Feasibility of dual-contrast fluorescence imaging of pathological breast tissues
Androniki Mitrou
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorXin Feng
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorAshraf Khan
Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School-Baystate, Springfield, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Anna N. Yaroslavsky
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Correspondence
Anna N. Yaroslavsky, Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, MA, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAndroniki Mitrou
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorXin Feng
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorAshraf Khan
Department of Pathology, University of Massachusetts Medical School-Baystate, Springfield, Massachusetts, USA
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Anna N. Yaroslavsky
Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, Massachusetts, USA
Correspondence
Anna N. Yaroslavsky, Advanced Biophotonics Laboratory, University of Massachusetts Lowell, Lowell, MA, USA.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorAndroniki Mitrou and Xin Feng contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
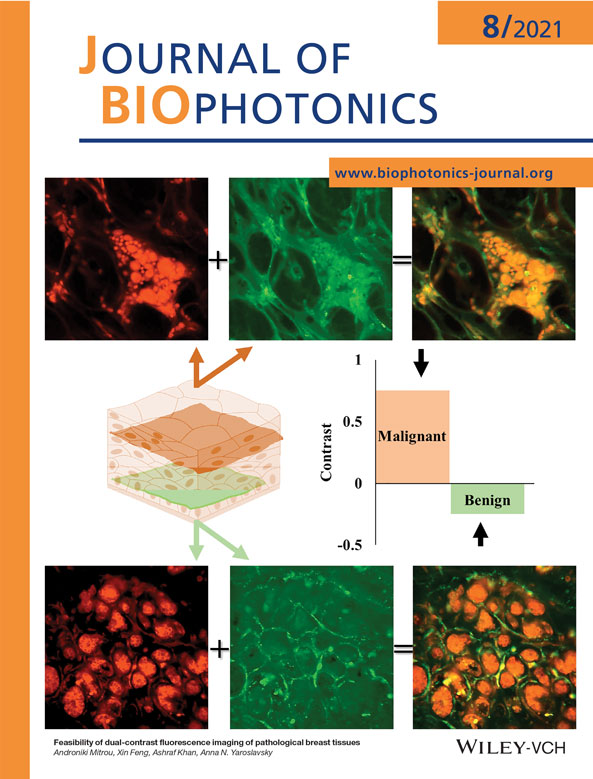
The combination of intravital dye, methylene blue (MB), with molecular cancer marker, pH low insertion peptide (pHLIP) conjugated with fluorescent Alexa532 (Alexa532-pHLIP), was evaluated for enhancing contrast of pathological breast tissue ex vivo. Fresh, thick breast specimens were stained sequentially with Alexa532-pHLIP and aqueous MB and imaged using dual-channel fluorescence microscopy. MB and Alexa532-pHLIP accumulated in the nuclei and cytoplasm of cancer cells, respectively. MB also stained nuclei of normal cells. Some Alexa532-pHLIP fluorescence emission was detected from connective tissue and benign cell membranes. Overall, Alexa532-pHLIP showed high affinity to cancer, while MB highlighted tissue morphology. The results indicate that MB and Alexa532-pHLIP provide complementary information and show promise for the detection of breast cancer.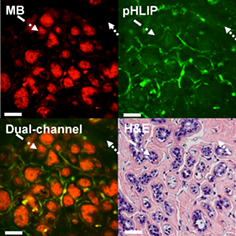
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available upon request.
REFERENCES
- 1 American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts & Figures 2020 (American Cancer Society, Inc, 2020).
- 2M. Sant, C. Allemani, R. Capocaccia, T. Hakulinen, T. Aareleid, J. W. Coebergh, M. P. Coleman, P. Grosclaude, C. Martinez, J. Bell, J. Youngson, F. Berrino, EUROCARE Working Group, [published correction appears in Int. J. Cancer 107(6), 1058 (2003)]Int. J. Cancer 2003, 106(3), 416.
- 3L. Wang, Sensors 2017, 17(7), 1572.
- 4J. G. Elmore, G. M. Longton, P. A. Carney, B. M. Geller, T. Onega, A. N. Tosteson, H. D. Nelson, M. S. Pepe, K. H. Allison, S. J. Schnitt, F. P. O'Malley, D. L. Weaver, JAMA 2015, 313(11), 1122.
- 5I. Georgakoudi, K. P. Quinn, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 14, 351.
- 6Q. R. Tummers, F. P. Verbeek, B. E. Schaafsma, M. C. Boonstra, J. R. van der Vorst, G.-J. Liefers, C. J. H. van de Velde, J. V. Frangioni, A. L. Vahrmeijer, Eur. J. Surg. Oncol 2014, 40(7), 850.
- 7S. Goodman, A. O'Connor, D. Kandil, A. Khan, Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2014, 138(1), 57.
- 8 Future cancer research priorities in the USA, Lancet Oncol 2017, 18(11), e653.
