Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Understanding Microscopic Properties of Light-Emitting Diodes from Macroscopic Characterization: Ideality Factor, S-parameter, and Internal Quantum Efficiency
- First Published: 10 May 2022
Light-Emitting Diodes and Defects
Defects affect the performance of an optoelectronic device in fundamental ways. Dong-Soo Shin and Jong-In Shim (article number 2200042) demonstrate how the macroscopic characterization can be utilized to obtain information on microscopic defects in the active region of the light-emitting diode. They successfully show that macroscopic parameters such as the ideality factor and the S-parameter are correlated with the internal quantum efficiency (IQE) and the high-resolution emission-microscope images that reflect the defects in the device.
Masthead
Review
Recent Progress on the Performance of Lead-Based Halide Perovskite APbX3 Detectors
- First Published: 01 March 2022
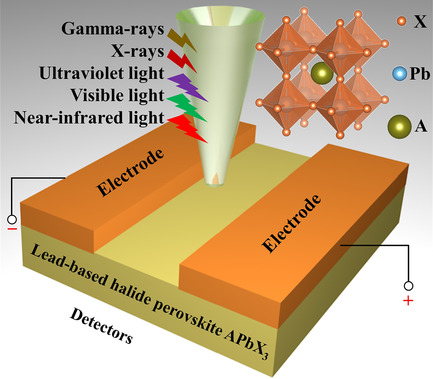
This review summarizes the photodetectors’ performance parameters and the X/γ-ray detectors’ recent progress of the lead-based halide perovskite APbX3 system. The research results of near-infrared-ultraviolet light devices are analyzed, the mechanism of the good photoelectric properties of FAPbX3 photodetectors is discussed, as well as several important outlooks for future research are proposed.
Research Articles
60 years of pss
Understanding Microscopic Properties of Light-Emitting Diodes from Macroscopic Characterization: Ideality Factor, S-parameter, and Internal Quantum Efficiency
- First Published: 04 February 2022
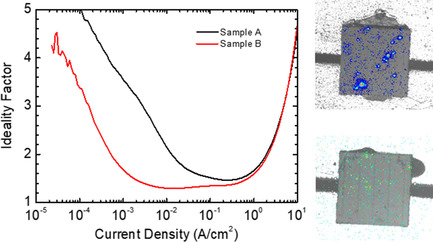
Macroscopic characterizations are utilized to extract information on the defect level and crystallinity of the epitaxial layers in the light-emitting diodes (LEDs). It is demonstrated from examples that the decreases in ideality factor and S-parameter at low currents contain useful information on the defect level of the active region in the device.
Characterization of Lattice Defects in Refractory Metal High-Entropy Alloy HfNbTaTiZr by Means of Positron Annihilation Spectroscopy
- First Published: 01 March 2022
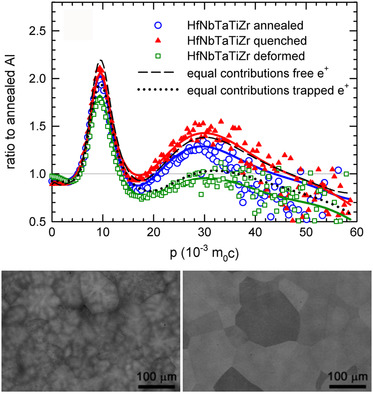
Positron lifetime measurement combined with coincidence Doppler broadening spectroscopy is used for investigation of lattice defects in refractory metal high-entropy alloy HfNbTaTiZr. Herein, it is revealed that vacancies in the alloy are not distributed randomly but are associated with Hf atoms. A comparison of experimental data with theoretical estimations indicates considerable ion relaxation around vacancies.
Preparation of NaV6O15 Nanosheet Cathodes with High Cycling Performance and Good Capacity Retention Rate in Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 26 February 2022
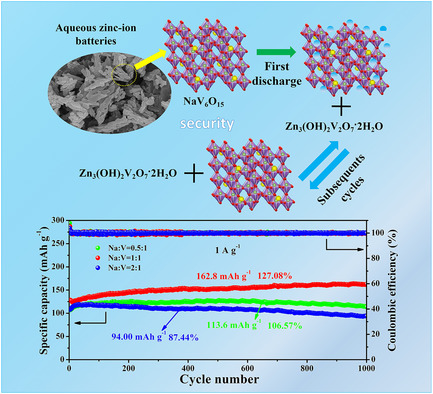
Herein, NaV6O15 nanosheets are synthesized by one-step molten salt method as cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries (AZIBs), which exhibit long cycle stability and high capacity retention. The synthesis method of the molten salt and mechanism analysis of NaV6O15 nanosheets provide a new perspective and reference significance for the practical application of AZIBs.
