Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Encapsulation Effects on Ge-Rich GeSbTe Phase-Change Materials at High Temperature
- First Published: 06 October 2024
In article number 2300448, Emmanuel Nolot, Gabriele Navarro, and co-workers investigate the effects of the encapsulating layer on the evolution of Ge-rich GeSbTe alloys combining Raman, FTIR, XRD, and TEM-EDX analyses. The results reveal that different encapsulations affect the crystallization kinetics and the vibrational properties upon annealing, leading to either homogeneous layers or heterogeneous morphologies with phase segregation happening in specific regions. Therefore, the choice of an encapsulating material not affecting the crystallization dynamic of the chalcogenide is necessary to ensure optimal performance in Phase-Change Memory.
Masthead
Guest Editorial
Research Article
Excellent Reliability Characteristics of Ovonic Threshold Switch Device with Higher-Temperature Forming Technique
- First Published: 30 November 2023
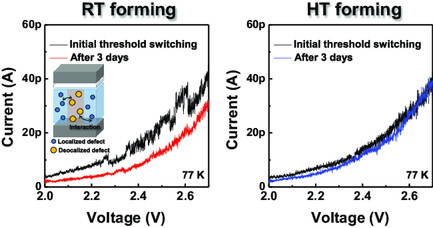
Higher-temperature forming technology is utilized for highly reliable ovonic threshold switch devices. The distribution of threshold voltage (Vth) and device drift characteristics depending on the forming temperature is investigated. Additionally, the trap analysis in cryogenic environment for investigation of random telegraph noise characteristics is presented.
Evidence of Heat-Assisted Atomic Migration in GeSe Self-Selecting Memory at High Operating Current Density
- First Published: 14 January 2024
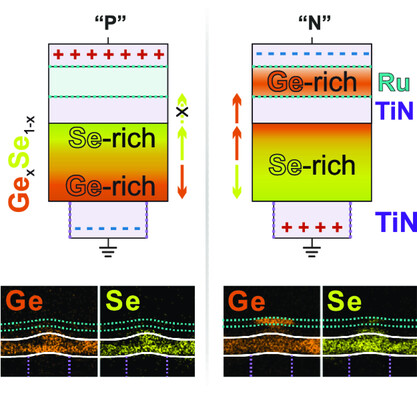
This work investigates the polarity effect in GexSe1–x threshold switches under various operating conditions. The mechanism behind the high-current behavior is elaborated by means of elemental mapping and is shown to be caused by atomic migration within device structure. At the same time, no major composition change is observed at a low operating current.
Programming Operations Analysis and Statistics in One Selector and One Memory Ovonic Threshold Switching + Phase-Change Memory Double-Patterned Self-Aligned Structure
- First Published: 06 February 2024
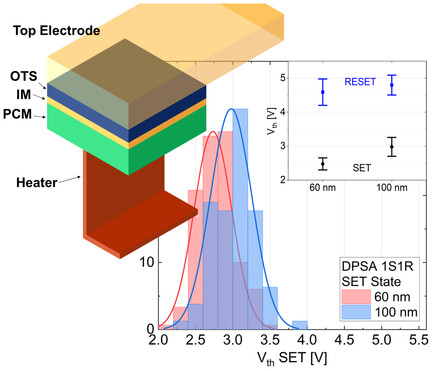
The article addresses the interplay of phase-change memory and ovonic threshold switching selectors in a novel double-patterned self-aligned architecture. A statistical analysis of programming, SET speed, reading, and cycling endurance is conducted. The viability of this technology is assessed on a kb-sized array by comparing different distribution models, resulting in the achievement of a memory window exceeding 2 V.
Modified Electronic Structure of Amorphous Mn–Si–Te for Ovonic Threshold Switch Application: Improved Thermal Stability by the Formation of Mn–Te Bonding
- First Published: 23 February 2024
Investigating the Polarity Dependence of Multilevel Cell Operation in Conventional Mushroom Phase-Change Memory Cells
- First Published: 27 November 2023
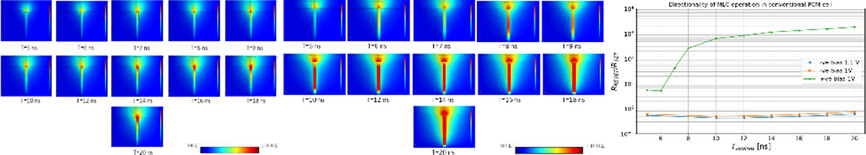
In this computational work, the bias dependence of multilevel cell operation in conventional mushroom phase-change memory cells is reported. An introduction to phase-change materials is provided first, followed by a detailed study on how thermoelectric effects govern the polarity dependence of gradual RESET, thereby highlighting an interesting challenge for their application as computational memory.