- 9G. J. Kelloft, K. A. Krohn, S. M. Larson, R. Weissleder, D. A. Mankoff, J. M. Hoffman, J. M. Link, K. Z. Guyton, W. C. Eckelman, H. I. Scher, J. O'Shaughnessy, B. D. Cheson, C. C. Sigman, J. L. Tatum, G. Q. Mills, D. C. Sullivan, J. Woodcock, Clin. Cancer. Res 2005, 11(22), 7967.
- 10D. A. Mankoff, Breast Cancer Res. 2008, 10(Suppl 1), S3.
- 11R. C. Adochite, A. Moshnikova, S. D. Carlin, R. A. Guerrieri, O. A. Andreev, J. S. Lewis, Y. K. Reshetnyak, Mol. Pharm. 2014, 11(8), 2896.
- 12Q. Meng, Z. Li, Int. J. Biomed. Imaging 2013, 2013, 230487.
- 13S. M. van de Ven, S. G. Elias, C. T. Chan, Z. Miao, Z. Cheng, A. De, S. S. Gambhir, Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18(4), 1073.
- 14X. Hun, Z. Zhang, Spectrochim. Acta A 2009, 74(2), 410.
- 15G. Balasundaram, C. Krafft, R. Zhang, K. Dev, R. Bi, M. Moothanchery, J. Popp, M. Olivo, J. Biophotonics 2021, 14(1), e202000280.
- 16B. W. Maloney, D. M. McClatchy, B. W. Pogue, K. D. Paulsen, W. A. Wells, R. J. Barth, J. Biomed. Opt 2018, 23(10), 1.
- 17M. A. Pinkert, L. R. Salkowski, P. J. Keely, T. J. Hall, W. F. Block, K. W. Eliceiri, J. Med. Imaging 2018, 5(1), 010901.
- 18R. Alfano and Y. Pu, Optical Biopsy for Cancer Detection in Lasers for Medical Applications, Ed: H. Jelinkova. Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK. 2013.
- 19M. R. Austwick, B. Clark, C. A. Mosse, K. Johnson, D. W. Chicken, S. K. Somasundaram, K. W. Calabro, Y. Zhu, M. Falzon, G. Kocjan, T. Fearn, S. G. Bown, I. J. Bigio, M. R. Keshtgar, J. Biomed. Opt 2010, 15(4), 047001.
- 20B. J. Tromberg, B. W. Pogue, K. D. Paulsen, A. G. Yodh, D. A. Boas, A. E. Cerussi, Med. Phys 2008, 35(6–1), 2443.
- 21J. Q. Brown, T. M. Bydlon, S. A. Kennedy, M. L. Caldwell, J. E. Gallagher, M. Junker, L. G. Wilke, W. T. Barry, J. Geradts, N. Ramanujam, PloS one 2013, 8(7), e69906.
- 22J. Wang, Y. Xu, K. J. Mesa, F. A. South, E. J. Chaney, D. R. Spillman, R. Barkalifa, M. Marjanovic, P. S. Carney, A. M. Higham, Z. G. Liu, S. A. Boppart, Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9(12), 6519.
- 23M. D. Keller, E. Vargis, N. de Matos Granja, R. H. Wilson, M. A. Mycek, M. C. Kelley, A. Mahadevan-Jansen, J. Biomed. Opt 2011, 16(7), 077006.
- 24J. Unger, C. Hebisch, J. E. Phipps, J. L. Lagarto, H. Kim, M. A. Darrow, R. J. Bold, L. Marcu, Biomed. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 1216.
- 25S. Abeytunge, B. Larson, G. Peterson, M. Morrow, M. Rajadhyaksha, M. P. Murray, J. Biomed. Opt 2017, 22(3), 34002.
- 26S. Mittal, K. Yeh, L. S. Leslie, S. Kenkel, A. Kajdascy-Balla, R. Bhargava, PNAS 2018, 115(25), E5651.
- 27D. S. Gareau, J. Biomed. Opt 2009, 14(3), 034050.
- 28M. Snuderl, D. Wirth, S. Sheth, S. Bourne, C. Kwon, W. T. Curry, M. P. Frosch, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Brain Pathol. 2013, 23(1), 73.
- 29S. Krishnamurthy, J. Q. Brown, N. Iftimia, R. M. Levenson, M. Rajadhyaksha, Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143(9), 1058.
- 30A. Parrish, E. Halama, M. T. Tilli, M. T. Freedman, P. A. Furth, J. Biomed. Opt 2005, 10(5), 051602.
- 31M. T. Tilli, M. C. Cabrera, A. Parrish, K. M. Torre, M. K. Sidawy, A. L. Gallagher, E. Makariou, S. A. Polin, M. C. Liu, P. A. Furth, J. Biomed. Opt 2007, 12(5), 051901.
