Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: steel research int. 2/2019
- First Published: 05 February 2019

Cover Photo:
The crystallographic textures and the anisotropy of 2507 super duplex stainless steel are investigated via uniaxial tension tests. The microtexture exhibits the different volume fraction ratios for the {001} and {111} orientations are the root cause of the anisotropy and 45° ears in 2507 super duplex stainless steel. Further details can be found in the article, number 1800397, by Jingyuan Li and co-workers.
Masthead
Contents
Communication
An Experimental Technique for Investigating the Skulling Behavior in the Blast Furnace Hearth
- First Published: 17 August 2018
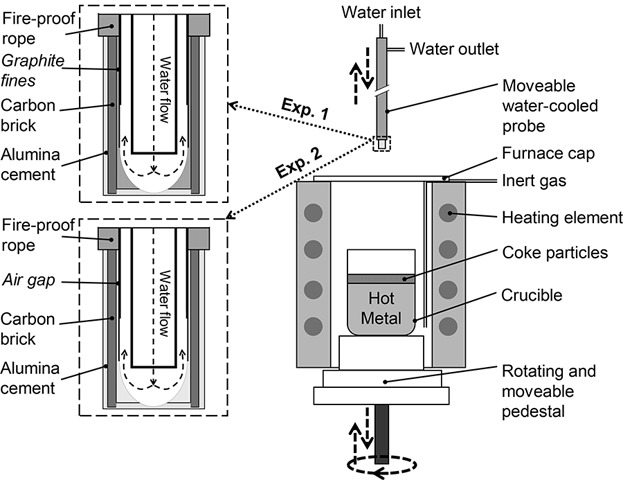
An experimental technique that can be adopted to investigate the skulling behavior in the blast furnace hearth is introduced in the present paper, where the feasibility and potential of the technique are demonstrated by a set of experimental runs. The technique is shown to be capable of producing chemical, thermal, and mechanical conditions similar to those in the real process.
Full Papers
The Crystallographic Textures and Anisotropy in 2507 Super Duplex Stainless Steel
- First Published: 04 December 2018
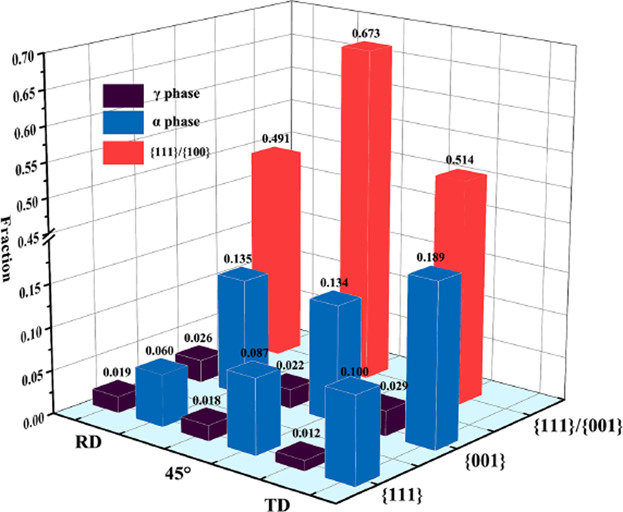
The effect of crystallographic textures on anisotropy in 2507 super duplex stainless steel is studied. The experimental material shows the noticeable planar anisotropy with the obvious 45° ears. The different volume fraction ratios for the {001} and {111} orientations are the root cause of the anisotropy in 2507 super duplex stainless steel.
