Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 16 April 2024

The cover image is based on the Commentary Non-scheduled short acting opioid to taper off opioids? by Renyu Liu et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.14705.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Molecular mechanism analyses of post-traumatic epilepsy and hereditary epilepsy based on 10× single-cell transcriptome sequencing technology
- First Published: 04 April 2024
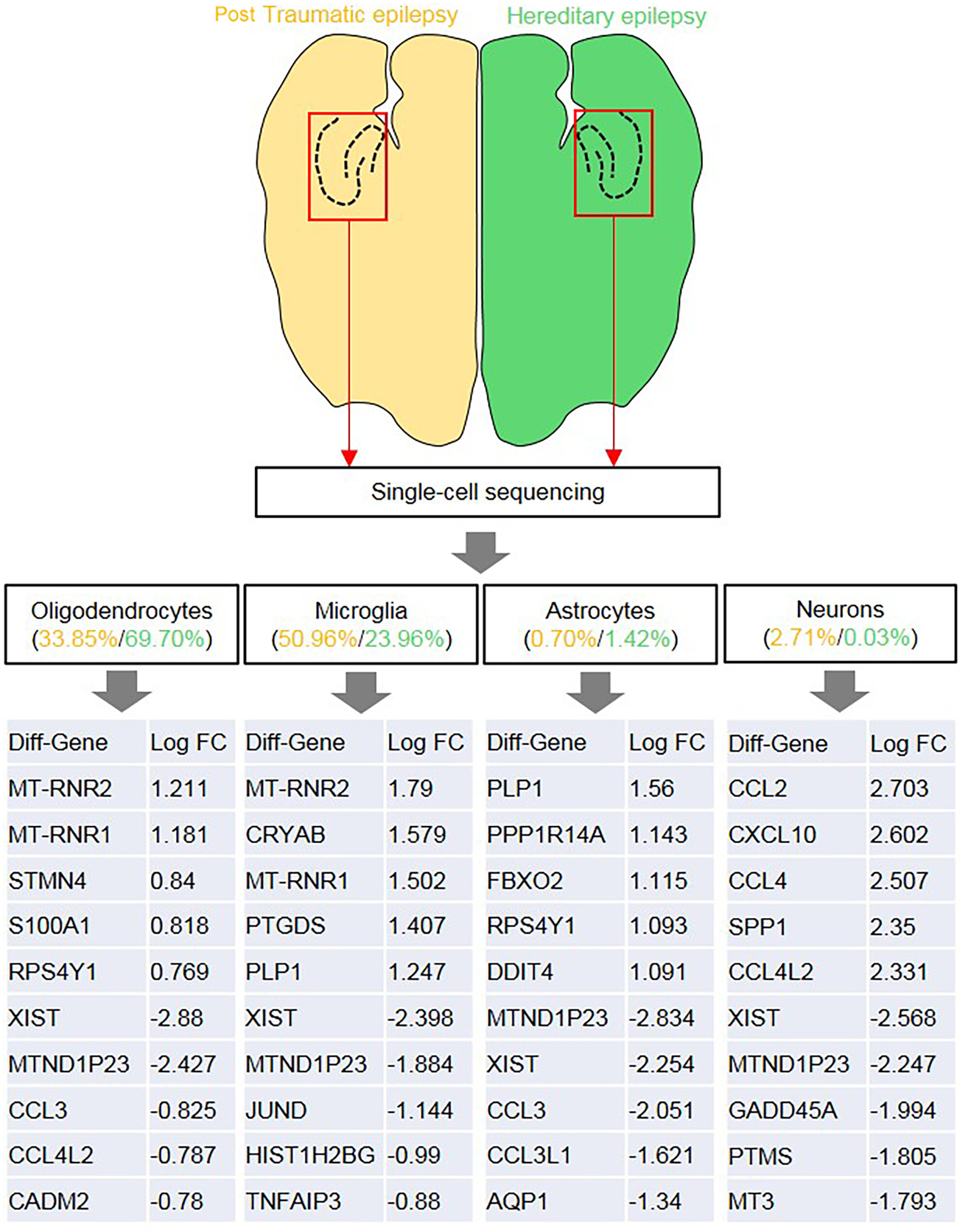
The reads obtained from 10× genomic platform of traumatic epilepsy and hereditary epilepsy were 39.56 M and 30.08 M. The Q30 of RNA reads over 91.6%. After filtering, 7479 traumatic epilepsy and 9357 hereditary epilepsy cells were left for further study. Over 96.4% of the reads are mapped to GRCh38/GRCm38. The cells were differentially distributed in two groups, with higher oligodendrocytes (6522 vs. 2532) and astrocytes (133 vs. 52), lower microglia (2242 vs. 3811) and neurons (3 vs. 203) were observed in hereditary epilepsy than traumatic epilepsy. The DEGs in four cell clusters were identified, with 25 in oligodendrocytes (13 upregulated and 12 downregulated), 87 in microglia (42 upregulated and 45 downregulated), 222 in astrocytes (115 upregulated and 107 downregulated), and 393 in neurons (305 upregulated and 88 downregulated). MTND1P23 (downregulated), XIST (downregulated), and RPS4Y1 (upregulated) were commonly expressed in four cell clusters. The DEGs in microglia and astrocytes were enriched in IL-17 signaling pathway. Our study explored the cell grouping between traumatic and hereditary epilepsy, and the transcriptome in different cells for the first time. Inflammatory and immune functions might be the main approaches in traumatic temporal lobe epilepsy of neurons.
SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a-PINK1-Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
- First Published: 04 April 2024
Stigmasterol alleviates neuropathic pain by reducing Schwann cell-macrophage cascade in DRG by modulating IL-34/CSF1R
- First Published: 04 April 2024
REVIEWS
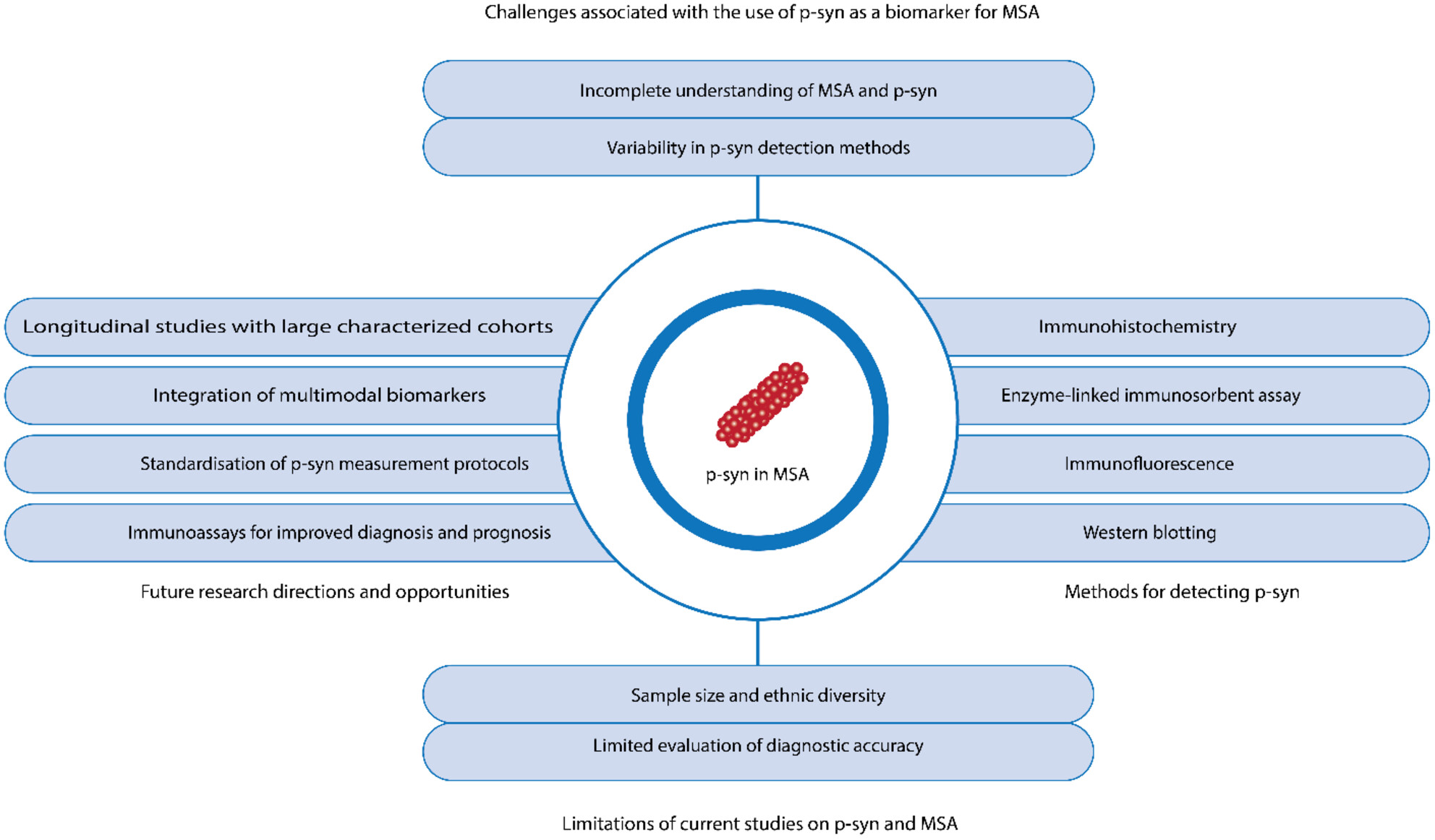
The potential of phosphorylated α-synuclein as a biomarker for the diagnosis and monitoring of multiple system atrophy
- First Published: 04 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
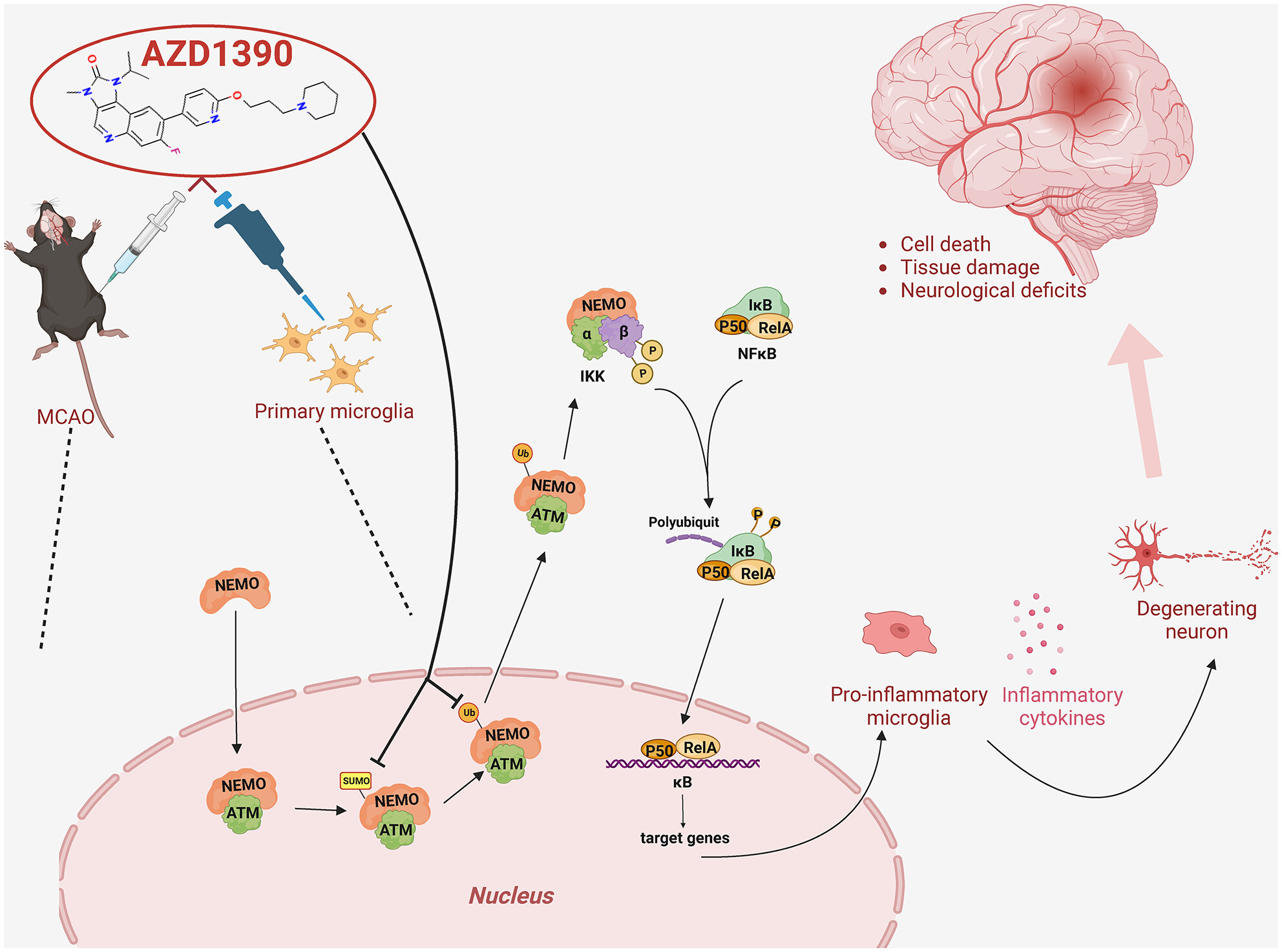
AZD1390, an ataxia telangiectasia mutated inhibitor, attenuates microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and ischemic brain injury
- First Published: 26 April 2024
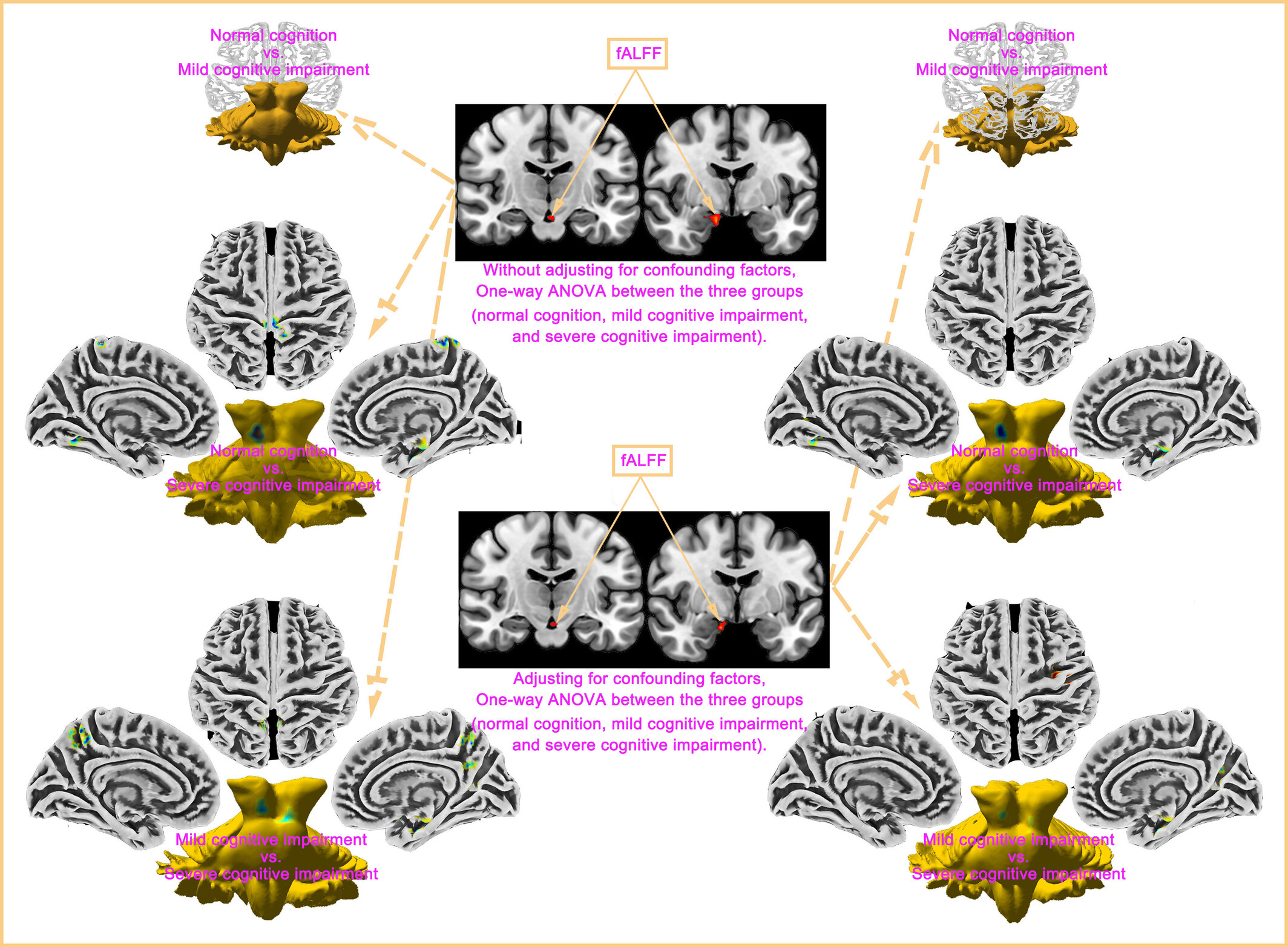
Spontaneous brain activity in the hippocampal regions could characterize cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 07 April 2024
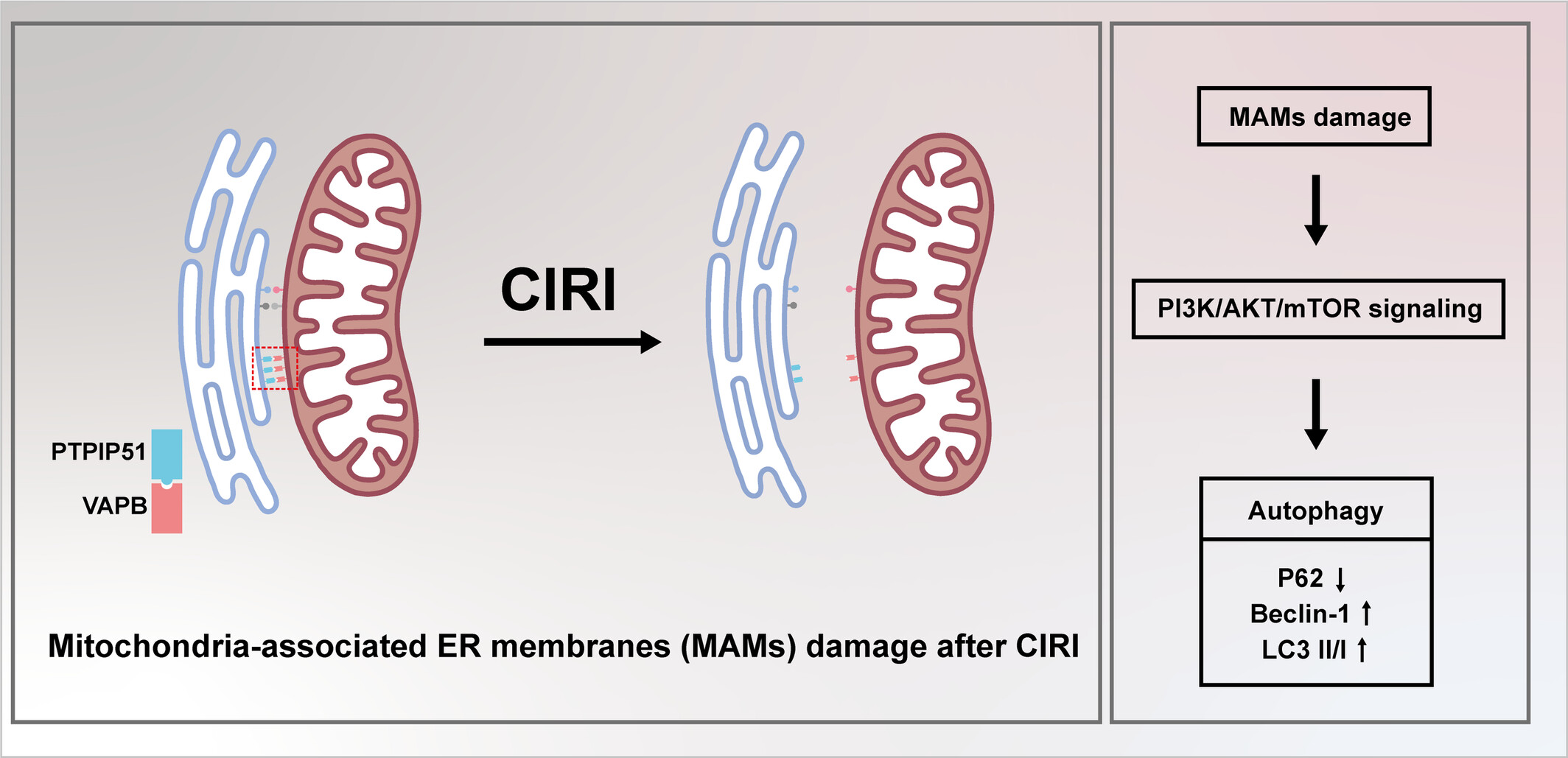
Mitochondria-associated endoplasmic reticulum membranes tethering protein VAPB-PTPIP51 protects against ischemic stroke through inhibiting the activation of autophagy
- First Published: 07 April 2024
REVIEWS
Deciphering the intricate linkage between the gut microbiota and Alzheimer's disease: Elucidating mechanistic pathways promising therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 07 April 2024
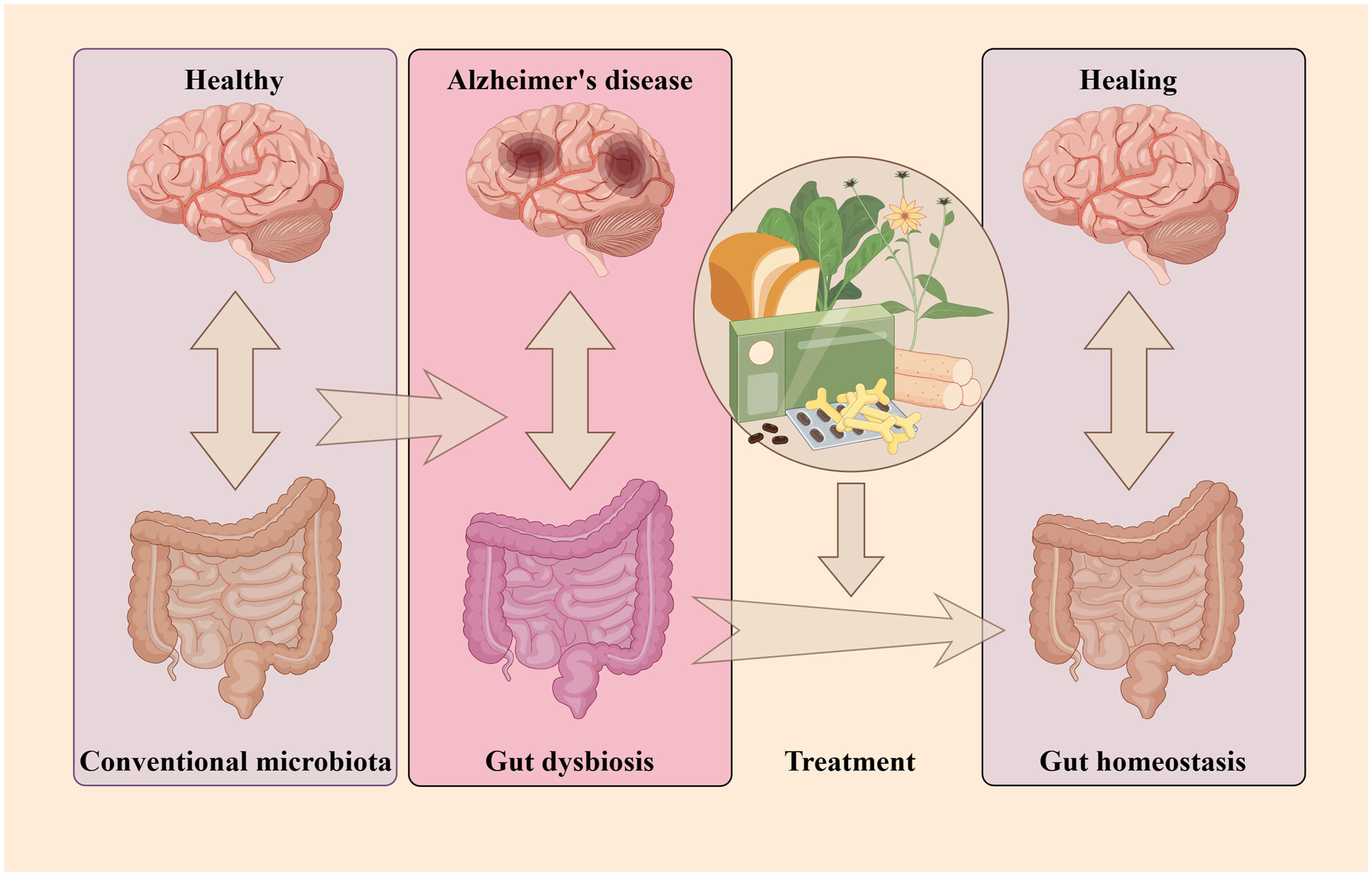
This review delves into the intricate relationship between the gut microbiota and Alzheimer's disease (AD), unraveling the close association between microbial changes and disease mechanisms. By elucidating relevant pathways, we present promising therapeutic strategies involving the modulation of the gut microbiota, opening new avenues for innovative treatments in AD. Graphical Abstract created By Figdraw.
