Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Autologous cytokine-induced killer (CIK) cells enhance the clinical response to PD-1 blocking antibodies in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A preliminary study
- Pages: 145-152
- First Published: 04 November 2020
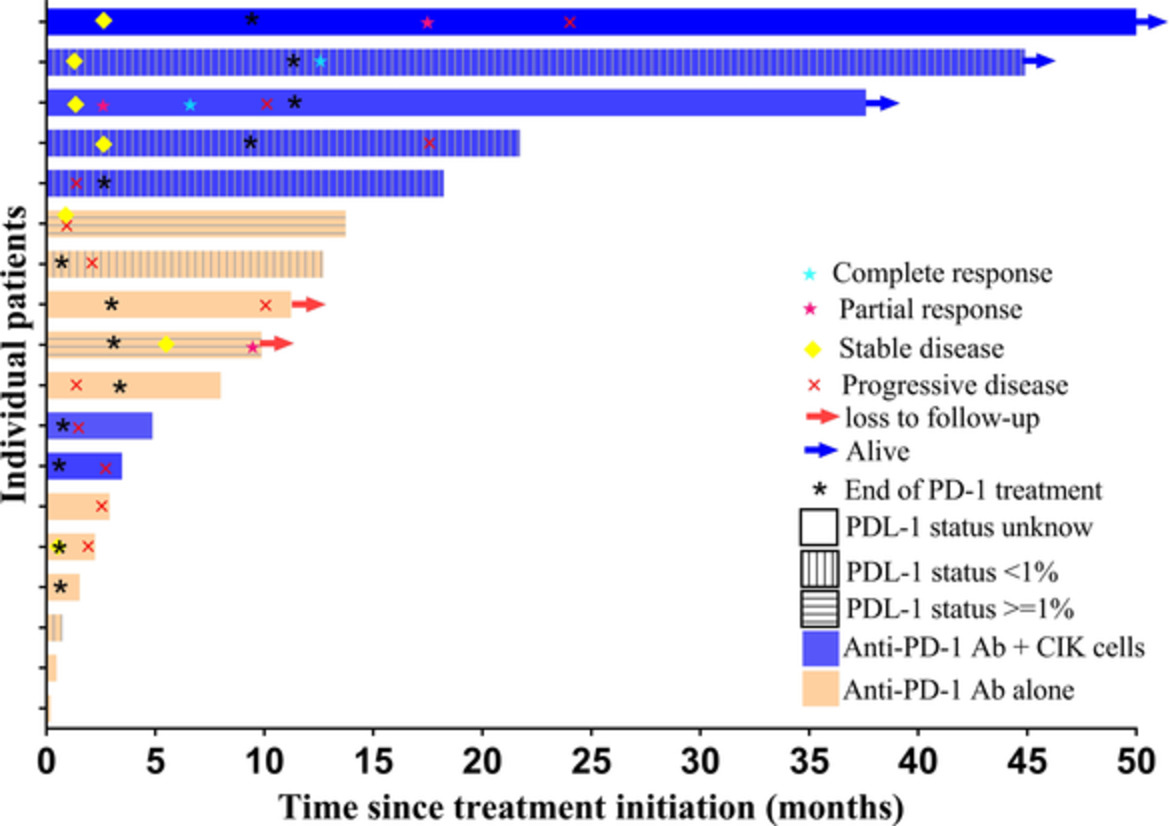
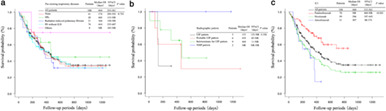
We conducted a retrospective study of PD-1 blocking antibodies (pembrolizumab or nivolumab) plus autologous CIK cells to assess the safety, effectiveness, and influence on immune function of this treatment in a total of 18 patients with advanced NSCLC. We found that disease control rate (DCR) was significantly higher in patients who received a combination of PD-1 blockade + CIK cell infusions than in those who received a PD-1 blocking antibody alone. This clinical study provides data support for further clinical trials in the future.
Outcome and risk factor of immune-related adverse events and pneumonitis in patients with advanced or postoperative recurrent non-small cell lung cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors
- Pages: 153-164
- First Published: 17 November 2020
Long-term outcomes of sentinel node identification using indocyanine green in patients with lung cancer
- Pages: 165-171
- First Published: 21 November 2020

We attempted to identify sentinel lymph nodes by indocyanine green in lung cancer surgery. The identification rate was 72.7%, and the accuracy rate was 100% immediately after surgery. In addition, we followed-up the cases for a long time to check for lymph node metastasis and verify whether the results of intraoperative sentinel biopsy were correct. After follow-up had been completed, the false-negative rate was 7.7% (1/13) and the accuracy rate was 93.8% (15/16) in this study.
