Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: steel research int. 3/2019
- First Published: 03 March 2019

Cover Photo:
The cover shows variations of air phase at the early stage of refilling process with time during ladle changeover operation of a five-strand bloom tundish when applying traditional and trumpet ladle shroud with optimized circular turbulence inhibitor. The faster expulsion velocity of air bubbles can be observed when using trumpet ladle shroud. Further details can be found in the article 1800497 by Qing Fang and co-workers.
Masthead
Contents
Full Papers
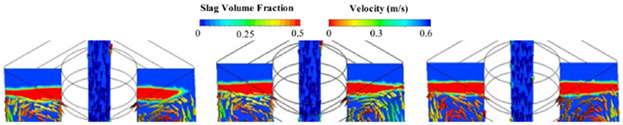
Multiphase Flow in a Five-Strand Tundish Using Trumpet Ladle Shroud during Steady-State Casting and Ladle Change-Over
- First Published: 27 December 2018
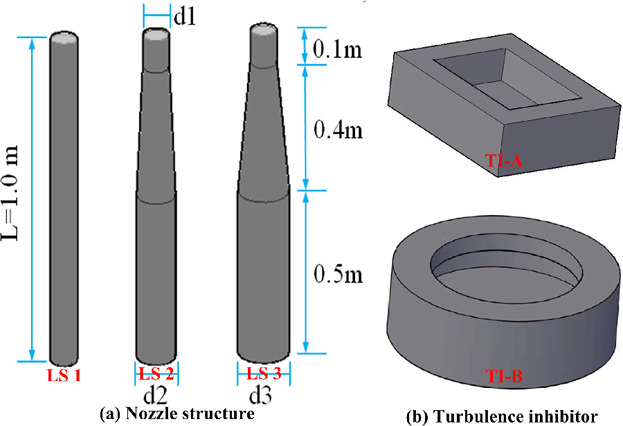
Mathematical and water models are performed to investigate the multiphase flow in a tundish during both steady-state casting and ladle change-over under different ladle shroud and turbulence inhibitor. The optimal combination should be LS 3 with TI-B by comprehensively considering the flow pattern, air and slag behaviors, and the qualification rate of flaw detection in steel rails is increased.
Angular Re-Positioning of a Five Ported SEN versus EMS Braking to Stabilize Flows at the Upper Slag-Liquid Steel Interface
- First Published: 27 December 2018
A Magneto-Hydrodynamic model is developed to study the effect of SEN's port's orientations under the influence of different rotary-EMS units within a curved square billet mold caster. The predicted results indicate that the SEN's angle of rotation along with electromagnetic stirring units can stabilize the liquid steel meniscus and create a uniform distribution of slag layer on top of it.
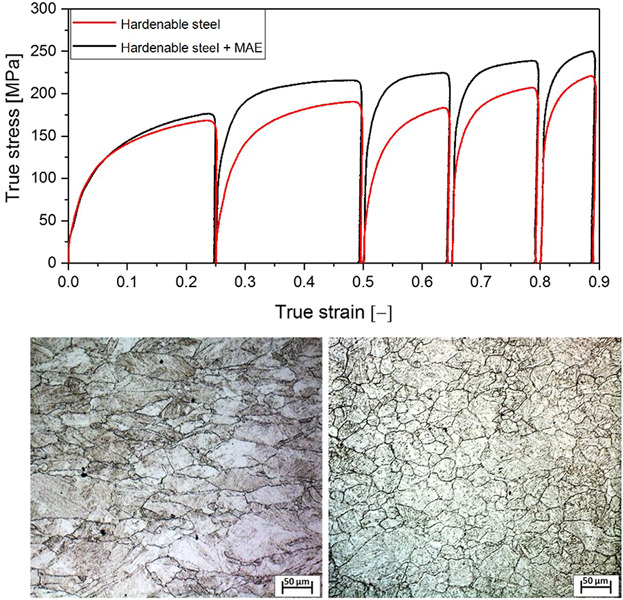
Strain-Induced Martensite and Reverse Transformation in 2304 Lean Duplex Stainless Steel and its Influence on Mechanical Behavior
- First Published: 13 November 2018
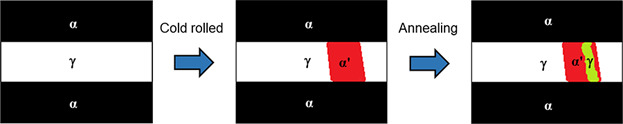
This study focuses on an evaluation of SIM and SIMRT in a 2304 LDSS, as well as its influence on the mechanical properties. The reversion process, α′-martensite → γ, occurs within the range of 600–900 °C. The SIMRT mechanism shows diffusional and shear reversion characteristics. The evolution microtexture is introduced.
