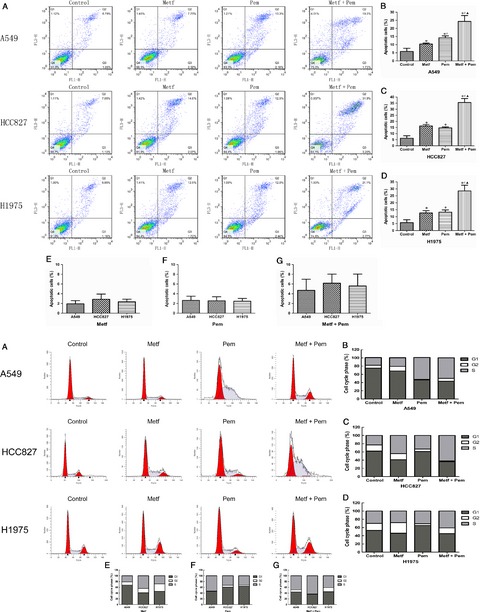
These results demonstrate that the combination of metformin and pemetrexed has a synergistic effect on the treatment of NSCLC cell lines by inducing apoptosis or blocking the cell cycle. Our data indicate that the combination of metformin and pemetrexed could have beneficial antitumor effects on NSCLC cells in vitro.
Transcriptome analysis in primary colorectal cancer tissues from patients with and without liver metastases using next-generation sequencing
- Pages: 1976-1987
- First Published: 26 July 2017
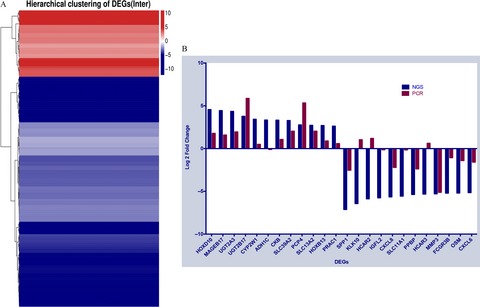
In this study, we performed next-generation sequencing profiling on primary colorectal tumor tissues obtained from three CRC patients with liver metastases and three CRC patients without liver metastases to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs) that might be responsible for the metastases process. The validation showed that three most significantly upregulated DEGs were HOXD10, UGT2A3, and SLC13A2 whereas the five most significantly downregulated DEGs were SPP1, CXCL8, MMP3, OSM, and CXCL6, respectively.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Mechanisms of breast cancer risk in shift workers: association of telomere shortening with the duration and intensity of night work
- Pages: 1988-1997
- First Published: 14 July 2017
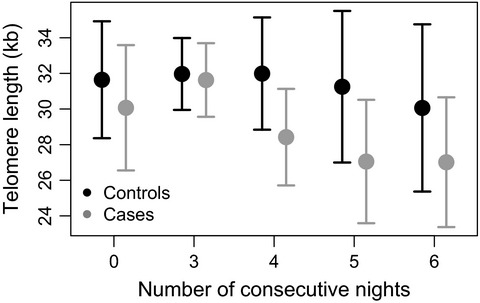
This study demonstrates that telomere shortening in night workers may be a plausible biological mechanism explaining the increased breast cancer risk in workers with long periods of consecutive night shifts. To our knowledge, this is a novel mechanism suggesting telomere shortening as a contributing factor for shift work-related breast cancer risk.
Hormone factors play a favorable role in female head and neck cancer risk
- Pages: 1998-2007
- First Published: 14 July 2017
Commentary
Evidence-based policy choices for efficient and equitable cervical cancer screening programs in low-resource settings
- Pages: 2008-2014
- First Published: 14 July 2017
The authors describe the challenges that confront cervical cancer screening programs in low-resource settings, including (1) optimizing screening test effectiveness; (2) achieving high screening coverage of the target population; and (3) managing screen-positive women. For each of these challenges, the authors highlight opportunities for efficient and equitable programming based on evidence from mathematical modeling analyses.