Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Prognostic impact of the cumulative dose and dose intensity of everolimus in patients with pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors
- Pages: 1493-1499
- First Published: 25 May 2017
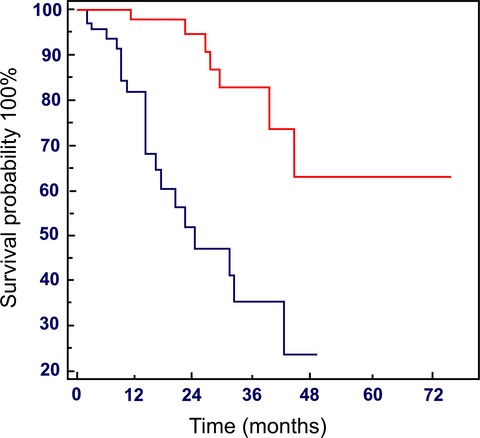
The aim of this work is to assess if cumulative dose (CD) and dose intensity (DI) of everolimus may affect survival of advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PNETs) patients. Median OS was 24 months in Group A (with cumulative dose ≤ 3000 mg) while in Group B (with cumulative dose > 3000 mg), it was not reached (HR: 26.9; 95% CI: 11.0–76.7; P < 0.0001). This should prompt efforts to continue everolimus administration in responsive patients up to at least 3000 mg despite delays or temporary interruptions.
Ultrasonography-driven combination antibiotic therapy with tigecycline significantly increases survival among patients with neutropenic enterocolitis following cytarabine-containing chemotherapy for the remission induction of acute myeloid leukemia
- Pages: 1500-1511
- First Published: 26 May 2017
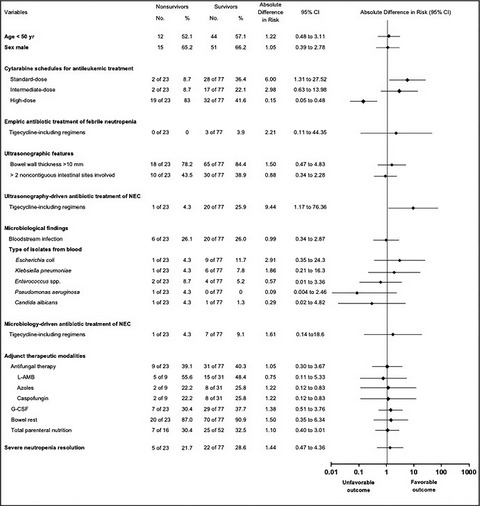
Prompt ultrasonography-driven combination antibiotic therapy for NEC improved survival among acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patient. Chemotherapy schedules with robust dosages of cytarabine for AML remission are associated with a high rate of NEC incidence and attributable mortality. Vigorous antibacterial therapy, specifically those also including tigecycline, may be effective in improving 30-day survival rate after NEC onset. This text corresponds to the final part of the abstract and it doesn't represent the legend to this figure.
Genetic variants of cell cycle pathway genes predict disease-free survival of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 1512-1522
- First Published: 22 June 2017
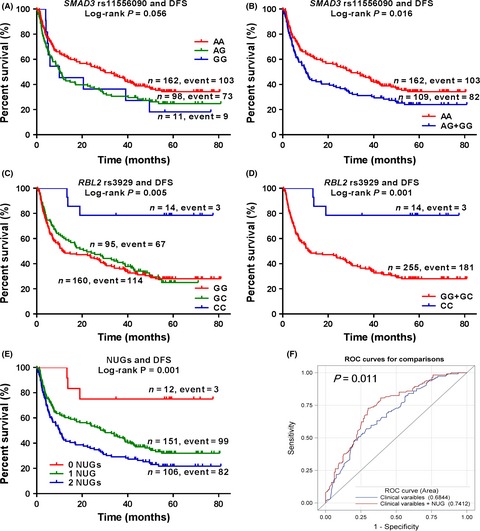
Associations between genetic variants of cell cycle pathway genes and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remain largely unknown. In this study, we evaluated the associations between 24 potential functional single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) of 16 main cell cycle pathway genes and disease-free survival (DFS) of 271 HCC patients who had undergone radical surgery resection. We identified two SNPs, i.e., SMAD3 rs11556090 A>G and RBL2 rs3929G>C, that may independently or jointly modulate the disease-free survival of HCC patients.