Characterization of Slag-Metal Emulsion and Its Impact on Foaming Behavior and Slopping in the LD Process
- First Published: 06 December 2018
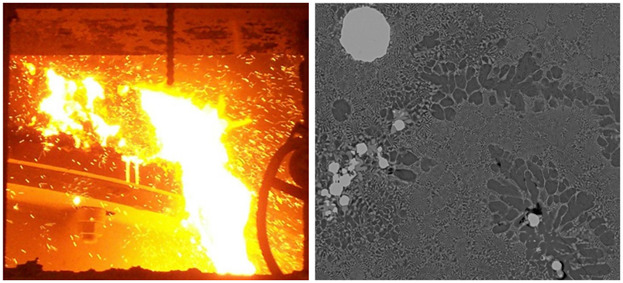
Samples from a 6-tonne pilot BOS vessel are examined by XRD and with SEM for the determination of emulsion-solid mix mineralogy and morphology. The study confirms the importance of minimizing the emulsion-solid mix apparent viscosity, but this without over-oxidizing the liquid slag phase, which would cause an increased gas generation within the slag-metal emulsion, increasing the risk of slopping.
The Effect of Aging Temperature on Microstructure and Tensile Properties of a Novel Designed Fe–12Mn–3Ni Maraging-TRIP Steel
- First Published: 26 August 2018
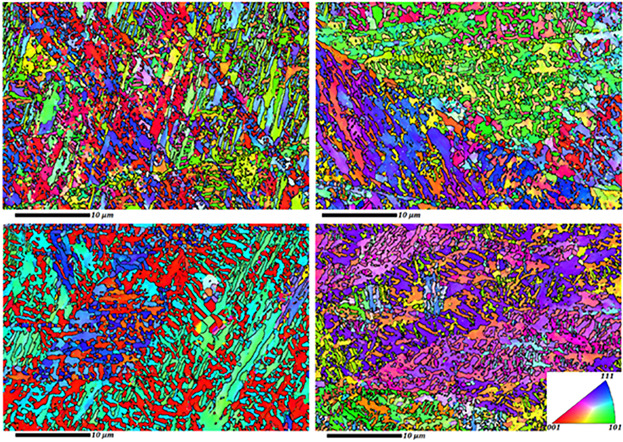
The aging response of a maraging-TRIP steel is studied in terms of phase transformation, texture evolutions, as well as mechanical properties. The results shows that HCP-ϵ martensite is nucleated at prior austenite grains and developed inside the grains during aging, where the K–S orientation relationship is realized for the BCC-α′ martensite, HCP-ϵ martensite, and FCC-γ austenite phases.
Formation of Eutectic Borocarbides in High Boron High Speed Steel during Non-Equilibrium Crystallization
- First Published: 11 September 2018
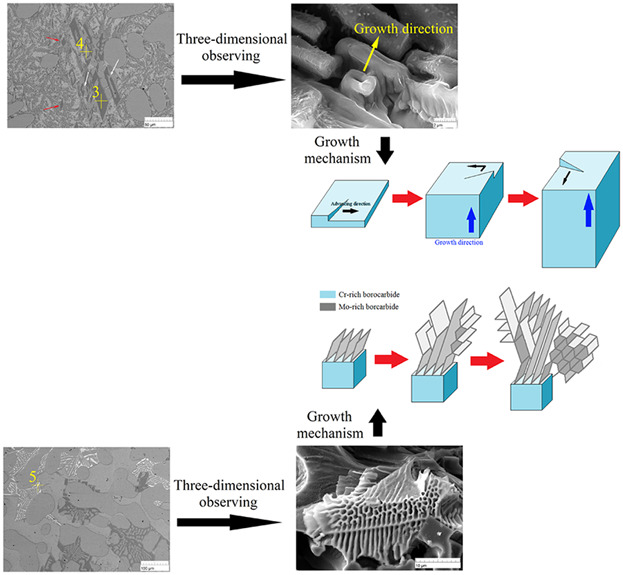
The as-cast microstructure of high boron high speed steel consists of α-Fe matrix, eutectic borocarbide M2(B,C), M3(B,C) boron-cementite, and M7(C,B)3 (M = Fe, Cr, Mo, V, Mn). During solidification, order of precipitation is Cr-rich borocarbide and Mo-rich borocarbide, respectively. Cr-rich borocarbide is the proeutecitc phase, which grows in the form of faceted-non faceted growth. The “hexagon” growth mechanism of Mo-rich borocarbide is discovered.