Osimertinib combined with bevacizumab for leptomeningeal metastasis from EGFR-mutation non-small cell lung cancer: A phase II single-arm prospective clinical trial
- Pages: 172-180
- First Published: 17 November 2020
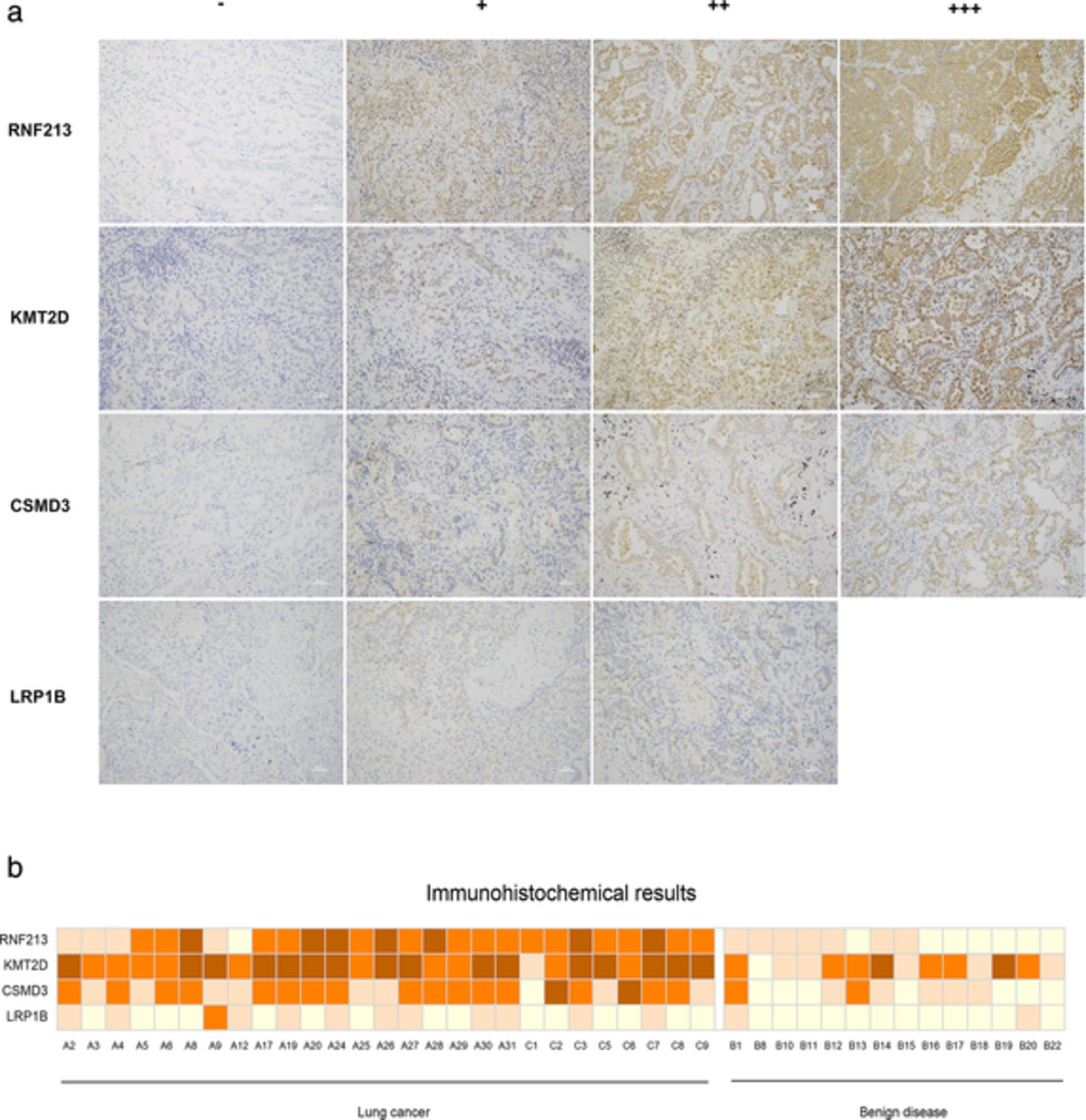
RNF213 gene mutation in circulating tumor DNA detected by targeted next-generation sequencing in the assisted discrimination of early-stage lung cancer from pulmonary nodules
- Pages: 181-193
- First Published: 16 November 2020
Tissue surface area and tumor cell count affect the success rate of the Oncomine Dx Target Test in the analysis of biopsy tissue samples
- Pages: 194-200
- First Published: 13 November 2020
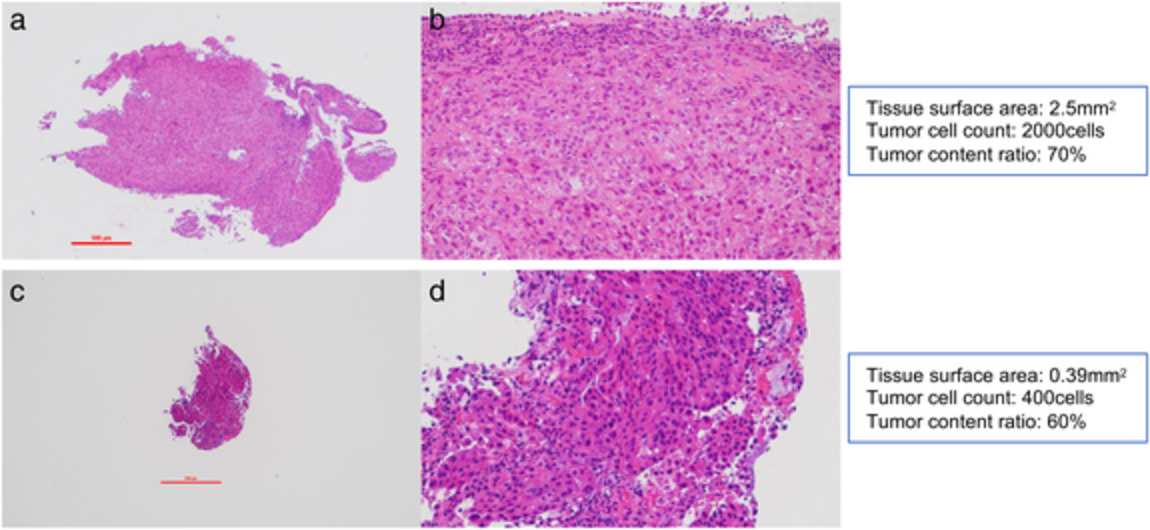
This study demonstrates that a tissue surface area >1.04 mm2 and tumor cell count >375 cells had a positive effect on the analysis success rate of the Oncomine Dx Target Test in the analysis of biopsy tissue samples. The criteria mentioned above will help to determine which tests should be performed; next-generation sequencing-based companion diagnostics or multiple single-gene testing.
