Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Secondary primary malignancies during the lenalidomide–dexamethasone regimen in relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma patients
- Pages: 3-11
- First Published: 18 November 2016
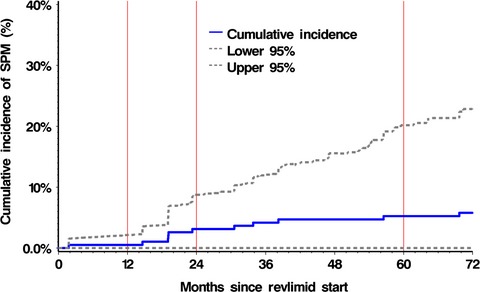
The cumulative incidence of secondary primary malignancies in our patients with relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma receiving Len-dex was 1.54% from diagnosis and 5.24% from initiation of lenalidomide. Older patients who received more Len-dex therapy and were on G-CSF support were at higher risk for secondary primary malignancy.
Efficacy, immunogenicity, and safety of the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine in Chinese women aged 18–25 years: event-triggered analysis of a randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 12-25
- First Published: 20 December 2016
This is the first long-term, large-scale, randomized clinical trial of human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination in China, where cervical cancer is a major concern. With a mean follow-up of approximately 57 months post-dose 1, the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine was efficacious against HPV-16/18-associated cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and infection, immunogenic, and had a clinically acceptable safety profile in young Chinese women. Prophylactic HPV vaccination and screening could potentially reduce the high HPV epidemic and cervical cancer burden in China.
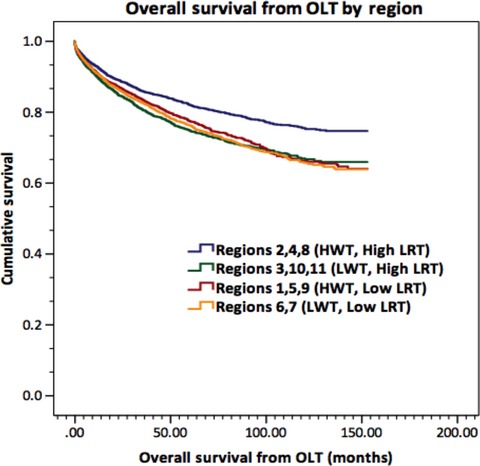
Independent prognostic factors for posttransplant survival in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing liver transplantation
- Pages: 26-35
- First Published: 16 November 2016
Responses to romidepsin by line of therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 36-44
- First Published: 16 December 2016
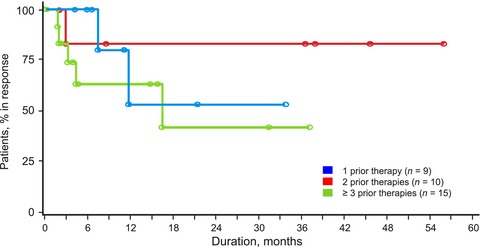
Patients with relapsed or refractory peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL) typically have a poor prognosis. Responses to treatment and long-term outcomes tend to worsen with increasing lines of therapy. Romidepsin is a potent class 1 histone deacetylase inhibitor approved by the US FDA for the treatment of PTCL in patients who have received ≥1 prior therapies. The analysis presented here demonstrated that romidepsin had similar responses and long-term outcomes in patients with 1, 2, and ≥3 prior lines of treatment, including in patients with disease refractory to the last prior therapy, thereby supporting the use of romidepsin for patients with relapsed or refractory PTCL regardless of the number of prior therapies.
Adjuvant treatment combining cellular immunotherapy with chemotherapy improves the clinical outcome of patients with stage II/III gastric cancer
- Pages: 45-53
- First Published: 27 October 2016
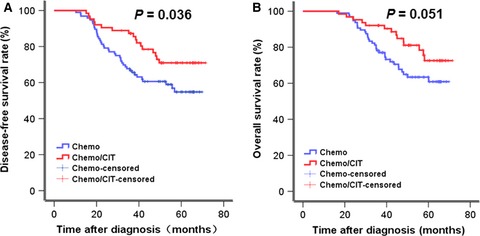
The adjuvant treatment combining chemotherapy with cellular immunotherapy is well tolerated and significantly improves the clinical outcome of patients with stage II/III gastric cancer (GC), when compared with chemotherapy alone, therefore warrants further attention in treatment for relapsed GC after tumor resection.
