Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Front Cover
Spin Hall Effect: Spin Hall Effect under Arbitrarily Polarized or Unpolarized Light (Laser Photonics Rev. 15(7)/2021)
- First Published: 07 July 2021

In article number 2100138, Minkyung Kim, Dasol Lee, and Junsuk Rho propose an approach towards the spin Hall effect of light that is independent of the incident polarization state. A symmetrical splitting of an incident light into two circularly polarized light is demonstrated under arbitrarily polarized light and unpolarized light when the two linear polarization states have the same reflection coefficient. The polarization-independent spin Hall effect of light will widen the applicability of the spin-dependent optical devices to cover randomly polarized or unpolarized sources.
Inside Front Cover
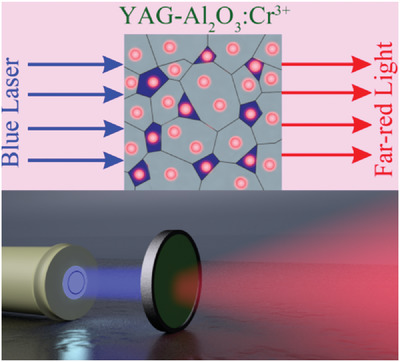
Far-Red-Emitting Ceramics: Near-Unity and Zero-Thermal-Quenching Far-Red-Emitting Composite Ceramics via Pressureless Glass Crystallization (Laser Photonics Rev. 15(7)/2021)
- First Published: 07 July 2021

In article number 2100060, Wenge Xiao, Guojun Zheng, Jianrong Qiu, and co-workers prepared far-red-emitting composite ceramics with near-unity internal quantum efficiency and zero-thermal quenching via pressureless glass crystallization, where the inside light scattering is finely tuned by controlling grain growth and the undesired concentration quenching is alleviated to achieve strong light absorption. Furthermore, a high-power laser-driven far-red lighting source with high luminescence saturation is demonstrated.
Inside Back Cover
Enhancing Photoluminescence: Photonic Bound States in the Continuum in Si Structures with the Self-Assembled Ge Nanoislands (Laser Photonics Rev. 15(7)/2021)
- First Published: 07 July 2021

The cover image illustrates the photonic crystal slab's eigenmode as demonstrated in article number 2000242 by Sergey Dyakov and co-workers. The cones represent the rotation of the electric vector during one period of electromagnetic oscillations. From this figure, one can determine the symmetry type of this mode and predict the features of the far-field emissivity of quantum emitters at the corresponding frequency.
Back Cover
Phase Recovery and Stability: Arbitrary Phase Access for Stable Fiber Interferometers (Laser Photonics Rev. 15(7)/2021)
- First Published: 07 July 2021

Practical systems for optical interference are critical to coherent signal processing in devices and networks. In article number 2000524, Roberto Morandotti, Michael Kues, and co-workers demonstrate an easily-deployable scheme for the retrieval of relative phase in fiber interferometric systems. The use of bright and dim/photon-level reference signals is contrasted, with pulsed references shown to enable temporal multiplexing with quantum signals.
Masthead
Reviews
Optical Vernier Effect: Recent Advances and Developments
- First Published: 28 May 2021

Recent developments in the application of the optical analog of the Vernier effect to fiber interferometers allow new levels of improved sensitivities and resolutions to be reached. This review provides a comprehensive analysis on the fundamentals of the effect from a sensing perspective. In addition, the distinct configurations and different variants are discussed, together with future challenges in the field.
Optical Fiber Optofluidic Bio-Chemical Sensors: A Review
- First Published: 09 June 2021
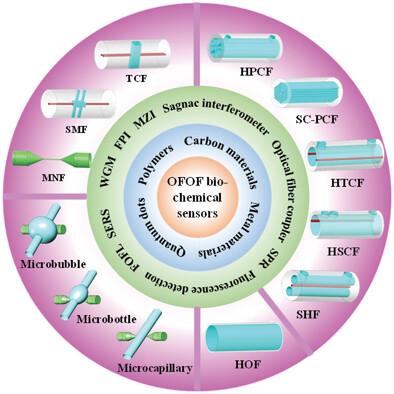
This review summarizes the rich and diverse types of optical fibers and some advanced functional materials that can be used to construct optical fiber optofluidic (OFOF) bio-chemical sensors. Furthermore, research progress and current status of OFOF bio-chemical sensors based on various sensing mechanisms are tracked. Finally, the existing challenges and future development trends of OFOF biochemical sensors are discussed.
