Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Preoperative assessment for minimally invasive lung surgery: Need an update?
- Pages: 3-4
- First Published: 19 November 2020
COMMENTARY
Single-cell transcriptome analysis of tumor-infiltrating B cells reveals their clinical implications in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 5-7
- First Published: 29 October 2020
MINI REVIEW
Diagnostic value of microRNAs for malignant pleural mesothelioma: A mini-review
- Pages: 8-12
- First Published: 22 November 2020
Malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) is a type of cancer originating from the pleura with high aggressiveness and poor prognosis, Laboratory biomarkers have significant advantages of reduced invasiveness, low cost, and are observer-independent, and therefore represent a promising diagnostic tool for MPM. Here, we reviewed the diagnostic value of microRNA for MPM.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
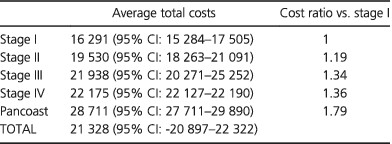
Estimated direct costs of non-small cell lung cancer by stage at diagnosis and disease management phase: A whole-disease model
- Pages: 13-20
- First Published: 21 November 2020
Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery lobectomy might be a feasible alternative for surgically resectable pathological N2 non-small cell lung cancer patients
- Pages: 21-29
- First Published: 18 November 2020
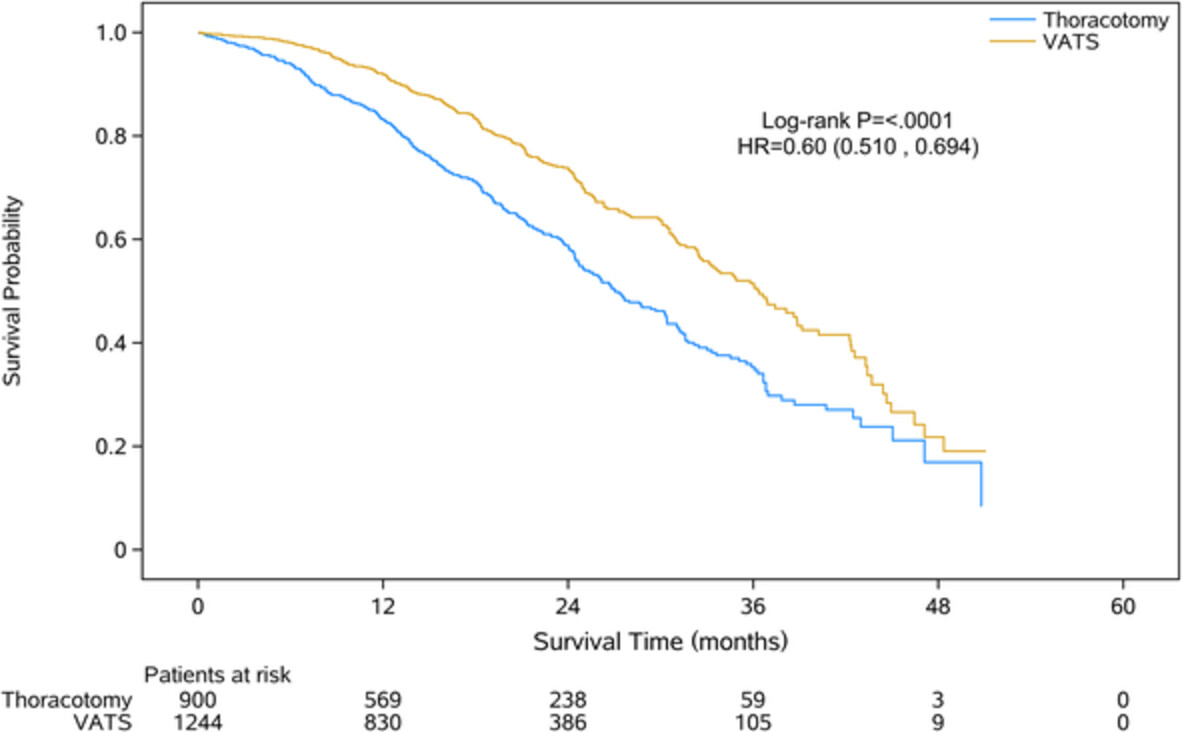
The present study aimed to investigate the clinical outcome of video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) versus open lobectomy for pathological N2 non-small cell lung cancer (pN2 NSCLC) using a large cohort of Chinese patients in real world conditions. VATS lobectomy might be a feasible alternative for pN2 NSCLC.