The high expression instead of mutation of p53 is predictive of overall survival in patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis
- Pages: 54-66
- First Published: 23 November 2016
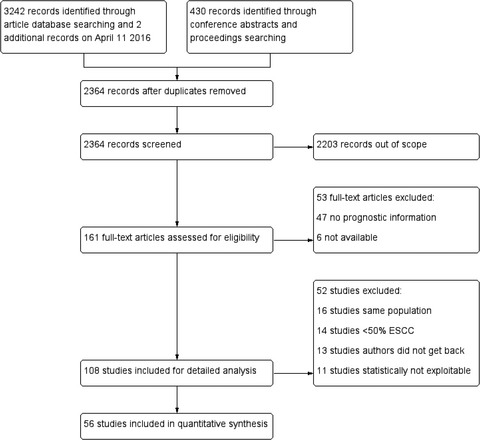
This is the first dedicated systematic review and meta-analysis regarding the independent prognostic value of p53 in patients with esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma. We identified a statistically significant negative impact of p53 high expression, instead of TP53 mutations, on overall survival of esophageal squamous-cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients.
microRNA from brush biopsy to characterize oral squamous cell carcinoma epithelium
- Pages: 67-78
- First Published: 18 December 2016
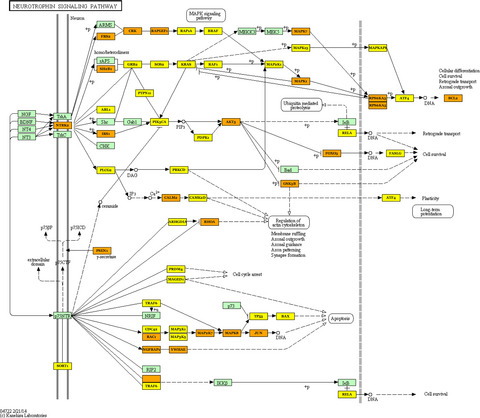
This study sought to identify tumor epithelial miRNA expression changes in oral squamous cell carcinoma to determine if these changes could be used to identify the disease noninvasively. By focusing on pure epithelium miRNA, acquired rapidly and simply with brush biopsy, we showed the potential to diagnose this disease with miRNA from epithelium. And we use a simple variation of standard pathway identification methods to minimize false positives and identify the neurotrophin signaling pathway as a target of these miRNAs.
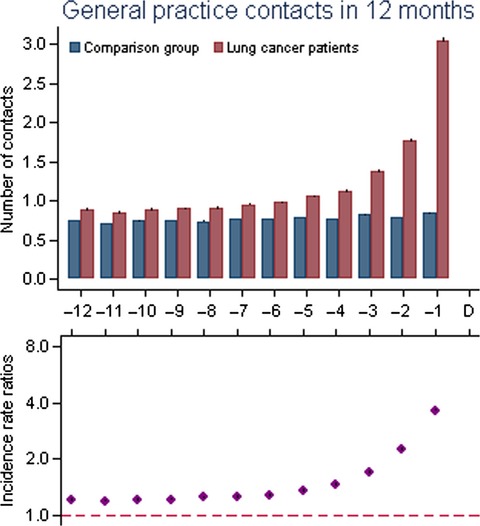
General practice consultations, diagnostic investigations, and prescriptions in the year preceding a lung cancer diagnosis
- Pages: 79-88
- First Published: 23 November 2016
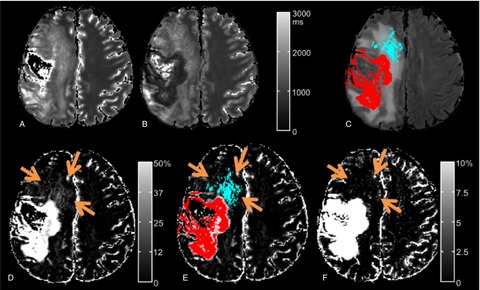
Quantitative T1-mapping detects cloudy-enhancing tumor compartments predicting outcome of patients with glioblastoma
- Pages: 89-99
- First Published: 28 November 2016
Efficacy and toxicity of the combination chemotherapy of thalidomide, alkylating agent, and steroid for relapsed/refractory myeloma patients: a report from the Korean Multiple Myeloma Working Party (KMMWP) retrospective study
- Pages: 100-108
- First Published: 01 December 2016
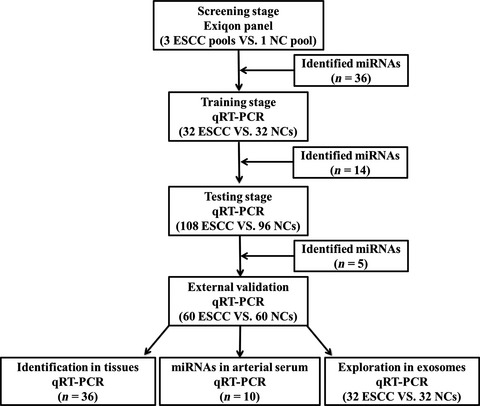
A novel serum microRNA signature to screen esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 109-119