EDITORIAL COMMENTARY
Non-scheduled short-acting opioid to taper off opioids?
- First Published: 07 April 2024
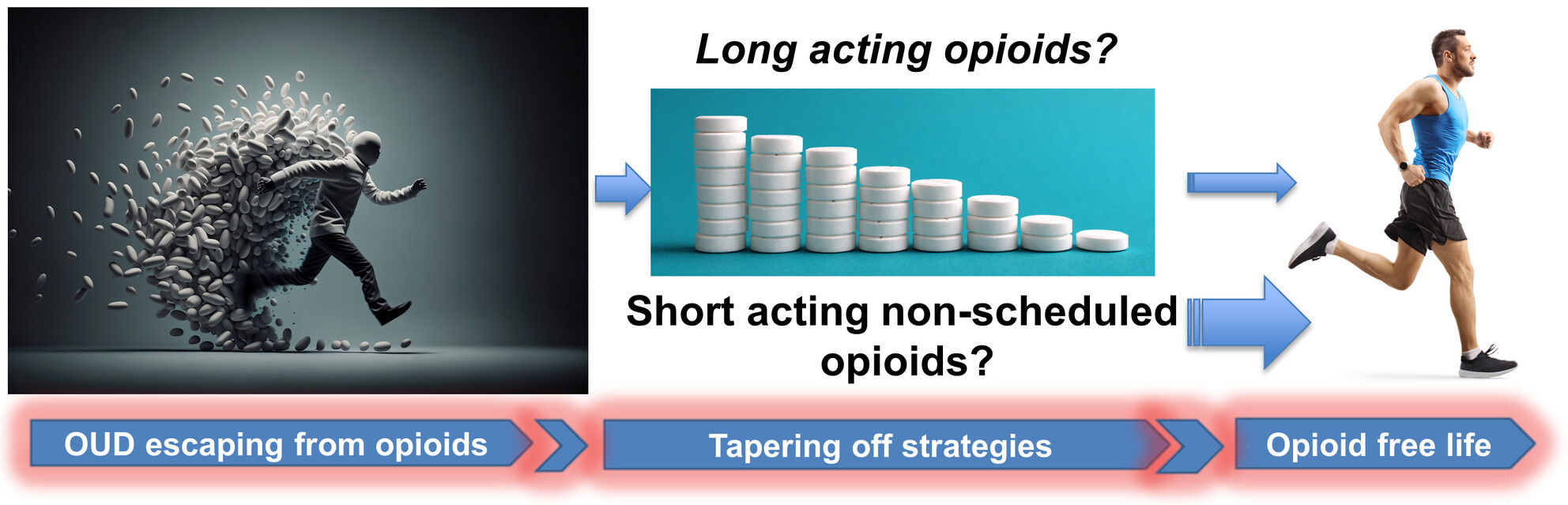
In this perspective, we are proposing to introduce a non-scheduled short-acting opioid into clinical practice given the significant need to find alternatives to taper off opioids and bridge buprenorphine and methadone therapies for opioid use disorders. Dezocine, a previously FDA approved non-scheduled opioid for pain management, is a potential candidate to explore. Dr. Renyu Liu obtained the images presented in this graphic abstract from Adobe Stock with standard licenses.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
DMT1 ubiquitination by Nedd4 protects against ferroptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage
- First Published: 18 April 2024
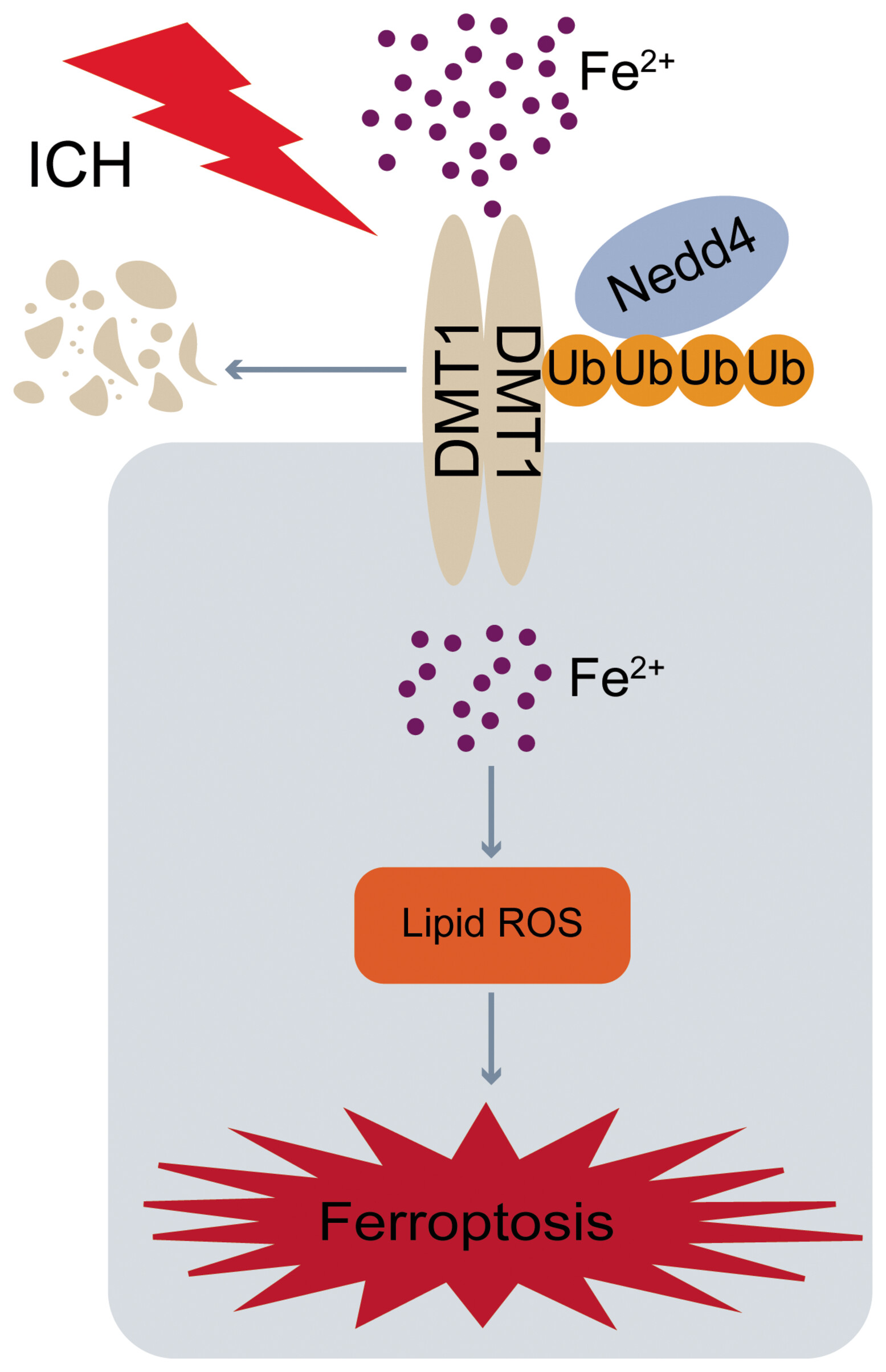
Upon ICH, the brain's DMT1 increased but decreased with Lentivirus-induced Nedd4 overexpression, implying a negative correlation. Nedd4 interacted with DMT1 at lysine residues 6, 69, and 277, resulting in ubiquitination and degradation of DMT1. Nedd4 overexpression relieved ferroptosis and aided ICH recovery, as indicated by functional analysis.
REVIEWS
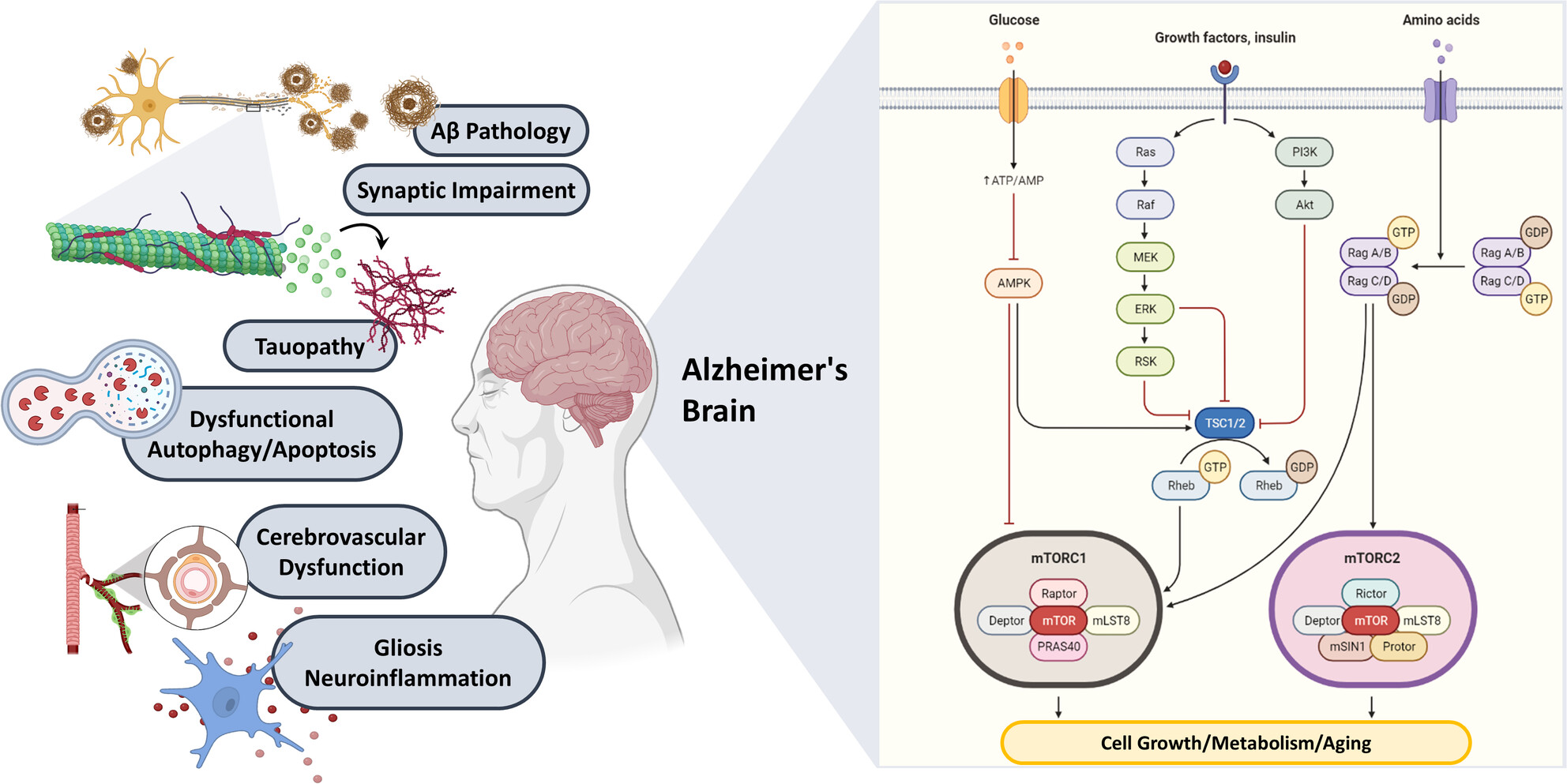
mTOR signaling and Alzheimer's disease: What we know and where we are?