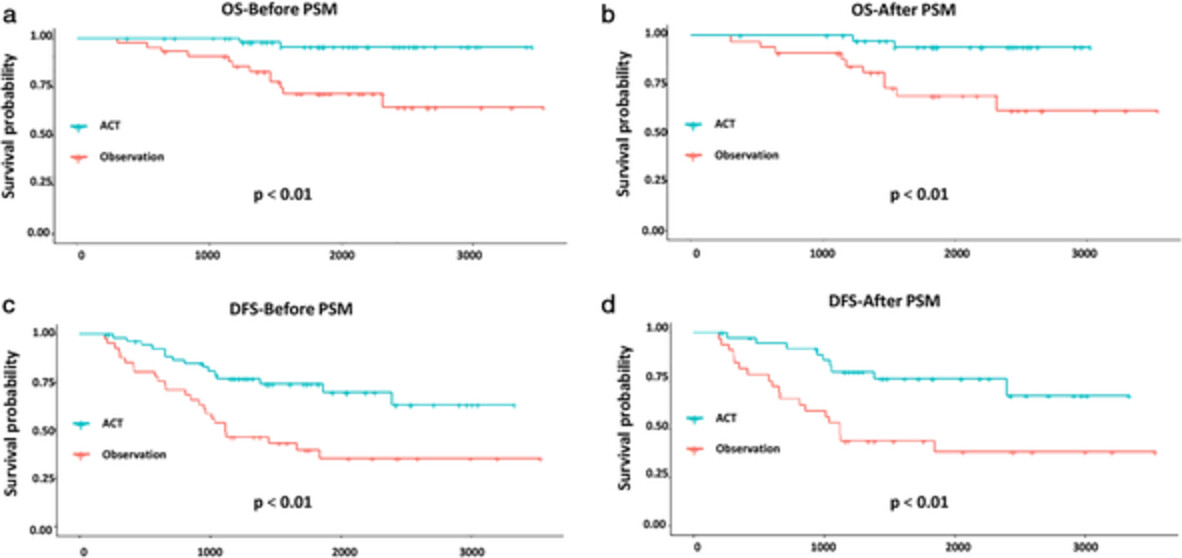
Influence of adjuvant chemotherapy on survival for patients with stage IB and IIA non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 30-39
- First Published: 27 October 2020
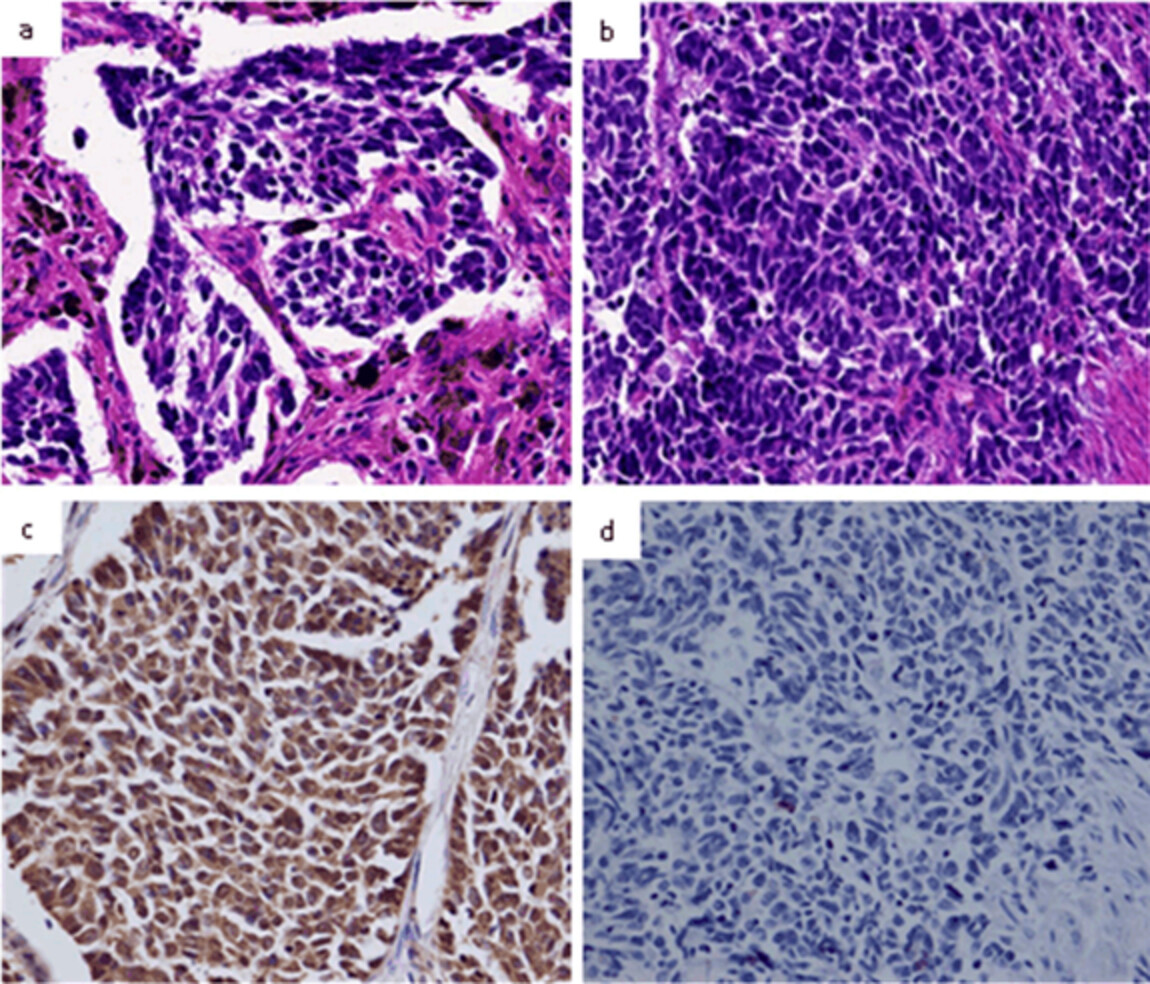
Clinicopathological features and prognostic implications of ASCL1 expression in surgically resected small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 40-47
- First Published: 15 November 2020
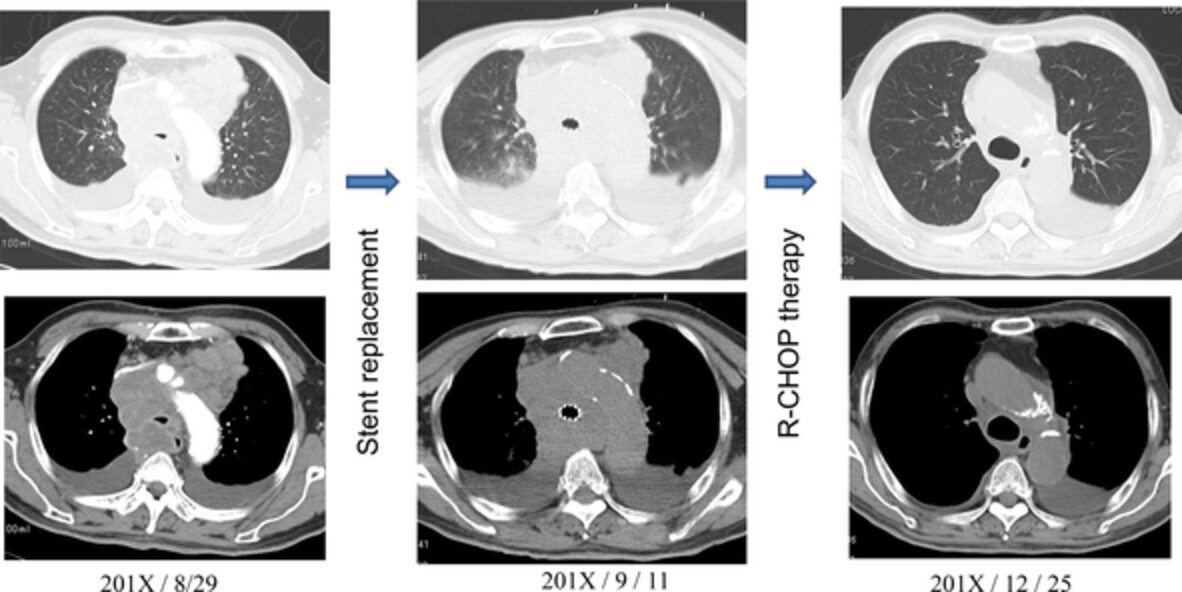
Clinical outcomes and survival following placement of self-expandable metallic stents for central airway stenosis and fistula
- Pages: 48-56