Validating impact of pretreatment tumor growth rate on outcome of early-stage lung cancer treated with stereotactic body radiation therapy
- Pages: 201-209
- First Published: 30 November 2020
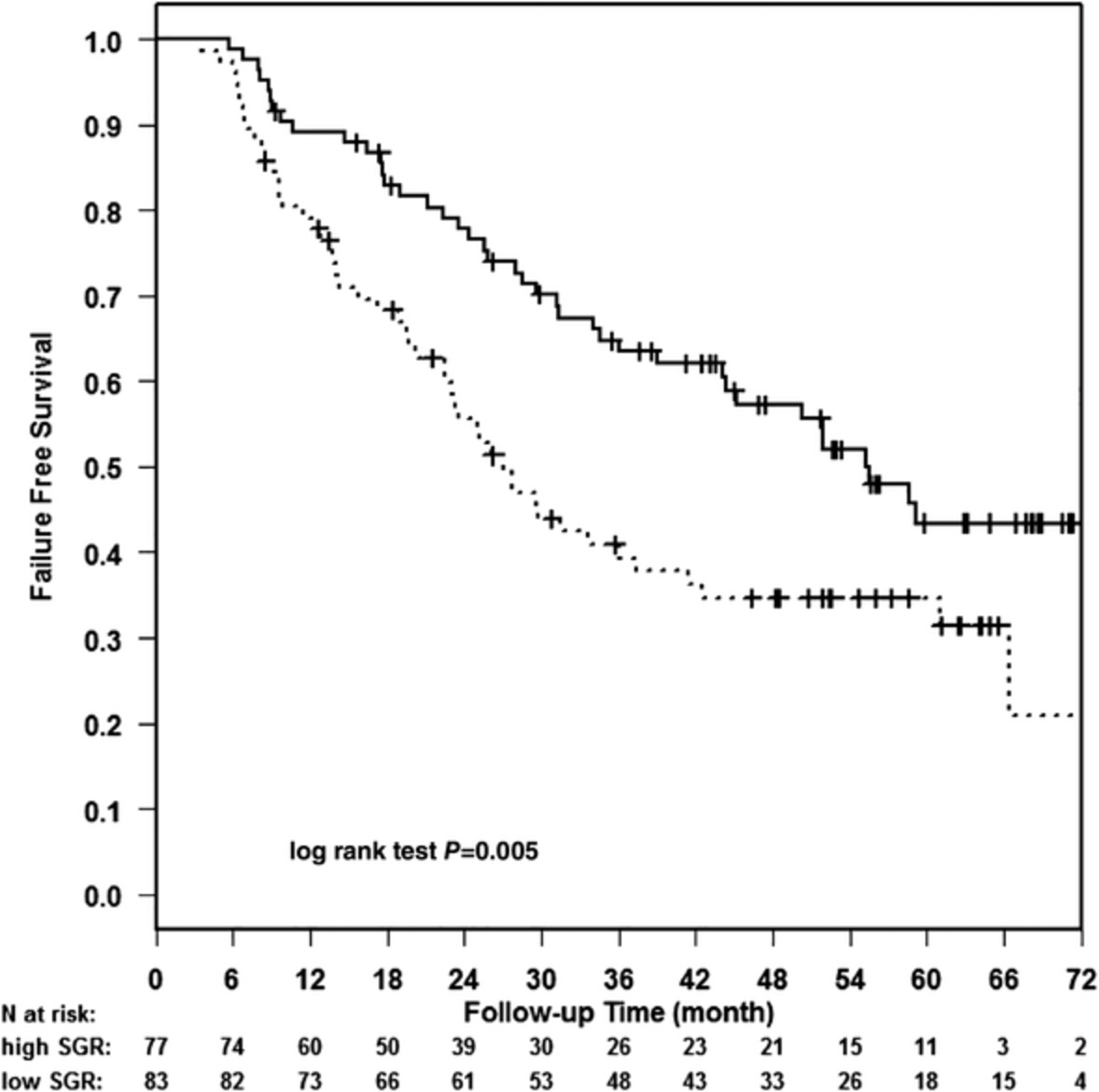
We demonstrated that tumor growth rate (GR) predicts treatment outcome in early-stage lung cancer patients treated with SBRT. We used specific growth rate (SGR) as a metric for pretreatment GR and its median (0.43 × 10-2) to group patients into high and low SGR cohorts. In this study, the same median SGR was validated in an independent dataset at a different cancer institution. Patients with high SGR tumors consistently had significantly lower survival and higher regional failure.