- First Published: 18 September 2023
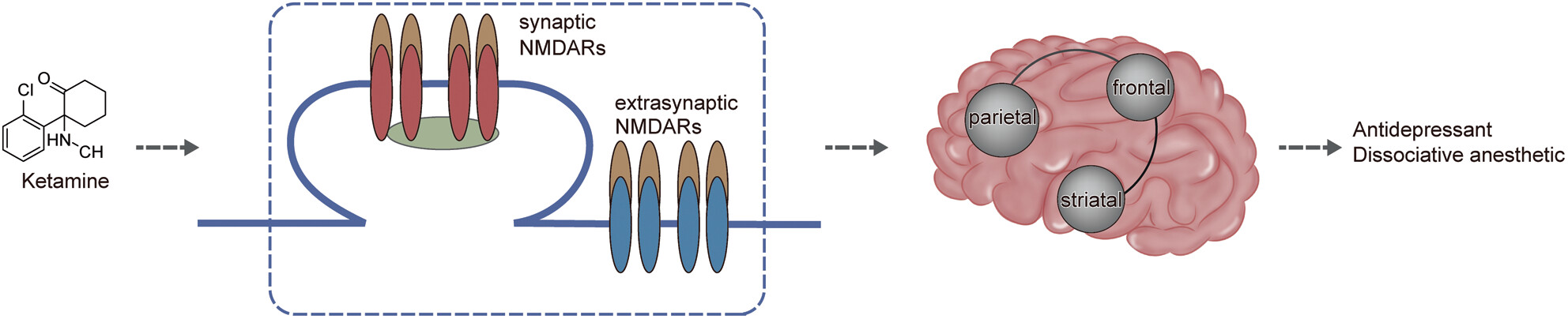
The role of NMDARs in the anesthetic and antidepressant effects of ketamine
- First Published: 07 September 2023
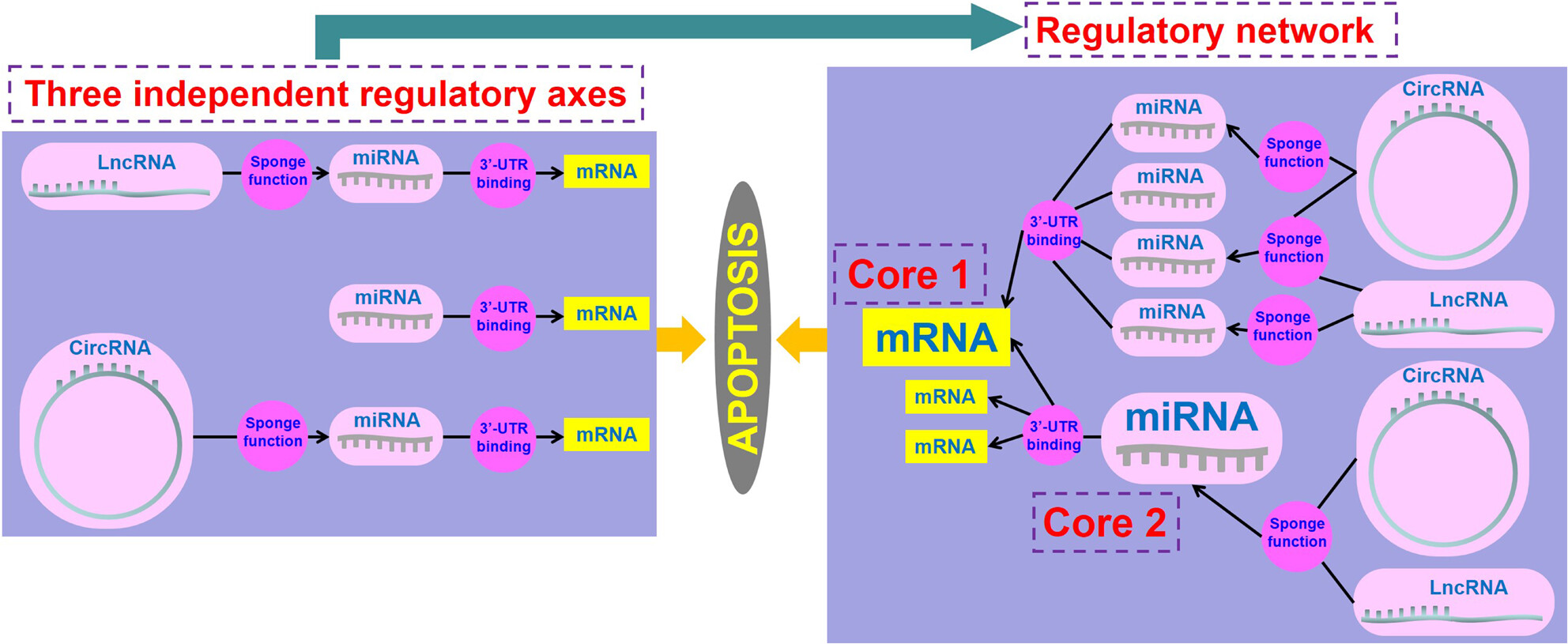
NcRNAs: A synergistically antiapoptosis therapeutic tool in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 22 September 2023
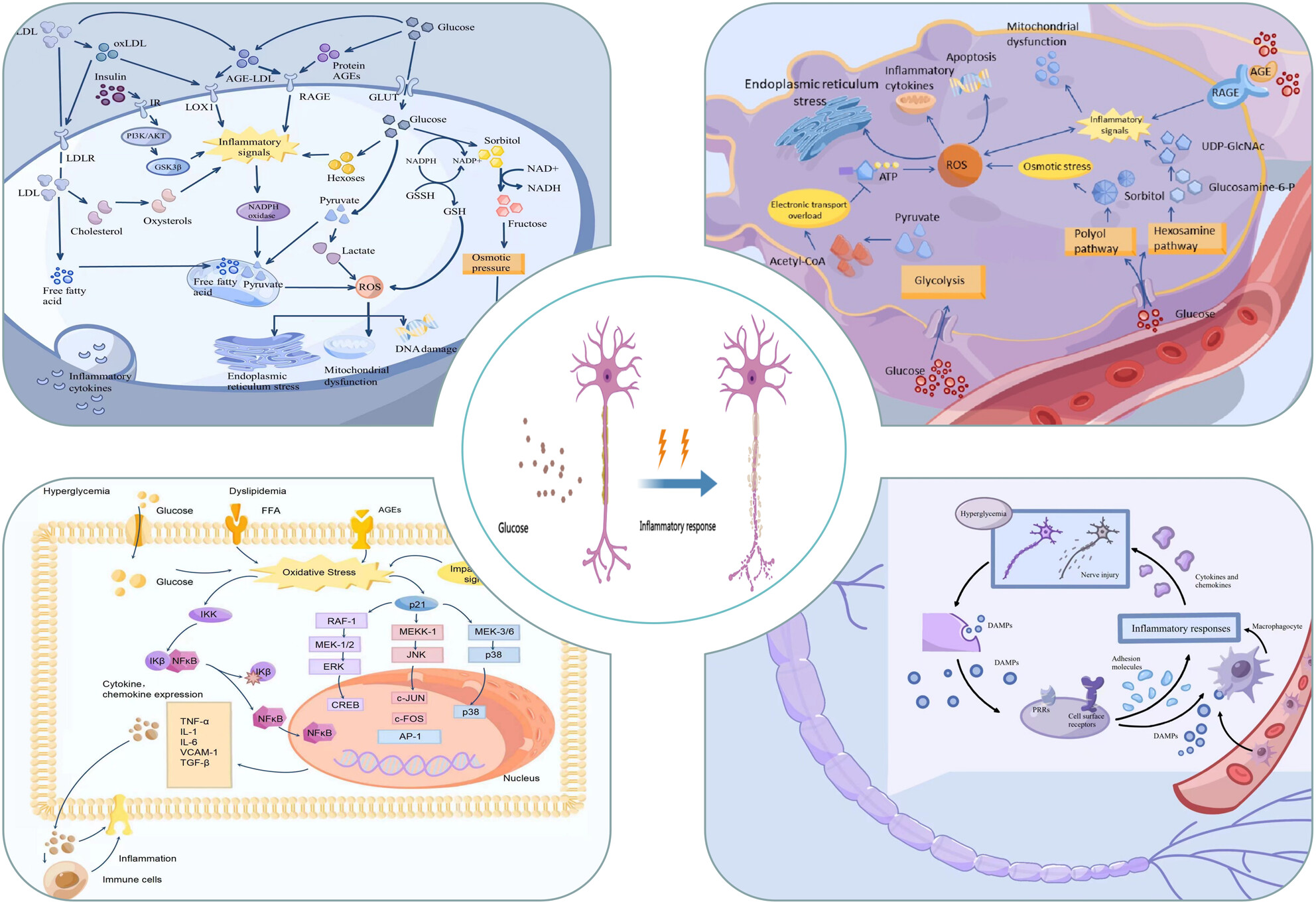
How inflammation dictates diabetic peripheral neuropathy: An enlightening review
- First Published: 05 October 2023
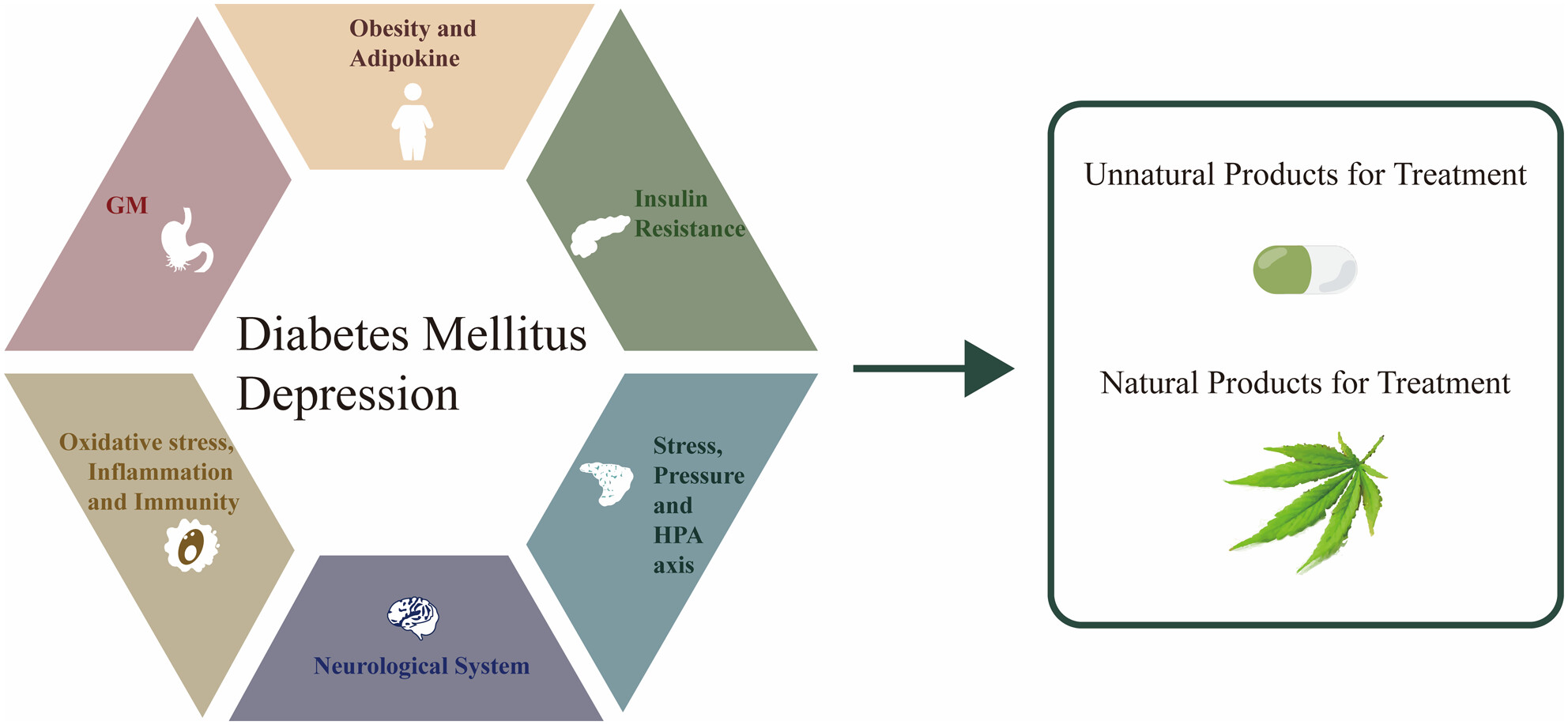
Neurological and metabolic related pathophysiologies and treatment of comorbid diabetes with depression
- First Published: 06 November 2023
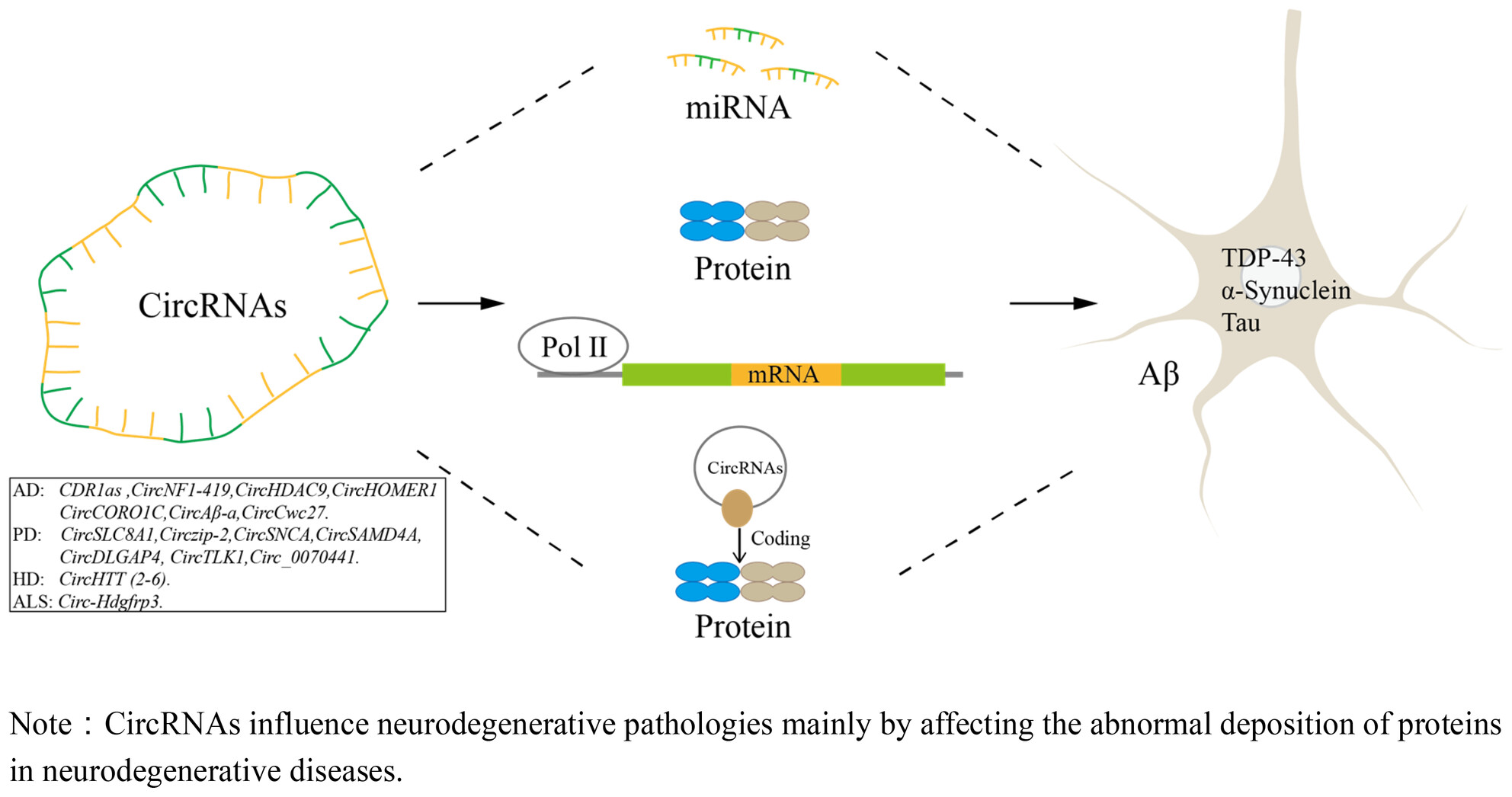