Understanding the Origin of Thermal Annealing Effects in Low-Temperature Amorphous Silicon Films and Solar Cells
- First Published: 26 February 2022
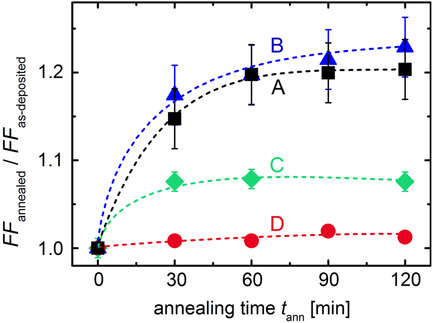
The performance of thin-film solar cells prepared at low deposition temperatures is substantially improved upon postdeposition annealing. The annealing behavior of all functional layers of the device and the solar cells of various configurations is systematically studied by various advanced characterization methods combined with computer simulations.
Influence of Silicon Substrate Surface Finish on the Screen-Printed Silver Metallization of Polysilicon-Based Passivating Contacts
- First Published: 23 March 2022
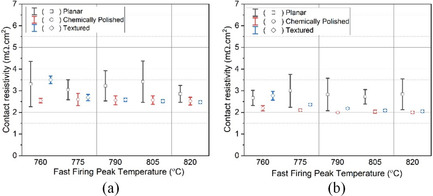
With the ever-increasing use of polysilicon passivated contact for solar cell application, the study of dependence of silicon substrate finish on the passivation and the metallization for these contact structures becomes even more important. Herein, the contact resistivity and metal-polysilicon recombination current density are explained for the samples with different surface finish.
Phase Control of Multivalent Vanadium Oxides VO x by Ion-Beam Sputter-Deposition
- First Published: 17 March 2022
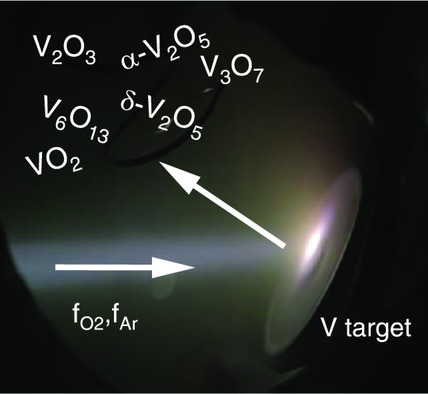
Vanadium oxide is of enormous scientific interest owing to a plethora of different modifications. It is demonstrated that ion-beam sputter-deposition allows us to reproducibly deposit defined thin-films of different phases. A pseudo-phase diagram of the different material phases dependent on the growth parameters is established and, in particular, the growth of polycrystalline V3O7 is verified.
Near Infrared Light-Sensing Organic Light-Dependent Resistors Based on Dialkoxybenzothiadiazole-Containing Conjugated Polymer
- First Published: 05 March 2022
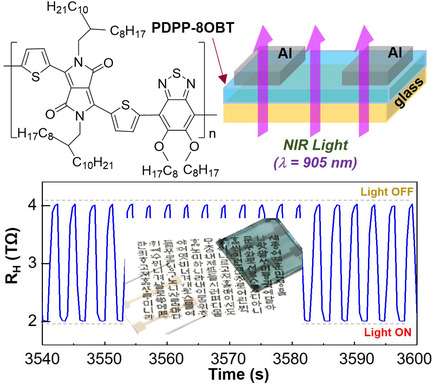
Herein, the poly[{3-(5-(7-methyl-5,6-bis (octyloxy)benzo[c][1,2,5]thiadiazol-4-yl)thiophen-2-yl)-6-(5-methylthiophen-2-yl)}-co-{2,5-bis(2-octyldodecyl)-2,5-dihydropyrrolo[3,4-c]pyrrole-1,4-dione}] (PDPP-8OBT) polymer is synthesized via Stille coupling reaction, and its films are applied as an active layer for near infrared light-sensing organic light-dependent resistors (NIR–OLDRs). The NIR-OLDRs with the thin (for semitransparent devices) and thick PDPP–8OBT films annealed at 150 °C can detect the 905 nm light used for light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems.