- First Published: 30 December 2016
High pretransplant hepcidin levels are associated with poor overall survival and delayed platelet engraftment after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- Pages: 120-128
- First Published: 01 December 2016
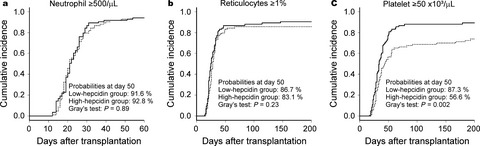
We previously showed that patients with hematologic malignancies exhibit dynamic changes in levels of hepcidin-25, which is the key regulator of systemic iron, during allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. In this study, we investigated the association of pre-transplant serum hepcidin-25 levels with overall survival, and found that the patients with high levels of pre-transplant hepcidin-25 had significantly lower overall survival than patients with low-hepcidin-25. Moreover, the incidence of platelet engraftment was significantly lower in patients with high pre-transplant hepcidin-25.
Does radiotherapy still have a role in unresected biliary tract cancer?
- Pages: 129-141
- First Published: 28 November 2016
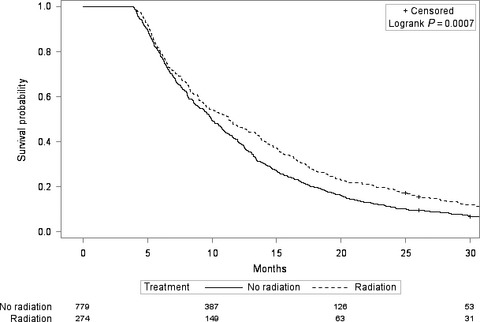
The benefits of radiotherapy for elderly patients with inoperable biliary tract cancer remain unclear due to the lack of randomized data given the rarity of this cancer. Using the SEER-Medicare database, we found that the use of radiotherapy has declined over time, and is influenced by tumor, patient, and socioeconomic factors, and that any survival benefit with radiotherapy is confined to those patients who received concurrent chemotherapy.
Survival prognostic factors for metachronous second primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 142-153
- First Published: 17 December 2016
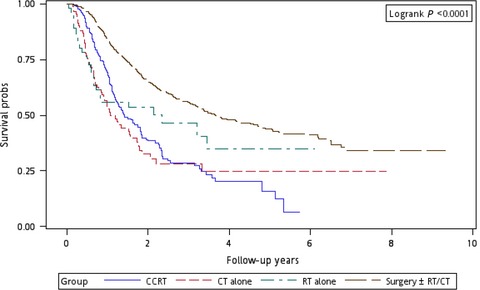
Metachronous second primary head and neck squamous cell carcinoma are rare and optimal therapeutic decisions for metachronous second primary head and neck squamous cell carcinomas (HNSCCs) are unclear. Suitable treatments and prognostic factors for the population were analyzed. This study is the first to estimate the prognostic factors of metachronous second primary HNSCCs.