Renal impairment and use of nephrotoxic agents in patients with multiple myeloma in the clinical practice setting in the United States
- Pages: 1523-1530
- First Published: 14 June 2017
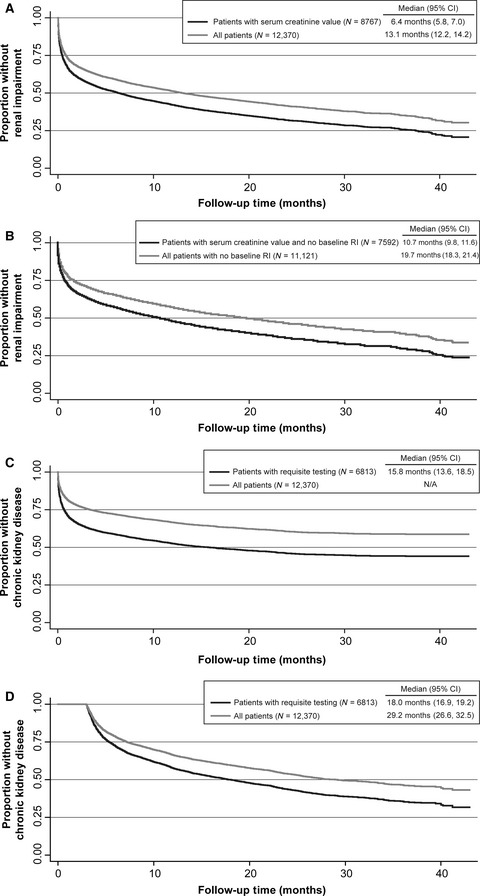
In this observational study, the prevalence of both renal impairment and chronic kidney disease was high in patients with multiple myeloma, affecting 61% and 50%, respectively, of patients in the OSCER cancer database in the US for the period 2012 to 2015. The onset of renal impairment was rapid after the multiple myeloma diagnosis; however, 40% of these patients nevertheless received concomitant nephrotoxic agents, most of which were intravenous bisphosphonates. As renal impairment is associated with reduced survival and may affect clinical management, preservation of renal function is critical, and non-nephrotoxic alternatives are warranted where possible in managing the multiple myeloma population.
Associations between ABO blood groups and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma: influence on resection status and survival
- Pages: 1531-1540
- First Published: 29 May 2017
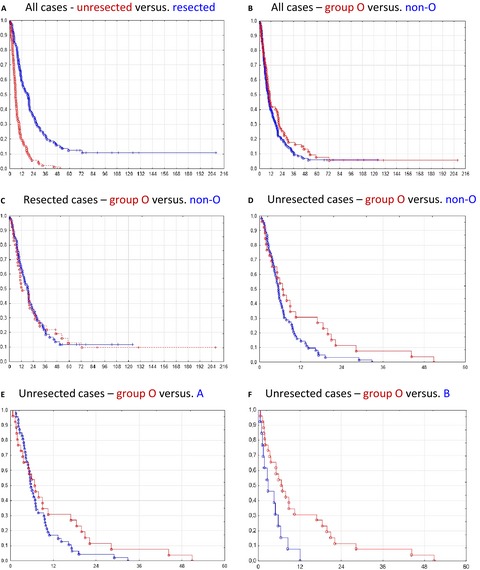
The relationship between ABO blood groups and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma was investigated in patients from Western Norway. There was an over-representation of blood group A among patients when compared with healthy blood donors, and this association could be fully attributed to the A1 subgroup. Blood group O was found to be protective, both when blood donors and random hospitalized patients were used as controls. The frequency of blood group O was particularly low among unresected patients, in whom this blood group also associated with better survival.
Melanoma complicating treatment with natalizumab for multiple sclerosis: A report from the Southern Network on Adverse Reactions (SONAR)
- Pages: 1541-1551
- First Published: 20 June 2017
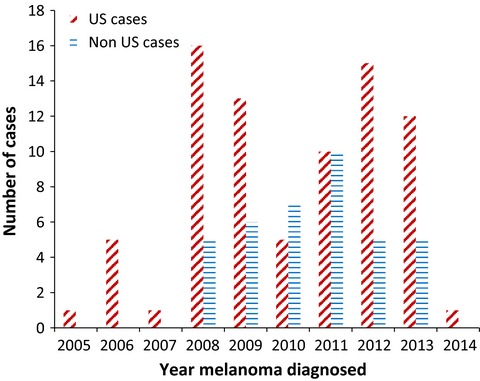
This article identifies a case of urethral melanoma developing shortly after initiating natalizumab therapy for multiple sclerosis. Literature review identifies seven cases of natalizumab-associated melanoma and FDA review identifies 133 cases of natalizumab-associated melanoma. Patients initiating natalizumab therapy may consider having a baseline dermatologic evaluation, particularly if cutaneous nevi are present.
Long-term survival benefit of upfront chemotherapy in patients with newly diagnosed borderline resectable pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 1552-1562
- First Published: 21 June 2017

This is a retrospective, intention-to-treat analysis of consecutive patients who were diagnosed with borderline resectable pancreatic cancer and primarily followed at the Johns Hopkins Hospital. The results from this study highlight the importance of upfront systemic therapy in the management of borderline resectable pancreatic cancer.