- First Published: 12 November 2020
Clinical characteristics and risk factors for in-hospital mortality of lung cancer patients with COVID-19: A multicenter, retrospective, cohort study
- Pages: 57-65
- First Published: 03 November 2020
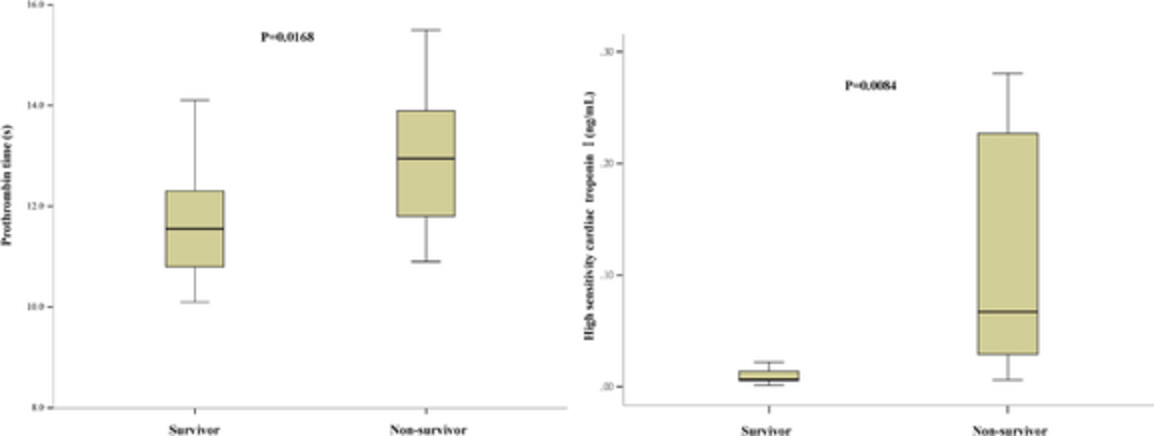
Lung cancer patients with COVID-19 have high in-hospital mortality with unique early symptoms and imaging features. Prolonged PT and elevated hs-TNI are independent risk factors for in-hospital mortality of lung cancer patients with COVID-19. They may be used to help clinicians predict prognosis at an early stage for lung cancer patients with COVID-19.