Influence of Fe2O3 Content on Acoustic Properties of Backing Materials and Development and Utilization of Acoustic Emission Sensors
- First Published: 26 February 2022
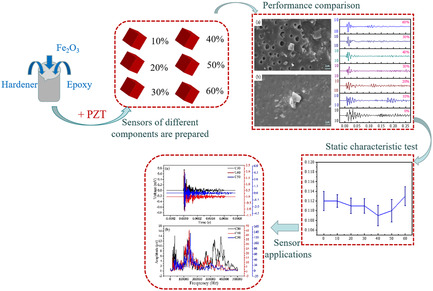
The content of Fe2O3 powder can control the acoustic properties of Fe2O3/ epoxy composites. The sensitivity and working bandwidth of AE sensor can be improved by using this material as back lining. The sensor has potential value in nondestructive testing of mechanical properties of materials such as concrete.
Cellular Automaton Simulation of Dendrite Growth in Solidification Process of Cr17 Stainless Steel under Mechanical Vibration
- First Published: 01 March 2022
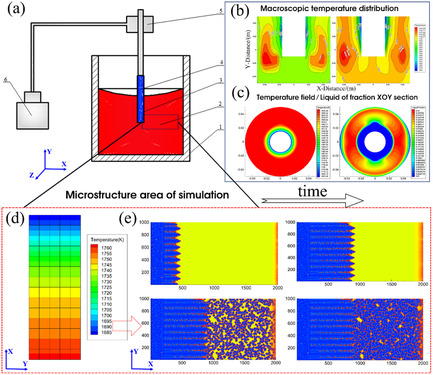
To study the evolution of the solidification structure under vibration-excited liquid metal nucleation technology, a cellular automaton model with coupled temperature field and dendrite growth was built. It was revealed that dendrites may be broken into fragments under vibrations; these fragments would become new nucleation cores and re-grow, increasing the number of dendrites and promoting the refinement of the structure.
Special Section: ALTECH 2021 – Analytical Techniques for Precise Characterization of Nano Materials Guest-Edited by Luca Boarino, Fernando Araujo de Castro, Philipp Hönicke, Yves Kayser, Marie-Christine Lépy
Implementation of Nanoscale Secondary-Ion Mass Spectrometry Analyses: Application to Ni-Based Superalloys
- First Published: 10 May 2022

Nickel-Based Superalloys
Nickel-based superalloys are used in the manufacturing of aircraft engine parts and are widely studied for their outstanding mechanical resistance at high temperatures. In article number 2100414, Jean Almoric and co-workers carried out a chemical characterization at very high resolution (<30nm) of a γ-γ' alloy allowing a semi-quantification of γ' precipitates. This is achieved with an innovative orthogonal time-of-flight SIMS integrated in a Focused Ion Beam/Scanning Electron Microscope UHV platform, called NanoSpace and made by Orsay Physics.
Guest Editorial
ALTECH 2021 – Analytical Techniques for Precise Characterization of Nano Materials
- First Published: 10 May 2022
Perspective
Nano−Micro Characterization of Defects on Silicon Surfaces: An Industrial Perspective of Metrology Challenges
- First Published: 03 December 2021
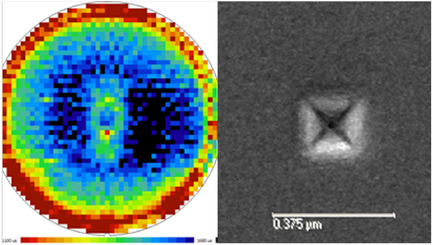
Herein, a few examples inside the area of crystallographic defects, morphological defects, and chemical impurities on silicon wafers, reviewing the relevance of metrology aspects on the defect analysis approach inside a manufacturing environment, are proposed. The discussion also involves the final product certification data reporting, which tends to convey in a very synthetic format the whole measurement and material control process.