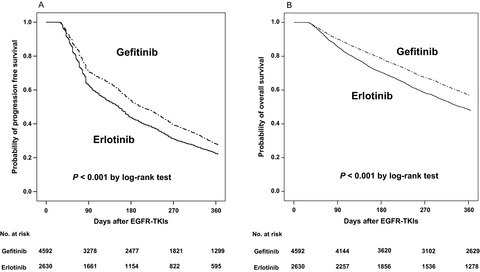
Gefitinib or erlotinib in previously treated non–small-cell lung cancer patients: a cohort study in Taiwan
- Pages: 1563-1572
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Impact of postoperative complications on the colorectal cancer survival and recurrence: analyses of pooled individual patients’ data from three large phase III randomized trials
- Pages: 1573-1580
- First Published: 22 June 2017
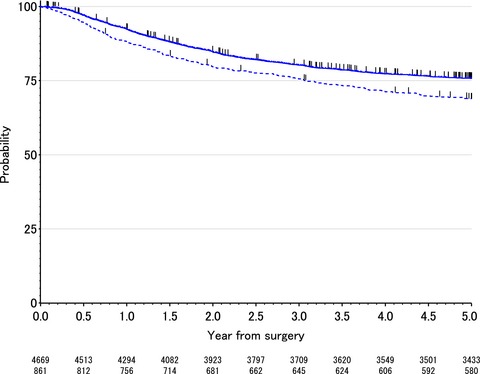
This study assessed the impact of postoperative complications on the colorectal cancer survival and recurrence after curative surgery using pooled individual patients’ data from three large phase III randomized trials. In this study, we found that postoperative complications can worsen the colorectal cancer survival and risk of recurrence. Surgical morbidity must be considered as a stratification factor in future phase III trials evaluating the effects of adjuvant chemotherapy on colorectal cancer.
Anti-PD-1 antibodies in metastatic uveal melanoma: a treatment option?
- Pages: 1581-1586
- First Published: 21 June 2017
Prognostic value of Notch receptors in postsurgical patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 1587-1600
- First Published: 31 May 2017
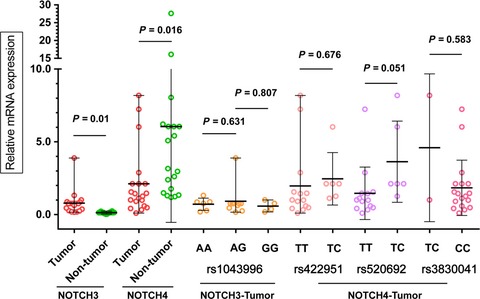
Our study aims to investigate the prognostic value of Notch receptors in postsurgical patients with hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Our findings collectively indicate that Notch receptors variants (rs1043996 in Notch3 and rs422951, rs520692, rs3830041 in Notch4) are independent predictive targets for overall survival (OS) in HBV-related HCC patients. Notch3 expression is a potential prognostic biomarker of OS and recurrence-free survival (RFS) prediction in HBV-related HCC patients following surgical treatment.
Review
Early ovariectomy reveals the germline encoding of natural anti-A- and Tn-cross-reactive immunoglobulin M (IgM) arising from developmental O-GalNAc glycosylations. (Germline-encoded natural anti-A/Tn cross-reactive IgM)
- Pages: 1601-1613
- First Published: 05 June 2017
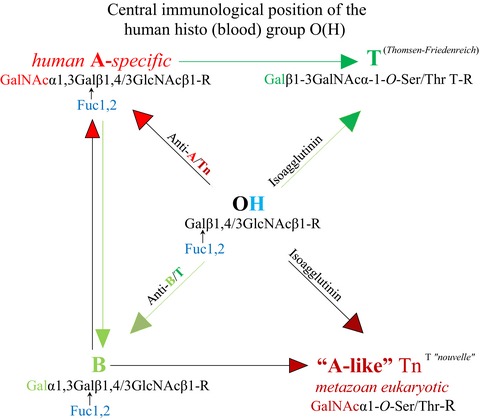
In mouse and man, the complementarity of the nonimmune anti-A/Tn cross-reactive IgM most likely occurs in a process of rapid glycosylations/deglycosylations, called “single cycle event”, which causes the release of an antibody molecule that displays a predetermined breaking point through the hydroxyl (–OH) functional group of terminal serine/threonine residues. The germline encoded anti-Tn cross-reactivity of the anti-A-specific isoagglutinin and the pronounced occurrence of anti-Tn reactivity in plasma from humans with histo (blood) group O(H), could contribute to the potential, currently discussed survival advantage of this group in the overall risk of developing cancer when compared with non-O blood groups.
Original Research
The prognostic impact of programmed cell death ligand 1 and human leukocyte antigen class I in pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 1614-1626
- First Published: 10 June 2017
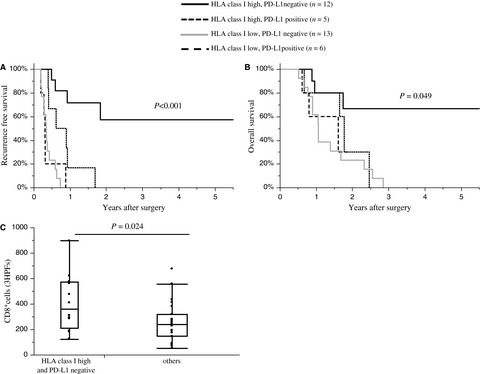
The expression of PD-L1 did not alter the patients’ prognosis if their tumors were HLA class I low, but it did for those with HLA class I high tumors. These findings suggest that the evaluation of PD-L1 and HLA class I expression is useful to predict the patients’ prognosis and HLA class I should be a new biomarker to select patients who may benefit from anti-PD-1/PD-L1-based immunotherapy.