Metagenome association study of the gut microbiome revealed biomarkers linked to chemotherapy outcomes in locally advanced and advanced lung cancer
- Pages: 66-78
- First Published: 27 October 2020
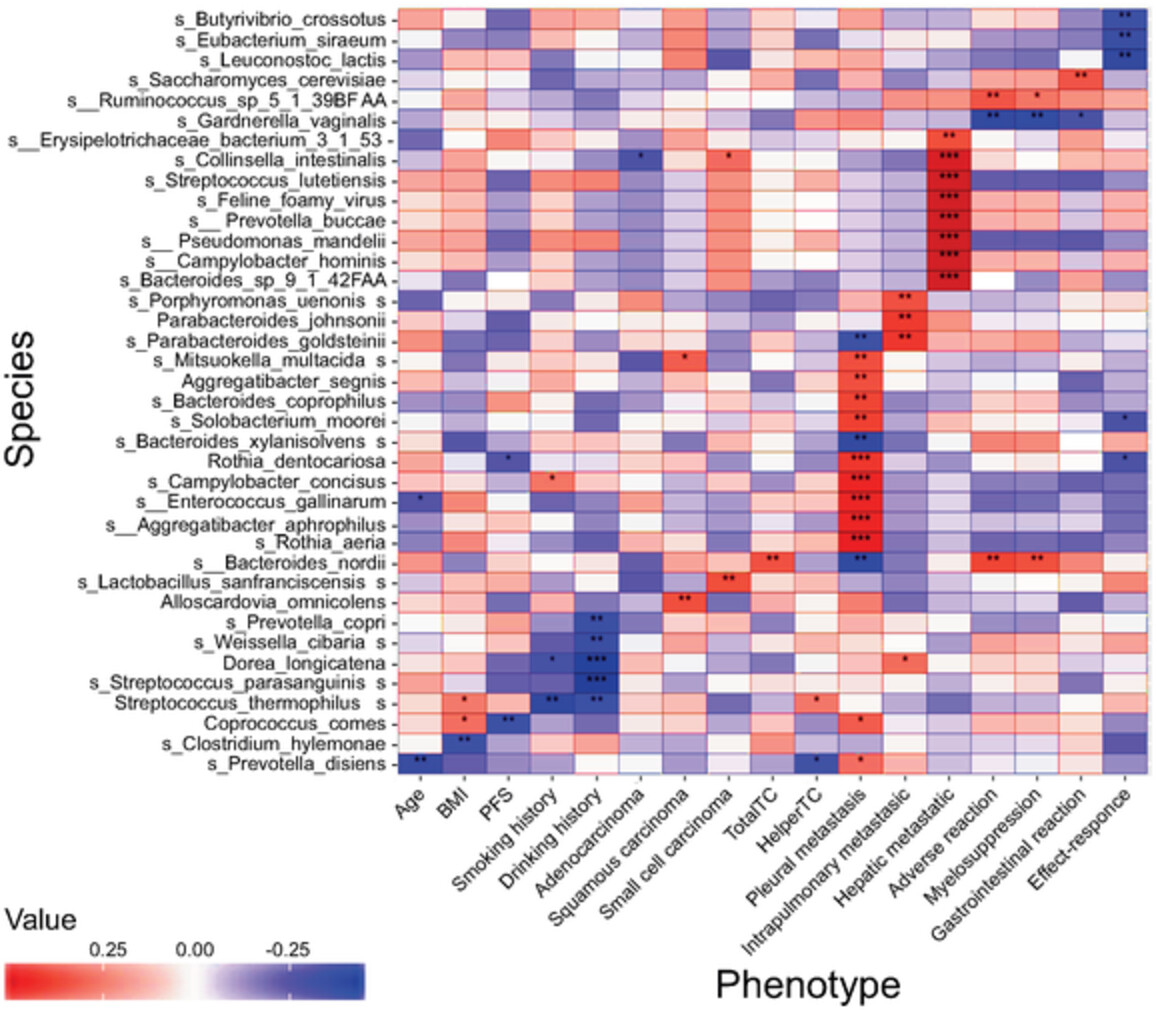
We describe a metagenome association study in lung cancer patients that analyzed the influence of the gut microbiome on chemotherapy outcomes, which is the first report of these associations. We found that certain specific bacterial species were associated with chemotherapy efficacy or lack thereof, and clinical indicators. Moreover, we showed an association between bacterial metabolic pathways and clinical outcomes. Our results indicate that certain bacterial species can be used as biomarkers for prediction of chemotherapy efficacy in lung cancer.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
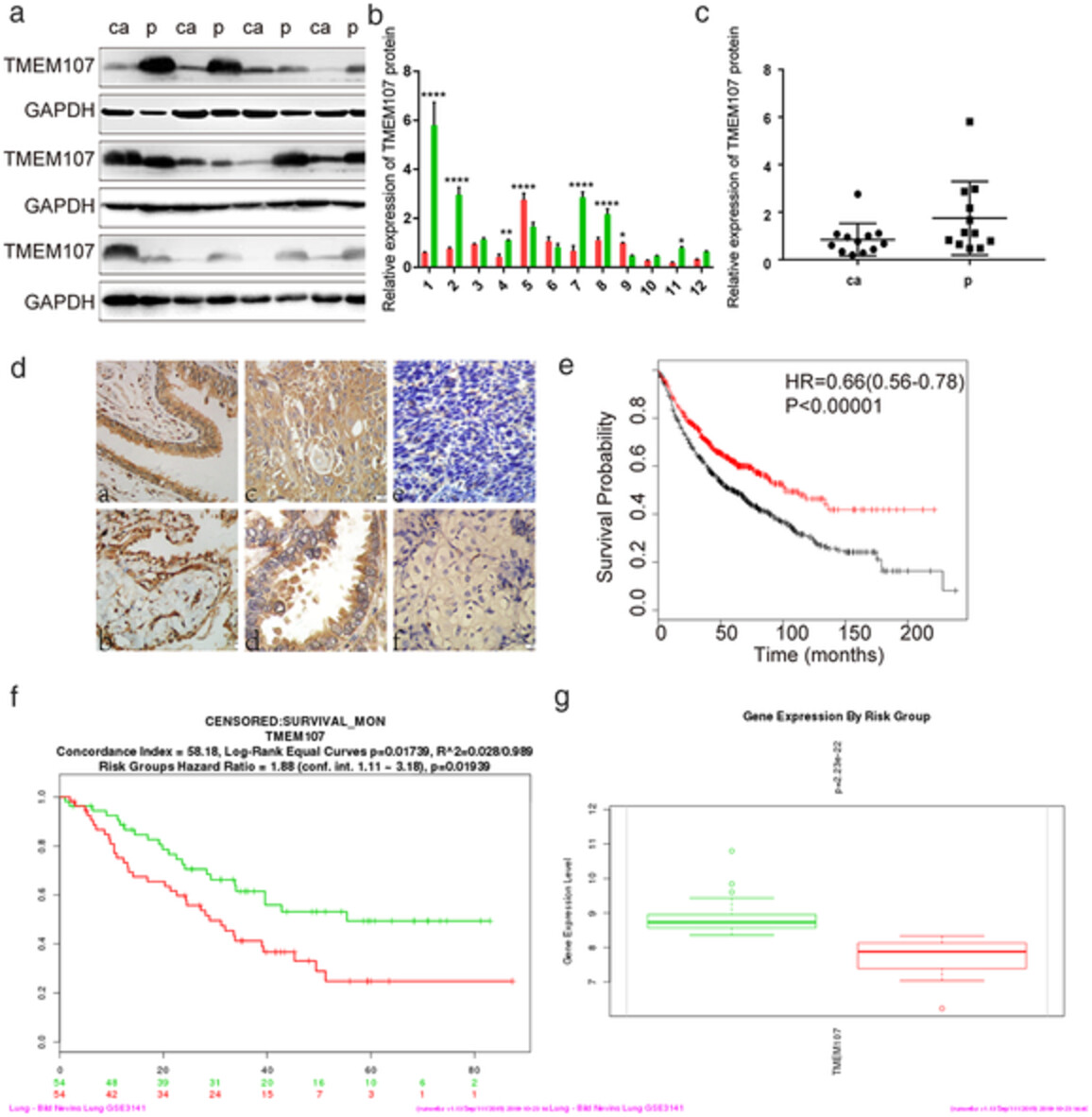
RETRACTED: TMEM107 inhibits EMT and invasion of NSCLC through regulating the Hedgehog pathway
- Pages: 79-89
- First Published: 29 October 2020
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Effectiveness of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients with uncommon EGFR mutations: A multicenter observational study
- Pages: 90-96
- First Published: 29 October 2020
Predictors of survival among Japanese patients receiving first-line chemoimmunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 97-105
- First Published: 30 October 2020
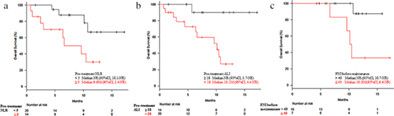
Immunological and nutritional markers could be useful for predicting the outcomes of first-line chemoimmunotherapy for Japanese patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Overall survival was significantly associated with the pretreatment values for the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and advanced lung cancer inflammation index, as well as the prognostic nutrition index at the end of induction therapy.