Reformation Behavior of Austenite in 2205 Duplex Stainless Steel with Rapid Heat Treatment
- First Published: 14 August 2018
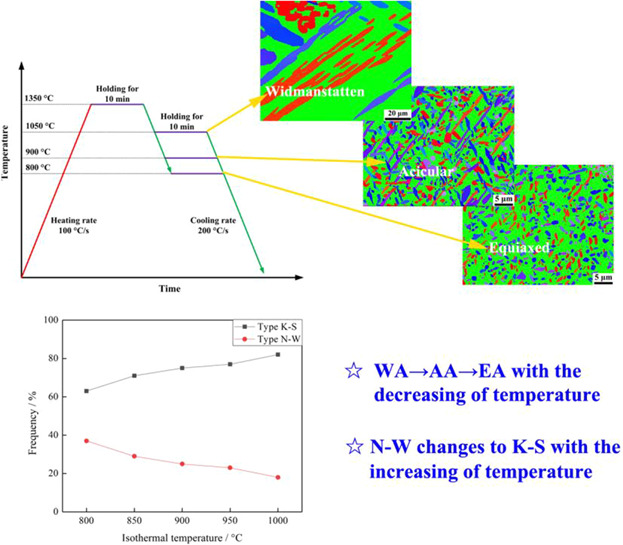
The reformation behavior of austenite in coarsened ferrite grains is studied by means of rapid heat treatment. The morphology of reformed austenite varies from widmanstatten austenite to acicular austenite and at last to equiaxed austenite with the decreasing of isothermal temperature. The orientation relationship between austenite and ferrite changes from N-W to K-S with the increasing of isothermal temperature.
Effects of Rolling Temperature on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties in an Ultrafine-Grained Low-Carbon Steel
- First Published: 04 September 2018
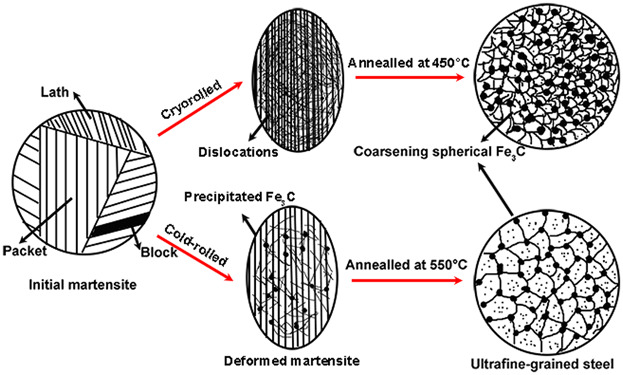
The schematic diagram of the formation of ultrafine grains in the low-carbon steels is presented in Figure 1. Large amount of dislocation is induced in cryorolled specimens and martensite dimension sharply decreases. Finer ultrafine ferrite grains are formed and the spherical Fe3C are coarsened in the cryorolled specimens. The decreased elongation is attributed to the coarse Fe3C in the cryorolled specimens.
Analysis of {100} Texture Formation in Vacuum Annealed Electrical Steel Based on Elastic Anisotropy and Surface Energy Anisotropy
- First Published: 13 November 2018

{100}<0uv> and {100}<011> textures develop in columnar grains of the surface layer by controlling cold rolling reduction and vacuum annealing with α → γ → α transformation. {100}<0uv> α seeds are retained during a low cold rolling reduction and recrystallization. Subsequently, {100} grains consume non-{100} grains on the surface by the elastic strain energy anisotropy during γ → α transformation.