Microstructural Analysis of the Recrystallization Behavior of Low Alloyed Steels
- First Published: 02 January 2019
This paper contains an investigation of the recrystallization behavior of low alloyed steels. Dilatometer tests and a metallographic analysis are applied to illustrate the recrystallization kinetics and the role of micro-alloying elements. The investigations provide insight in the microstructural evolution during a hot-rolling scenario and an easy-to-applicable technique for the design of thermomechanically processed steels.
Measurement of Ce/Ti Content in Austenitic Stainless Steel Welding Wire
- First Published: 02 January 2019
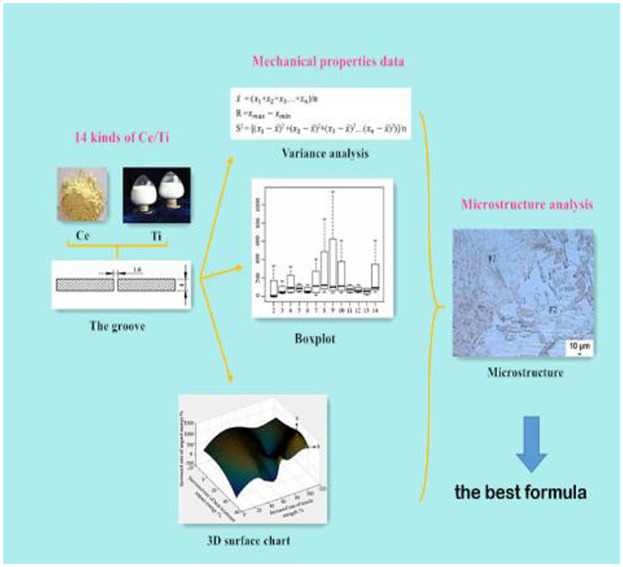
In order to improve the mechanical properties of welded joints, 14 kinds of Ce/Ti are added to austenitic stainless steel wire by uniform design. After welding, a series of mechanical properties tests are conducted according to national standards. Then, the best formula is obtained through analysis of variance, box diagram, and 3D surface figure.
The Effect of Martensite-Austenite Constituent Characteristics on the Mechanical Behavior of Quenched-Partitioned Steel at Room Temperature
- First Published: 09 October 2018
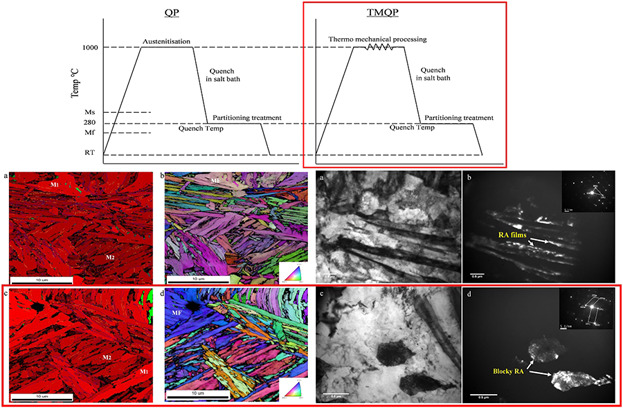
The present study deals with the effect of constituent phase characteristics on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Quenched and partitioned steel. The TMP route is employed to modify the microstructures, to produce better mechanical properties. The final microstructures include initial and fresh martensite and retained austenite with film or blocky morphology in a wide range of size.