A Comparison of ddPCR and ARMS for detecting EGFR T790M status in ctDNA from advanced NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance
- Pages: 154-162
- First Published: 20 December 2016
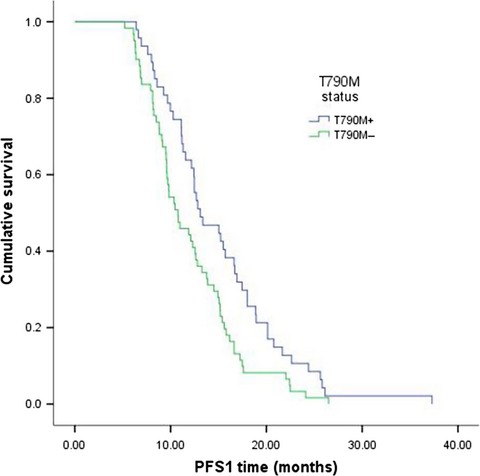
Our study demonstrates the feasibility and sensitivity of detecting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) T790M status in plasma samples from NSCLC patients with acquired EGFR-TKI resistance. The ddPCR assay detecting in plasma ctDNA T790M may provide an alternative method in some situations. Patients with acquired T790M mutation at the time of progression have gradual progression compared to those without T790M mutation. And T790M-positive patients have better clinical outcomes to EGFR-TKIs than T790M-negative patients.
Impact of treatment on progression to castration-resistance, metastases, and death in men with localized high-grade prostate cancer
- Pages: 163-172
- First Published: 20 December 2016
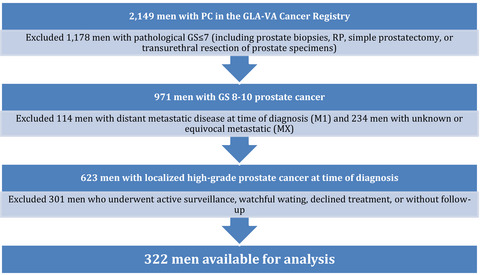
Men with high-grade prostate cancer (HGPC) are at a greatest risk of disease progression. Clinical risk factors associated with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), metastases, and prostate cancer-specific mortality (PCSM) were identified in a contemporary HGPC cohort. Men with these risk factors may benefit from combinatorial therapies that include definitive treatment of the primary tumor.
Outcome after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in Asian breast cancer patients
- Pages: 173-185
- First Published: 20 December 2016
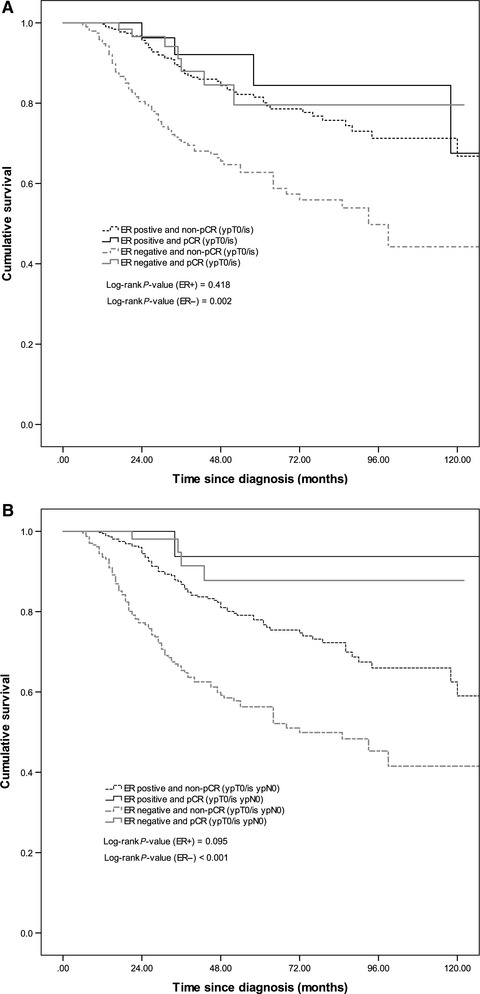
Most existing evidence on response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy are from western countries, where tumor characteristics are different from Asia. This study is one of the largest studies done in Asia to determine the demographic of breast cancer patients who underwent neoadjuvant chemotherapy, clinicopathologic predictors for response to treatment, their long-term survival in an actual clinical practice setting, and the prognostic value of pathological complete response on overall survival in Asia.