Original Papers
On-Demand Coherent Perfect Absorption in Complex Scattering Systems: Time Delay Divergence and Enhanced Sensitivity to Perturbations
- First Published: 18 May 2021
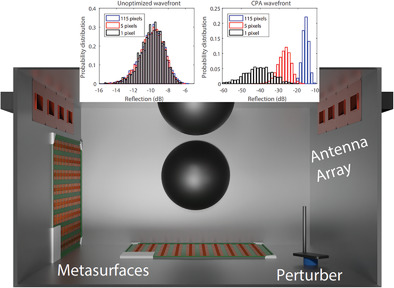
A theoretical link between the coherent perfect absorption (CPA) scattering anomaly in chaotic cavities, the associated time delay divergence, and the resulting optimal sensitivity to minute arbitrary system perturbations is established. The results are confirmed in microwave experiments implementing eight-channel CPA in a chaotic cavity “on demand” at an arbitrary frequency by tuning the cavity's scattering properties with programmable metasurfaces.
Optical Implementation of 2 × 2 Universal Unitary Matrix Transformations
- First Published: 28 May 2021
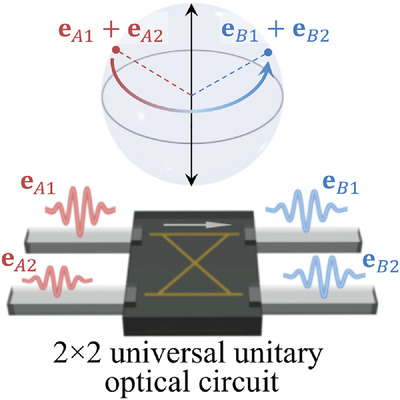
A 2 × 2 universal unitary optical circuit is a system that is able to linearly transform two (classical or quantum) optical wave packets and into any pair of optical wave packets and having the same global energy as that of the input. The transformation may be interpreted as a rotation on the surface of the Bloch sphere.
Waveguide-Coupled Colloidal Quantum Dot Light Emitting Diodes and Detectors on a Silicon Nitride Platform
- First Published: 26 May 2021
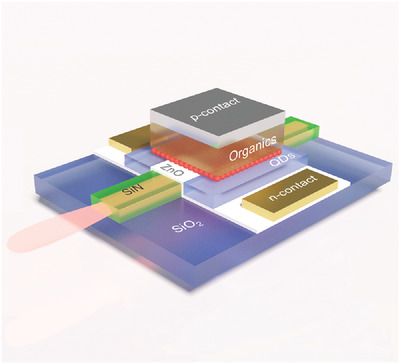
Integrated light-emitting diodes based on CdSe/CdS quantum dots, with emission directly coupled to a silicon nitride waveguide are demonstrated. The devices feature a current density up to 100 A cm−2 and a maximum on-chip power density of almost 1.5 W cm−2 in a single-mode waveguide. Operated as detectors, they have a low dark current of 1.5 µA cm−2.
Photonic Bound States in the Continuum in Si Structures with the Self-Assembled Ge Nanoislands
- First Published: 03 June 2021
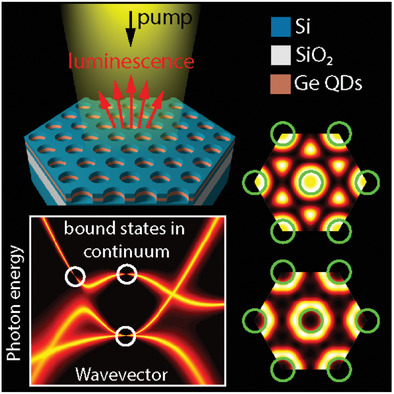
The photoluminescence of germanium nanoislands in a silicon photonic crystal slab with a hexagonal lattice can be dramatically enhanced due to the bounds states in continuum. The corresponding quality factor of the peaks in the emission spectra is 2200 and the photoluminescence enhancement factor is more than 100. The symmetry of the eigenmodes is described in terms of group theory.