Regulatory mechanism of circular RNAs in neurodegenerative diseases
- First Published: 21 October 2023
The regulatory role and clinical application prospects of circRNA in the occurrence and development of CNS tumors
- First Published: 12 November 2023
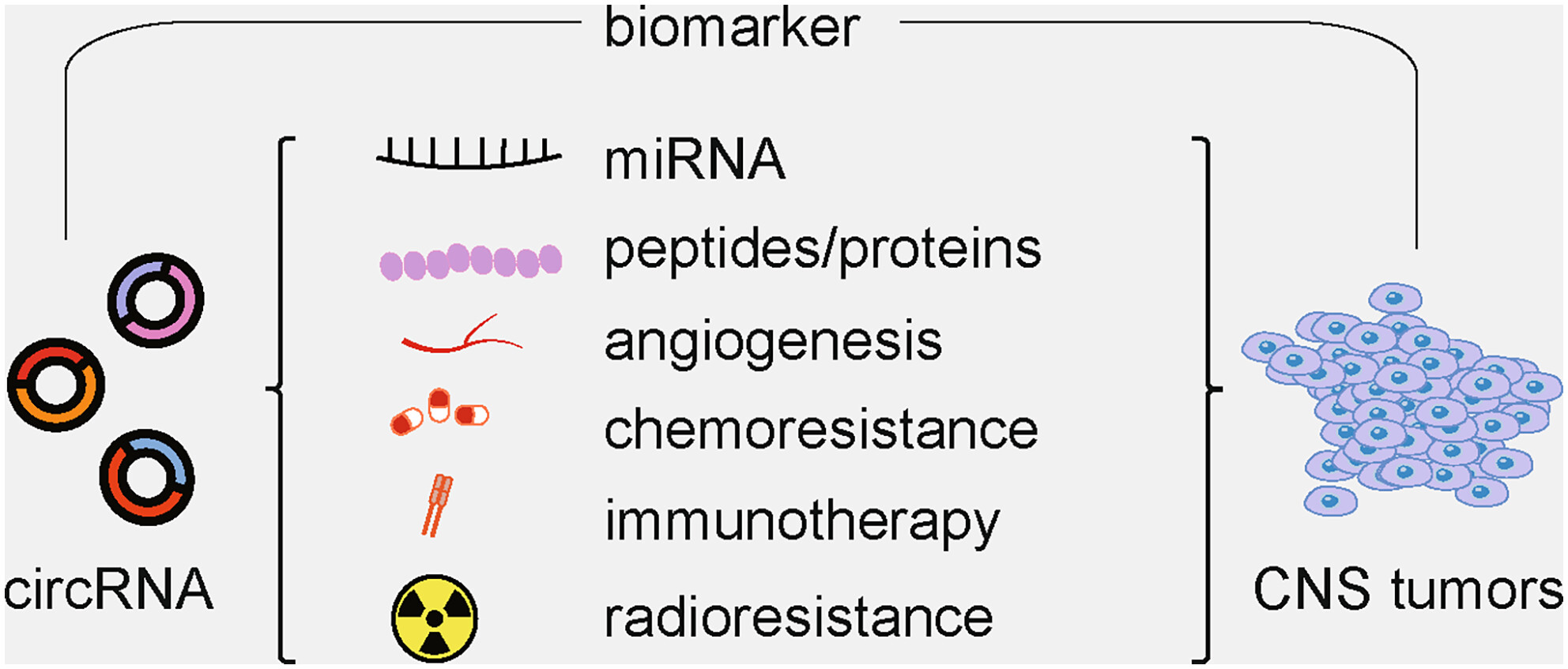
The precise risk factors and molecular mechanisms underlying CNS tumors remain unverified. Growing evidence suggests that Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have numerous significant biological functions in disease progression. In this review, we provide an overview of the relationship between circRNAs and CNS tumors and discuss the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of circRNAs in CNS tumors.