Research Articles
Implementation of Nanoscale Secondary-Ion Mass Spectrometry Analyses: Application to Ni-Based Superalloys
- First Published: 05 November 2021
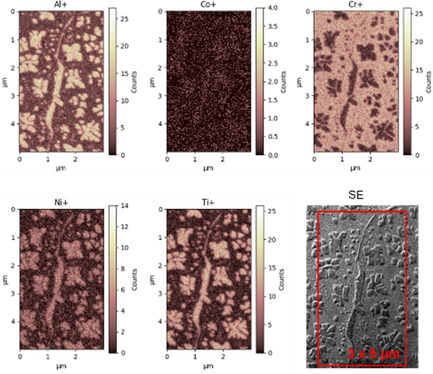
Herein, the development of an innovative orthogonal time-of-flight secondary-ion mass spectrometry implemented in focused ion beam (using a Ga source)/scanning electron microscope is reported. The capabilities of this instrument are demonstrated with the nanoscale characterization of Ni-based superalloys at very high resolution (<30 nm) and high mass resolution (4500 on 28Si).
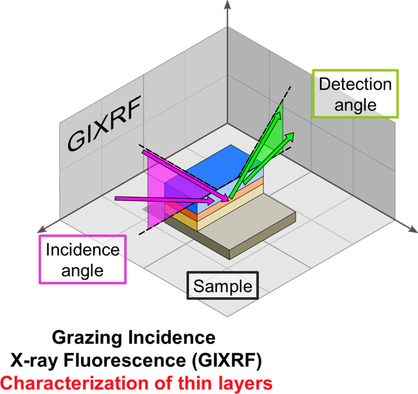
Reference-Free Combined X-Ray Reflectometry−Grazing Incidence X-Ray Fluorescence at the French Synchrotron SOLEIL
- First Published: 08 August 2021
Time-Resolved Grazing Incidence X-Ray Absorption Spectroscopy for the In Situ Investigation of the Initial Stages of Sputter-Deposited Copper Thin Films
- First Published: 22 September 2021
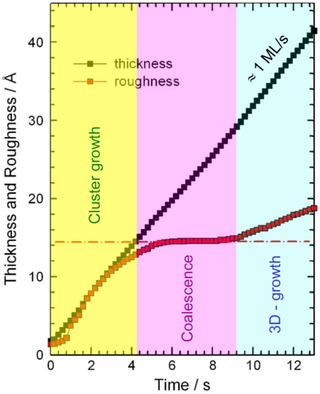
A detailed analysis of time-resolved, grazing incidence X-ray absorption spectroscopy data provides access to the dynamics of structure formation during thin film growth by sputtering. For Cu thin films, nanometer-sized clusters appear during the first few seconds, coalescence is subsequently observed for about 5 s, and 3D growth of copper occurs for films of about 3 nm thickness and more.
The Impact of Surface Voltage on Photoluminescence Response for the Detection of Copper and Iron Contamination in Silicon
- First Published: 07 October 2021
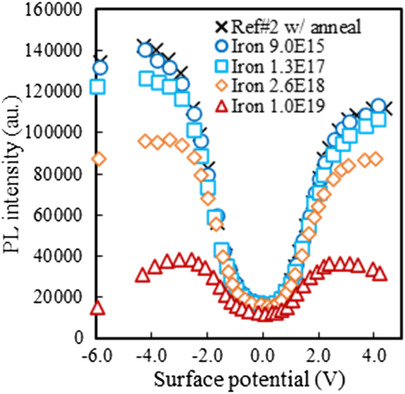
Bias dependent photoluminescence (PL) is explored as a high sensitivity technique to characterize iron and copper contamination diffused in crystalline silicon. Herein, a strong increase in metallic contamination sensitivity with PL measurement by the minimization of surface recombination processes with enhanced field effect passivation using corona charges is shown.
Modified Ramped Current Stress Technique for Monitoring Thin Dielectrics Reliability and Charge Degradation
- First Published: 29 January 2022
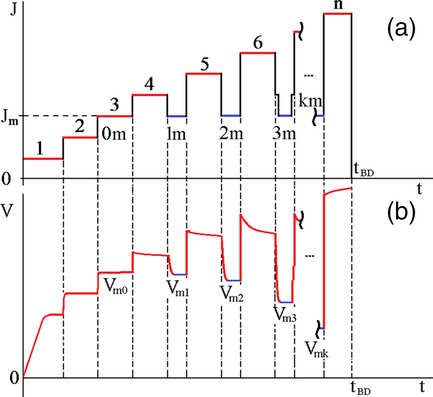
Herein, a novel technique to monitor electro-physical characteristics of metal–insulator–semiconductor (MIS) devices and control their charge state is proposed. The suggested method is based on a JEDEC standard method, which is the current stress technique (J-Ramp). The proposed method gives the capability to predict the malfunction of MIS devices at an earlier stage in comparison with the J-Ramp.