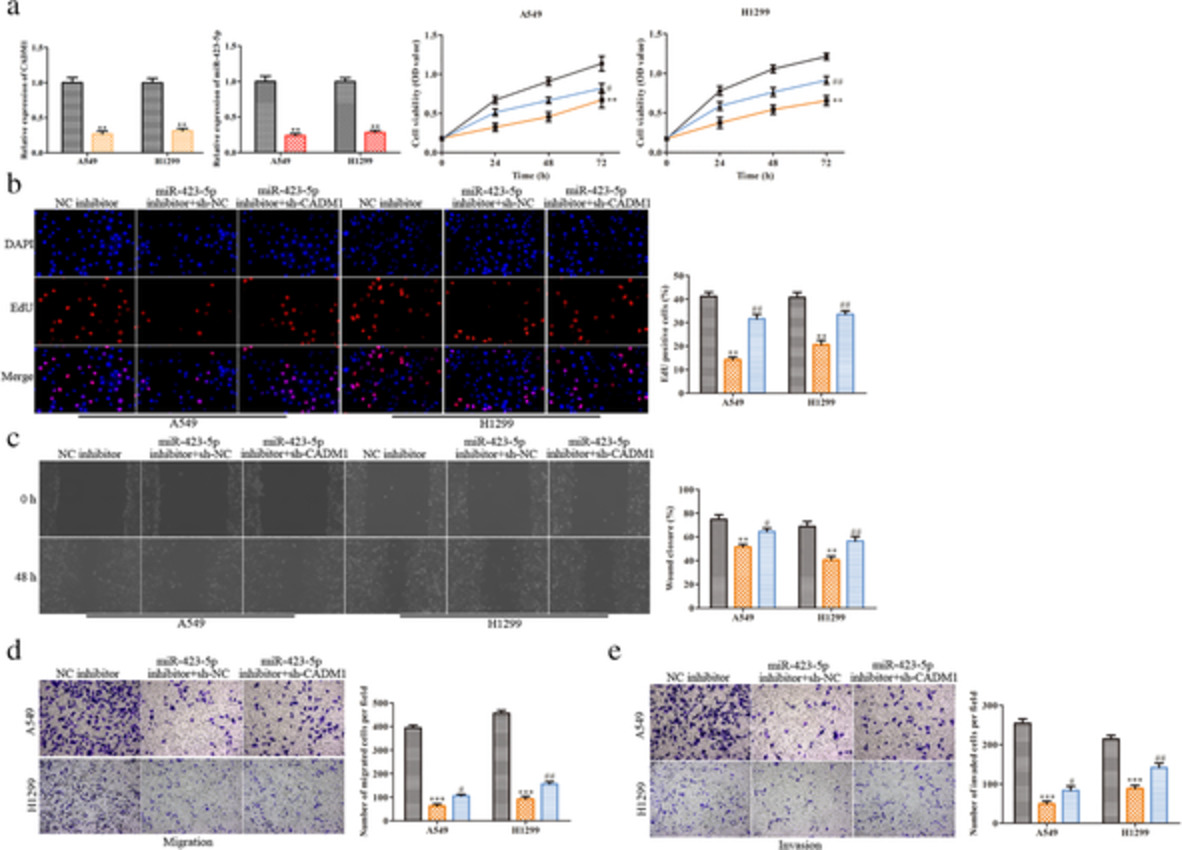
MiR-423-5p aggravates lung adenocarcinoma via targeting CADM1
- Pages: 210-217
- First Published: 18 November 2020
Immune microenvironment features and efficacy of PD-1/PD-L1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer patients with EGFR or HER2 exon 20 insertions
- Pages: 218-226
- First Published: 18 November 2020
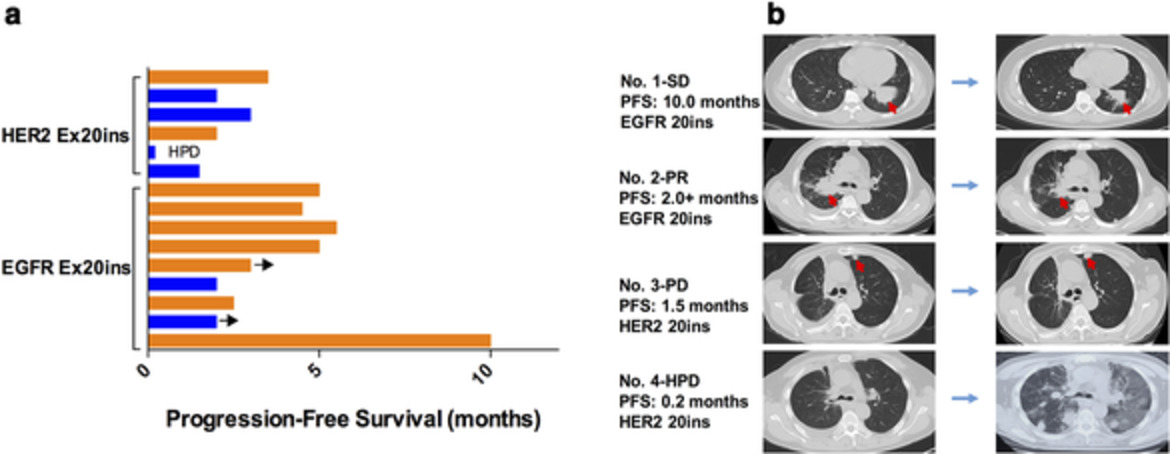
NSCLC patients with EGFR/HER2 Ex20ins had similar genomic characteristics and distinct immune features when compared to common EGFR mutations. Patients with EGFR Ex20ins had significantly higher PD-L1 expression than those with HER2 mutations, which may be the potential reason for the different responses to PD-1/PD-L1 blockage.
