Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Second malignancy in advanced or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer after the advent of molecular targeted drugs and immunotherapy
- Pages: 2291-2297
- First Published: 07 October 2024
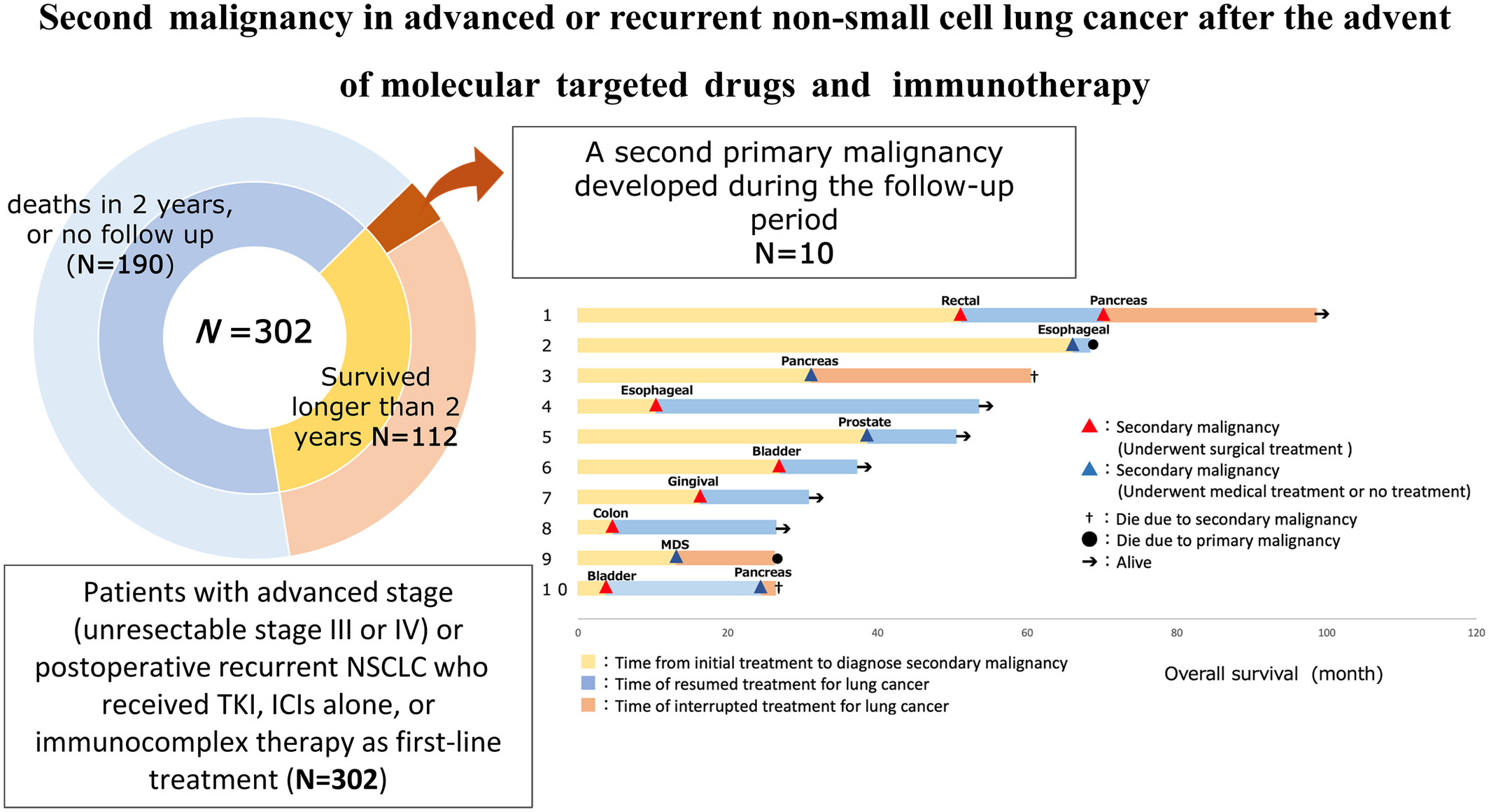
The advent of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer has resulted in an increasing number of long-term survivors. Consequently, the emergence of second malignancy may have implications for their prognosis. This study found that 8.9% of patients with advanced NSCLC who received TKIs, ICIs, or immune combination therapy and survived ≥ 2 years developed second malignancy. It was suggested that by performing screening and examinations for the second malignancy, both malignancies could be controlled.
