Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 06 February 2023

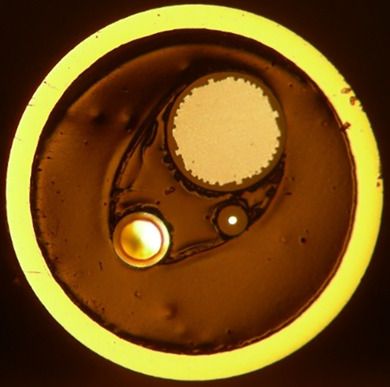
This work studied two-photon collagen crosslinking (CXL) in human corneal lenticules induced by near infrared femtosecond laser, possessing the advantages of multiphoton absorption and near-infrared light. The corneal stiffness can be enhanced by up to 296% without significantly reducing corneal transparency (<3%), paving the way to treat ophthalmic disorders such as keratoconus by 3D CXL of in vivo human cornea with higher safety, precision and efficacy.
Further details can be found in the article by Zhenzhou Cheng, Nan Zhang, Le Chang, Pengfei Qi, Lin Zhang, Lie Lin, Yan Wang, and Weiwei Liu (e202200160).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 06 February 2023

Confocal Raman microscopy provides composition and constitution of label-free samples at high spatial-resolution. In this study, the histology of atherosclerotic arteries was measured using a custom-built confocal Raman microscopy that was developed to improve imaging speed, diffraction efficiency, and spectral resolution. Additionally, the machine learning method was used to enhance the accuracy of classification. Results show that each layer of arteries and lipid-rich inflamed plaque can be successfully characterized.
Further details can be found in the article by Jingchao Xing, Dong-Ryoung Lee, Jin Won Kim, and Hongki Yoo (e202200243).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Highlighting nuances of blue light phototherapy: Mechanisms and safety considerations
- First Published: 23 September 2022
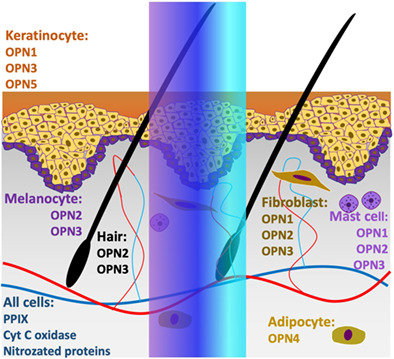
Blue light phototherapy provides dermatological and systemic disease treatments. Its therapeutic effect relies on well-orchestrated chromophores and photoreceptor groups in skin and hair follicle cells. Through a “slightly ajar” curtain, we are evidencing this interplay between photons and cells, eager to unravel its complexity to create safer and more effective therapies. This work synergizes biophotonics, photodermatology and cutaneous biology highlighting the “shades” of blue light; modes of action and the balance between risks and benefits of blue light therapy.
LETTER
Histological classification of atherosclerotic arteries using high-speed confocal Raman microscopy with machine learning
- First Published: 13 October 2022
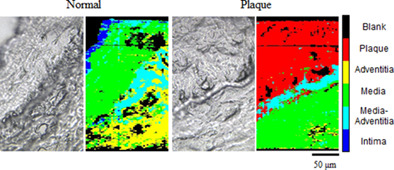
Confocal Raman microscopy is a useful tool to observe composition and constitution of label-free samples at high spatial resolution. We have developed a method to improve imaging speed, diffraction efficiency, and spectral resolution of confocal Raman microscopy. In addition to the novel imaging technique, the machine learning method enables confocal Raman microscopy to visualize accurate histology of tissue sections. We have demonstrated the performance of the proposed method by measuring histological classification of atherosclerotic arteries and compared the histological confocal Raman images with the conventional staining method.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Two-photon collagen crosslinking in ex vivo human corneal lenticules induced by near-infrared femtosecond laser
- First Published: 24 September 2022
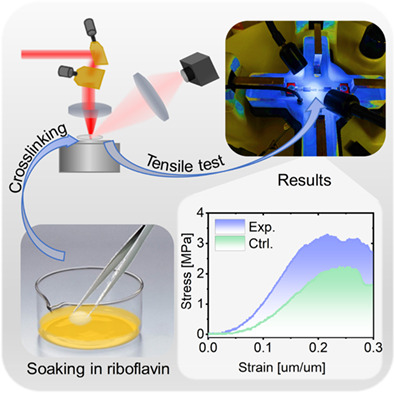
Here we studied two-photon collagen CXL in ex vivo human corneal lenticules induced by near-infrared femtosecond laser, which exploits the advantages of both multiphoton absorption and near-infrared light, can be used to induce CXLs in collagen-rich tissues with higher precision and safety. It enabled the corneal stiffness to be enhanced by up to 296% without obviously reducing corneal transparency (<3%), suggesting that it could potentially be developed as a safer treatment for ophthalmic disorders such as keratoconus.