Thymoma-associated myasthenia gravis: Clinical features and predictive value of antiacetylcholine receptor antibodies in the risk of recurrence of thymoma
- Pages: 106-113
- First Published: 03 November 2020
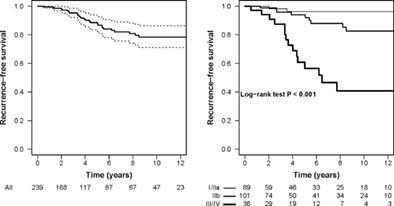
In our paper, we retrospectively analyzed the changes in antiacetylcholine receptor antibody (AChR-Ab) titer before and after thymectomy and the clinical features of thymoma-associated myasthenia gravis (TAMG) patients in order to identify clinical and serological predictors of thymoma recurrence. Our study emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach among Neurologists, Oncologists and Thoracic Surgeons, and identifies subgroups of MG patients with high risk of thymoma recurrence who therefore need a more accurate follow-up.
CASE REPORTS
Remarkable response to dacomitinib in a patient with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis due to EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 114-116
- First Published: 28 October 2020
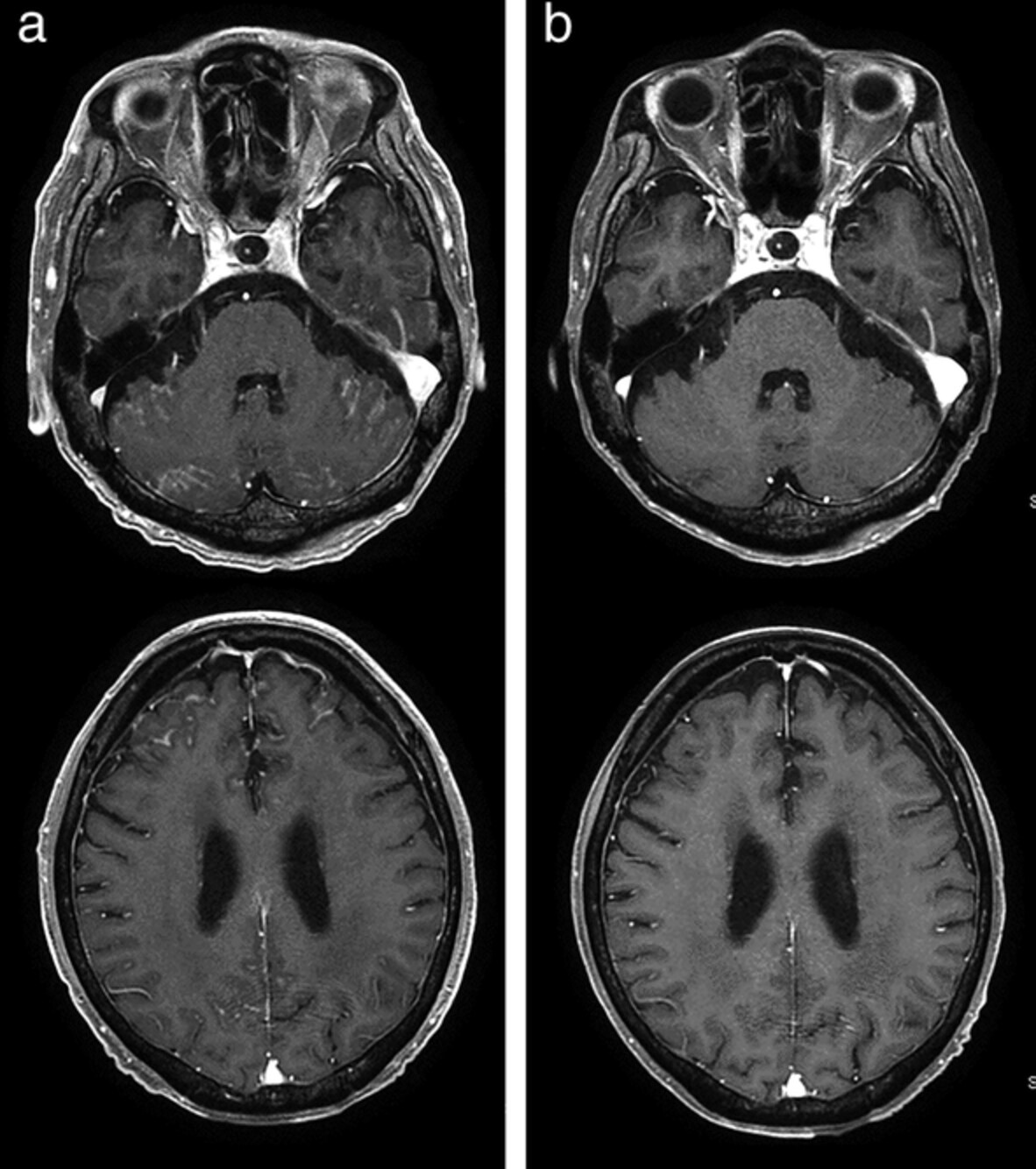
Although dacomitinib is a standard therapeutic option for patients with EGFR-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), its efficacy in patients with CNS lesions is unclear. Here, we describe a case of EGFR-mutant NSCLC with leptomeningeal carcinomatosis that was successfully treated with dacomitinib.