The prediction models for postoperative overall survival and disease-free survival in patients with breast cancer
- Pages: 1627-1638
- First Published: 24 May 2017
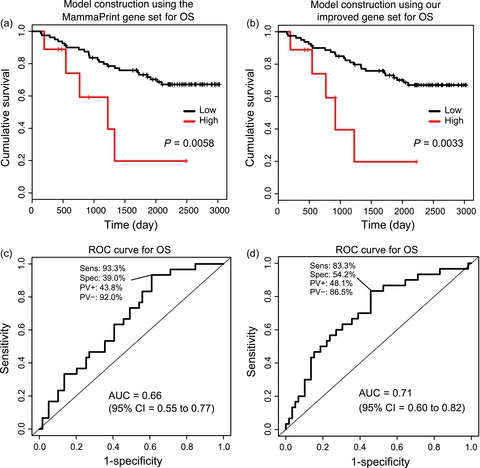
This study reports an analysis of prediction models for postoperative overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) in patients with breast cancer, in which we incorporated genes we found associated with the postoperative survival into MammaPrint genes, often used to predict prognosis of patients with early-stage breast cancer, and constructed postoperative OS and DFS prediction models using a Cox proportional hazard model. Not only did our models achieve an area of a receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.71 and 0.60 on an independent test set, but the KM curves also showed a statistically significant difference between the predicted high- and low-risk groups in both OS (log-rank trend test P = 0.0033) and DFS (log-rank trend test P = 0.00030).
Dual addressing of thymidine synthesis pathways for effective targeting of proliferating melanoma
- Pages: 1639-1651
- First Published: 13 June 2017
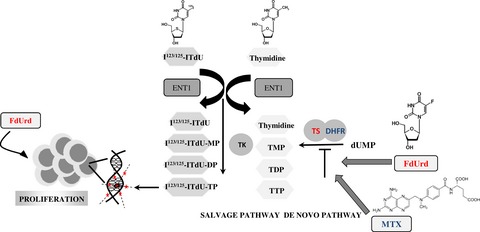
FdUrd increases mitotic activity in melanoma cells and inhibits pyrimidine de novo synthesis pathway, leading to efficient uptake of salvage thymidine synthesis pathway targeting Auger electron-emitting thymidine analog 123/125I-ITdU. The DNA-incorporated 123/125I-ITdU induces severe DNA damages (double-strand breaks) and consequently cell apoptosis.
Cancer Biology
Short Report
Overexpression of the human antigen R suppresses the immediate paradoxical proliferation of melanoma cell subpopulations in response to suboptimal BRAF inhibition
- Pages: 1652-1664
- First Published: 01 June 2017
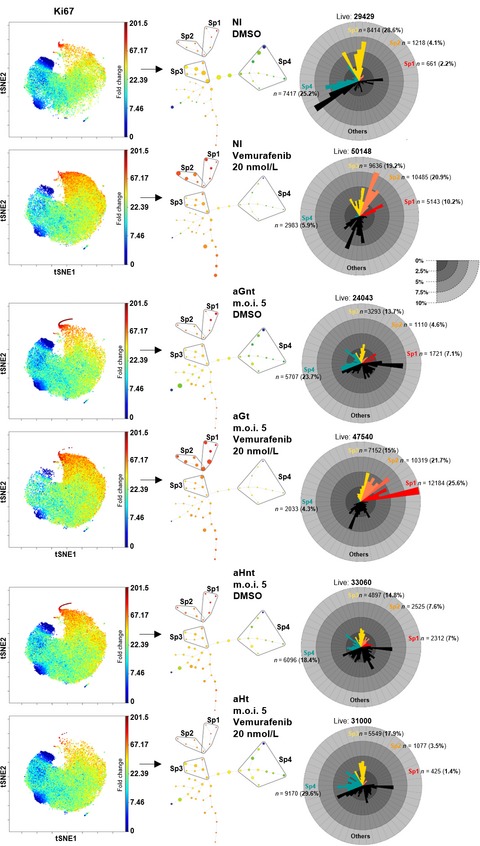
Tumor heterogeneous response of melanoma cells to targeted therapies is limiting their efficacy. In this study, using single-cell mass cytometry, we were able to track within the heterogeneous response of a melanoma BRAFV600-sensitive cell line, the paradoxically proliferating subsets of cells that emerge as an immediate response to suboptimal BRAF inhibition. Moreover, we were able to show that the overexpression of the human antigen R overcomes such immediate heterogeneous response. This study initiates a new avenue to prevent the occurrence of adaptive resistance to targeted therapies.