- 32L. M. Schiffhauer, J. N. Boger, T. A. Bonfiglio, J. M. Zavislan, M. Zuley, C. A. Fox, BMC Cancer 2009, 9(265).
- 33R. Patel, A. Khan, D. Wirth, M. Kamionek, D. Kandil, R. Quinlan, A. N. Yaroslavsky, J. Biomed. Opt 2012, 17(6), 066008.
- 34M. Ragazzi, S. Piana, C. Longo, F. Castagnetti, M. Foroni, G. Ferrari, G. Gardini, G. Pellacani, Mod. Pathol. 2014, 27(3), 460.
- 35J. L. Dobbs, H. Ding, A. P. Benveniste, H. M. Kuerer, S. Krishnamurthy, W. Yang, R. Richards-Kortum, J. Biomed. Opt 2013, 18(10), 106016.
- 36J. L. Mueller, J. E. Gallagher, R. Chitalia, M. Krieger, A. Erkanli, R. M. Willett, J. Geradts, N. Ramanujam, J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142(7), 1475.
- 37S. Krishnamurthy, A. Cortes, M. Lopez, M. Wallace, S. Sabir, K. Shaw, G. Mills, Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2018, 142(3), 396.
- 38A. N. Yaroslavsky, X. Feng, A. Muzikansky, M. R. Hamblin, Sci. Rep 2019, 9(1), 940.
- 39S. Malik, P. Jermain, X. Feng, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Opt. Eng 2019, 58(8), 082415.
- 40X. Feng, A. Muzikansky, A. Ross, M. Hamblin, P. Jermain, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Biomed. Opt. Express 2019, 10(8), 4237.
- 41E. Salomatina, A. Muzikansky, V. Neel, A. N. Yaroslavsky, J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105(10), 102010.
- 42Z. Tannous, M. Al-Arashi, S. Shah, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Lasers Surg. Med. 2009, 41(1), 10.
- 43M. Al-Arashi, E. Salomatina, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Lasers Surg. Med. 2007, 39, 696.
- 44A. N. Yaroslavsky, J. Barbosa, V. Neel, C. DiMarzio, R. R. Anderson, J. Biomed. Opt 2005, 10(1), 014011.
- 45R. Patel, A. Khan, R. Quinlan, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Cancer Res. 2014, 74(17), 4685.
- 46O. A. Andreev, D. M. Engelman, Y. K. Reshetnyak, Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 97.
- 47D. Weerakkody, A. Moshnikova, M. S. Thakur, V. Moshnikova, J. Daniels, D. M. Engelman, O. A. Andreev, Y. K. Reshetnyak, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2013, 110(15), 5834.
- 48J. Makki, Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2015, 8, 23.
- 49L. Salvatorelli, L. Puzzo, G. M. Vecchio, R. Caltabiano, V. Virzì, G. Magro, Cancers 2020, 12(3), 609.
- 50M. van Seijen, E. H. Lips, A. M. Thompson, S. Nik-Zainal, A. Futreal, E. Shelley Hwang, E. Verschuur, J. Lane, J. Jonkers, D. W. Rea, J. Wesseling, the PRECISION team, Br. J. Cancer 2019, 121, 285.
- 51L. C. Hartmann, T. A. Sellers, M. H. Frost, W. L. Lingle, A. C. Degnim, K. Ghosh, R. A. Vierkant, S. D. Maloney, V. S. Pankratz, D. W. Hillman, V. J. Suman, J. Johnson, C. Blake, T. Tlsty, C. M. Vachon, L. J. Melton, D. W. Visscher, N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 229.
- 52T. T. Tapmeier, A. Moshnikova, J. Beech, D. Allen, P. Kinchesh, S. Smart, A. Harris, A. McIntyre, D. M. Engelman, O. A. Andreev, Y. K. Reshetnyak, R. J. Muschel, PNAS 2015, 112(31), 9710.
- 53J. Golijanin, A. Amin, A. Moshnikova, J. M. Brito, T. Y. Tran, R. Adochite, G. O. Andreev, T. Crawford, D. M. Engelman, O. A. Andreev, Y. K. Reshetnyak, D. Golijanin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113(42), 11829.
- 54P. Bacchetti, S. G. Deeks, J. M. McCune, Sci. Transl. Med 2011, 3(87), 87ps24.
- 55J. C. F. de Winter, Pract. Assess. Res. Evaluation 2013, 18(10).
- 56C. J. Morgan, Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L873.
- 57J. Brito, B. Golijanin, A. Moshnikova, C. Mueller-Leonhard, B. Gershman, O. A. Andreev, Y. K. Reshetnyak, A. Amin, D. Golijanin, Urology 2020, 139, 134.
- 58J. Q. Brown, T. M. Bydlon, L. M. Richards, B. Yu, S. A. Kennedy, J. Geradts, L. G. Wilke, M. K. Junker, J. Gallagher, W. T. Barry, N. Ramanujam, IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron 2010, 16(3), 530.