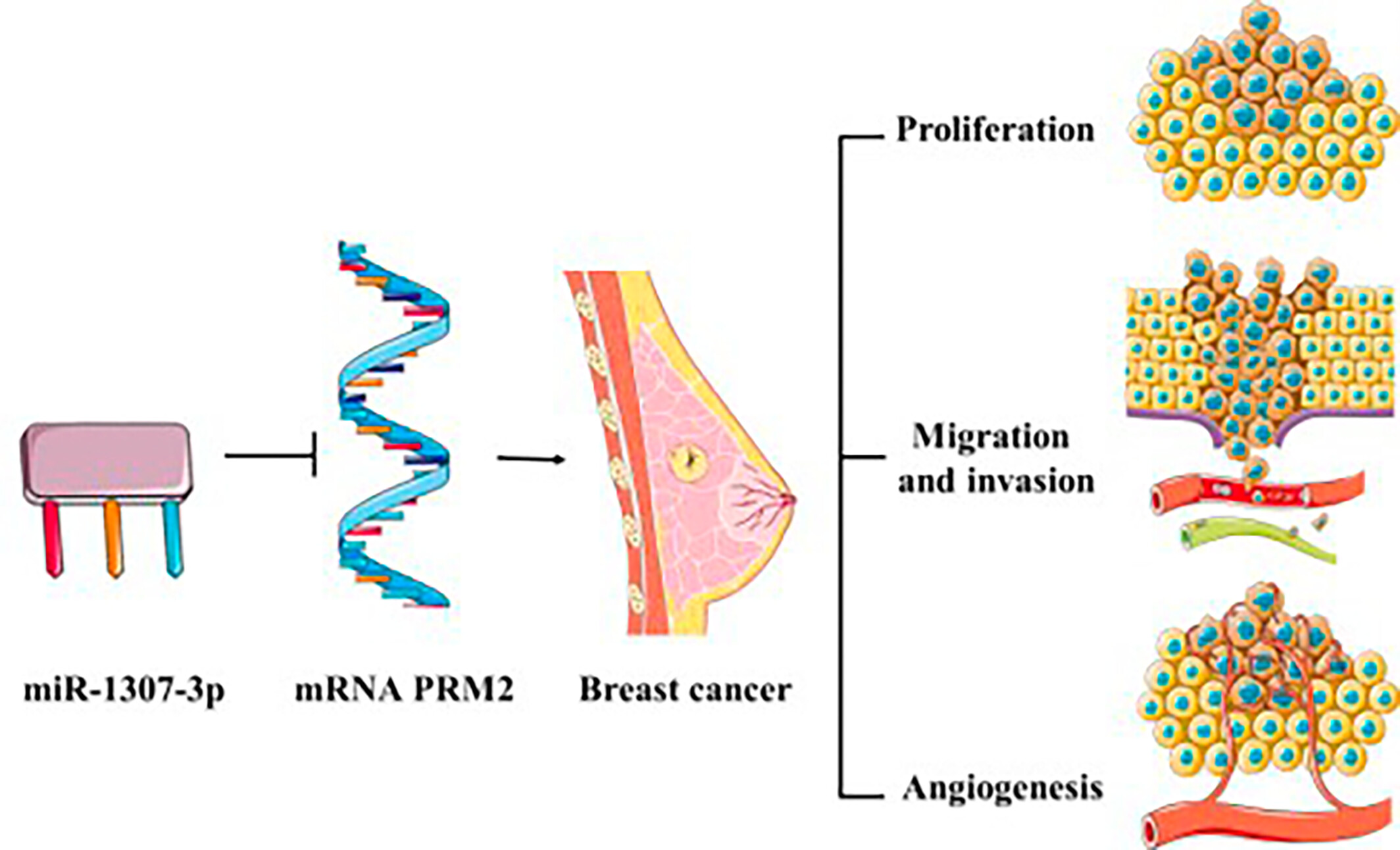
MicroRNA-1307-3p contributes to breast cancer progression through PRM2
- Pages: 2298-2308
- First Published: 09 October 2024
Prophylactic cranial irradiation in patients with resected small-cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2309-2318
- First Published: 09 October 2024
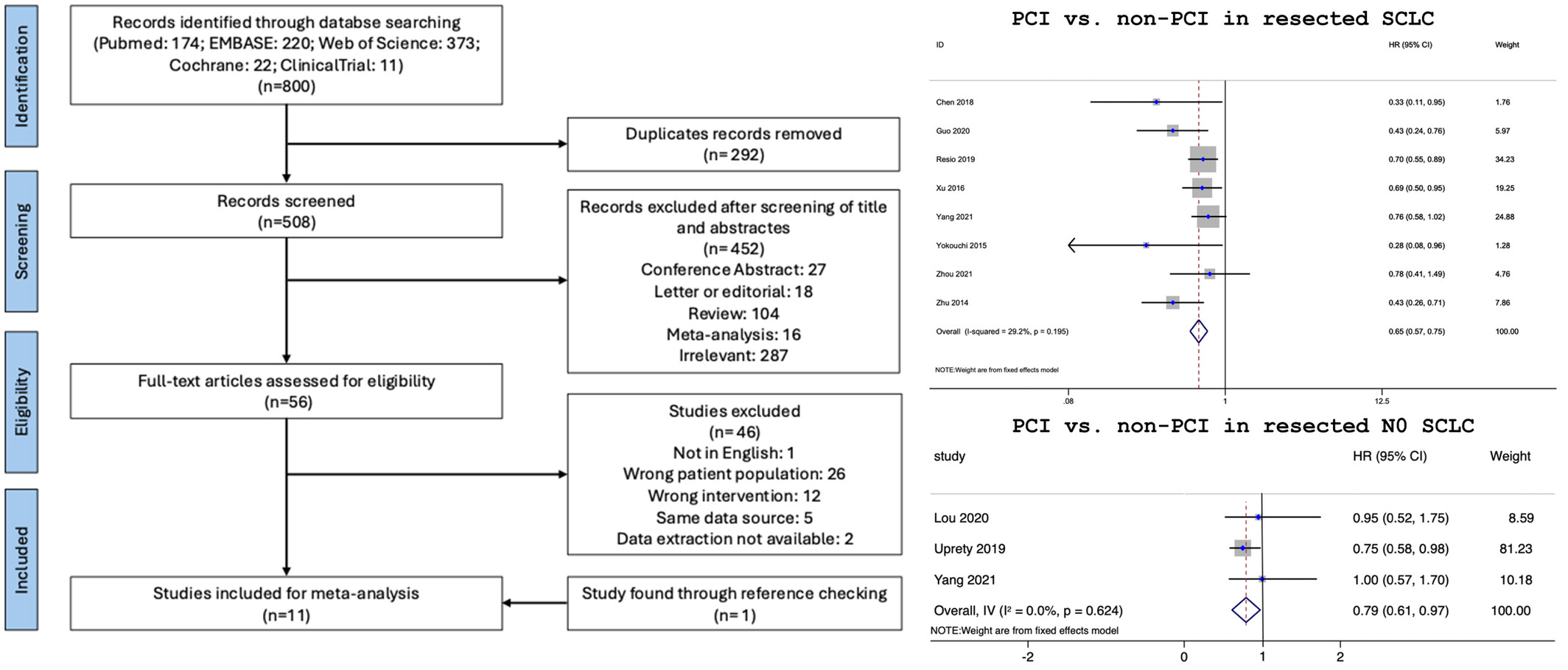
We conducted a meta-analysis to evaluate the efficacy of prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) in resected small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients. The use of PCI delayed brain recurrence and improved overall survival in patients with resected, stage I–III SCLC. Importantly, patients with N0 SCLC can also benefit from postoperative PCI.
