Dynamic change in optical properties of a nanoparticle embedded tumor phantom for plasmonic photothermal cancer therapeutics
Funding information: Indian Council of Medical Research, Grant/Award Number: 5/3/8/83/ITR-F/2020-ITR
Abstract
In this study, the temporal dynamic changes in optical properties of gold nanorods (GNR) embedded tumor phantom, during photothermal interaction, are reported for plasmonic photothermal therapeutics. Tumor mimicking bilayer phantoms were prepared by using 1% agarose incorporated with 0.1% coffee powder, 0.3% intralipid solution as epidermis layer; 3% intralipid solution and 0.3% human hemoglobin (Hb) powder as dermis layer. On incorporating GNRs of concentrations 10, 20, and 40 μg/ml within the phantom, the absorption coefficients increases 4–8 times, while there is minimal change in the reduced scattering coefficients. Further the absorption coefficient increased by ~8% with the incorporation of GNRs of concentration 40 μg/ml, while no considerable dynamic change in the optical properties is observed for the phantom embedded with GNRs of concentrations 10, and 20 μg/ml. The discussed results are useful for the selection of GNRs dose for pre-treatment planning of plasmonic photothermal cancer therapeutics.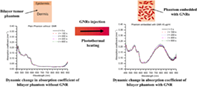
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.




