Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 03 September 2023
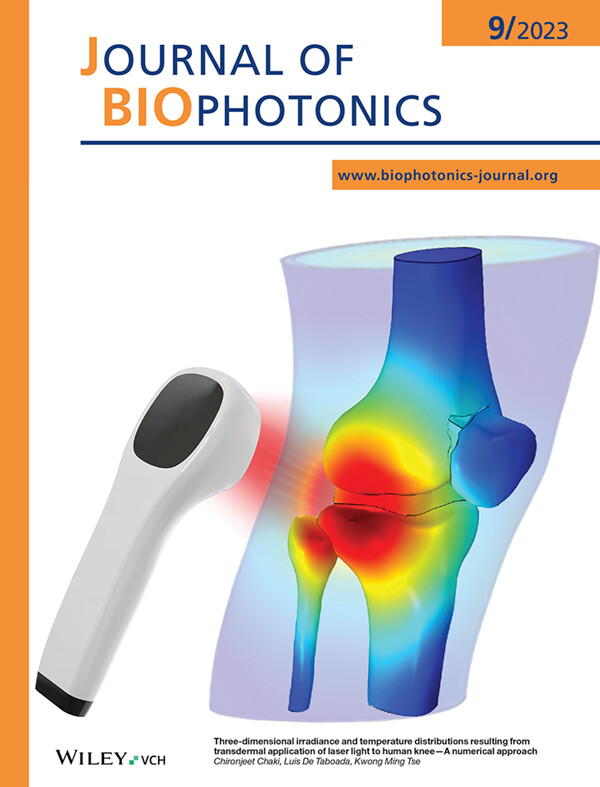
In order to deliver safe and effective transdermal deep tissue light therapy (tDTLT), the study simulates laser light propagation in an anatomical human knee model to assess the light transmittance and absorption-driven thermal changes for various commonly used near-infrared wavelengths (600-1200nm) at multiple skin-applied irradiances. A robust methodology and guidance for investigating high-power laser therapy dosing prior to clinical research are provided, ensuring the safe and effective delivery of tDTLT.
For further details please visit the article by Chironjeet Chaki, Luis De Taboada, and Kwong Ming Tse (e202200283).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Emerging clinical applications in oncology for non-invasive multi- and hyperspectral imaging of cell and tissue autofluorescence
- First Published: 05 June 2023
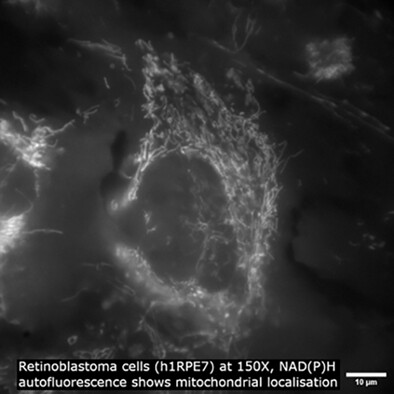
Hyperspectral and multispectral imaging of cell and tissue autofluorescence employs fluorescence imaging, without exogenous fluorophores, across multiple excitation/emission combinations. This technology can enable the non-invasive, stain-free characterisation of cells and tissues, and has shown great promise for advancing tumour diagnosis and surgical margin definition.
Advanced flow cytometry for biomedical applications
- First Published: 01 June 2023
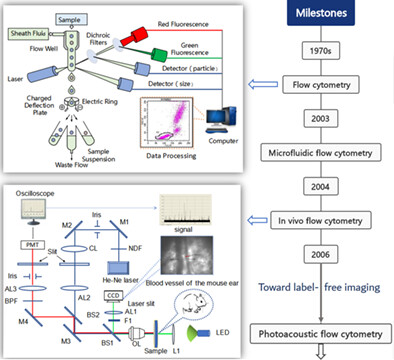
Notable advancements of flow cytometry (FC) have been achieved in recent years, which expands its capabilities to detect physical, chemical, and biological characteristics in a population of flowing cells or particles. This review presents a big picture of the advanced flow cytometers and provides both a clear understanding of their mechanisms and some fresh insights into their biomedical applications. The review also highlights the existing challenges and the latest trends aiming to raise the awareness of FC with its potential improvements.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Three-dimensional irradiance and temperature distributions resulting from transdermal application of laser light to human knee—A numerical approach
- First Published: 01 June 2023
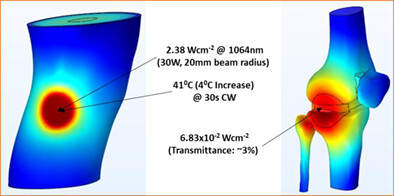
In order to deliver safe and effective transdermal deep tissue light therapy, we simulate laser light propagation in an anatomical human knee model to assess the light transmittance and absorption-driven thermal changes for various commonly used near-infrared wavelengths (600–1200 nm) at multiple skin-applied irradiances. Our study provides a robust methodology and guidance for investigating high intensity light therapy dosing prior to clinical research, ensuring safe and effective tDTLT delivery.