Postoperative radiotherapy for pathological stage IIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer with positive surgical margins
- Pages: 227-234
- First Published: 27 November 2020
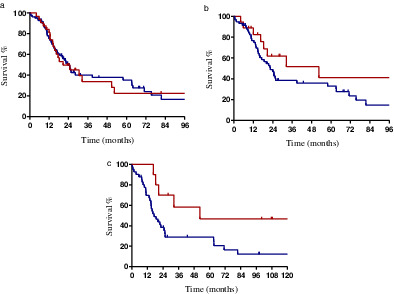
Postoperative radiotherapy (PORT) has been recommended to treat patients with positive surgical margins. However, the existing evidence is controversial and high-level evidence is lacking. In our study, the PORT group had markedly, but not statistically significant, longer median OS compared with the non-PORT group in R1 resection patients. OS was significantly longer in the R1 resection patients receiving adjuvant CRT than the surgery alone group.
Clinical implication of minimal presence of solid or micropapillary subtype in early-stage lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 235-244
- First Published: 24 November 2020
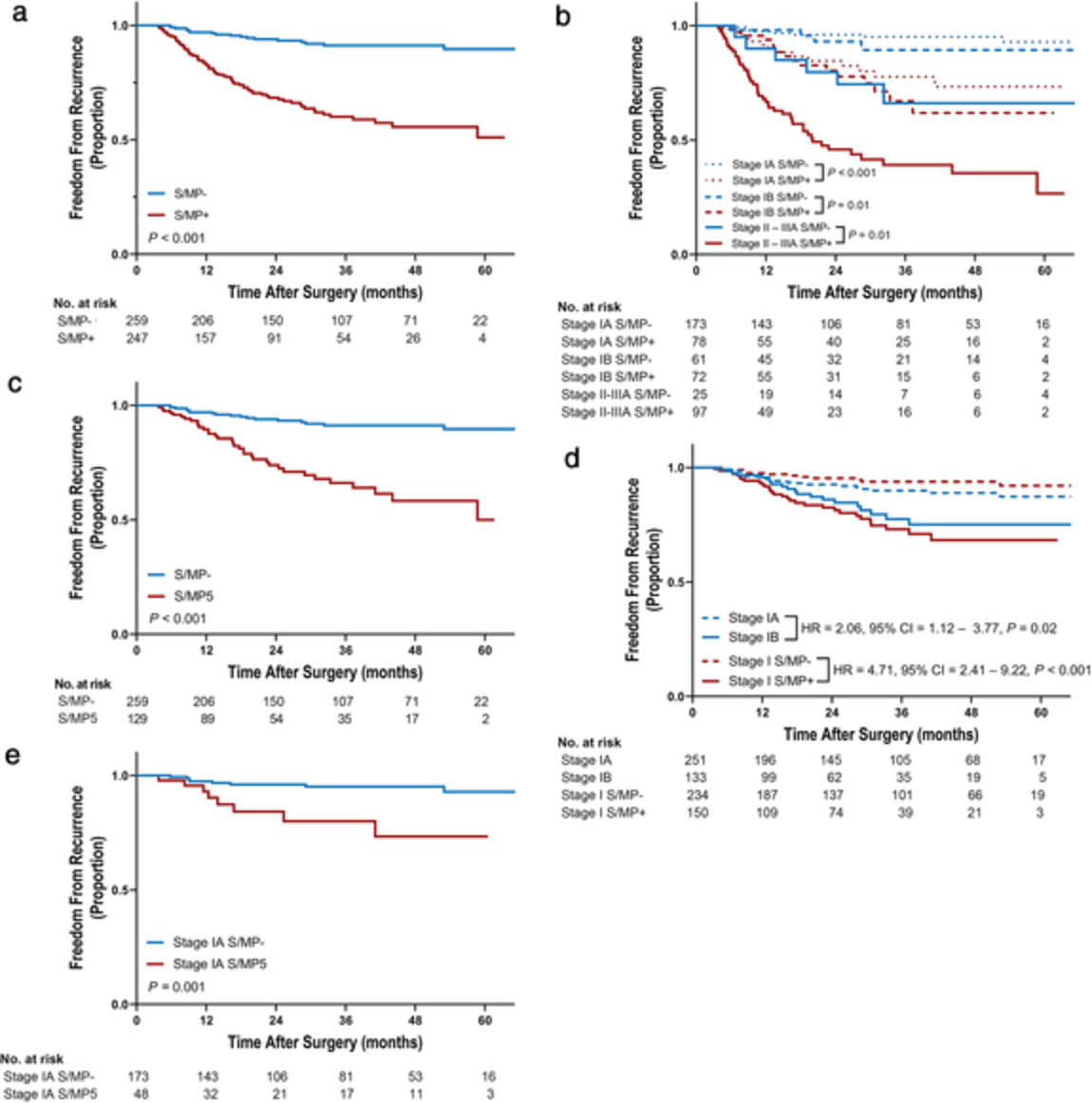
We demonstrated that only minimal presence of solid or micropapillary component was profoundly associated with aggressive clinicopathological features and poor prognosis after complete resection even in stage IA lung adenocarcinoma.
