Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 12 August 2021
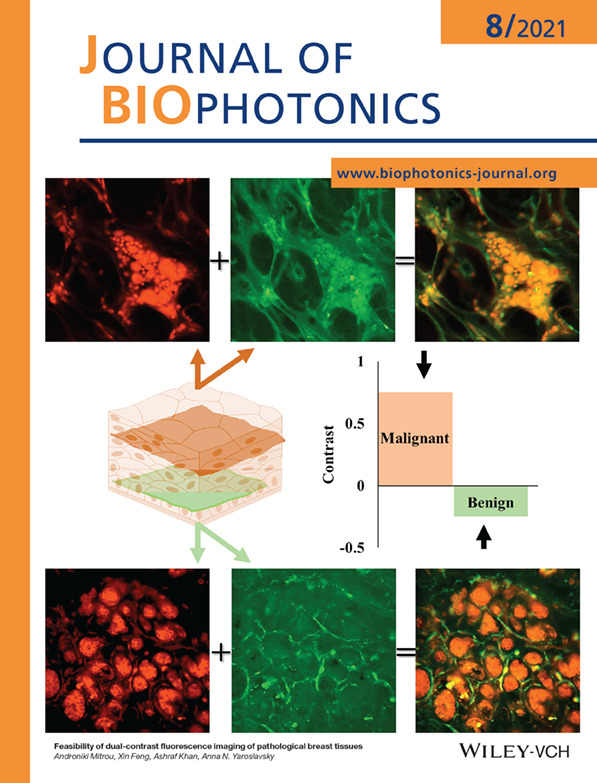
Confocal fluorescence imaging of pathological breast tissue stained with the combination of intravital dye, Methylene Blue (MB), with molecular cancer marker, pH low insertion peptide (pHLIP) conjugated with fluorescent Alexa532 (Alexa532-pHLIP) enables reliable discrimination of breast cancer from benign tumors.
Further details can be found in the article by Androniki Mitrou, Xin Feng, Ashraf Khan, Anna N. Yaroslavsky (e202100007).
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTERS
Optical coherence hyperspectral microscopy with a single supercontinuum light source
- First Published: 18 May 2021
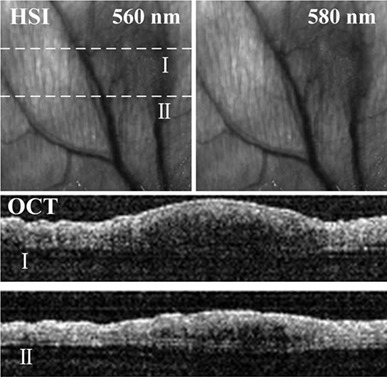
An optical coherence hyperspectral microscopy with a single supercontinuum light source is presented. The microscopy consists of optical coherence tomography (OCT) and hyperspectral imaging (HSI), which can visualize the structural and functional characteristics of biological tissues. The system performance is verified by normal mice ears, and the practical applications of the microscopy are further performed in 4T1 and inflammation Balb/c mice ears in vivo. The experimental results demonstrate that the microscopy has potential to provide complementary information for clinical applications.
Multimodal data acquisition at SARS-CoV-2 drive through screening centers: Setup description and experiences in Saarland, Germany
- First Published: 13 May 2021
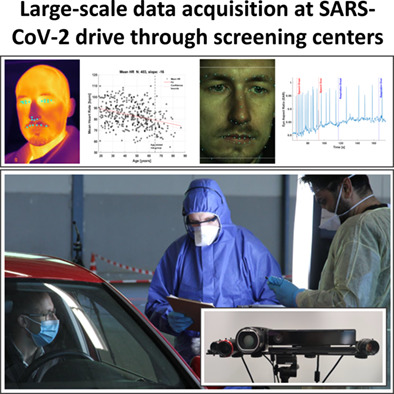
To combat the global health emergency caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and potential future events, the acquisition of datasets for the development of screening methods based on computational analysis of video and audio data is essential. Large-scale data acquisition datasets with high quality at SARS-CoV-2 drive through testing station is possible without disturbing the flow of operation.