Photobiomodulation increases uprighting tooth movement and modulates IL-1β expression during orthodontically bone remodeling
- First Published: 10 May 2023
The loss of a tooth can move adjacent and the antagonist teeth, which makes difficult prosthetic rehabilitation. Anchorage systems, such as mini-implants, have been increasingly used as a treatment option. Recent studies have shown that photobiomodulation (PBM) can accelerate the orthodontic movement and decrease pain in intrusion movement. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of PBM on the acceleration of orthodontic movement of molar intrusion and its effect on pain and inflammation of periodontal tissues. Results show that photobiomodulation has increased uprighting tooth movement and also modulates IL-1β expression during orthodontically bone remodeling.
Microvasculature and microstructure alteration in dry-type high myopia
- First Published: 26 April 2023
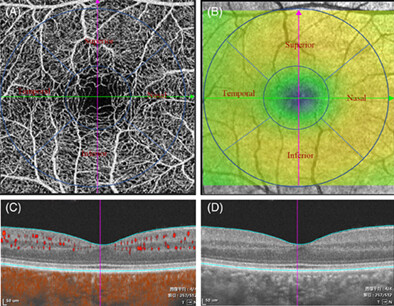
Myopic macular degeneration is one of the leading causes of blindness. We found morphological alterations in the vasculature and structure of the retina in early high myopia. The retinal thicknesses of macular fovea increased significantly with the increase of vascular densities. We thought the impairment of retinal microstructure reduction is more likely related to reduced oxygen and nutrients due to microvessel density decreases.
Data for characterization of the optical properties of Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar) blood
- First Published: 02 June 2023
Animal welfare in Atlantic salmon aquaculture can be improved by facilitating novel physiological sensing principles such as pulse oximetry, provided that tissue optical properties are known. In this work, extinction properties of three constituents of Atlantic salmon blood have been characterized using a photo spectrometer in the VIS–NIR (450–920 nm), and blood cell size has been measured using a Coulter counter as part of light scattering property evaluations. Results indicate that pulse oximetry sensors originally intended for human applications may thus be used to estimate blood oxygenation levels for this species.
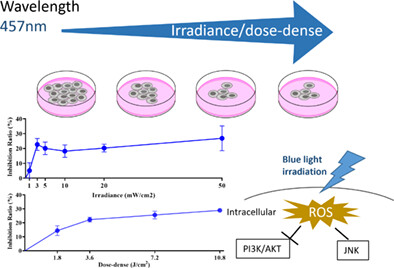
Effect of blue light on the cell viability of A549 lung cancer cells and investigations into its possible mechanism
- First Published: 02 June 2023
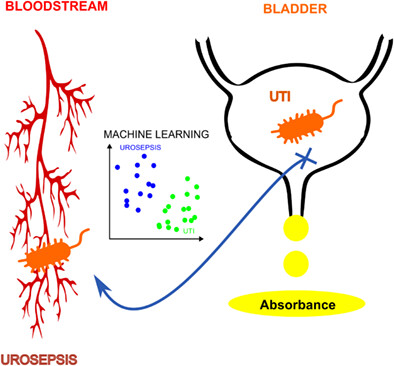
Optical method supported by machine learning for urinary tract infection detection and urosepsis risk assessment
- First Published: 07 June 2023
Ex vivo fluorescence imaging for the identification of rhodamine-labeled bovine serum albumin and chitosan-coated gold and silver nanoparticles
- First Published: 01 June 2023
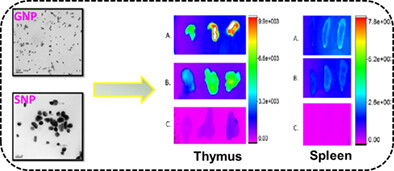
Therapeutic potential and toxic effects of in vivo administered gold nanoparticles (GNP) and silver nanoparticles (SNP) depend on their distribution in different tissues. GNP and SNP were coated with the labeled conjugates of bovine serum albumin and chitosan by adsorption. The results strongly suggest significant tissue distribution of nanoparticles (NPs) following oral administration. Ex vivo imaging can be used as a specific and sensitive method to study the distribution of NP in vivo.