Elastic-Plastic Finite Element Analysis of Tension Leveling with Non-Associated Flow Rule and Mixed Hardening
- First Published: 10 December 2018
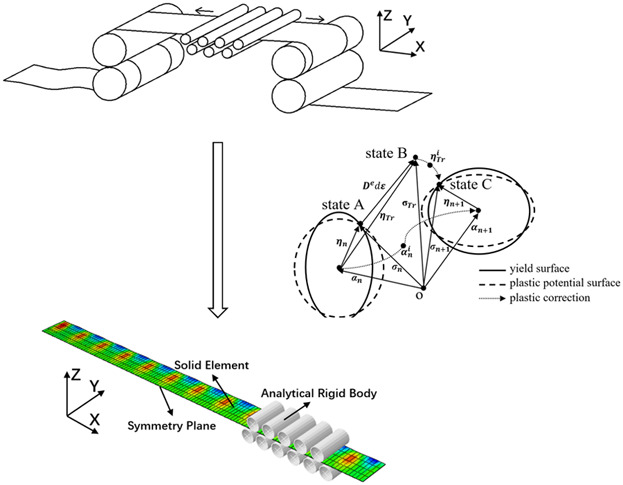
An advanced constitutive model is constructed to achieve the 3D finite element analysis of tension leveling with high accuracy in this investigation. The tension leveling process for the curl, gutter, and waviness defects are simulated with the constructed consititutive model. The simulation results for SPCC are also compared with experimental results from literature.
Enhancing the Mechanical Properties of Al-Containing Medium Mn Steel Through Warm Rolling and Intercritical Annealing
- First Published: 21 December 2018
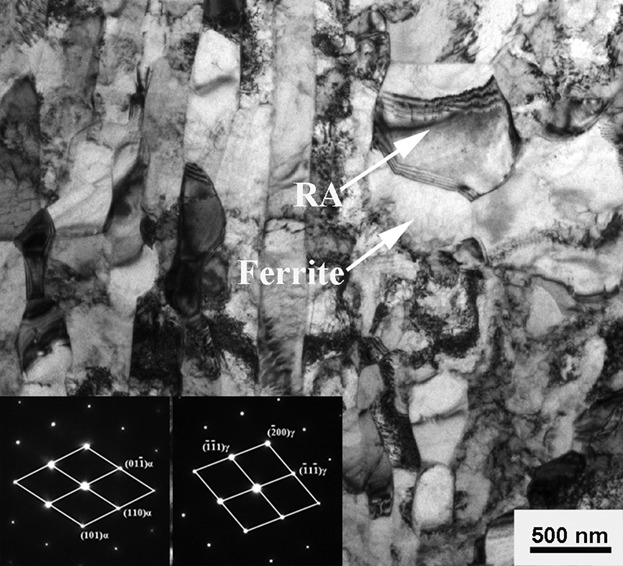

This investigation attempts to further enhance the mechanical properties of medium Mn steel through warm rolling and intercritical annealing. The results show a significantly enhanced combination of strength and ductility is obtained, which is superior to that of previously investigated medium Mn steels. It is thus a promising and feasible approach to further enhance the properties of medium Mn steel.
On-Line Estimation of Liquid Levels in the Blast Furnace Hearth
- First Published: 13 November 2018
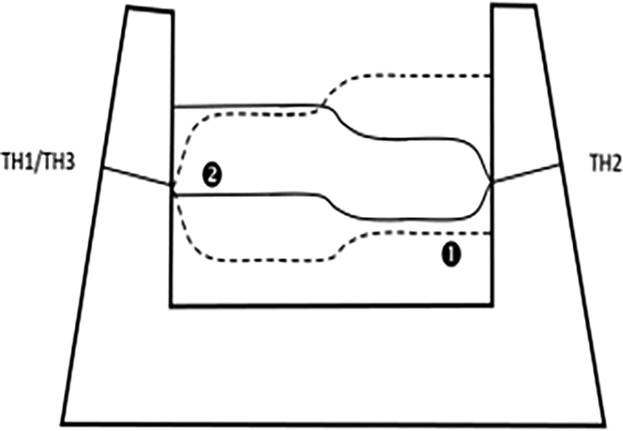
An on-line model estimates the liquid levels in the blast furnace hearth using production data of an operating furnace. The model considers different hearth regions with individual iron and slag levels and it includes level corrections to address possible level drifting. The paper studies several cases with different model parameters.