Liquid crystal precursor system as a vehicle for curcumin-mediated photodynamic inactivation of oral biofilms
- First Published: 28 September 2022
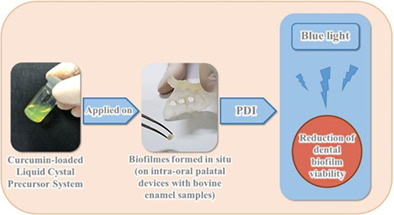
Curcumin has great potential as a photosensitizer, but it has low solubility in aqueous solutions. This study reports the antimicrobial efficacy of photodynamic inactivation (PDI) mediated by a curcumin-loaded liquid crystal precursor (LCP) on in situ dental biofilms. The LCP system retained curcumin and released it slowly and continuously, thus protecting the drug from photodegradation. LCP with curcumin is considered effective for the photoinactivation of dental biofilms, but the PDI efficacy may differ based on the host's individual characteristics.
Comparative analysis of dermal collagen and lipids in cereblon ablated mice using a multimodal nonlinear optical system
- First Published: 12 August 2022
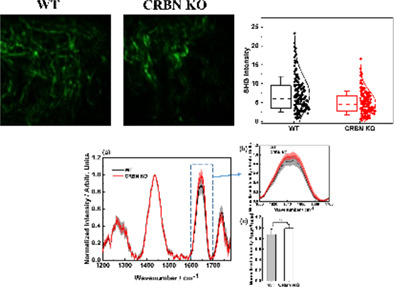
A multimodal nonlinear optical system was used for comparative analysis of lipids and collagen in cereblon-depleted mouse skin tissues. We found more unsaturated fatty acids and decreased levels of dermal collagen fibers from cereblon knockout skin tissues. Our findings provide proof of principle that the optical tool can be an additional apparatus to investigate future biomedical research.
Tri-mode optical biopsy probe with fluorescence endomicroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, and time-resolved fluorescence spectroscopy
- First Published: 05 September 2022
Energy compensated synthetic aperture focusing technique for photoacoustic microscopy
- First Published: 12 September 2022
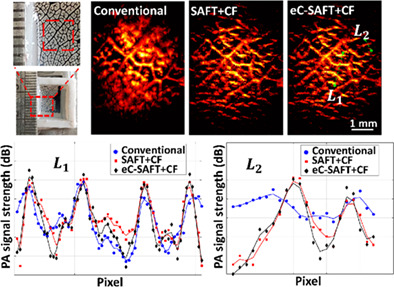
We report an adaptive energy-compensated synthetic aperture focused technique (eC-SAFT) for improving the imaging performance of PAM in terms of DOF, spatial resolution, and SNR. In addition to coherency and time-delay (in conventional SAFT), this beamforming-based reconstruction algorithm takes into account acoustic energy loss following Beer-Lambert's law. Experimental validation studies performed in tissue-mimicking (Agar) phantoms, complex leaf veins, and chicken breast tissues demonstrate that the proposed eC-SAFT+CF outperforms conventional SAFT+CF.
Dynamic change in optical properties of a nanoparticle embedded tumor phantom for plasmonic photothermal cancer therapeutics
- First Published: 24 September 2022
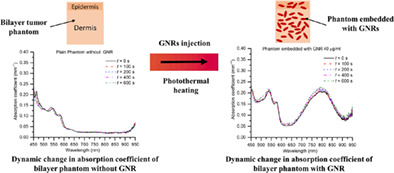
(GNR) of concentrations 10, 20, and 40 μg/ml embedded within a bilayer tumor phantom can increase the absorption coefficient of the phantom by 4–8 times within the spectral range of 750–850 nm. For the dynamic changes in optical properties (during photothermal interaction), it is observed that the absorption coefficient increases by ~8% with the incorporation of GNRs of concentration 40 μg/ml, while no considerable dynamic change in the optical properties is observed of the phantom embedded with GNRs of concentrations 10 and 20 μg/ml during photothermal interaction.