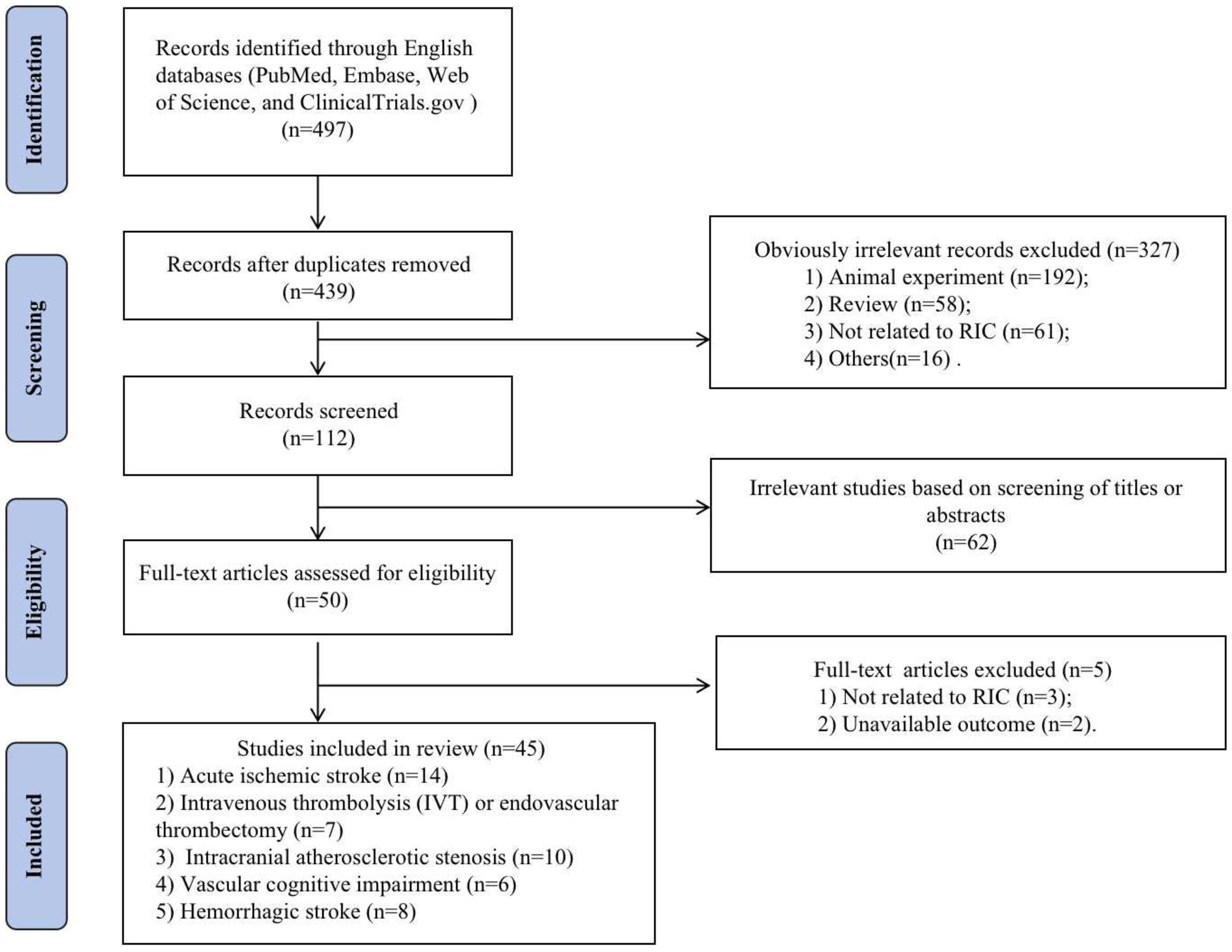
Remote ischemic conditioning after stroke: Research progress in clinical study
- First Published: 06 November 2023
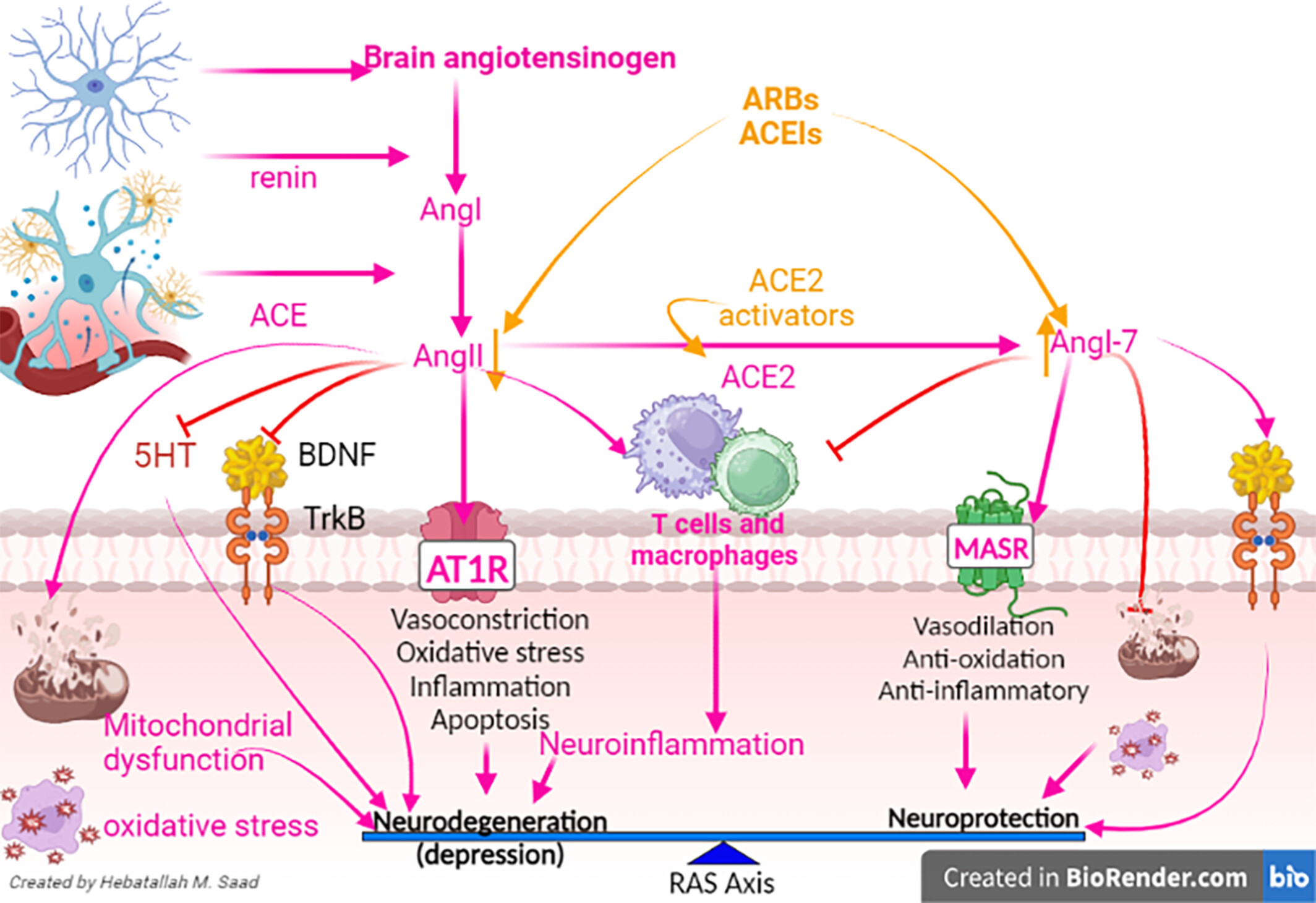
Role of brain renin–angiotensin system in depression: A new perspective
- First Published: 12 November 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The prevalence and risk factors study of cognitive impairment: Analysis of the elderly population of Han nationality in Hunan province, China
- First Published: 22 September 2023
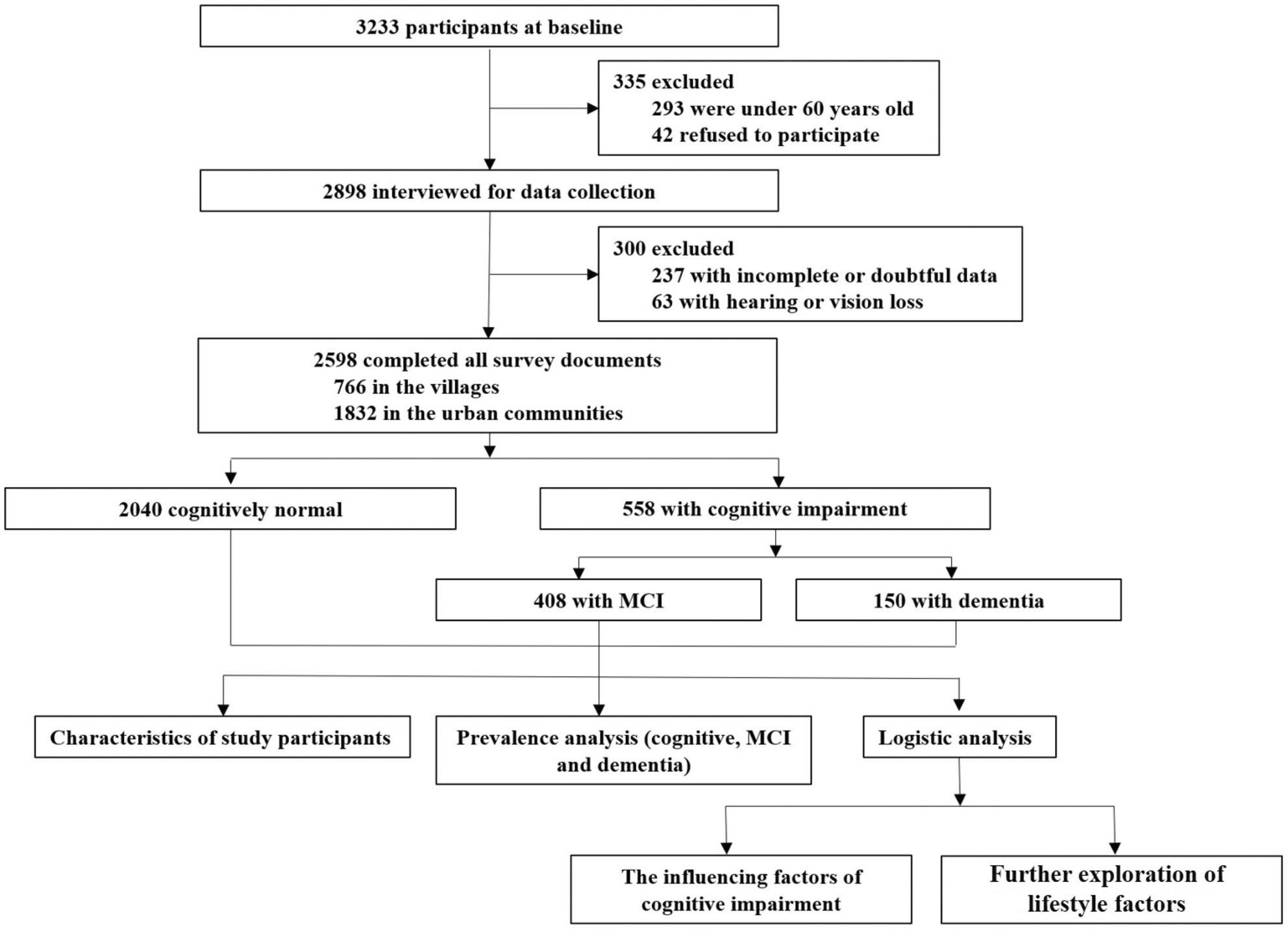
We performed a cross-sectional study on the cognitive function of the Han elderly population in southern China and the target population coverage rate was high, reaching 73%. A representative prevalence rate of cognitive impairment was obtained, and the relevant risk factors were comprehensively analyzed.
Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis identifies potent CpG signature for temzolomide response in non-G-CIMP glioblastomas with unmethylated MGMT promoter: MGMT-dependent roles of GPR81
- First Published: 13 October 2023

By analyzing DNA methylation microarray data and clinical information of glioblastomas (GBMs) that do not have glioma-CpGs island methylator phenotype (G-CIMP) but have an unmethylated promoter of O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase (unMGMT), a panel of 64 CpGs and a 10-CpG risk score signature were discovered and validated with specific linkage to temozolomide (TMZ) efficacy. Experimental data provided biological clues behind the risk signature. The 64 CpGs and in particular the 10-CpG signature may serve as promising predictive biomarker candidates for guiding optimal usage of TMZ in GBMs with G-CIMP- and unMGMT.