Detection and Numerical Simulation of Non-Metallic Inclusions in Continuous Casting Slab
- First Published: 02 January 2019
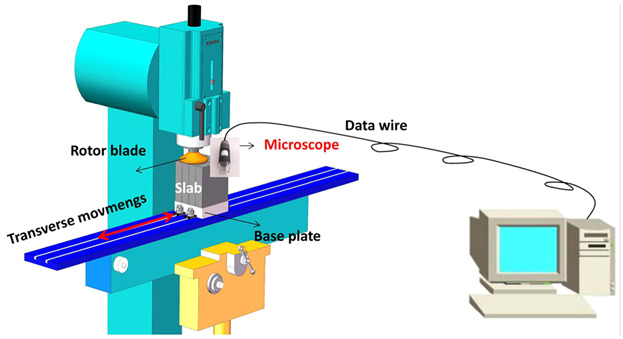
A high-efficiency fast-detection platform (FDP) is set up to detect the spacial distribution of non-metallic inclusions in a continuous casting slab. A large eddy simulation (LES) model coupled with solidification is developed to predict the inclusions in slab. Two main sources of inclusions are identified: slag entrapment and reoxidation of molten steel.
Effects of Coincident Site Lattice Grain Boundaries and Ordered Structures on Mechanical Properties of High Silicon Steel
- First Published: 06 December 2018
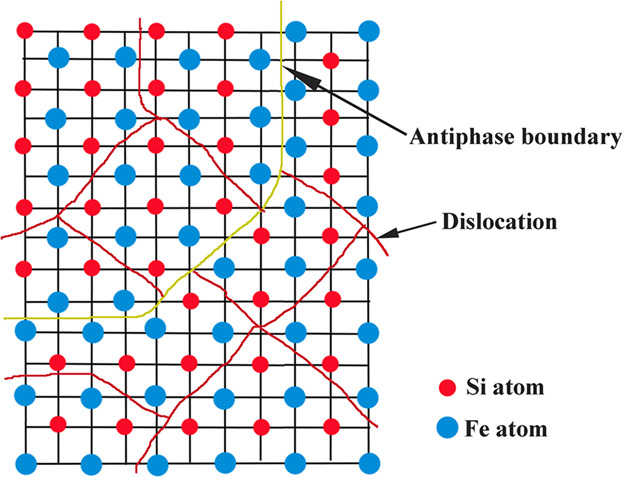
The coincident site lattice (CSL) grain boundaries and ordered structures of Fe–6.9 wt%Si alloy are investigated through different warm rolling reductions. The plastic deformation ability of warm-rolled sheets depends on the content of CSL boundaries and the fragmentation behavior of ordered structures. The high rolling reduction is conducive to the improvement of plastic deformation ability.