High-security photoacoustic identity recognition by capturing hierarchical vascular structure of finger
- First Published: 18 May 2021
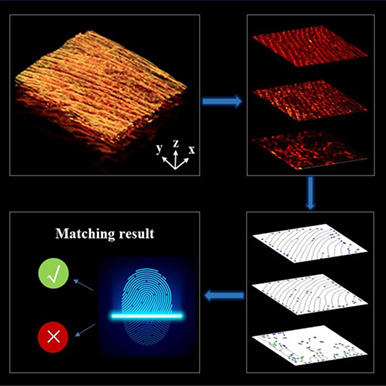
In this study, a novel triple-layers biometric recognition method, based on photoacoustic microscopy, is proposed to improve the security of biometric identity recognition. Using the photoacoustic (PA) dermoscope, three-dimensional absorption-structure information of the fingers was obtained. Then, by combining U-Net, Gabor filtering, wavelet analysis and morphological transform, a lightweight algorithm called photoacoustic depth feature recognition algorithm (PADFR) was developed to automatically realize stratification (the fingerprint, blood vessel fingerprint and venous vascular), extracting feature points and identity recognition.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Feasibility of dual-contrast fluorescence imaging of pathological breast tissues
- First Published: 19 May 2021
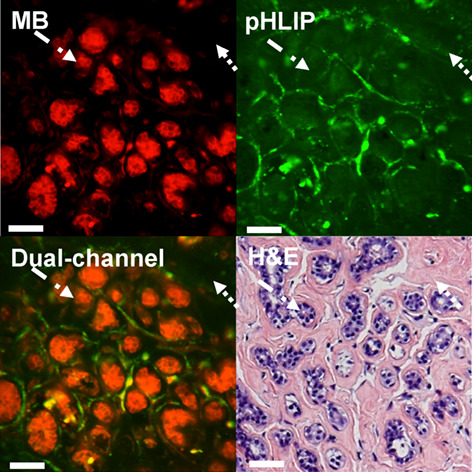
The combination of intravital dye, methylene blue (MB), with molecular marker, pH low insertion peptide (pHLIP), conjugated with Alexa532 (Alexa532-pHLIP), was evaluated for enhancing contrast of pathological breast tissue. Alexa532-pHLIP and MB accumulated in the cytoplasm and nuclei of cancer cells, respectively. Alexa532-pHLIP showed high affinity to cancer, while MB highlighted tissue morphology. MB and Alexa532-pHLIP provide complementary information and show promise for the detection of breast cancer. In the images of benign fibroadenoma, methylene blue (MB) emphasizes nuclei of tumor cells and Alexa532-pHLIP (pHLIP) presents nonspecific staining of fibrous stroma. Merged dual-channel image showing distribution of both stains is presented side-by-side with respective H&E histopathology. Dotted arrow: Fibrous component; dash-dotted arrow: Glandular/epithelial component. Bar: 50 μm.
Diurnal variation of corneal elasticity in healthy young human using air-puff optical coherence elastography
- First Published: 02 January 2021
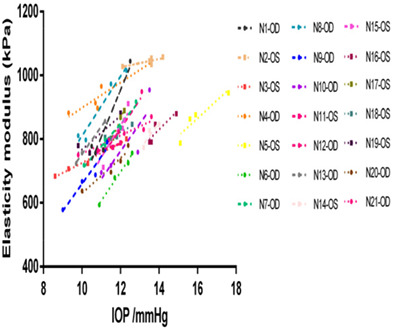
Using air-puff optical coherence elastography, diurnal variation in normal young human corneal elasticity is investigated. Based on the multi-level model, corneal elasticity has a linear positive relation with intraocular pressure (IOP), but not central corneal thickness and time point. A new indicator, corneal elasticity change rate, is proposed to present the magnitude of corneal elasticity change caused by 1 mmHg IOP, which can increase the comparability of results between individuals.