Our results suggest that minimal presence of these subtypes is a strong prognostic factor which should be taken into account in the risk assessment for adjuvant chemotherapy in lung adenocarcinoma.
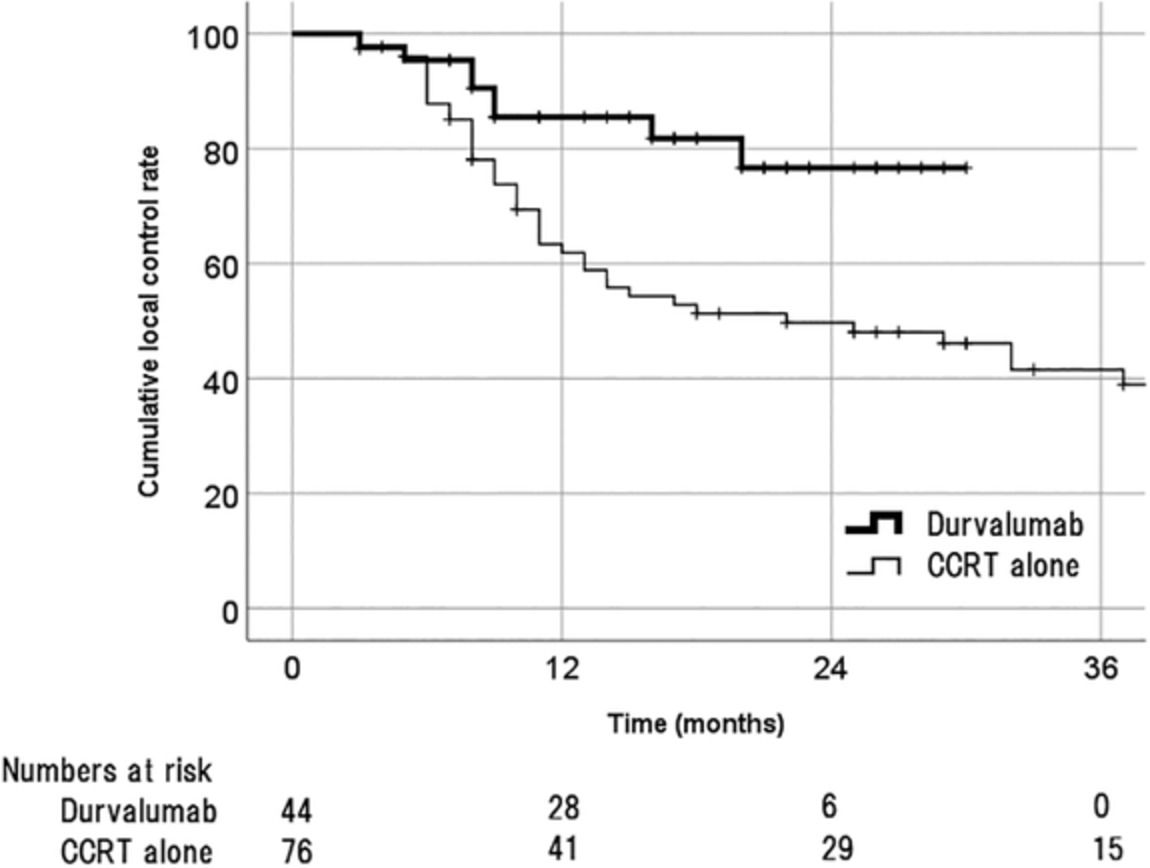
Effect of durvalumab on local control after concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer in comparison with chemoradiotherapy alone
- Pages: 245-250
- First Published: 01 December 2020
Comparison of adequacy between transbronchial lung cryobiopsy samples and endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration samples for next-generation sequencing analysis
- Pages: 251-258
- First Published: 03 December 2020
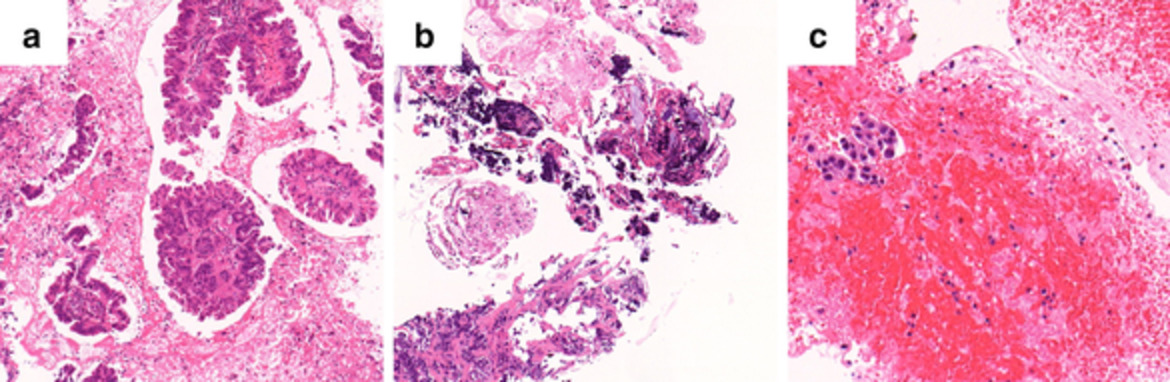
The adequacy for next generation sequencing (NGS) in transbronchial lung cryobiopsy (TBLC) and endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA) samples remains unclear. We found the mean number of genes which could not be assessed via NGS was significantly lower in TBLC samples than EBUS-TBNA samples. TBLC could obtain adequate samples with a high concentration of uncrushed tumor cells for NGS.