Microalloying Precipitation during Hot Rolling of Seamless Tubes in a Continuous Mandrel Mill
- First Published: 10 December 2018
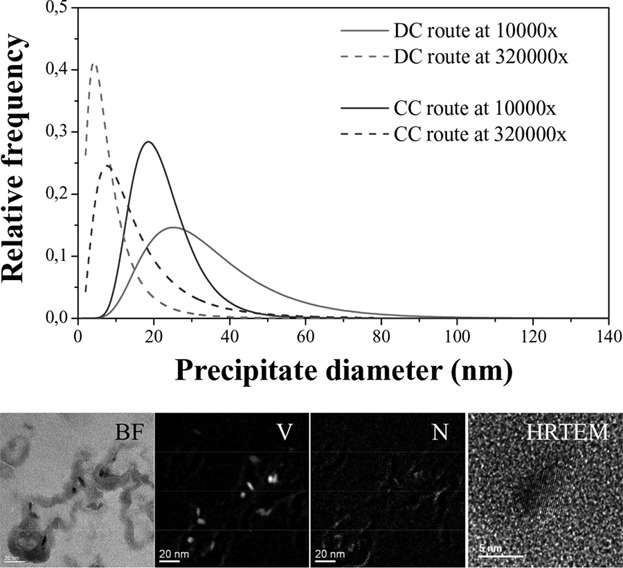
Processing of seamless tubes has unique characteristics such as the possibility of promoting phase transformation before finishing. This characteristic was simulated by hot torsion in a V-N steel and the samples were characterized by TEM. Particles size distributions were accessed by HAADF and typical precipitates were characterized by EDX, PEELS and EFTEM. Effects on microstructure and mechanical properties were discussed.
Microstructure and Hardness Evolution during Deformation near Ae3 in a Cr–Mn–Ti Gear Steel
- First Published: 28 August 2018
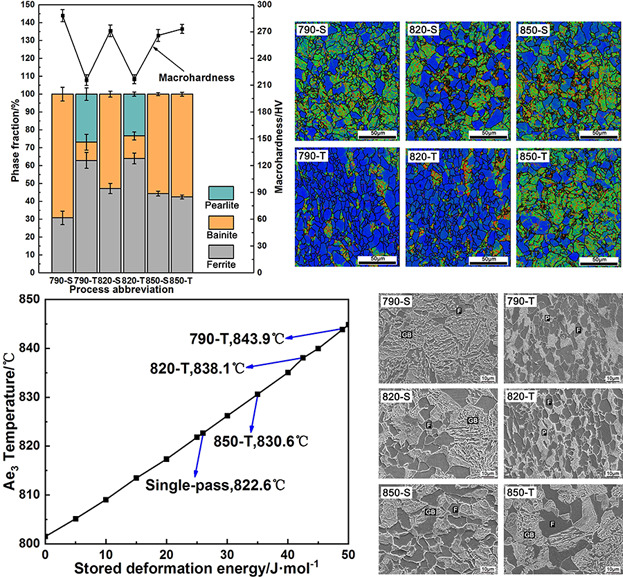
The different thermomechnical routes are applied to investigate the microstructure and hardness in a Cr–Mn–Ti gear steel. The microstructural observation suggests that ferrite and pearlite transformation are promoted by adding one-pass deformation near Ae3, which leads to the decrease of macrohardness. A mathematical model is developed to predict ferrite transformation in different processes.
Effect of Single Power Two Circuits Electroslag Remelting Process on the Ingot Solidification Quality
- First Published: 05 September 2018
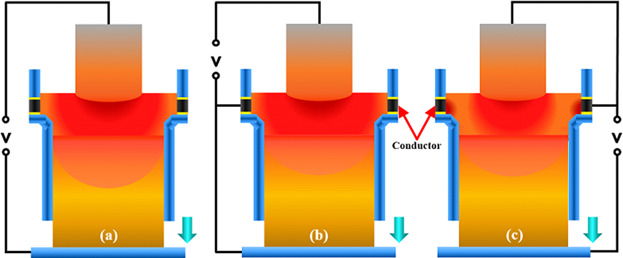
The remelting ingots are manufactured by ESRW and the single-power, two-circuit electroslag remelting process with different power supply circuits with the dimensions of Φ250 mm × 450 mm. Compared with ESRW process, ESR-STCCM can significantly improve the solidification quality of remelting ingot, especially for ESR-STCCM-D process. ESR-STCCM-D process is suitable for remelting large-scale ingot and high alloy ingot.