Venous thromboembolism in metastatic urothelial carcinoma or variant histologies: incidence, associative factors, and effect on survival
- Pages: 186-194
- First Published: 20 December 2016
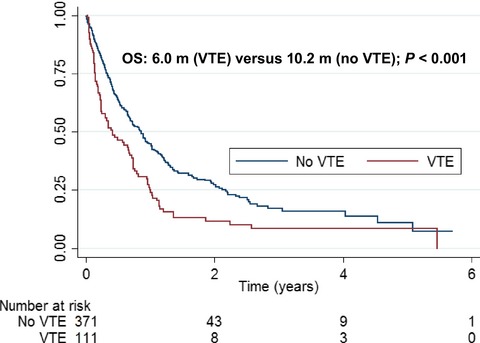
Venous thromboembolism is common and has a negative impact on survival in patients with metastatic urothelial tract cancers. Non-urothelial histology, renal dysfunction, and the presence of cardiovascular disease or risk factors for cardiovascular disease increase a patient's risk for venous thromboembolism; however, there is no statistical difference in thrombotic risk between chemotherapy regimens.
Impact of genomic profiling on the treatment and outcomes of patients with advanced gastrointestinal malignancies
- Pages: 195-206
- First Published: 28 December 2016
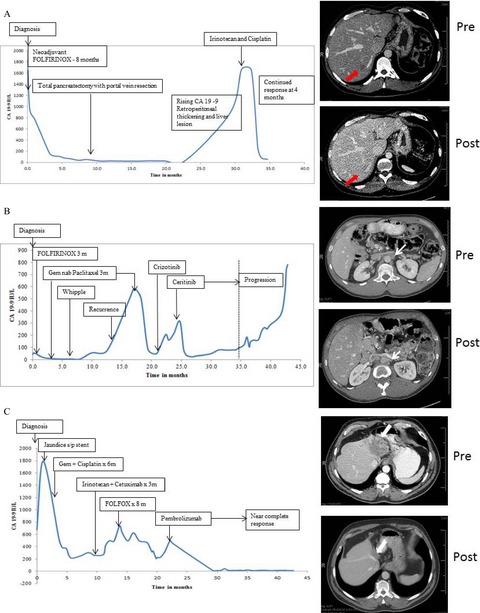
Genomic profiling-guided therapy can lead to clinical benefit and improved progression-free survival in patients with advanced gastrointestinal (GI) malignancies. Attempting genomic profiling earlier in the course of treatment prior to functional decline may allow more patients to benefit from these therapies.
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Whole-exome sequencing predicted cancer epitope trees of 23 early cervical cancers in Chinese women
- Pages: 207-219
- First Published: 20 December 2016
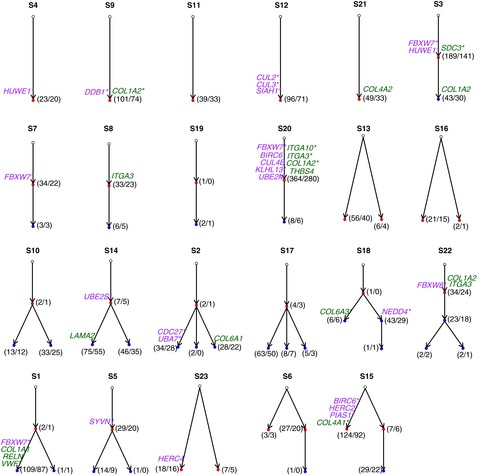
To search for the optimal therapeutic targets, we investigated the hierarchy structure of the somatic mutations of 23 early cervical cancers of Chinese women using whole-exome sequencing approach. We found that individual cancer displayed a unique phylogenetic tree and “cancer neo-epitope tree” comprising different set of subpopulations, genetic mutations and associated neo-epitopes, which are predicted according to their strong binding with major histocompatibility complex class I molecules (MHC-I). Conceivably, the neo-epitopes at the top of the tree were the optimal immunotherapeutic targets, possessing the potential to mediate T-cell killing of the descendant cells.