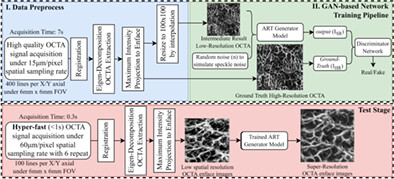
A hand-held optical coherence tomography angiography scanner based on angiography reconstruction transformer networks
- First Published: 01 June 2023
NIR and THz spectroscopy: An experimental investigation toward nicotine-related devices
- First Published: 01 June 2023
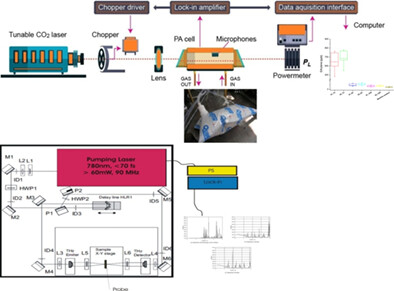
Using CO2 laser photoacoustic spectroscopy (CO2 LPAS) system and terahertz time-domain spectroscopy (THz-TDS) this study examined the content of nicotine-delivery products measuring breath ethylene as a by-product of oxidative stress and transmission spectra of tobacco and nicotine in smoking products.
Laser speckle contrast imaging based on spatial frequency domain filtering
- First Published: 01 June 2023

We develop a novel method to separate dynamic speckles from static speckles by spatial frequency domain filtering and the time domain averaging of the speckle pattern. It can address the problems of nonuniform background, small dynamic range, low contrast, and contrast-to-noise ratio in conventional laser speckle contrast imaging. Furthermore, it exhibits superior computational efficiency.
Scattered-light-sheet microscopy with sub-cellular resolving power
- First Published: 07 June 2023
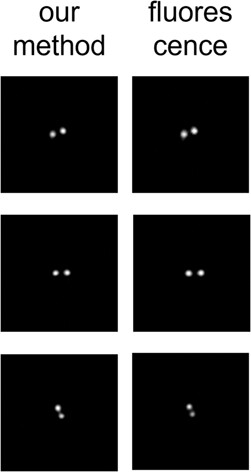
Scattering-based light-sheet microscopy, a more than 100 years old microscopy technique, has recently re-emerged as a key label-free tissue imaging method. Here, we present an advancement of this method that enables both subcellular resolution and low levels of irradiance. We validated this approach by imaging carbon deposits in yeast and bacteria (Figure) with increased specificity and no staining.
Figure: PHB granule imaging in Methylobacterium extorquens by light-sheet scattering and fluorescence.
The mitochondrial-related effect of the 905 nm photobiomodulation therapy on 50B11 sensory neurons
- First Published: 01 June 2023
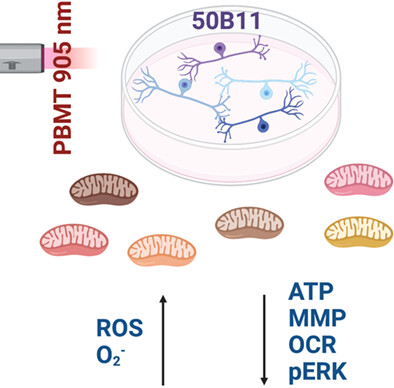
The mitochondrial-related effect of the 905 nm photobiomodulation therapy (PBMT) on 50B11 sensory neurons: an increment of total reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial O2− and a decrement of adenosine triphosphate, mitochondrial membrane potential oxygen consumption rate, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation was found after PBMT.