Carburization Behavior of Siderite Pellets in CO–CO2–H2 Mixtures
- First Published: 20 November 2018
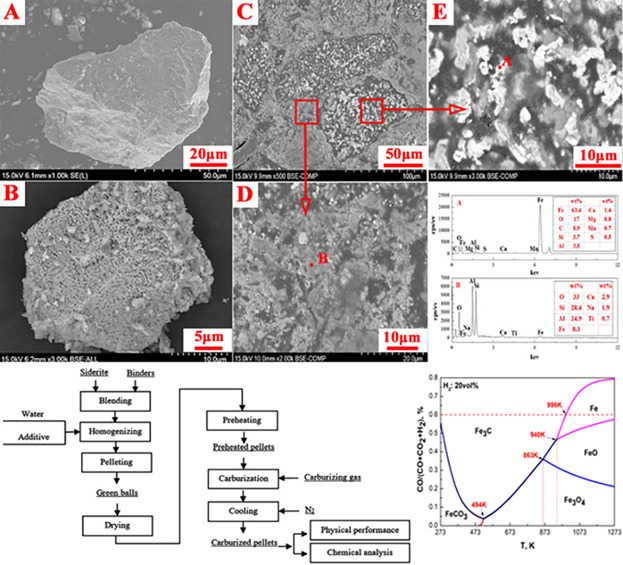
The carburization behavior of siderite pellet is investigated to provide a new way for siderite utilization. Siderite is proved as a suitable iron ore for carburization in the range of 600–650 °C. Carburization of roasted product of siderite pellet ranking from the easiest to the hardest is Fe, FeO, Fe2O3, and Fe3O4, respectively.
Analyses and Calculation of Steel Scrap Melting in a Multifunctional Hot Metal Ladle
- First Published: 06 December 2018
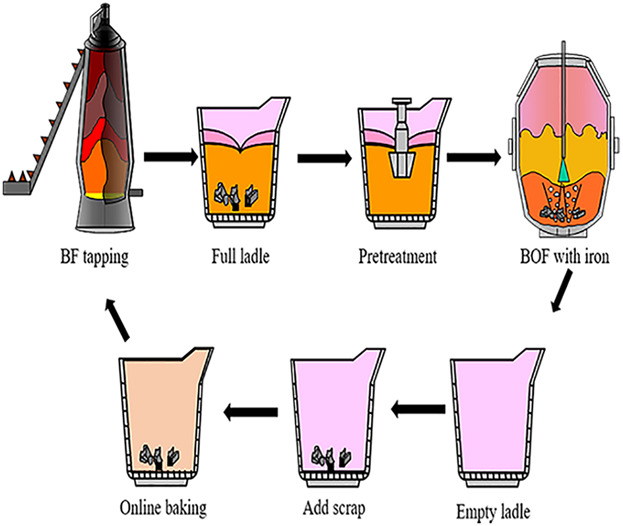
In this paper, a scheme of adding scrap steel to the multifunctional ladle before hot metal tapping is proposed. The effects of the addition of different types of scrap steel pretreated at various temperatures are examined using numerical calculation and simulation. The scheme and numerical analysis results can be valuable references for practical engineering application.
High Efficiency Dephosphorization by Mixed Injection during Steelmaking Process
- First Published: 18 December 2018
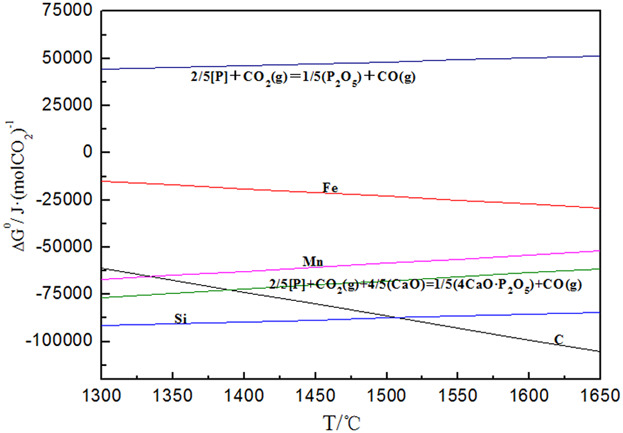
A new dephosphorization technology with introduction of partial CO2 into O2 is proposed during steelmaking process. Through the an alysis of thermodynamics and kinetics, it is found that CO 2 can participate in dephosphorization, strengthen s tirring ability, and control the bath temperature. Furthermore, industrial experiments are performed in a 30t steelmaking converter and a 300t special dephosphorization converter, respectively, which obtains good dephosphorization results.