Interaction of Injector Design, Bubble Size, Flow Structure, and Turbulence in Ladle Metallurgy
- First Published: 21 September 2018
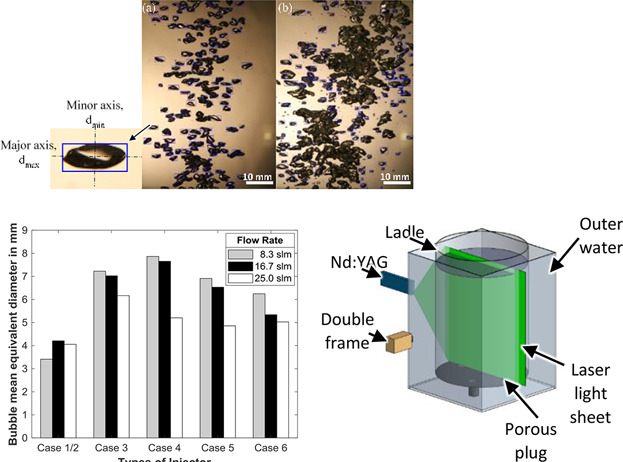
The interaction of injector design, bubble size distribution, flow structure, and turbulence in ladle metallurgy are studied with an air-water model scaled at 1:3 of an industrial 185 t ladle furnace. The flow field velocity and turbulent kinetic energy are visualized by the Particle Image Velocimetry (PIV) measurements whereas the bubble sizes are investigated with a MATLAB image processing technique.
On the Spheroidizing Annealing Behavior in Cr/Nb Microalloyed Medium Carbon Steels
- First Published: 31 August 2018
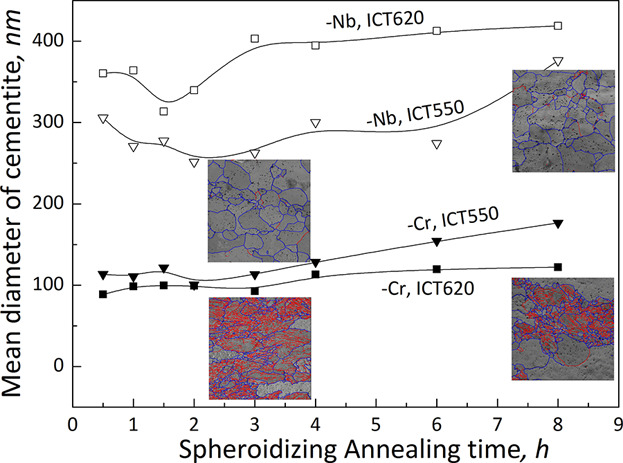
Two medium carbon steels, which are, respectively, microalloyed with Cr and Nb, exhibit different spheroidizing annealing behaviors. A dedicated computational work is carried out to interpret the experimentally observed metallurgical phenomenon, which includes cementite growth and coarsening kinetics, solute dragging, or Zener pinning due to Nb, recrystallization of ferritic matrix, and their interaction.