Rapid determination of Proteus mirabilis susceptibility to antibiotics using infrared spectroscopy in tandem with random forest
- First Published: 28 September 2022
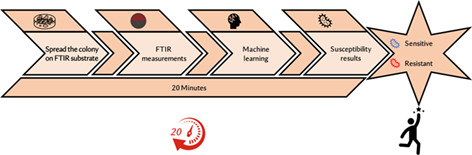
Resistant bacterial infections to antibiotics have a broad influence on the quality and economic burden of patients' and families' lives. To start effective treatment as quickly as possible, rapid laboratory identification of bacterial antibiotic resistance is crucial. The Fourier-transform infrared/based machine-learning enables faster determination of antibiotic resistance, within ~20 min of isolated bacterial colonies. Rapid determination of bacterial resistant to antibiotic is a main step towards the limitation of development and spreading of multidrug resistant bacteria.
Identification of circulating biomarkers of Crohn's disease and spondyloarthritis using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- First Published: 16 September 2022
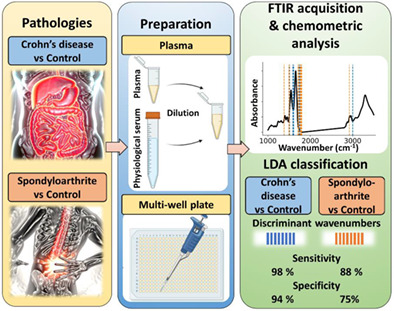
Crohn's disease (CD) and spondyloarthritis (SpA) are two-related chronical inflammatory diseases, affecting the digestive trac and joints respectively. Both diseases are hard to diagnose with certainty as their symptoms are varied and not necessary specifics. Here is proposed a new tool for their diagnostic: the use of Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy on plasma samples. From the molecular signatures, CD and SpA patients can be distinguished from control with an accuracy of 97% and 85% respectively.
Quantitative determination of concentration profiles of skin components and topically applied oils by tailored multivariate curve resolution-alternating least squares using in vivo confocal Raman micro-spectroscopy
- First Published: 15 September 2022
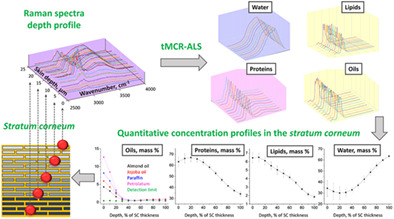
The tMCR-ALS method applied to high-wavenumber Raman spectra of the stratum corneum has been applied for quantitative determination of the concentration profiles of its main components water, lipids, proteins, and topically applied drugs using Raman spectra of the pure materials variable in depth. tMCR-ALS requires these loadings and material densities to calculate a match of depth-dependent excitation and Raman signal attenuations, that is, the currently used normalization on keratin is unnecessary.
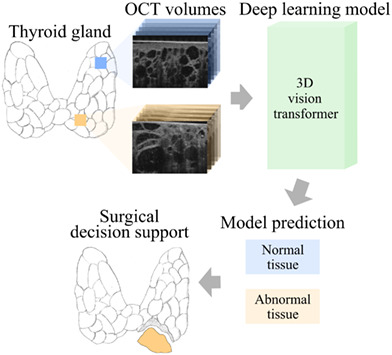
Diseased thyroid tissue classification in OCT images using deep learning: Towards surgical decision support
- First Published: 06 October 2022
Single-shot optical projection tomography for high-speed volumetric imaging of dynamic biological samples
- First Published: 10 September 2022
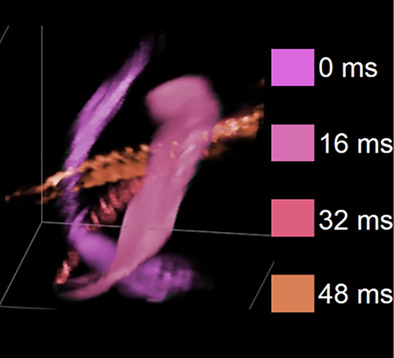
A proof-of-principle system capable of single-shot optical projection tomography of a ~1 mm3 volume is presented. A camera-limited rate of 62.5 volumes/s is demonstrated, applied to both transmitted and fluorescence imaging of nonanesthetized zebrafish embryos. The system works by simultaneously acquiring 8 projection images on four cameras, followed by iterative reconstruction, with a component cost under £5000.