Migration of breast cancer cell lines in response to pulmonary laminin 332
- Pages: 220-234
- First Published: 22 November 2016
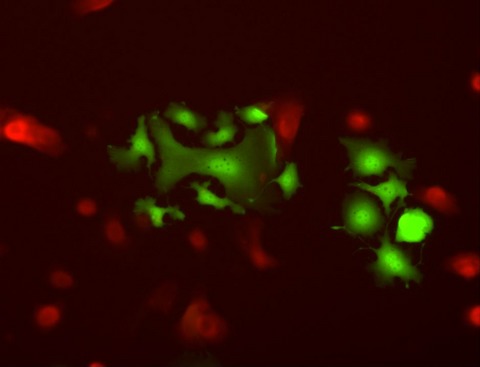
This study demonstrates that laminin 332 in lung epithelium has the potential to induce tumor migration, which in turn is a requirement for metastasis. This investigation provides evidence that the tumor promoting potential of laminin 332 in lung may originate in the microenvironment rather than in tumor cells alone. The findings raise the possibility that laminin 332 plays a role in pulmonary breast carcinoma metastases and that it may provide a target for antimetastasis therapy.
Muscle RAS oncogene homolog (MRAS) recurrent mutation in Borrmann type IV gastric cancer
- Pages: 235-244
- First Published: 28 November 2016

This is the first report of the genomic profile of Borrmann type IV gastric cancer. We found that muscle RAS oncogene homolog (MRAS) is recurrently mutated in Borrmann type IV gastric cancer. We also detected IGF1R gene amplification and that it was correlated with high levels of mRNA and protein expression.
DLL4 overexpression increases gastric cancer stem/progenitor cell self-renewal ability and correlates with poor clinical outcome via Notch-1 signaling pathway activation
- Pages: 245-257
- First Published: 28 November 2016
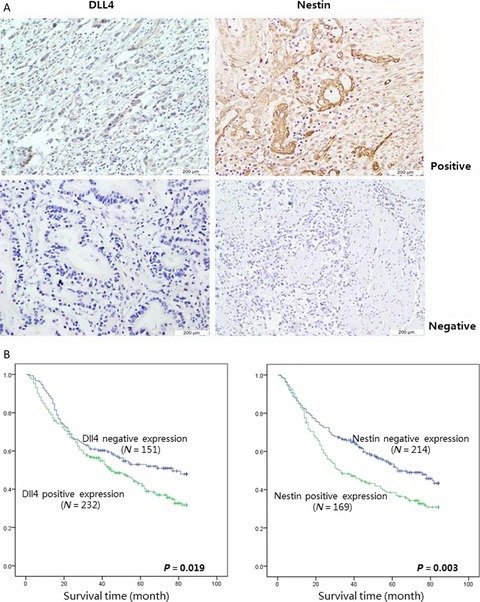
DLL4 expression is associated with TNM stage and cancer metastasis, with high amounts of DLL4 leading to poor outcome. DLL4 silencing inhibited the self-renewal ability of GCSPCs and increased their multidifferentiation capacity, resulting in reduced GCSPC ratios. DLL4 knockdown also blocked the Notch-1 pathway, weakening invasion ability, and resistance to 5-FU chemotherapy.