Investigation on Gasification Reaction Behavior and Kinetic Analysis of Iron Coke Hot Briquette under Isothermal Conditions
- First Published: 18 October 2018
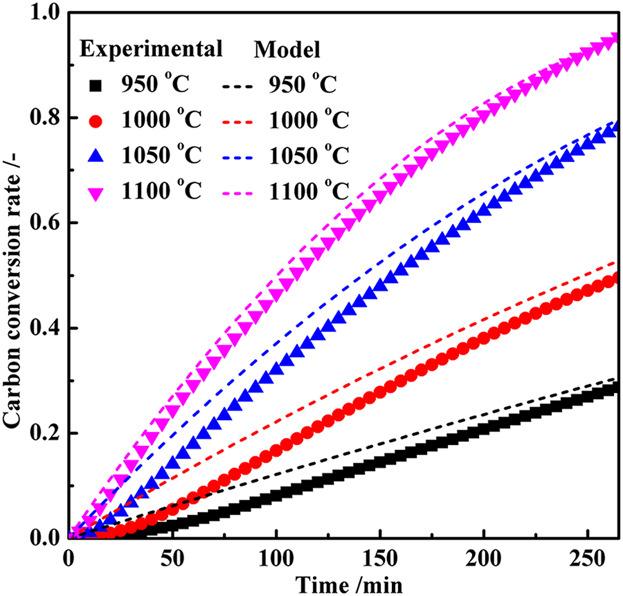
In this paper, the gasification reaction behavior and kinetic analysis of iron coke hot briquette is experimentally investigated under isothermal conditions. The reaction mechanism of iron coke hot briquette gasified with CO2 is revealed. Simultaneously, the most appropriate mechanism function for iron coke hot briquette gasification is confirmed and the kinetic parameters are conducted.
Modeling of the Effect of the Gas Flow Rate on the Fluid Flow and Open-Eye Formation in a Water Model of a Steelmaking Ladle
- First Published: 02 November 2018
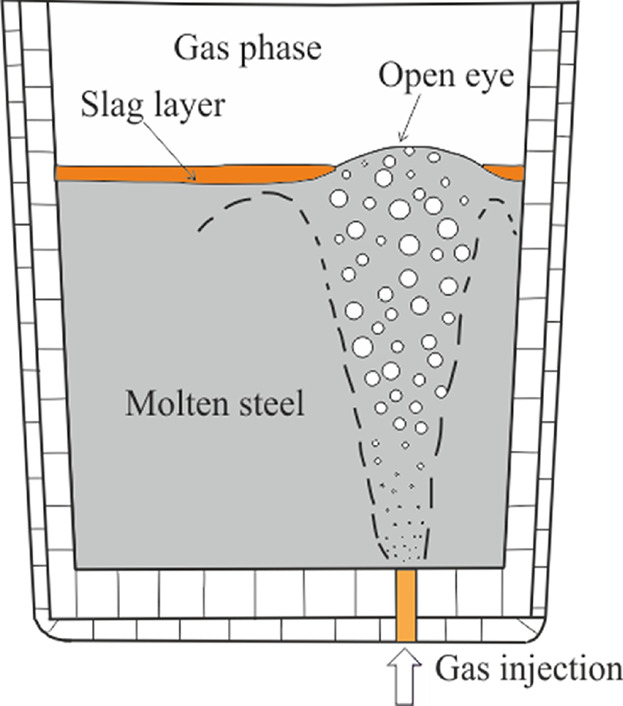
In ladle refining process, gas stirring is employed to homogenize the chemical composition, removal of inclusions and intensify the rate of refining reactions. The slag layer in the ladle plays an important role in refining the molten steel, as it encourages the slag–steel reactions. In the current work, the effect of gas flow rate on the slag open-eye area is been studied through physical and numerical modeling.