Breather Molecular Complexes in a Passively Mode-Locked Fiber Laser
- First Published: 09 June 2021
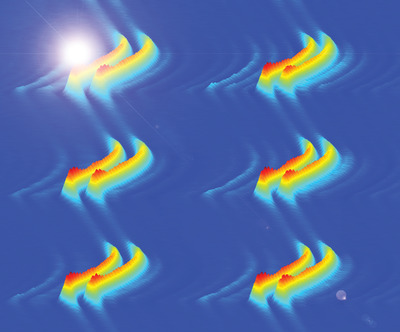
Soliton molecules show striking dynamics that fuel the analogy with matter molecules, such as vibration and resonant excitation. Contrary to the significant progress made in the study of stationary soliton molecules, the existence of breathing soliton molecules is less explored. Here, different types of breather molecular complexes are demonstrated by tailoring the dispersive wave mediated long-range interaction of breathers.
Research Articles
Arbitrary Phase Access for Stable Fiber Interferometers
- First Published: 04 May 2021
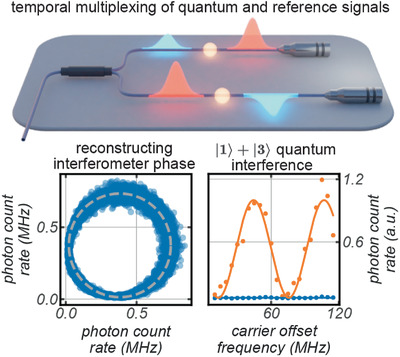
An easily deployable scheme for the retrieval and stabilization of relative phase in fiber interferometric systems is demonstrated, exhibiting long-term and phase-independent stability. The use of bright and dim/photon-level reference signals is contrasted; pulsed references are shown to enable temporal multiplexing with quantum signals. The radiofrequency-controlled interference of high-dimensional entangled states is demonstrated, supporting the scheme's readiness for advanced use cases.
Near-Unity and Zero-Thermal-Quenching Far-Red-Emitting Composite Ceramics via Pressureless Glass Crystallization
- First Published: 04 June 2021
Observation of “Frozen-Phase” Propagation of THz Pulses in a Dispersive Optical System
- First Published: 24 May 2021
Spatiotemporal propagation of light pulses in dispersive systems always suffer a severe phase variation. Here, the authors demonstrate a “frozen-phase” propagation of THz pulses in subwavelength waveguide through a complete cancellation of first-order dispersion. This is the first time “soliton-like” propagation pulses are shown by a linear technique work on phase.
Near-Zero Index Photonic Crystals with Directive Bound States in the Continuum
- First Published: 24 May 2021
The experimental observation of a novel dielectric photonic crystal structure is presented that has near-zero refractive index of 0.02 and exhibits directive bound states in the continuum (BIC) for in-plane polarization. A thin Si photonic crystal slab is fabricated and characterized with an experimentally confirmed Q-factor over 103 around the near-zero index wavelength.
Wavepacket Self-Rotation and Helical Zitterbewegung in Symmetry-Broken Honeycomb Lattices
- First Published: 26 May 2021
Zitterbewegung refers to a prediction that relativistic Dirac electrons can exhibit rapid oscillatory motion in vacuum. Zitterbewegung of light beams is experimentally and theoretically demonstrated in symmetry-broken honeycomb photonic lattices and is related to wavepacket self-rotation, which is manifested in spiraling helical intensity patterns. The pattern helicity is valley dependent, arising from the Berry curvature and topology of the system.