Generalized herpes zoster and cutaneous metastasis during chemotherapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A case report
- Pages: 117-121
- First Published: 28 October 2020
Total minimally invasive McKeown esophagectomy in an esophageal cancer patient with situs inversus totalis: A case report
- Pages: 122-127
- First Published: 05 November 2020
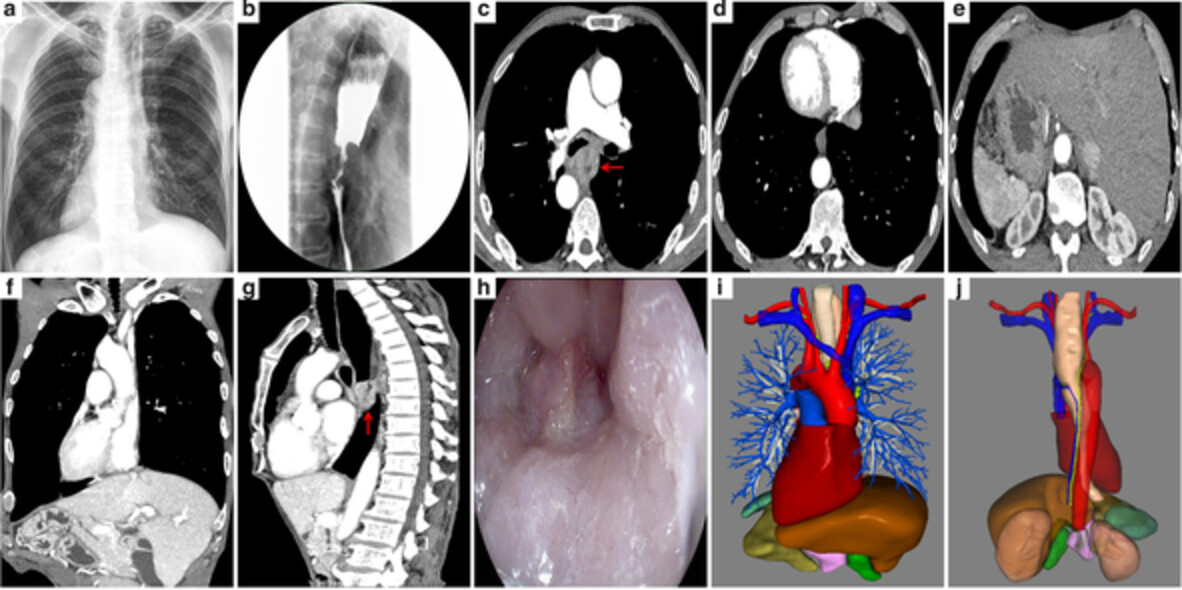
Situs inversus totalis (SIT) is an extremely rare anomaly characterized by a left-to-right reversal of all the thoracic and abdominal organs. Only 11 cases of esophageal cancer with SIT have been reported worldwide, most of which underwent hybrid minimally invasive esophagectomy (MIE) but not total MIE. Here we report a case of esophageal cancer with SIT successfully treated by total MIE, with right lateral-prone position adopted during the thoracic procedure.
Rare case of apatinib acquired resistance induced by point mutation of WRN p.V697F through activation of the PI3K/AKT apoptosis-inhibiting pathway
- Pages: 128-132
- First Published: 22 November 2020
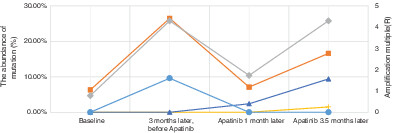
Our research group recently treated a 50-year-old female patient with multiple chemotherapy-resistant, poorly differentiated lung squamous cell carcinoma. After multiple treatment attempts and regression events, the patient was treated with apatinib, which resulted in the development of a novel mutation and treatment resistance. We believe that this report will be of interest to the readership because it expands the known repertoire of mutations that can occur in lung cancer after various treatments, particularly following treatment with apatinib.