Polarization coherency matrix tomography
- First Published: 02 June 2023
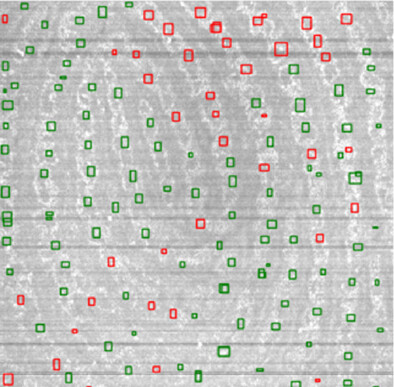
A polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PS-OCT) based polarization coherency matrix tomography combining polarization coherency matrix with Mueller matrix is proposed for the determination of complete polarization properties of tissue. The sample Mueller matrix are applied for deriving fully polarized optical properties of the sample based on the elliptical diattenuator and the elliptical retarder, which could determine the chiral structure of sweat ducts, which cannot be revealed by traditional PS-OCT.
Automatic lumen and anatomical layers segmentation in IVOCT images using meta learning
- First Published: 08 June 2023
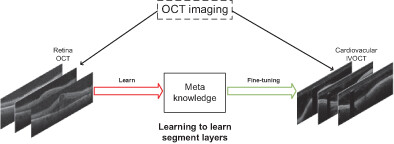
Optical coherence tomography is widely used to image different tissues, for example, retina and cardiovascular. Both tissues have a hierarchical layer structure. Hence, an automatic layers segmentation method based on meta-learning was proposed, which utilizes the bi-level gradient strategy to learn the shared meta-knowledge of how to segment layers on retina OCT images and quickly adapt to layers segmentation on cardiovascular IVOCT images with only a few labeled IVOCT images.
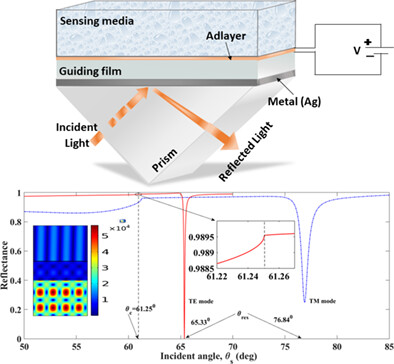
A novel tunable metal-clad planar waveguide with 0.62PMN-0.38PT material for detection of cancer cells
- First Published: 06 June 2023
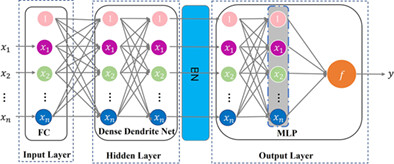
Gradient boosting DD-MLP Net: An ensemble learning model using near-infrared spectroscopy to classify after-stroke dyskinesia degree during exercise
- First Published: 06 June 2023
Digital diaphanoscopy of maxillary sinus pathologies supported by machine learning
- First Published: 05 June 2023
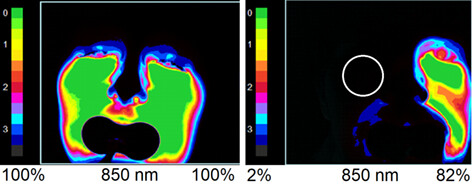
Digital diaphanoscopy allows to reveal a decrease in the intensity of probing radiation in the sinus with pathology (a decrease in its transparency), while in a healthy sinus, which is airy, the absorption of radiation is weak. The sensitivity and specificity of the proposed method are 0.88 and 0.98, respectively.
Sampling volume assessment for wearable multimodal optical diagnostic device
- First Published: 07 June 2023
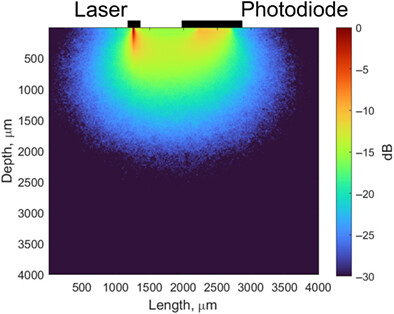
This study describes the process and results of numerical Monte Carlo simulation of optical radiation propagation in laser Doppler flowmetry and fluorescence spectroscopy channels of a wearable diagnostic device. The changes in the sampling volume depending on the anatomical features of the skin and technical parameters of the device are shown.