Original Research
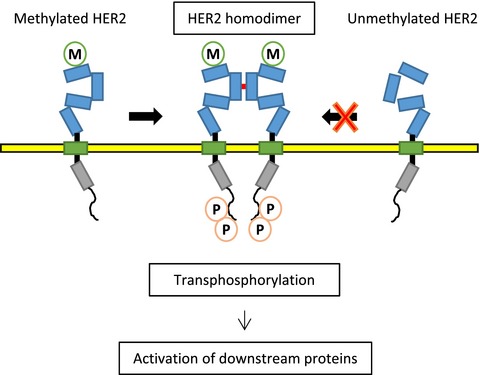
Protein lysine methyltransferase SMYD3 is involved in tumorigenesis through regulation of HER2 homodimerization
- Pages: 1665-1672
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Comparative molecular profiling of HPV-induced squamous cell carcinomas
- Pages: 1673-1685
- First Published: 29 May 2017
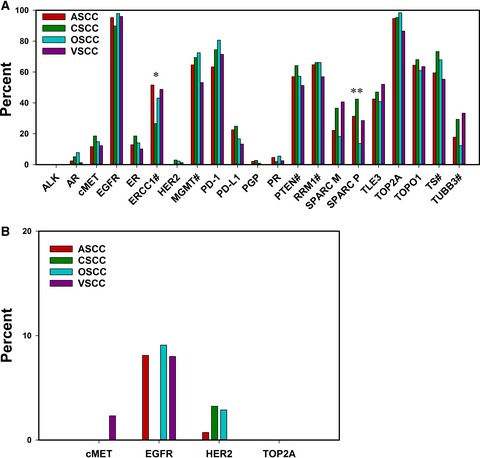
The manuscript describes our multiplatform testing and analysis of 743 samples of anal, cervical, oropharyngeal, and vulvar squamous cell carcinomas to identify molecular signatures common to HPV-induced cancers. We specifically focused on biomarkers which may be predictive of treatment efficacy and aid in determining treatment regimens. Examination of 79 biomarkers revealed striking similarities between the different cancers types, including similar rates of oncogene mutation, gene amplification, PD-L1 expression, and MGMT and RRM1 silencing which indicates that treatment protocols may be similarly effective in these different cancers.
MiR-375/SLC7A11 axis regulates oral squamous cell carcinoma proliferation and invasion
- Pages: 1686-1697
- First Published: 19 June 2017
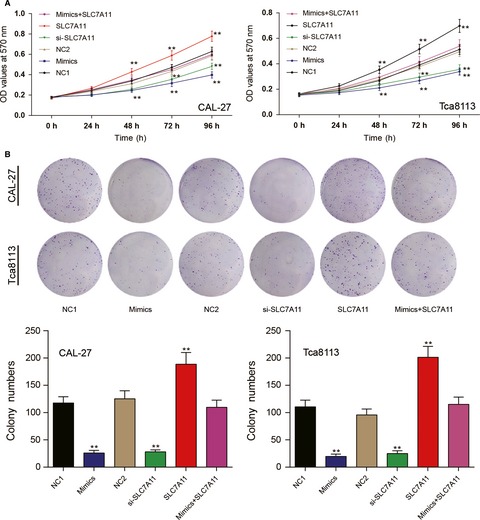
MTT, colony formation, Transwell, wound healing assays and flow cytometry were used to detect oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) cell viability, proliferation, invasion, migration and apoptosis, respectively. Collective data suggested that miR-375 served as a tumor suppressor via regulating SLC7A11. Replenishing of miR-375 or knockout of SLC7A11 could be therapeutically exploited.
In vitro additive antitumor effects of dimethoxycurcumin and 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer cells
- Pages: 1698-1706
- First Published: 02 June 2017
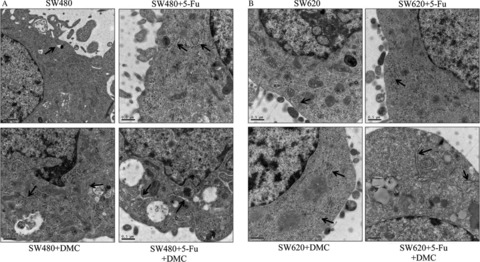
Dimethoxycurcumin (DMC) is a kind of lipophilic analog of curcumin, an effective antitumor substance for colon cancer, with great improvement in chemical and metabolic stability. Chemotherapy, represented by 5-fluorouracil (5-Fu), plays a key role in the current management of colon cancer. In this study, we revealed an additive antitumor effect of DMC and 5-Fu in colon cancer cells, which was closely related to induction of apoptosis, stimulation of G0/G1 phase arrest, increasing of ROS production, decreasing of mitochondrial membrane potential, and enhancing of endoplasmic reticulum expansion.
A three-gene signature from protein–protein interaction network of LOXL2- and actin-related proteins for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma prognosis
- Pages: 1707-1719
- First Published: 29 May 2017

LOXL2 forms an interaction network with actin-related proteins in ESCC. The three-gene signature (LOXL2, CDH1, and FN1) exceeds the power of the current staging system in evaluating ESCC prognosis. The high performance of the signature was validated in mRNA and protein levels among three cohorts of patients.