Joint time-frequency analysis of visible laser reflections in a sheep heart
- First Published: 02 May 2021
Correct placement of cardiovascular devices in the heart is clinically important. The feasibility of placing an optical fiber near and in a beating heart in a live sheep in order to illuminate the tissues thereof with structured light patterns and temporospatially analyzing the reflections in the frequency domain in order to gain information about the illuminated tissues is described. Clinical context, laboratory apparatus, methods and results are presented and discussed.
Transcriptomic analysis of mechanism of melanoma cell death induced by photothermal therapy
- First Published: 17 March 2021
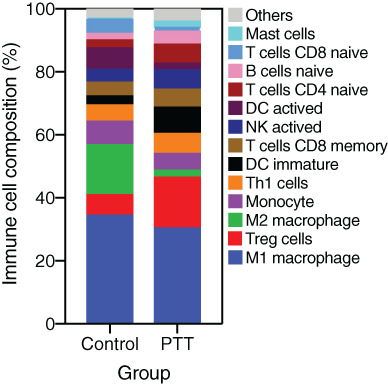
- Photothermal therapy (PTT) exhibited a good outcome on melanoma.
- Genes expressions and Immune cell compositions were quantified after PTT treatment.
- Most of differentially expressed genes involved in immune response and inflammatory response.
- M2 macrophage composition was decreased after PTT treatment.
A spatial resolution evaluation method of endoscopic optical coherence tomography system using the annular phantom
- First Published: 14 May 2021
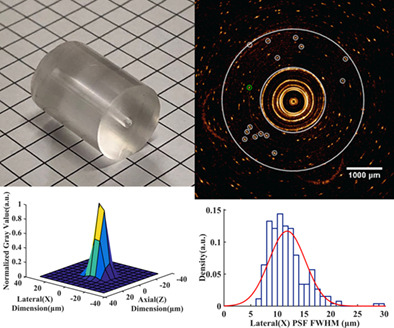
Huang et al. propose a spatial resolution estimate method of the endoscope OCT system. The annular phantom can provide dynamic scanning imaging evaluation closer to the endoscopic OCT system actual working status. The imaging results of the annular phantom are analyzed using PSF to determine the spatial resolution of the endoscope OCT system.
Thermo-optic measurements and their inter-dependencies for delineating cancerous breast biopsy tissue from adjacent normal
- First Published: 27 May 2021
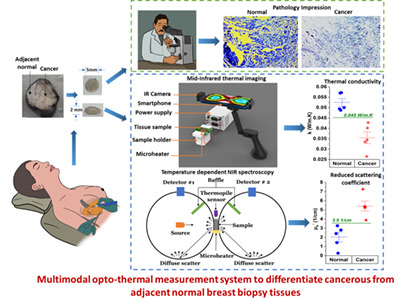
We propose a novel multimodal thermo-optic measurement tool that is non-ionizing, portable, and affordable and used to delineate the cancerous tissue from the adjacent normal breast biopsy tissue. The tool can perform preliminary analysis and give immediate feedback to the clinician in the operating room to support and aid the histopathology results. The tool quantifies the bulk thermal properties (thermal conductivity and specific heat) and optical properties (reduced scattering and absorption coefficient) of the tissue.
Pebrine diagnosis using quantitative phase imaging and machine learning
- First Published: 07 May 2021
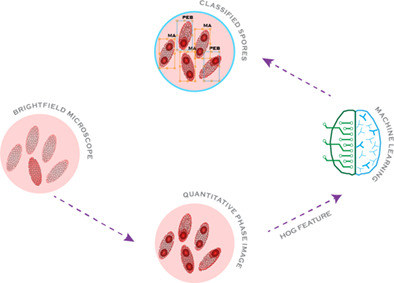
Pebrine is the most dreaded infectious disease in the sericulture field. If found in any silkworm, the whole crop is burned and the farm is disinfected to avoid further contamination. Conventional approaches are not reliable for the detection of pebrine. Therefore, this paper proposes a novel multi-model approach based on quantitative phase imaging (QPI) and machine learning. The QPI technique exhibits the intrinsic contrast of the internal structures embedded in the phase images of test specimens, used by machine learning algorithm to accurately identify pebrine spores.