Developing GeSbTe Superlattice Through Understanding of the Reversible Phases and Engineering Its Interspaces
- First Published: 28 June 2024

The inherent vacancies play a crucial role in the GeSbTe superlattice. GeSbTe superlattice has different phases among the reversible phases depending on the degree of alignment of these vacancies. The reversible phases of GeSbTe superlattice correspond to stable (hexagonal-close packed) and metastable (cubic) crystal phases, not crystal and amorphous, which is progressed in alloy-based PCM.
Low RESET Current Mushroom-Cell Phase-Change Memory Using Fiber-Textured Homostructure GeSbTe on Highly Oriented Seed Layer
- First Published: 05 June 2024
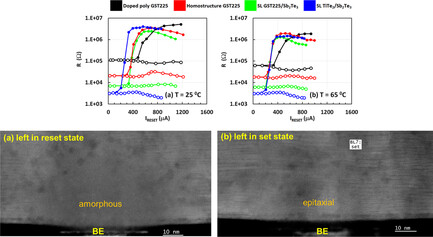
Herein, a low RESET current 1T1R mushroom-cell phase-change memory (PCM) device that uses fiber-textured homostructure GeSbTe (GST) grown on highly oriented TiTe2 seed layer is reported. The homostructure device outperformed the industry standard device, that uses doped polycrystalline GST, on most figures of merit. The homostructure devices are also benchmarked against superlattice (SL) PCM devices with 10 periods of 5/5 nm GST/Sb2Te3 grown on the TiTe2 seed layer, and are found to have same low RESET current. It is also observed by transmission electron microscopy that the alternating layers of GST/Sb2Te3 and TiTe2/Sb2Te3 in SL devices is intermixed in the switched region after the devices are cycled with RESET/SET pulses. Additionally, when the SL device is left in the SET state, the intermixed switched region crystallinity is textured and exhibits van der Waals gaps. The SL PCM devices require a precise layered structure that is hard to yield on a full wafer scale. In contrast, fiber-textured homostructure PCM cells reported here are easily manufacturable, while providing similarly low RESET current and low-resistance drift, which makes this device suitable for analog artificial intelligence computation.
Quantitative Scanning Transmission Electron Microscopy–High-Angle-Annular Dark-Field Study of the Structure of Pseudo-2D Sb2Te3 Films Grown by (Quasi) Van der Waals Epitaxy
- First Published: 18 January 2024
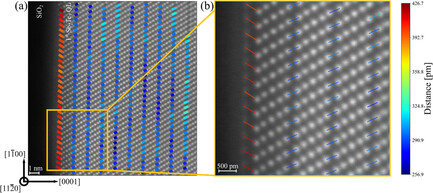
Well-oriented out-of-plane Sb2Te3 films are characterized by scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM). A true van der Waals gap under the first Sb2Te3 quintuple layer enables successful growth. The key parameter is having 1–2 Te-rich atomic layers. Quantitative STEM tools are developed to provide detailed information on the atomic arrangement with a few pm precision.
Investigation of Phase Segregation Dynamics in Ge-Rich GST Thin Films by In Situ X-Ray Fluorescence Mapping
- First Published: 07 March 2024
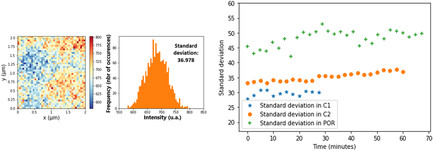
This article discusses the dynamics of phase segregation in Ge-rich GST thin films monitored by synchrotron X-ray fluorescence. As Ge-rich GeSbTe is a good candidate for future automotive applications in phase change memories, understanding its crystallization kinetics and elemental dynamics is key to improving the performance of phase change materials.
Encapsulation Effects on Ge-Rich GeSbTe Phase-Change Materials at High Temperature
- First Published: 29 January 2024
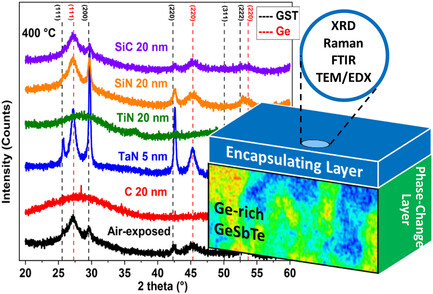
This study explores the impact of different encapsulating materials on the evolution of Ge-rich GesbTe (GGST) films at high temperatures. The encapsulation layer thickness should be tuned to protect from oxidation and delamination. Carbon, Titanium Nitride and Silicon Carbide result in more homogeneous crystallization of GGST. Tantalum Nitride and Silicone Nitride induce disruptive effects due to interfacial heterogeneous nucleation.
