Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Interface Engineering of CZTS/TiO2 Heterojunction Using Wide-Bandgap Ga2O3 Passivation Interlayer for Efficient Charge Extraction
- First Published: 22 July 2022
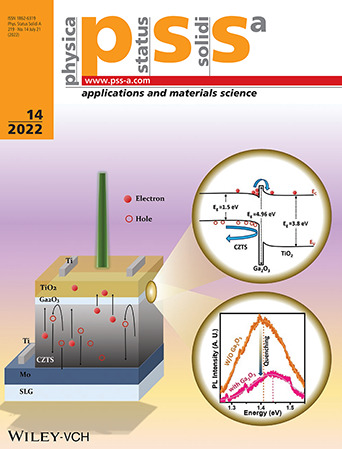
Field-Effect Passivation
The implementation of Ga2O3 thin film effectively passivates the CZTS/TiO2 heterojunction by blocking holes away from the buffer layer and acts as an electron-selective contact. This hole-blocking layer reduces interface recombination evident from significant photoluminescence quenching. More information can be found in article number 2200001 by Mukesh Kumar and co-workers.
Masthead
Review
60 years of pss
Hyperdoped Crystalline Silicon for Infrared Photodetectors by Pulsed Laser Melting: A Review
- First Published: 24 May 2022
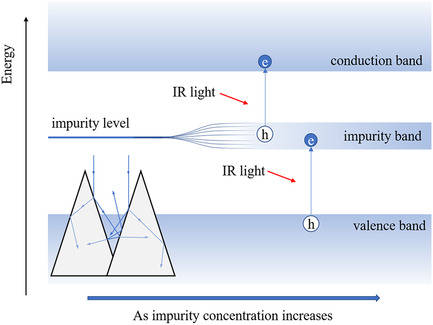
Herein, a review of the fundamentals and research progress of hyperdoped silicon and related infrared photodetectors in the past few decades is given. Earlier research on chalcogen hyperdoping opens up the way to use silicon as infrared photodetectors and later research on transition metals hyperdoping provides new opportunities for further improvements of device properties.
Research Articles
60 years of pss
Interface Engineering of CZTS/TiO2 Heterojunction Using Wide-Bandgap Ga2O3 Passivation Interlayer for Efficient Charge Extraction
- First Published: 06 May 2022
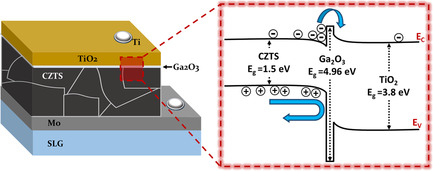
To address the carrier recombination issue at the CZTS/TiO2 heterojunction, a thin Ga2O3 interfacial layer is deposited which passivates electrically active interface trap states. The additional built-in electric field created by the high density of fixed charges in the Ga2O3 dielectric layer declines the probability of photoexcited electron–hole recombination at the interface and enhances charge transfer.
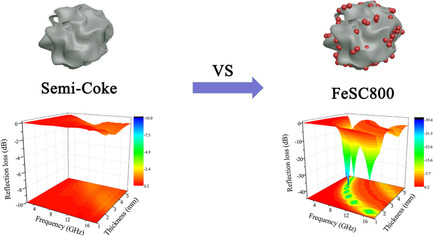
Magnetic Carbon Composites Derived from Coal Hydrogasification Residue for Microwave Absorption
- First Published: 13 May 2022
The Performance Shift due to Light Irradiation on the Electrode of an All-Solution-Processed Semitransparent Polymer Solar Cell
- First Published: 12 May 2022
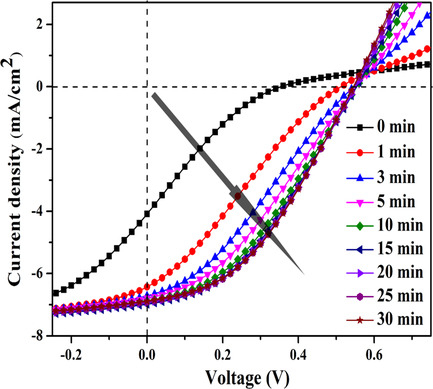
Semitransparent polymer solar cell (PSC) with the structure of ITO/PEIE/P3HT:PCBM/PEDOT:PSS (PEG) is fabricated using all solution processing without vacuum. The performance of semitransparent PSCs is greatly enhanced after short exposure to white light irradiation, which is mainly ascribed to the conductivity increase in PEDOT:PSS due to the conformation change of PEDOT chains by ultraviolet light irradiation.