Prognostic impact of MutT homolog-1 expression on esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 258-266
- First Published: 05 December 2016
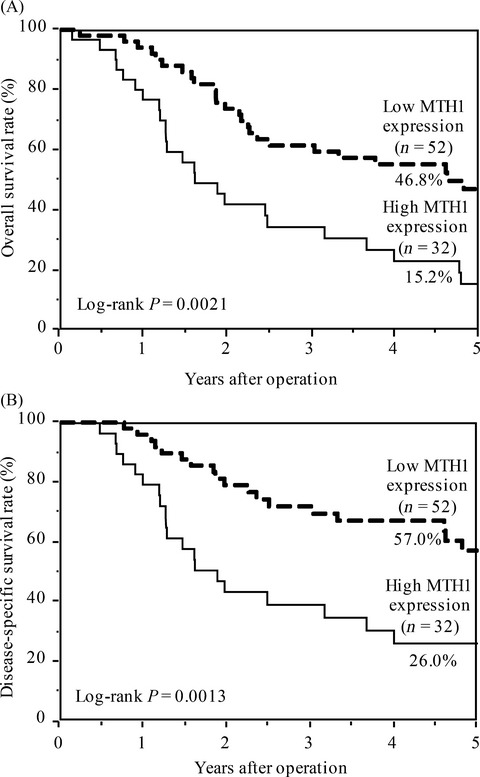
MTH1 is a pyrophosphatase that hydrolyzes oxidized dNTPs in dNTP pool. This is the first study to show a correlation between MTH1 expression and malignancy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). The enhanced MTH1 expression strongly correlates with tumor progression and is an independent prognostic factor in ESCC.
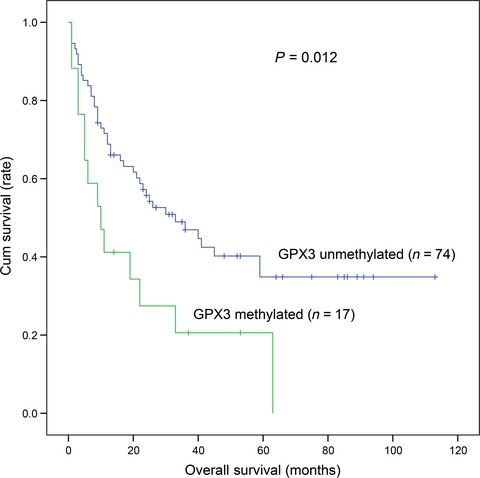
GPX3 methylation in bone marrow predicts adverse prognosis and leukemia transformation in myelodysplastic syndrome
- Pages: 267-274
- First Published: 28 November 2016
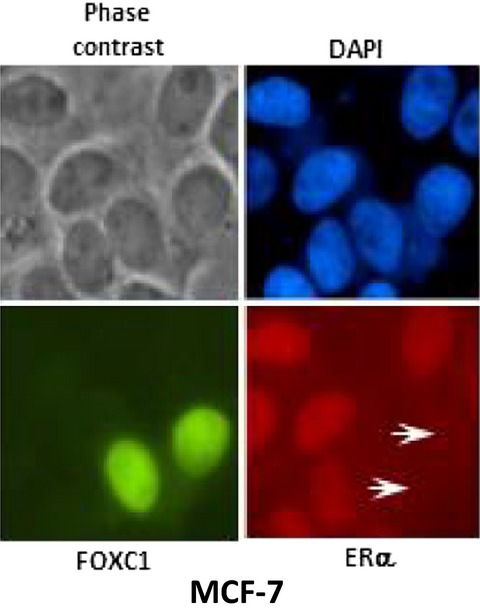
FOXC1 is associated with estrogen receptor alpha and affects sensitivity of tamoxifen treatment in breast cancer
- Pages: 275-287
- First Published: 28 December 2016
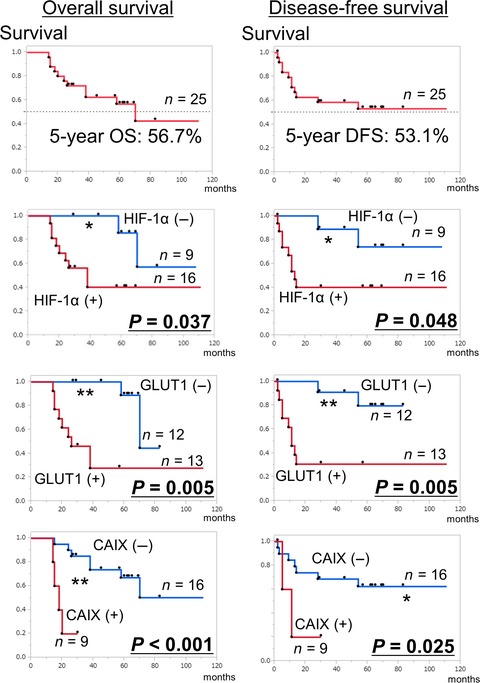
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 promotes chemoresistance of lung cancer by inducing carbonic anhydrase IX expression
- Pages: 288-297
- First Published: 28 December 2016
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Risk stratification of adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma using immunophenotyping
- Pages: 298-309
- First Published: 30 December 2016
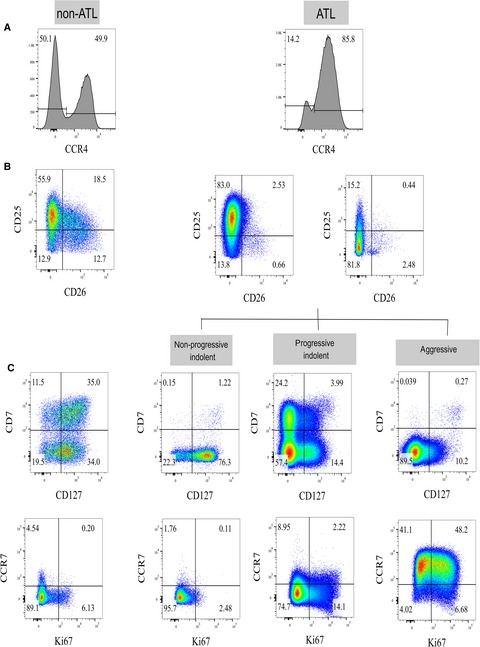
Adult T-cell leukemia/lymphoma (ATL) has a highly variable clinical course and better prognostic markers are urgently required. Our study has shown human T-lymphotropic virus type 1 (HTLV-1)-infected cells have a CD4+ CCR4+ CD26− immunophenotype. Within this population, CD7− immunophenotype suggests a diagnosis of ATL, CCR7+ immunophenotype identifies aggressive ATL, while CCR7− CD127− immunophenotype identifies progressive indolent ATL.