Microstructure and Properties of 1.0C–1.5Cr Bearing Steel in Processes of Hot Rolling, Spheroidization, Quenching, and Tempering
- First Published: 02 January 2019
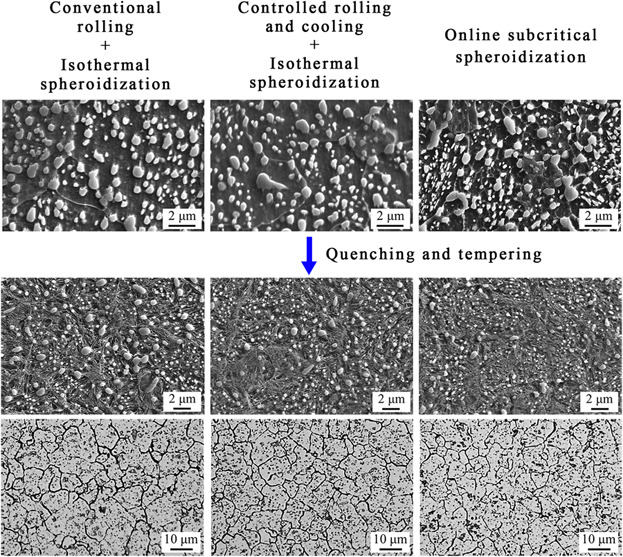
A novel online subcritical spheroidization annealing technology is proposed. Compared with conventional process, a much finer microstructure can be obtained by the proposed online subcritical spheroidization. After quenching from 850 °C and tempering, the mean diameter of undissolved cementite decreases by at least 20%, and prior austenite grain size decreases by about 27%.
Effects of Carbon and Boron on Structure and Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel Coatings Fabricated by Laser Remanufacturing
- First Published: 11 December 2018
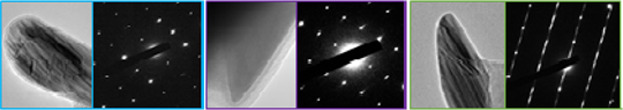
The coatings of austenitic stainless steel powder with various contents of carbon and boron are fabricated using laser remanufacturing technique. A new synchronous lateral powder feeding device is adopted to avoid surface oxidation of molten pool. The tensile strength and hardness are enhanced by increasing the content of carbon and boron, while the plasticity is deteriorated.
Transformation Behavior and Properties of Carbide-Free Bainite Steels with Different Si Contents
- First Published: 21 December 2018
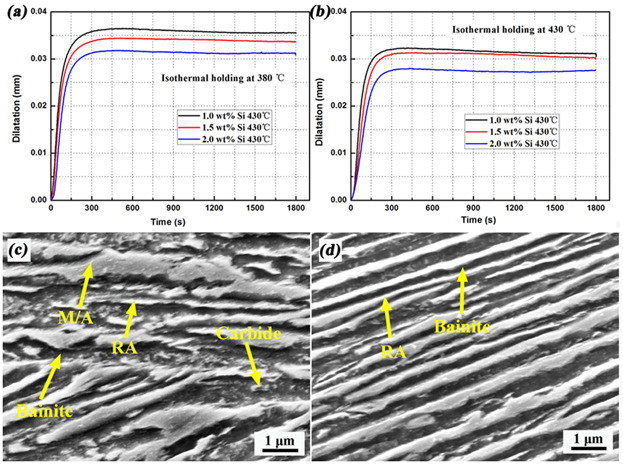
The bainite transformation behavior and properties of low carbon carbide-free bainitic steels containing different Si contents are investigated. Although the transformation kinetics of bainite is retarded and the final bainite amount decreases with increasing Si content, both the strength and total elongation improve with the increase of Si content due to the finer microstructure and less carbides. The dilatation curves austempering at: (a) 380 °C and (b) 430 °C; and the typical SEM microstructure: (c) austempering at 380 °C for low-Si sample and (d) austempering at 430 °C for high-Si sample.