Crystallization of Amorphous N-Doped Ge-Rich GST Layers Deposited on a Polycrystalline GST Template
- First Published: 30 January 2024
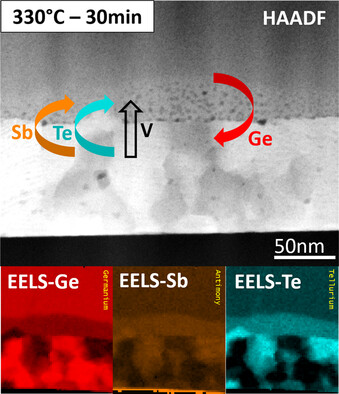
In situ transmission electron microscopy and ex situ chemical analysis reveal that a nitrogen-doped Ge-rich GeSbTe (GGSTN) layer, in contact with a crystalline GeSbTe template, crystallizes at a lower temperature than needed for bulk crystallization. Contrary to expectations, the phenomenon is not attributed to solid-phase epitaxy but rather to a reduction in Ge content within the GGSTN layer.
Study of Ge-Rich Ge–Sb–Te Device-Dependent Segregation for Industrial Grade Embedded Phase-Change Memory
- First Published: 22 January 2024
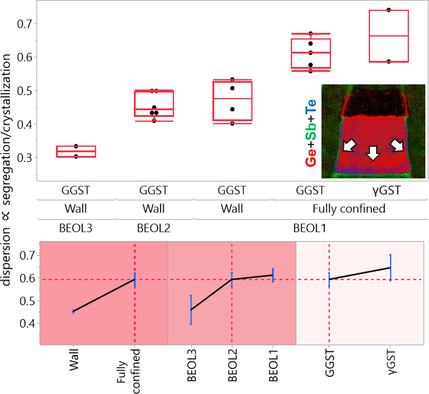
Herein, Ge-rich Ge–Sb–Te segregation in the function of different device and process parameters is studied. A statistical methodology, returning metrics to quantify material segregation, is exploited to analyze the effects of confinement and composition. Moreover, the present test case is compared with previous results, returning a comprehensive fit of all the known sources of segregation.-
Flexible Electronics Applications of Ge-Rich and Se-Substituted Phase-Change Materials in Nonvolatile Memories
- First Published: 11 January 2024
Flexible electronics that are easy to manufacture and integrate into everyday items require suitable nonvolatile memory technology. Here, Ge-rich GeSbTe and Se-substituted GeSbSeTe phase-change alloys for such applications are explored. Key material properties are measured using four-point probe electrical testing, Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray diffraction. Devices suited to write-once and rewritable memory implementations are investigated, through simulation and experiment.
Thickness-Dependent Bandgap and Atomic Structure in Elemental Tellurium Films
- First Published: 14 February 2024
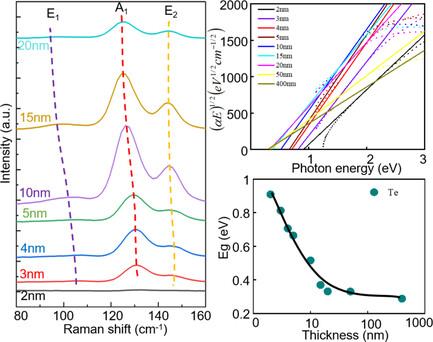
In this research, with the help of ab initio molecular dynamics calculation, a low-cost and feasible approach is proposed to effectively increase the bandgap of Te films via thinning the thickness. This increase of bandgap further suppresses the leakage current of elemental Te switching devices, and paves the way for future application in large-array-scale 3D high-density phase-change memory.
Atomic Structure and Dynamics of Unusual and Wide-Gap Phase-Change Chalcogenides: A GeTe2 Case
- First Published: 30 January 2024
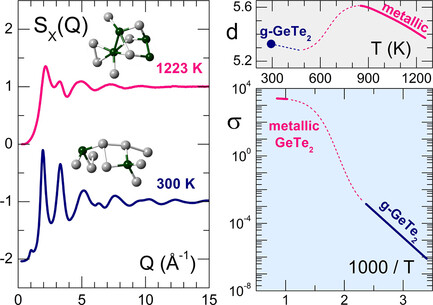
Unconventional phase-change telluride GeTe2 is promising for THz metasurfaces and the controlled crystallization of 2D materials. Its chemical metastability, represented by GeTe2 ⇌ GeTe + Te, seems to be related to high internal pressure in the metallic melt compared to a less dense semiconducting glass film, exhibiting contrasting structural and electronic properties.
Optical Properties of GeSe1−xTex Chalcogenide Materials Promising for on-Chip Low and Ultra-Low Loss Reconfigurable Photonics and Nonlinear Devices
- First Published: 15 May 2024
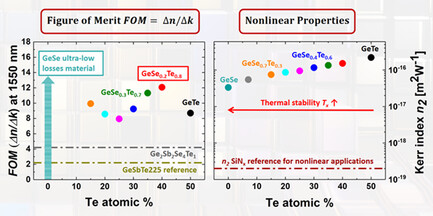
The highly promising linear and nonlinear optical properties of new thin films of GeSe1−xTex chalcogenide materials in the amorphous as-deposited state, and after crystallization, are revealed here. By modifying the Te content of GeSe1−xTex thin films, it is possible to tailor their linear and nonlinear optical properties to optimize them for a wide range of innovative optical and photonic applications.