Zinc Enrichment in In-Plant Electrostatic Precipitator Dust Recycling by Air Classification in Converter Steelmaking
- First Published: 04 October 2018
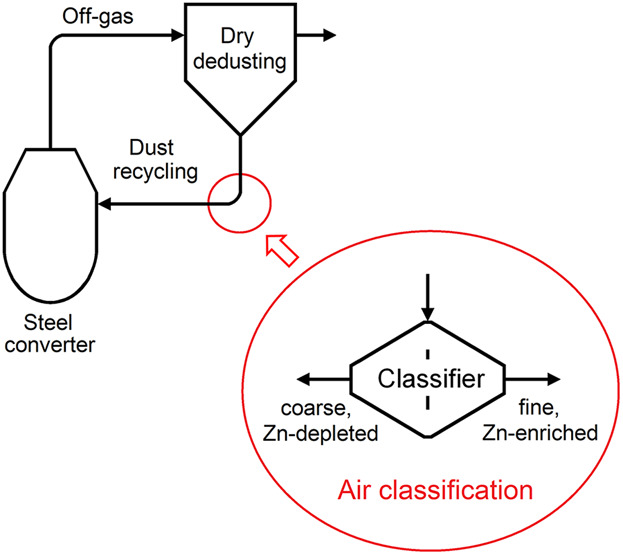
Several steel mills having a dry converter off-gas de-dusting systems apply in-plant dust recycling. Thereby, the Zn content of the dust increases steadily until the desired concentration in the dust for discharge is reached. By air classification of the dust, the required average number of times a Zn atom has to be volatilized can be reduced by 35–72%.
Effects of Blast Furnace Main Trough Geometry on the Slag-Metal Separation Based on Numerical Simulation
- First Published: 12 November 2018
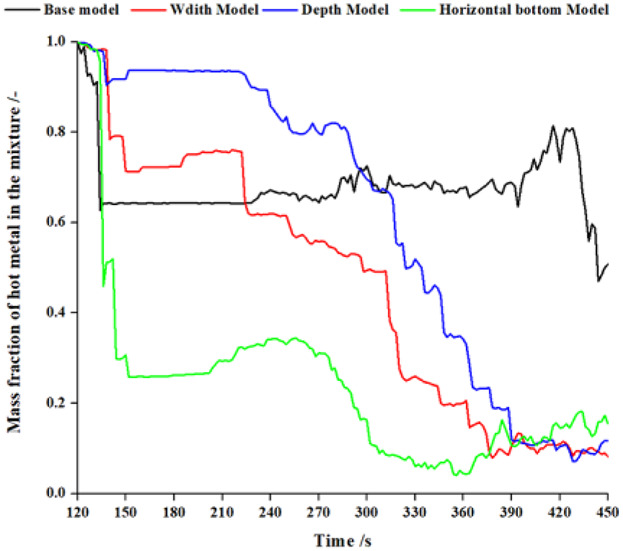
Comparing with the base model of main trough, the horizontal bottom model decreases the mass fraction of hot metal in the mixture in the slag port most, followed by the width model and the depth model. Therefore, the main trough with a horizontal bottom is recommended to decrease the hot metal loss associated with the slag.
The Impact of Deformation Conditions on Divorced Eutectoid Transformation in Bearing Steels
- First Published: 21 October 2018
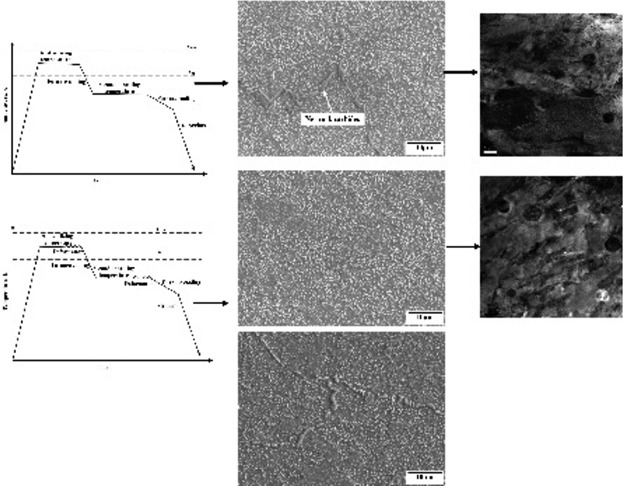
The impact of deformation on divorced eutectoid transformation in bearing steel is investigated. The optimum condition is single-pass deformation at 1073K with a reduction of 30%. In this condition, only ≈0.5 h isothermal treatment is adequate to complete the spheroidizing process, and the mean particle after deformation is decreased to ≈0.2 μm, significantly finer than the conventional practice.