A High-Performance Sound Insulation Component for Filter Capacitors Based on Coiled-up Acoustic Metamaterials
- First Published: 13 May 2022
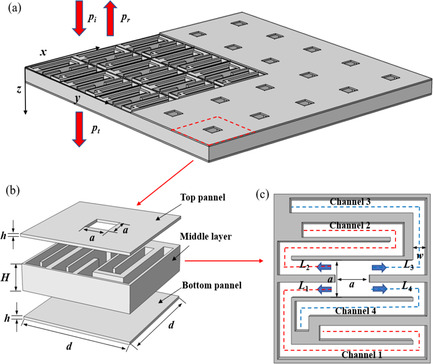
In the light of the spectrum characteristics of filter capacitor noise, a high-performance sound insulation component (HSIC) based on coiled-up acoustic metamaterials is developed. By efficiently absorbing its main harmonic components, HSIC can insulate the noise of filter capacitor significantly, which is 4.5 dB(A) higher than that of a homogeneous panel with same area density.
Excellent Lubricity of PVA/PEG/CS Composite on Ceramic Surface and Stainless Steel Friction Pair
- First Published: 13 May 2022
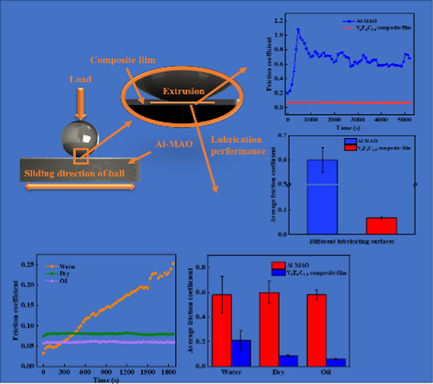
When the mass ratio of PVA: PEG: CS is 5:5:1.5, the friction coefficient reaches 0.068 under long-time running through the effect of hydrogen bond. Compared with the working condition without composite film, the lubrication performance is improved by ten times. The results show that the lubrication performance is excellent.
Microstructure and Composition Comparison of Ti- and Ta-Doped Nb3Al Superconducting Wires Fabricated by RHQT Process
- First Published: 13 May 2022
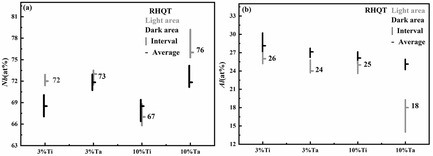
A15 phase powder-in-tube (PIT) transformed and body-centered cubic (bcc) phase as-quenched (Nb1−xTix)3Al and (Nb1−xTax)3Al (x = 0.03, 0.1) wires are prepared by rapid heating, quenching, and transformation (RHQT) method. The effects of Ti and Ta additions on the crystal structure, microstructure, and superconducting properties of Nb3Al superconductors are compared and analyzed by X-ray diffractometer (XRD), micro-XRD, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), and magnetic properties tests.