Effects of mobile phone emissions on human red blood cells
- First Published: 19 April 2021
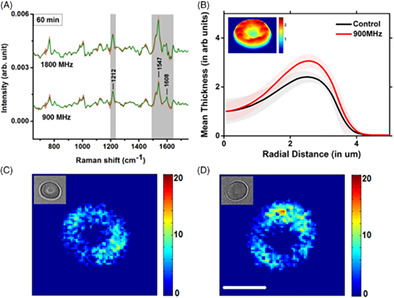
The use of mobile phones is now widespread but possible health hazards from the associated microwave emission are merely understood. The results of our studies, using single cell Raman spectroscopy on the effects of 900 and 1800 MHz mobile signals on human red blood cells, show a reduction in oxygen affinity of the cells upon exposure. Assuming the mobile signals may influence the membrane transport of calcium ions and subsequently the metabolic processes, further studies using fluorescent probes and quantitative phase microscopy were performed and the results support the suggested mechanism.
Fast denoising and lossless spectrum extraction in stimulated Raman scattering microscopy
- First Published: 16 May 2021
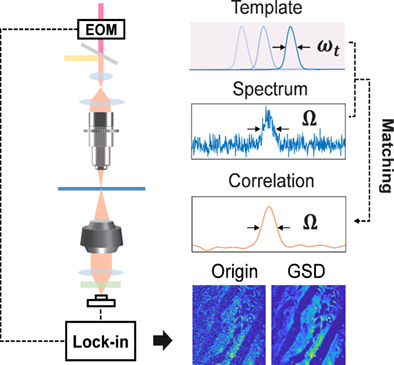
The imaging speed and sensitivity are limited by the noise of light beam probing the Raman process in stimulated Raman scattering (SRS) spectroscopy and microscopy. In this paper, a fast non-average denoising and loss-less Raman spectral extraction method based on self-reinforcing signal-to-noise ratio enhancement algorithm is proposed. This method reduces the cost and complexity of SRS system and allows for high spectral and image quality improvement.
Ex-vivo fluorescence confocal microscopy with digital staining for characterizing basal cell carcinoma on frozen sections: A comparison with histology
- First Published: 14 May 2021
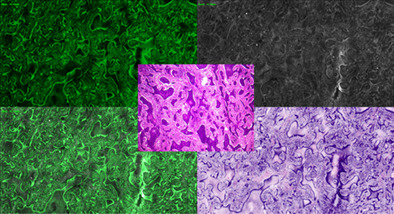
The introduction of digital staining in ex-vivo confocal microscopy allows a more intuitive comparison with hematoxylin and eosin stained conventional histology. This pilot study on basal cell carcinoma and frozen sections highlights the diagnostic potential of this new technique to support bedside surgery.
Cross-domain retinopathy classification with optical coherence tomography images via a novel deep domain adaptation method
- First Published: 02 May 2021
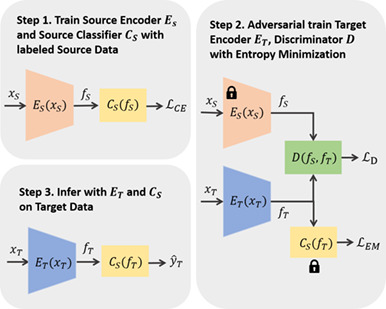
We propose a novel deep domain adaptation method to train a model on a labeled dataset and adapt it to an unlabelled dataset (collected under different conditions). The experiment results indicate this method can significantly outperform existing methods for retinopathy classification on OCT images with the classification accuracies of 0.915, 0.959 and 0.990 under three cross-domain scenarios, demonstrating that the proposed method can learn discriminative features for retinopathy classification.