CASE REPORTS
Complete response of squamous cell carcinoma of the lung following treatment with pembrolizumab in an elderly patient: A case report
- Pages: 259-263
- First Published: 10 November 2020
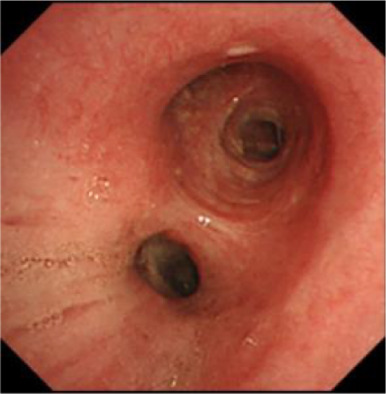
Here, we present a case of an elderly patient who had a complete response of non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) following treatment with pembrolizumab. The complete response was maintained for one and a half years after discontinuation of two years of treatment. In elderly patients with NSCLC with PD-L1 expression of more than 50%, pembrolizumab should be considered as first-line treatment with the treatment period, and mechanism suggested in this report.
Anti-PD-1 therapy plus chemotherapy showed superior and durable survival benefit in a patient with small cell esophageal cancer: A case report
- Pages: 264-267
- First Published: 11 November 2020
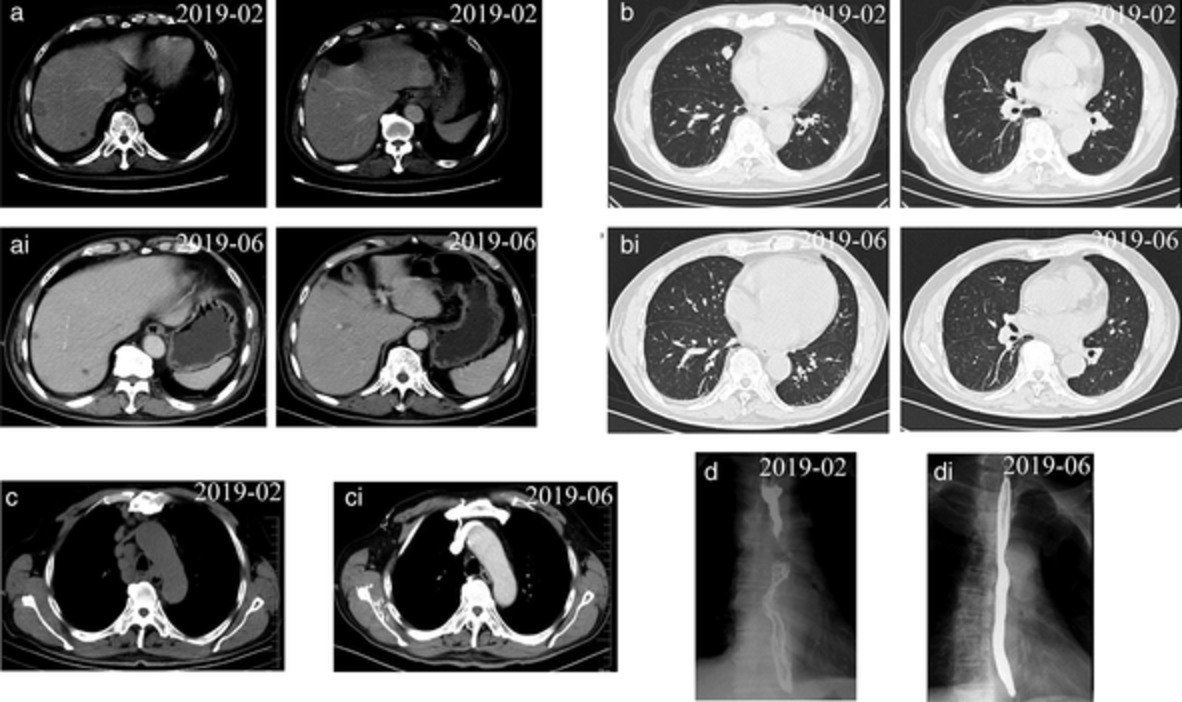
Treatment strategy for primary lung cancer in a lung highly compressed by giant emphysematous bullae: A case report
- Pages: 268-271
- First Published: 11 November 2020
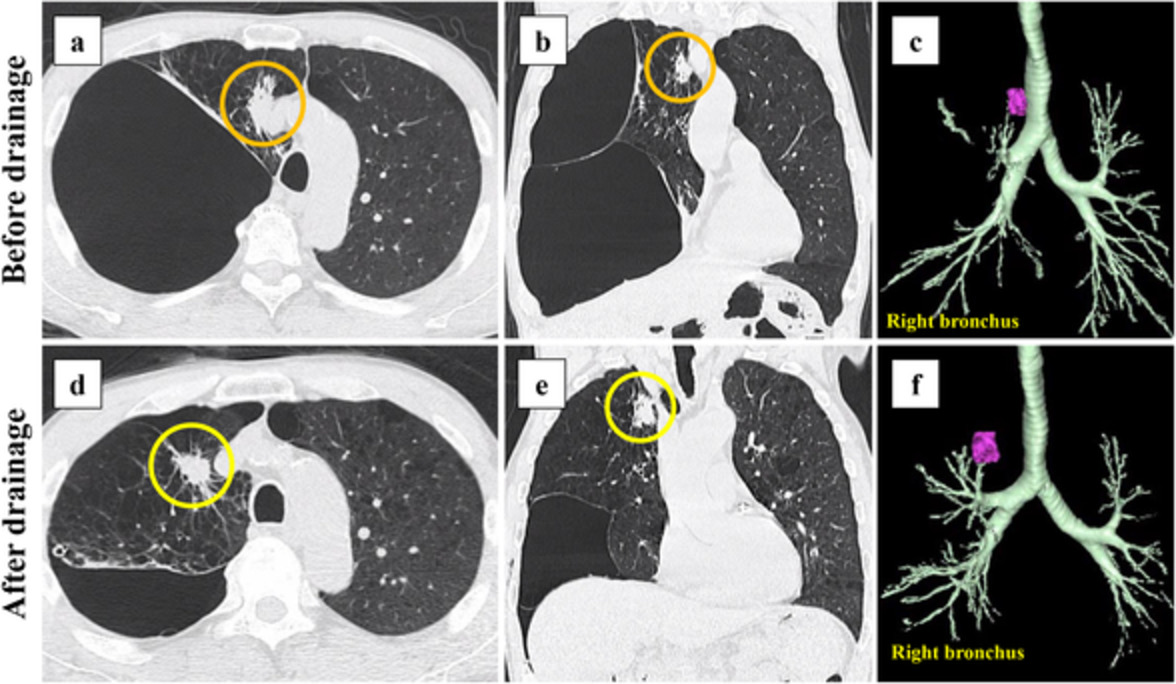