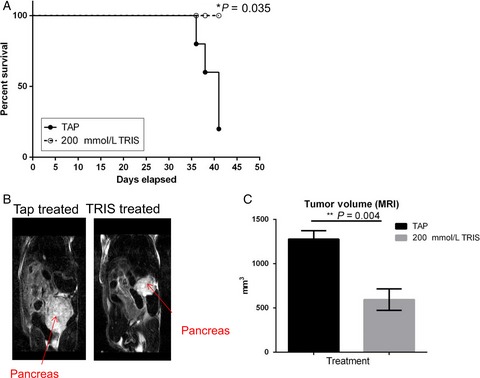
Tris–base buffer: a promising new inhibitor for cancer progression and metastasis
- Pages: 1720-1729
- First Published: 29 May 2017
Morphologic characterization of residual DNA methylation in the gastric mucosa after Helicobacter pylori eradication
- Pages: 1730-1737
- First Published: 30 May 2017
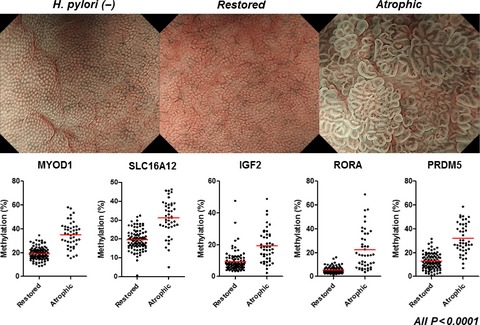
Residual DNA methylation in the gastric mucosa after Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) eradication may have a role in gastric carcinogenesis, but the morphologic characteristics of this methylation anomaly have not been clearly described. We showed that the morphologic features visualized by the magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy well characterize the DNA methylation status in the gastric mucosa after H. pylori eradication, suggesting its reliability to estimate the “field defect”.
Comparative proteomic profiling of the serum differentiates pancreatic cancer from chronic pancreatitis
- Pages: 1738-1751
- First Published: 01 June 2017
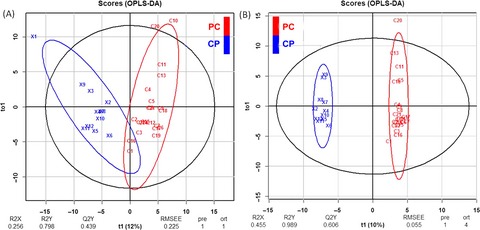
Serum proteomics has the potential to find the candidate biomarkers for various types of cancers enabling differential diagnosis. We have performed HDMSE of serum samples from chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer patients and quantified hundreds of proteins. Exhaustive statistical analyses such as OPLS-DA, PCA, ROC curve analyses and multiple pathway analyses were performed which provided dysregulated pathways in these diseases and high-confidence potential biomarker candidates were proposed.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Cervical cancer screening in a low-resource setting: a pilot study on an HPV-based screen-and-treat approach
- Pages: 1752-1761
- First Published: 04 June 2017
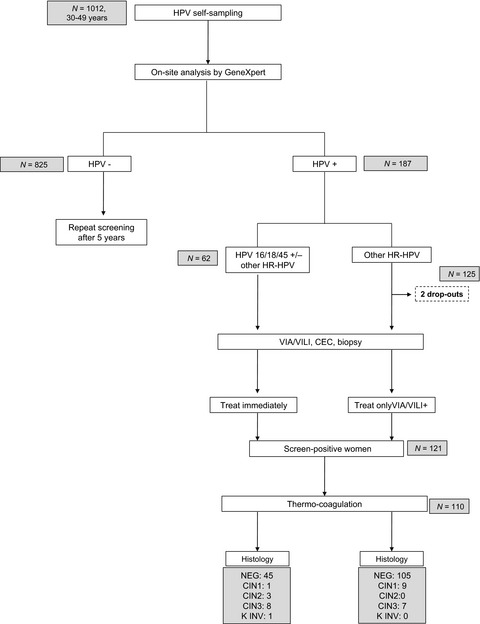
This study assesses the feasibility of a cervical cancer (CC) screen-and-treat 1-day approach including vaginal self-sampling and point-of-care HPV testing in a developing country. This approach may contribute to improving the effectiveness of CC prevention programs and decrease CC mortality in low-resource countries.