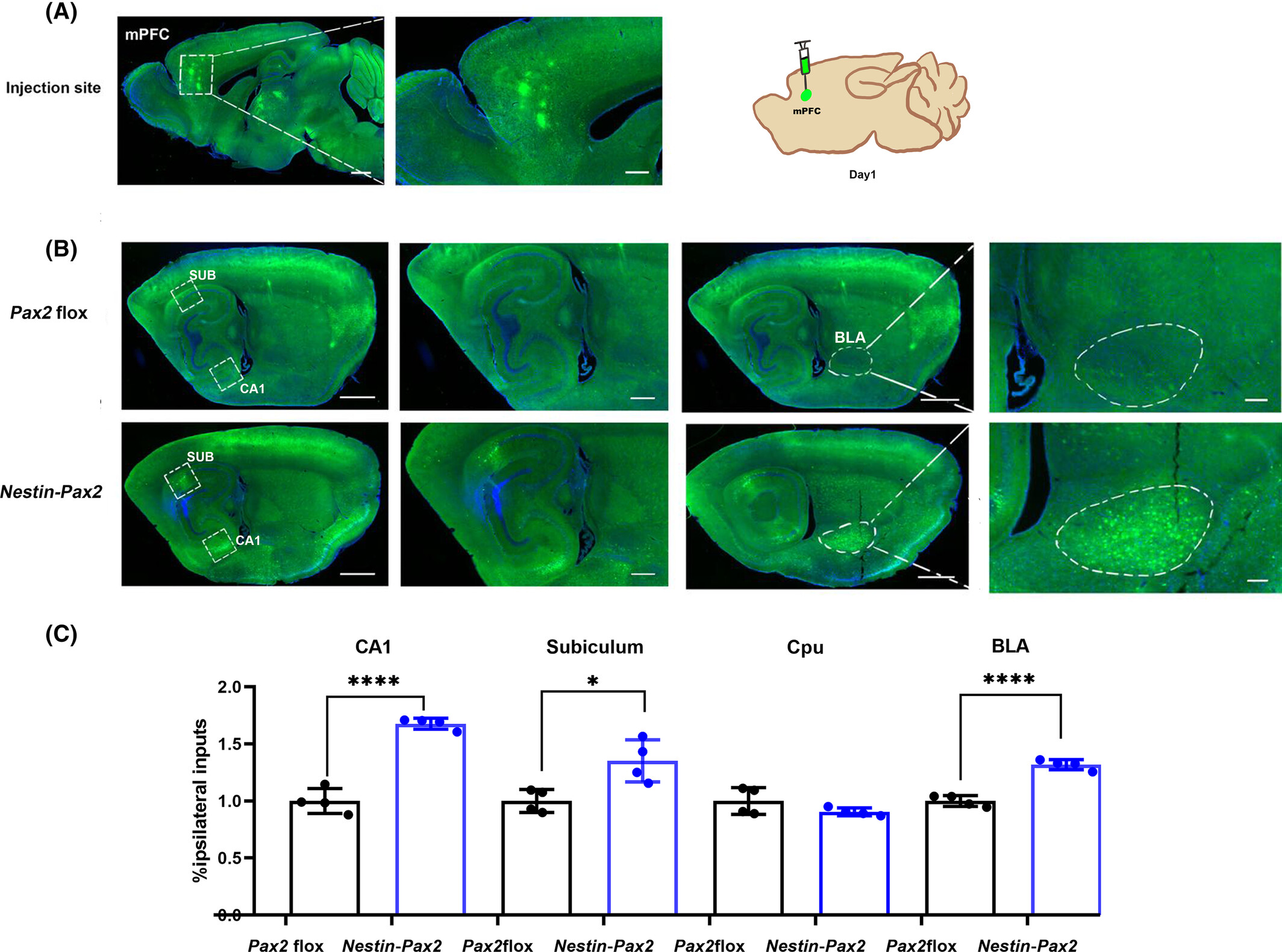
Impaired neural circuitry of hippocampus in Pax2 nervous system-specific knockout mice leads to restricted repetitive behaviors
- First Published: 03 October 2023
Integrated transcriptomic and proteomic profiling reveals the key molecular signatures of brain endothelial reperfusion injury
- First Published: 03 October 2023
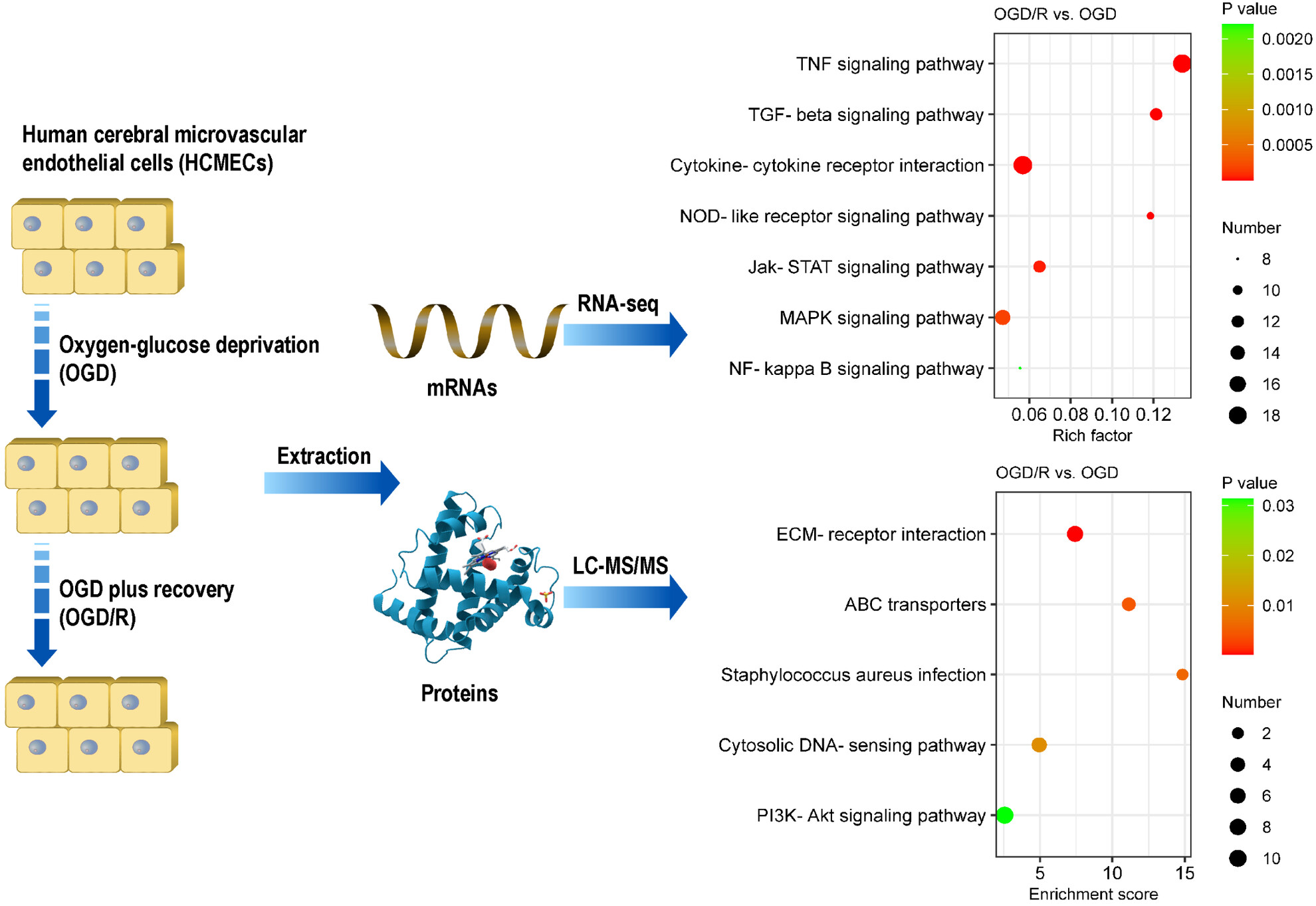
Transcriptomic analysis of human cerebral microvascular endothelial cell (HCMEC)/D3 cells subjected to OGD/R showed that the top significantly changed signaling pathways were mostly associated with inflammatory responses, especially the TNF signaling pathway. Reperfusion-induced differentially expressed proteins were primarily involved in extracellular matrix destruction and remodeling, impairment of endothelial transport function, and inflammatory responses.
A TGF-β signaling-related lncRNA signature for prediction of glioma prognosis, immune microenvironment, and immunotherapy response
- First Published: 18 October 2023

A TGF-β signaling-related lncRNA signature has been established in glioma, which can be used for prognostic judgment, immune infiltration status speculation, and immunotherapy response prediction. Furthermore, in vitro experiments confirmed that silencing of TGF-β signaling-related lncRNA could inhibit the proliferation of glioma cells. This study provides candidate biomarkers with clinical application value for glioma.
Disrupted functional connectivity of the habenula links psychomotor retardation and deficit of verbal fluency and working memory in late-life depression
- First Published: 07 October 2023
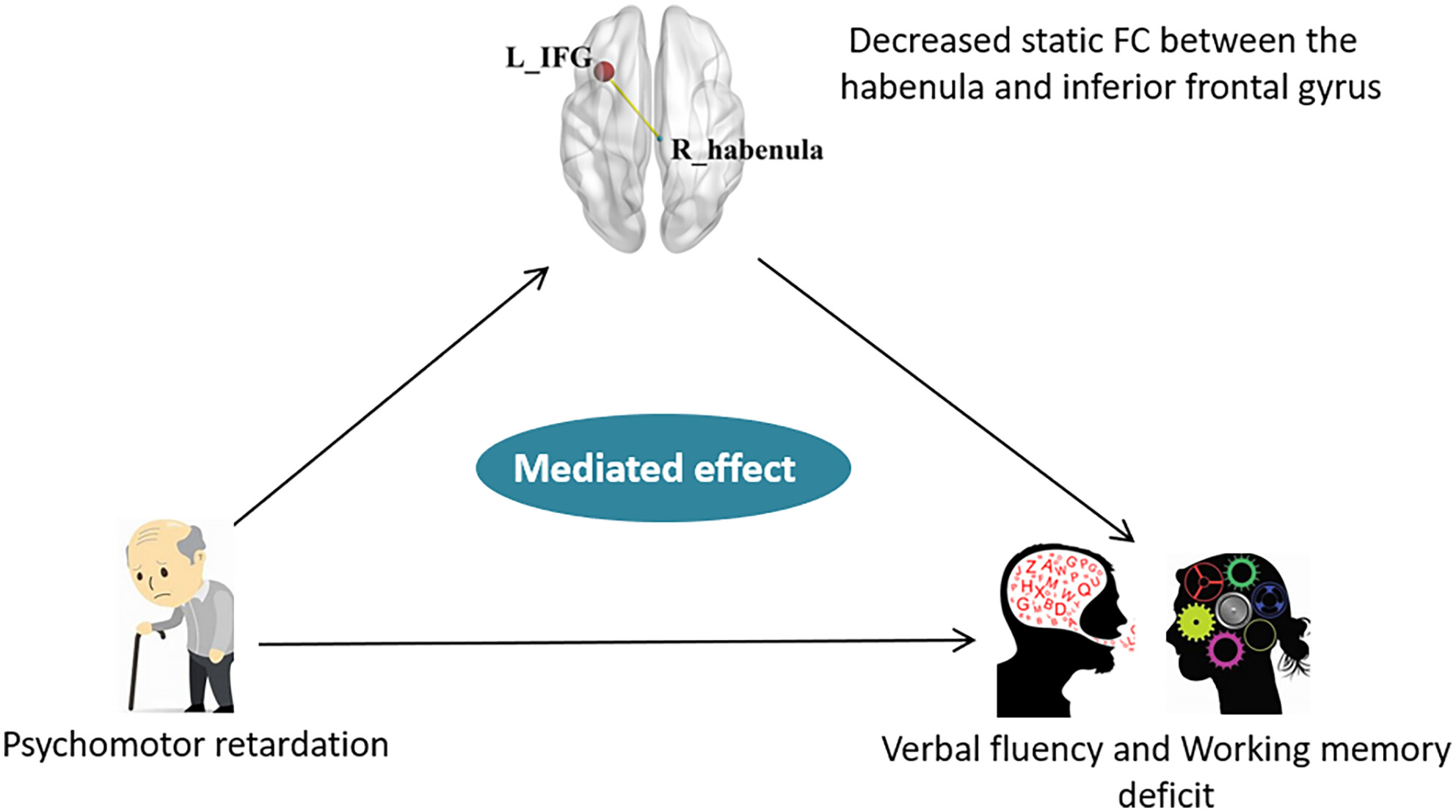
Patients with late-life depression (LLD) exhibited decreased static FC between the right habenula and bilateral IFG compared with healthy controls, and this decreased FC was involved in the underlying pathway connecting psychomotor retardation and deficit of verbal fluency and working memory. The present results provide a more in-depth understanding of their pathological mechanism, and could inform the development of more targeted and effective therapeutic interventions, improving the management and treatment outcomes for LLD.