SOX17 expression in tumor-penetrating vessels in relation to CD8+ T-cell infiltration in cancer stroma niches
- Pages: 2319-2326
- First Published: 09 October 2024
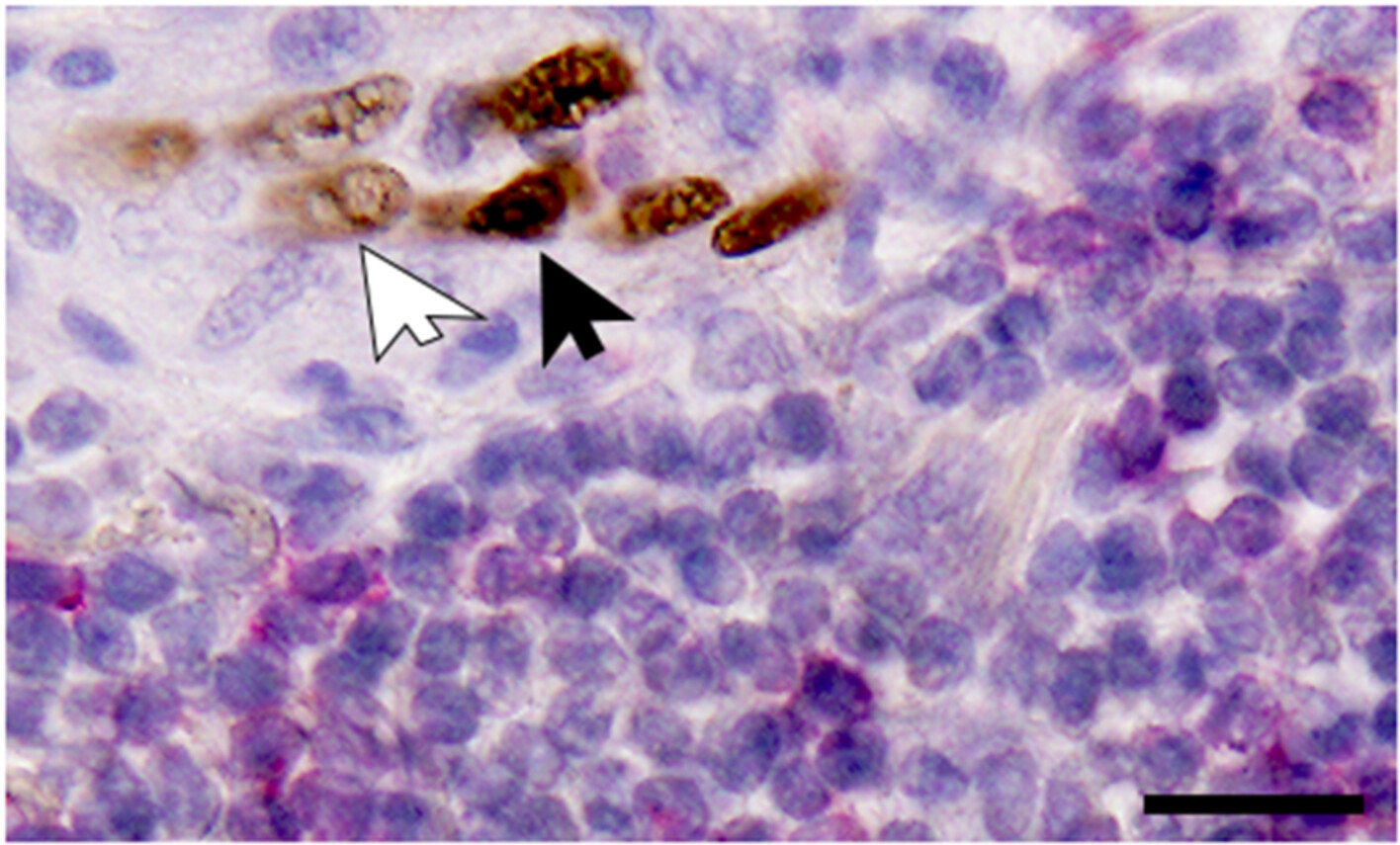
Sex-determining region Y-related high-mobility group box 17 protein (SOX17) immunoreactivity was observed in TECs with high endothelial venule (HEV) features, including a plump, almost cuboidal appearance of varying degrees (a). SOX17 immunoreactivity was nonuniform and rather heterogenous even in adjacent endothelial cells (black and white arrows indicate robust and weak SOX17 immunoreactivity, respectively). The numerous red-stained CD8+ T lymphocytes present around the SOX17-positive HEVs are notable.