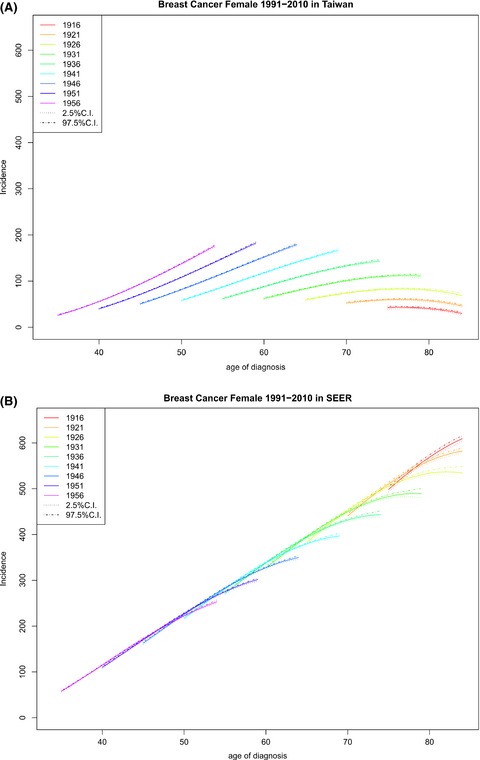
Comparison of annual percentage change in breast cancer incidence rate between Taiwan and the United States—A smoothed Lexis diagram approach
- Pages: 1762-1775
- First Published: 31 May 2017
Racial disparities in survival outcomes by breast tumor subtype among African American women in Memphis, Tennessee
- Pages: 1776-1786
- First Published: 14 June 2017
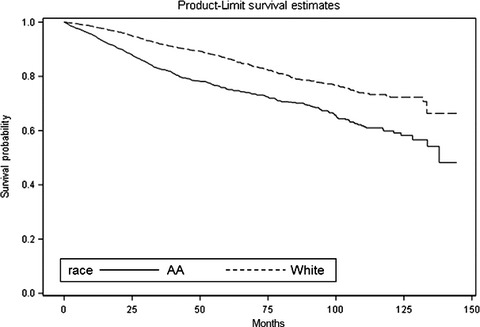
Breast cancer mortality is highest among African American (AA) women in Memphis, TN. When stratified by breast tumor subtype, AA women with triple-negative breast cancer and luminal B/HER2- breast tumors had the highest risk of mortality compared to European American women. These findings highlight the need for targeted interventions to reduce breast cancer disparities in AA populations, particularly those in Memphis, TN.
Predictors of BRCA1/2 genetic testing among Black women with breast cancer: a population-based study
- Pages: 1787-1798
- First Published: 19 June 2017
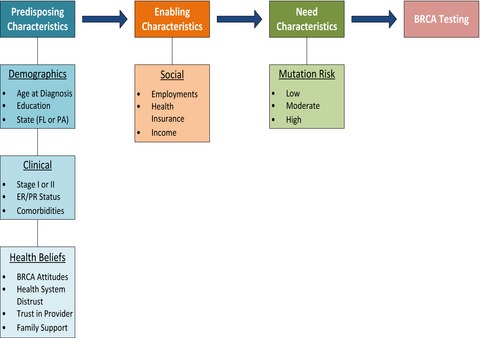
Our study identifies predictors of BRCA testing among Black women treated for breast cancer and examines differences between BRCA testers and nontesters. We conducted an analysis of 945 Black women ages 18–64 diagnosed with localized or regional-stage invasive breast cancer in Pennsylvania and Florida between 2007 and 2009. Logistic regression was used to identify predictors of BRCA 1/2 testing. Few (27%) (n = 252) of the participants reported having BRCA testing. In the multivariate analysis, we found that perceived benefits of BRCA testing (predisposing factor) ([OR], 1.16; 95% CI: 1.11–1.21; P < 0.001), income (enabling factor) ([OR], 2.10; 95% CI: 1.16–3.80; P = 0.014), and BRCA mutation risk category (need factor) ([OR], 3.78; 95% CI: 2.31–6.19; P < 0.001) predicted BRCA testing.
Longitudinal study of quality of life in advanced cancer patients on home parenteral nutrition
- Pages: 1799-1806
- First Published: 29 May 2017
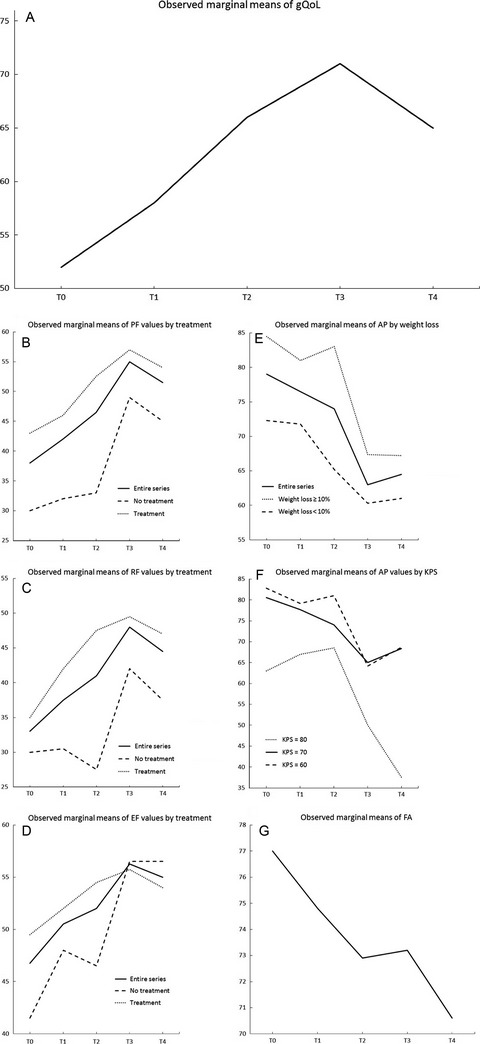
In this prospective, longitudinal study that included 111 adults advanced cancer patients, global quality of life, physical functioning, role functioning, and emotional functioning had a statistically significant trend over time. At the univariate analyses, the determinants significantly associated with changes in trend over time for physical, role, and emotional functioning were oncologic treatments. Global quality of life improved during home parenteral nutrition even in advanced cancer patients on oncologic treatments.