Lung adenocarcinoma with repetitive endotracheal/endobronchial metastasis 20 years after surgery: A case report
- Pages: 133-136
- First Published: 14 November 2020
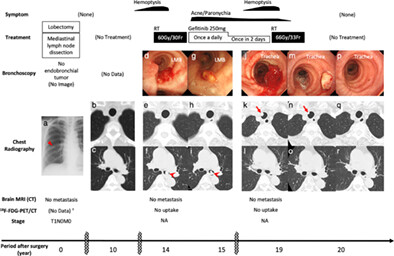
This is the first reported case of repetitive localized endotracheal/endobronchial metastasis of primary lung adenocarcinoma with mild lymphatic invasion that occurred twice over a 20-year period after complete resection. Observation of the trachea/bronchus over a long period post operation could be important in monitoring for endotracheal/endobronchial metastasis, particularly if lymphatic invasion is confirmed in the primary tumor.
IMAGING IN THORACIC CANCER
Novel device to prevent droplets in bronchoscopy during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic
- Pages: 137-139
- First Published: 04 November 2020
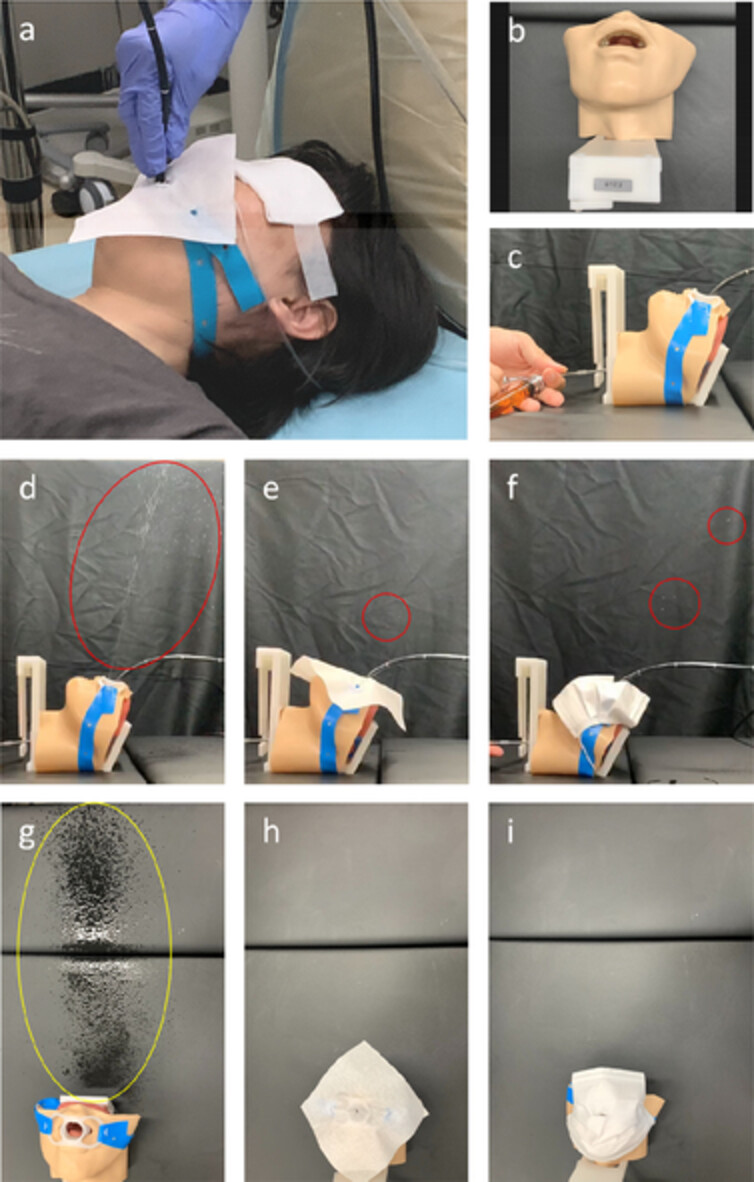
We modified the method of protection to reduce the exposure of health-care workers (droplets) without restricting operability during bronchoscopy. Our method is inexpensive, simple, utilizes disposable materials and prevents interpatient infections. Its routine use during transoral bronchoscopy may be considered due to its simplicity.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Is the case really a SMARCA4-deficient thoracic sarcoma?
- Page: 140
- First Published: 19 October 2020
Response to ‘Is the case really a SMARCA4-deficient thoracic sarcoma?’
- Page: 141
- First Published: 18 November 2020