The efficacy and safety of a novel PD-1/CTLA-4 bispecific antibody cadonilimab (AK104) in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A multicenter retrospective observational study
- Pages: 2327-2338
- First Published: 11 October 2024
CASE REPORT
Remarkable pathological response to neoadjuvant tepotinib in lung adenocarcinoma with MET exon 14 skipping mutation: A case report
- Pages: 2339-2343
- First Published: 29 September 2024
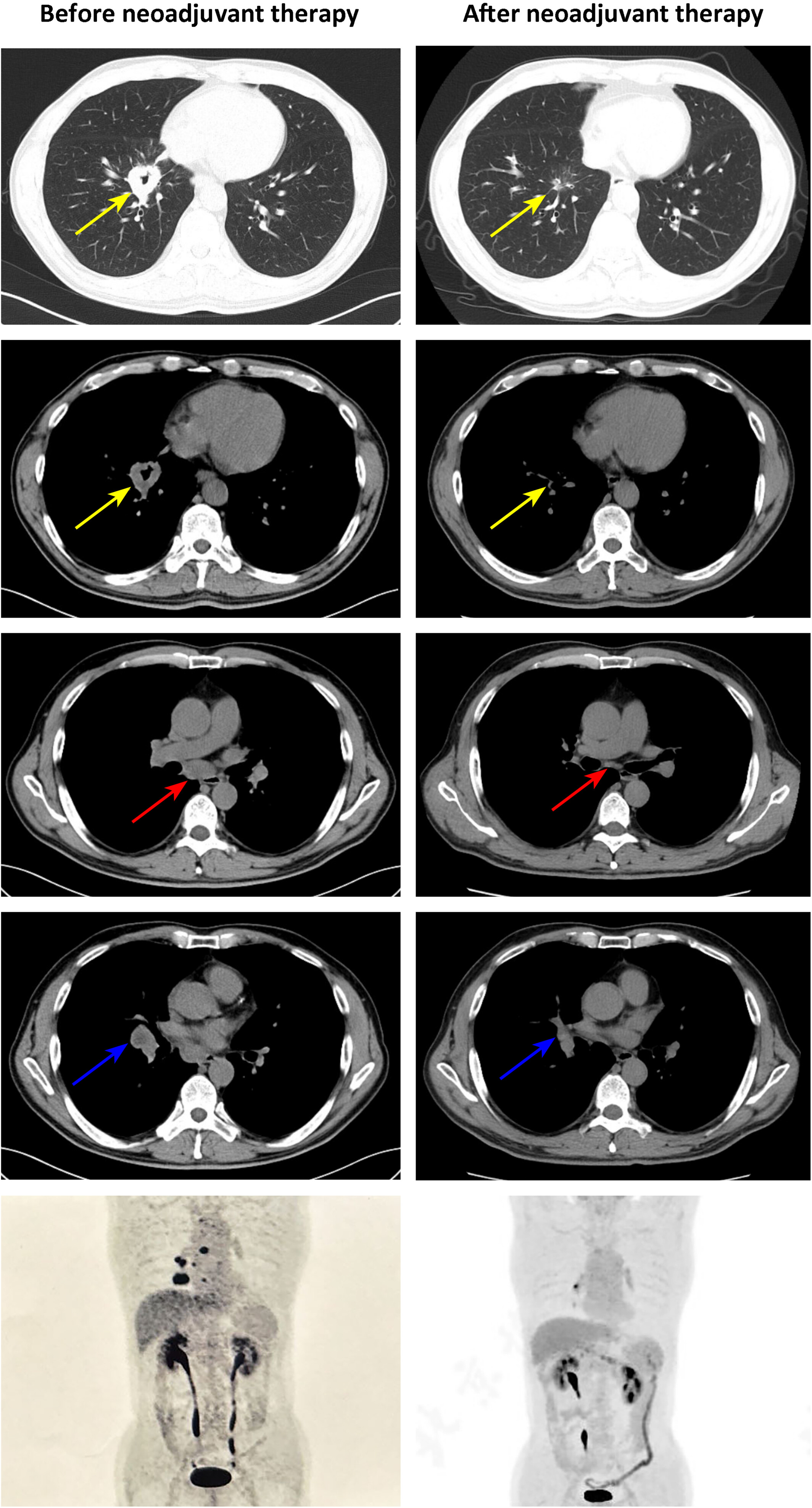
This report describes a 60-year-old man with stage IIIA (cT2N2M0) lung adenocarcinoma harboring a METex14 skipping mutation. After initial treatment with savolitinib was discontinued due to grade 4 transaminitis, the patient was switched to tepotinib. Six months later, significant tumor shrinkage was observed, and surgery revealed remarkable pathological response with no residual tumor in lymph nodes (ypT2N0M0, IB). Postoperative tepotinib continued, with no relapse at 6-month follow-up. The arrows in different colors highlight different involved sites: yellow arrows — primary tumor lesion; red arrows — 7th lymph node; blue arrows — right hilar lymph node.