Lung cancer that develops in lung tissue highly compressed by a giant emphysematous bulla is rare, and is difficult to diagnose. After performing intracavity drainage of a giant emphysematous bulla, the remaining lung re-expands and the bronchial shift improves; subsequently, bronchoscopy makes it possible to diagnose lung cancer in the remaining lung.
Dabrafenib and trametinib therapy in an elderly patient with non-small cell lung cancer harboring the BRAF V600E mutation
- Pages: 272-276
- First Published: 20 November 2020
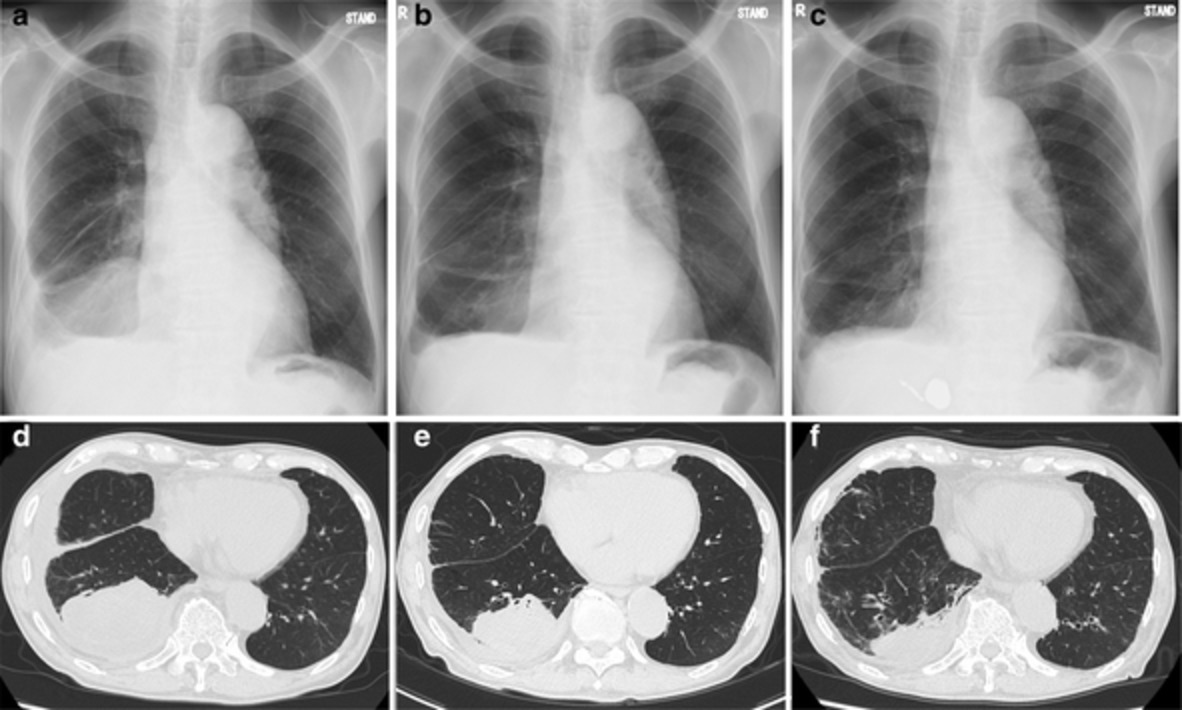
An 86-year-old male patient, who had been diagnosed with lung adenocarcinoma with BRAF V600E mutation, received dabrafenib and trametinib combination chemotherapy. The tumor shrunk rapidly; however, therapy was discontinued after 40 days because adverse events (hypoalbuminemia, peripheral edema, and pneumonia) developed. Although this targeted combination therapy seemed to cause relatively severe adverse events compared with single-agent targeted therapy in this “oldest old” elderly patient, the marked tumor shrinkage prolonged the patient's life and helped him to maintain a good general condition.