Laser Thermal Treatment-Induced Mg x Zn1−x O Gradient Film and Photodetector with Solar-Blind UV Response
- First Published: 19 May 2022
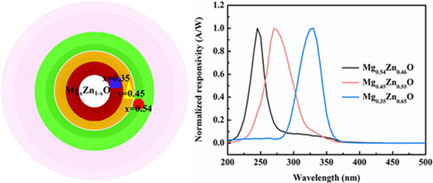
The Mg x Zn1−x O gradient film is realized by the sol–gel method and laser thermal treatment process. The Mg2+ component of the Mg x Zn1−x O gradient film varies from x = 0.35 to x = 0.54 due to the radial distribution of laser thermal treatment temperature. The MSM structure devices based on Mg x Zn1−x O gradient film show a wide response spectrum from 330 to 245 nm.
Effect of InGaN Channel on Radio-Frequency Performance in High-Electron-Mobility Transistors with an InAlGaN Barrier
- First Published: 24 May 2022
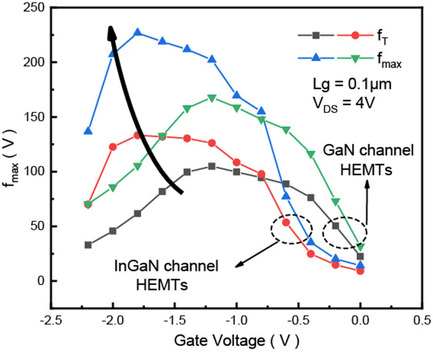
The conduction band energy has been raised by replacing the GaN channel with the InGaN channel in AlInGaN/GaN HEMTs, thus the carrier confinement at the channel bottom is greatly enhanced. Better carrier confinement increases the peak transconductance and the fT and fmax are improved by 27.88% and 35.33% when compared to GaN channel devices.
Synthesis, Characterization, and Typical Application of Nitrogen-Doped MoS2 Nanosheets Based on Pulsed Laser Ablation in Liquid Nitrogen
- First Published: 24 May 2022
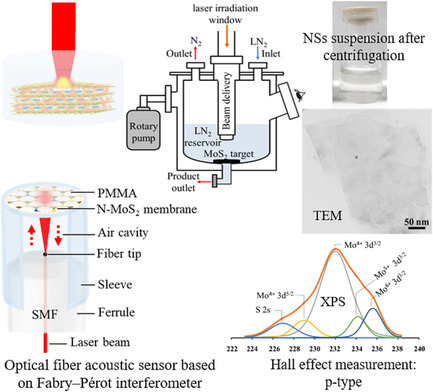
The pulsed laser ablation of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) target is carried out in liquid nitrogen to synthesize three-layer nitrogen-doped MoS2 nanosheets with p-type properties. Various microanalyses are examined to characterize the nanosheets. Then, spin coating/fishing method is used to fabricate MoS2 diaphragm which is assembled in Fabry–Pérot optical fiber-acoustic sensor to achieve the greatest sensitivity ever seen.
Electric Arc Synthesis of Composite Ni–C, NiO–C Nanomaterials: Structure and Electrochemical Properties
- First Published: 21 May 2022

Plasma-chemical synthesis allows to produce Ni–NiO–C nanomaterial. Ni nanoparticles are surrounded by a carbon matrix. Burning out of amorphous and low graphitizable carbon structures improves the material's electrical conductivity and electrochemical properties as supercapacitor electrodes. Higher temperature calcination leads to deterioration of the electrochemical properties due to carbon burning out and nanoparticle agglomeration.
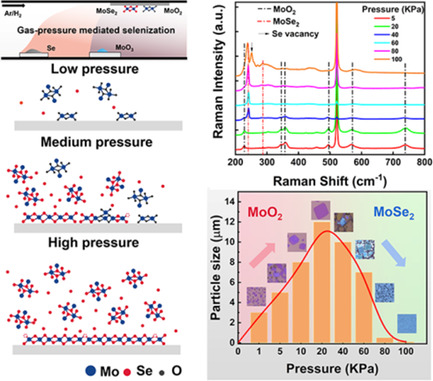
Controllable Selenization Transformation from MoO2 to MoSe2 by Gas Pressure-Mediated Chemical Vapor Deposition
- First Published: 25 May 2022