Low-power compact continuous-wave stimulated emission depletion microscopy
- First Published: 02 September 2022
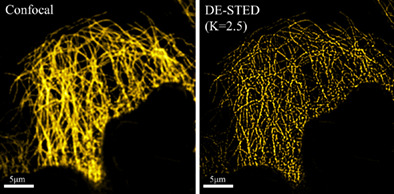
We have built a compact CW-STED system on a 45 × 60 cm breadboard. Then verify the feasibility and potential of DE in the home-built CW-STED system. The experimental results demonstrate that the home-built CW-STED with the digitally enhanced (DE) method not only can obtain very high resolution but also that the system is simple and low cost, indicating that CW-STED combined with digitally enhanced has great potential for various applications.
Vascular elasticity measurement of the great saphenous vein based on optical coherence elastography
- First Published: 06 September 2022
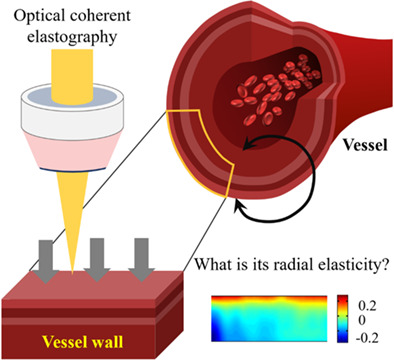
This research aims to measure the radial elasticity of ex vivo GSV using optical coherence elasticity (OCE) imaging method. We performed OCE elastography on isolated GSV vessels. The images before and after static pressure are registered, the displacement field before and after pressure is calculated, and the strain field is obtained by combining the relationship between strain and displacement, to obtain the radial elastic modulus of GSV. This method can be used in vascular bypass or stent surgery to obtain the mechanical properties of blood vessels immediately and provide quantitative indicators for precise treatment.
Identification of blood species based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy and convolutional neural network
- First Published: 23 September 2022
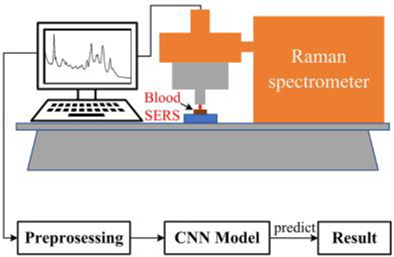
In this paper, surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy technology is used to carry out the research on the species identification of trace blood, and convolutional neural network algorithm is used to distinguish the SERS spectra of 19 species, with an accuracy rate of 98.79%. Our study provides an effective and reliable method for identification and classification of trace amount of blood.
Polarization clustering of biological structures with Mueller matrix parameters
- First Published: 18 October 2022
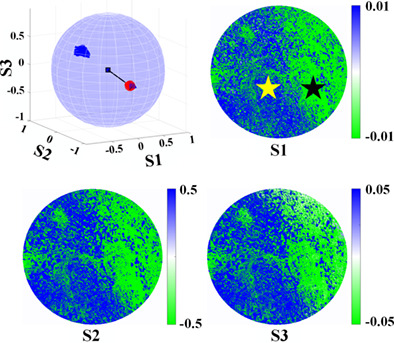
Mueller matrix imaging polarimetry (MMIP) is a promising technique for the characterization of biological tissues, including the classification of microstructures in pathological diagnosis. To expand the parameter space of Mueller matrix parameters, we propose new vector parameters (VPs) according to the Mueller matrix polar decomposition method. We measure invasive bladder cancer (IBC) with extensive necrosis and high-grade ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) with MMIP, and the regions of cancer cells and fibrotic stroma are classified with the VPs.
COMMENTS
Comment on “Feasibility of Raman spectroscopy as a potential in vivo tool to screen for pre-diabetes and diabetes”
- First Published: 28 October 2022
ERRATUM
ERRATUM: Kidney decontamination during perfusion for transplantation procedure: In vitro and ex vivo viability analysis
- First Published: 18 December 2022
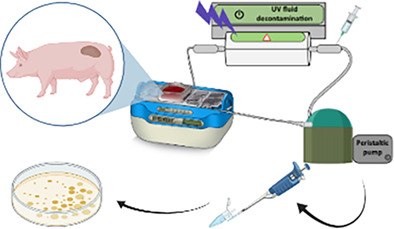
The graphical abstract generally represents the objective of the work, presenting a sequence of experiments as are the final ex vivo studies of the article. Initially, it shows the organ extracted from the pig being perfused in the perfusion machine with contaminated HTK and at the same time this liquid is decontaminated by the UV-C decontamination system, obtaining results after plating the collected samples to verify bacterial growth.