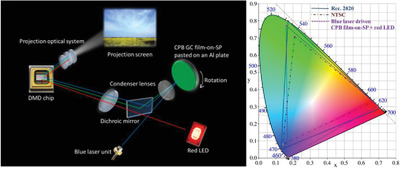
Stable CsPbBr3-Glass Nanocomposite for Low-Étendue Wide-Color-Gamut Laser-Driven Projection Display
- First Published: 26 May 2021
Resonant Nonlinear Synthetic Metasurface with Combined Phase and Amplitude Modulations
- First Published: 02 June 2021
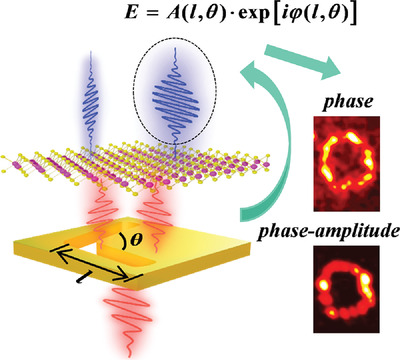
The resonant nonlinear synthetic metasurface consisting of V-shaped plasmonic nanohole and WS2 monolayer is proposed and used to demonstrate high-efficient second-harmonic (SH) metalens and quality-improved SH holographic imaging. This proposed resonant nonlinear synthetic metasurface enables multilevel amplitude and phase combined modulations of the SH beam, which is of great potential in holographic displays, optical information security, and multifunctional nonlinear photonic devices.
Multiple Kerker Anapoles in Dielectric Microspheres
- First Published: 02 June 2021
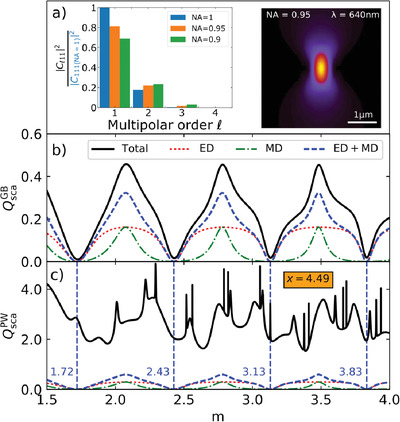
This work shows that Kerker conditions and non-radiating anapoles can be induced in nano-and-microsized dielectric spheres by illuminating with a pure dipolar field (PDF). As a matter of interest, it is also demonstrated that experimentally accessible tightly-focused Gaussian beams mimic the abovementioned light-scattering properties under PDF illumination. This phenomenon strongly motivates future experimental verification.
Spin Hall Effect under Arbitrarily Polarized or Unpolarized Light
- First Published: 04 June 2021
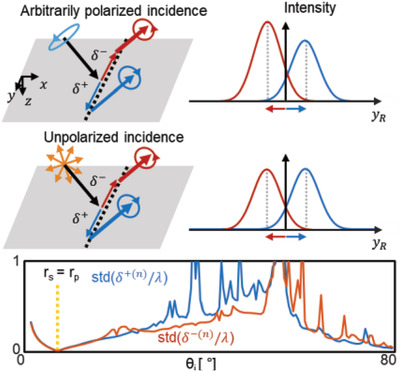
Whereas the spin Hall effect of light depends on the polarization state of incidence, the polarization dependency is eliminated by equalizing reflection coefficients for two linear polarizations. A symmetrical splitting in both shift and intensity under superposition of random polarizations demonstrates that the spin Hall effect under unpolarized light can possess the whole symmetries of that under linearly polarized light.
Unraveling the Role of Crystallization Dynamics on Luminescence Characteristics of Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes
- First Published: 07 June 2021
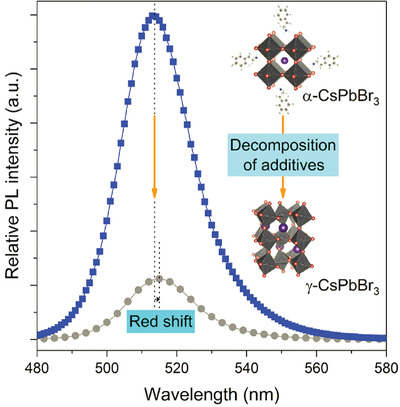
The critical role of crystallization dynamics on luminescence properties of CsPbBr3 perovskite films has been clarified, and the ethanolamine interface engineering strategy induces the fast crystallization with pure cubic phase (α-CsPbBr3), revealing a substantial boost in luminance and efficiency of light-emitting diodes. Performance degradation occurs due to phase transition from α-CsPbBr3 to orthogonal γ-CsPbBr3 along with the appearance of PbBr2.