An inflammatory biomarker-based nomogram to predict prognosis of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an analysis of a prospective study
- Pages: 310-319
- First Published: 10 November 2016
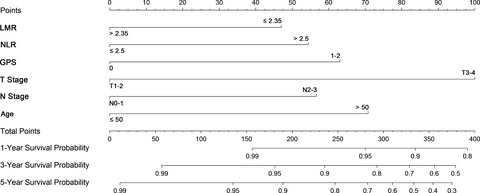
Pretreatment Glasgow prognostic score (GPS), NLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR), LMR of 388 nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients who were recruited prospectively in the 863 Program No. 2006AA02Z4B4 were assessed. After multivariate analysis of the 249 patients of the development set, age, T stage, N stage, and GPS, NLR, LMR appeared to be independent prognostic factors of 5-year disease-specific survival (DSS), and a nomogram was established to predict the DSS based on these factors. The model was validated in 139 patients of the validation set.
Marijuana use and inpatient outcomes among hospitalized patients: analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample database
- Pages: 320-329
- First Published: 28 November 2016
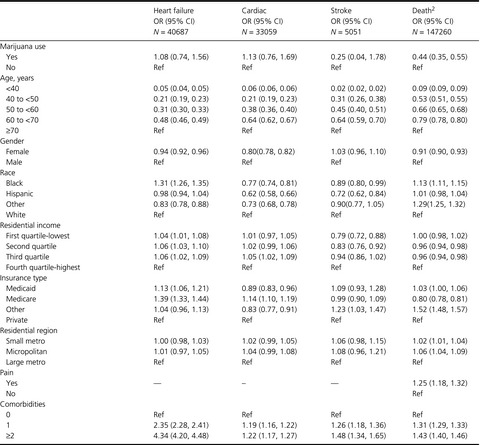
In view of the rapidly increased use of marijuana in the general population. There is significant interest in examining the health effects of marijuana use among adults in general, but more importantly among those with health conditions or chronic diseases. In this study we examined the relationships between marijuana use and health outcomes among hospitalized patients, including hospitalized patients with and without a diagnosis of cancer.