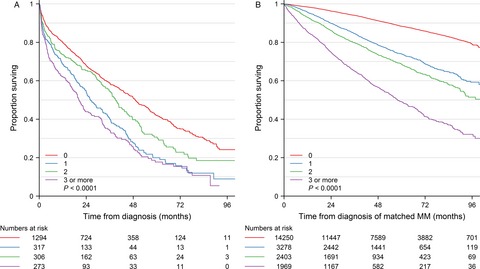
The impact of comorbidity on mortality in multiple myeloma: a Danish nationwide population-based study
- Pages: 1807-1816
- First Published: 22 June 2017
Neonates with cancer and causes of death; lessons from 615 cases in the SEER databases
- Pages: 1817-1826
- First Published: 22 June 2017
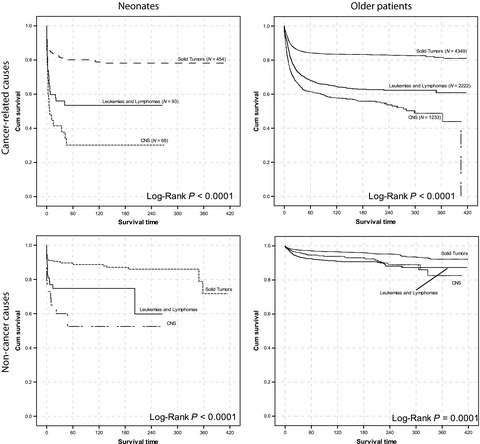
Neonates with solid tumors had the highest 5-year OS, followed by those with leukemia or CNS tumors. Except for neuroblastoma, all neonatal tumors showed inferior outcomes compared to that in the older group. The proportion of neonates who died from causes other than cancer was significantly higher than that of the older children but in general, the outcome of neonatal cancers has not improved over the last 34 years.
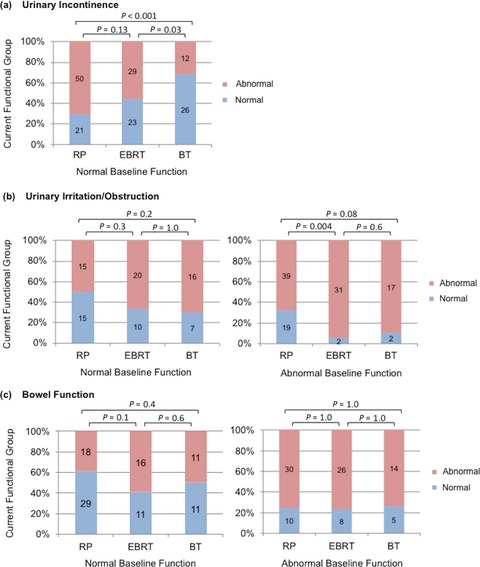
Long-term quality of life after definitive treatment for prostate cancer: patient-reported outcomes in the second posttreatment decade
- Pages: 1827-1836
- First Published: 31 May 2017
A state-wide initiative to promote genetic testing in an underserved population
- Pages: 1837-1844
- First Published: 29 May 2017
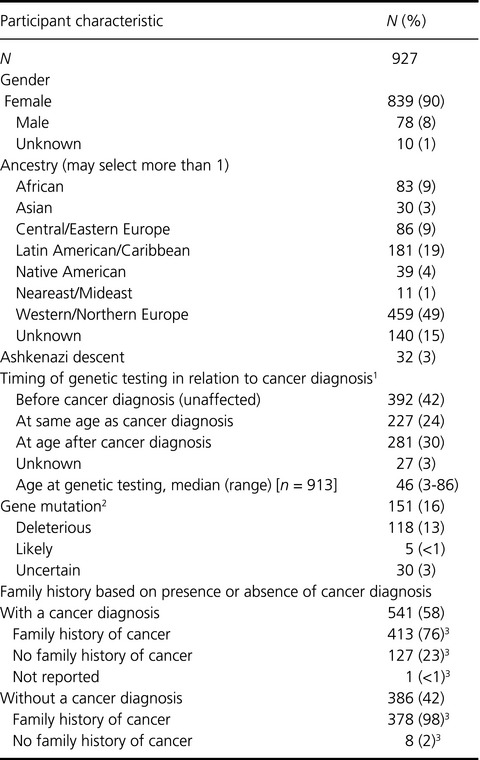
In 2009, the Cancer Resource Foundation (CRF), implemented the Genetic Information for Treatment Surveillance and Support (GIFTSS) program to cover the out–of-pocket expenses associated with cancer predisposition genetic testing. In this study, we (i) Describe the characteristics of participants in the Massachusetts (MA) GIFTSS program and (ii) evaluate mutations found in this diverse sample. The data from this study describe genetic testing outcomes in this high-risk underserved community.