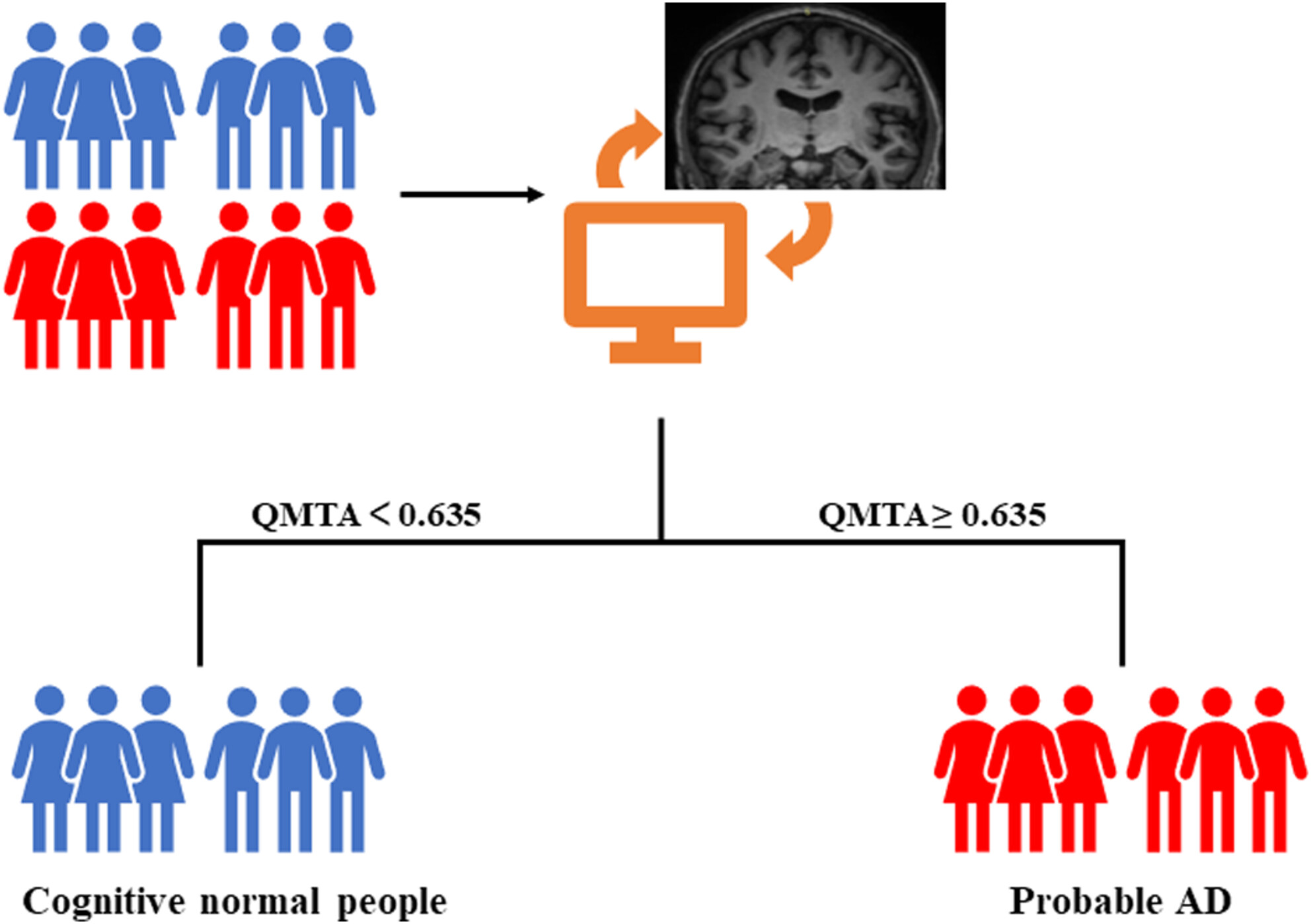
The role of visual rating and automated brain volumetry in early detection and differential diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 21 October 2023
Truncated Dyrk1A aggravates neuronal apoptosis by inhibiting ASF-mediated Bcl-x exon 2b inclusion
- First Published: 21 October 2023
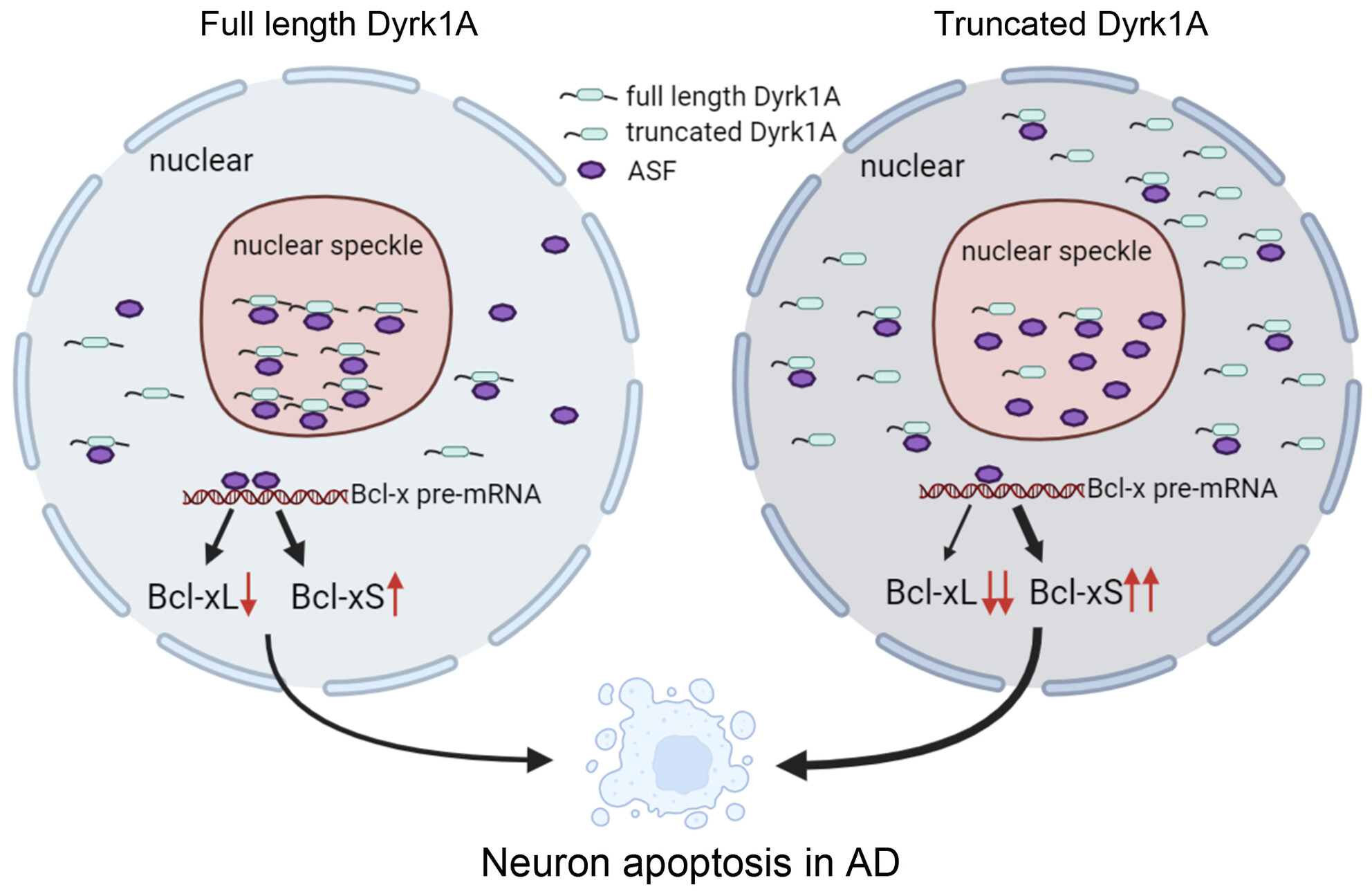
The full length Dyrk1A phosphorylated ASF and inhibited ASF-mediated Bcl-xL exon 2b inclusion leading to cell apoptosis. Moreover, the truncated Dyrk1A deleting the C-terminus exhibited equidistribution in the nucleoplasm and stronger interaction with ASF, leading to decreased ratio of Bcl-xL/Bcl-xS and neuronal apoptosis in AD.
Expression and metabolism profiles of CVT associated with inflammatory responses and oxygen carrier ability in the brain
- First Published: 30 October 2023

Adult rats were subjected to CVT and MCAO models. Multi-omics (RNA-seq and untargeted metabolomics) analysis were performed to construct the transcriptome and metabolism profiles of rat brains after CVT and also MCAO. The differential gene analysis, functional annotation, and enrichment analysis were also performed.
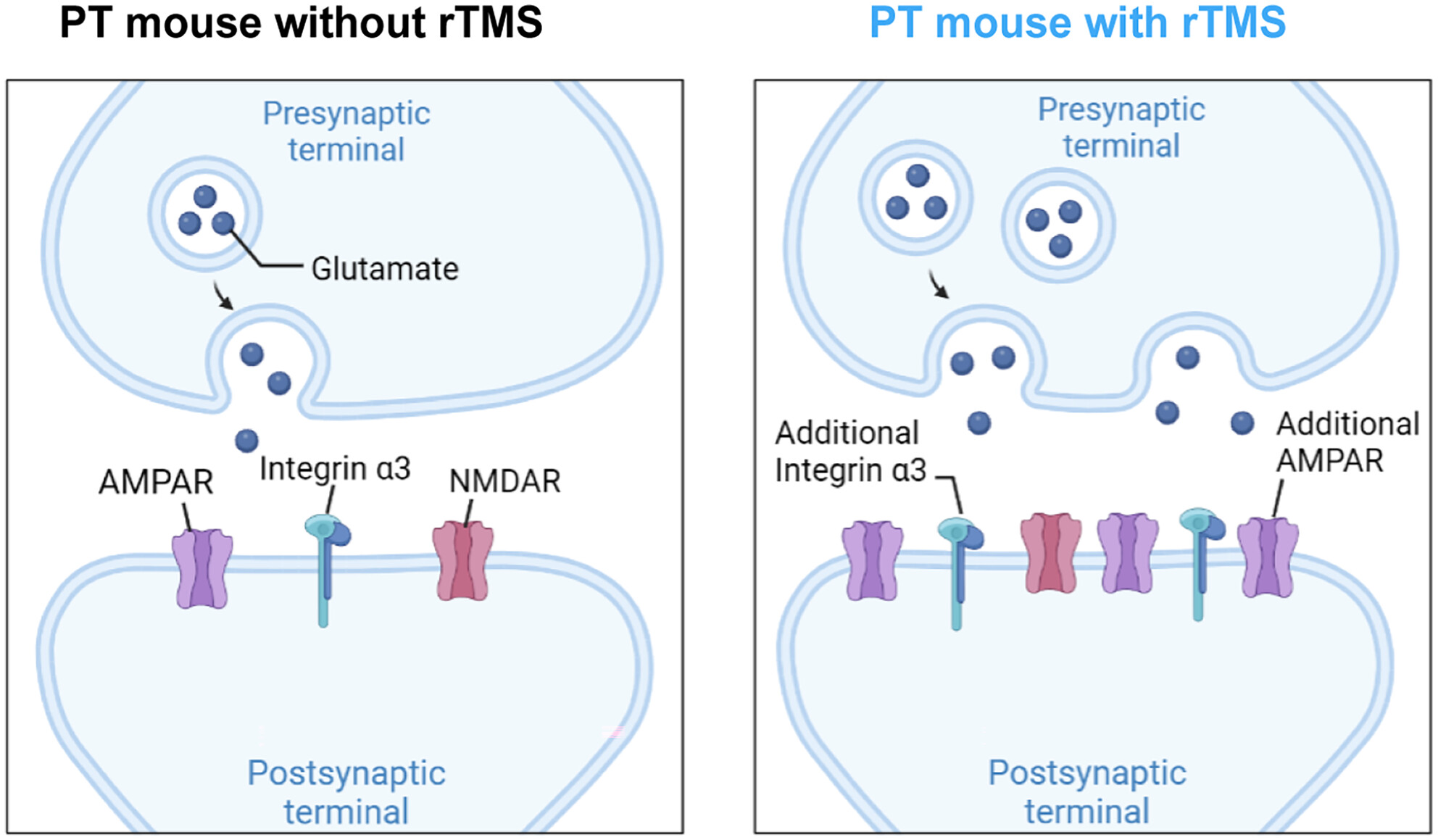
Integrin α3 is required for high-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation-induced glutamatergic synaptic transmission in mice with ischemia
- First Published: 23 October 2023
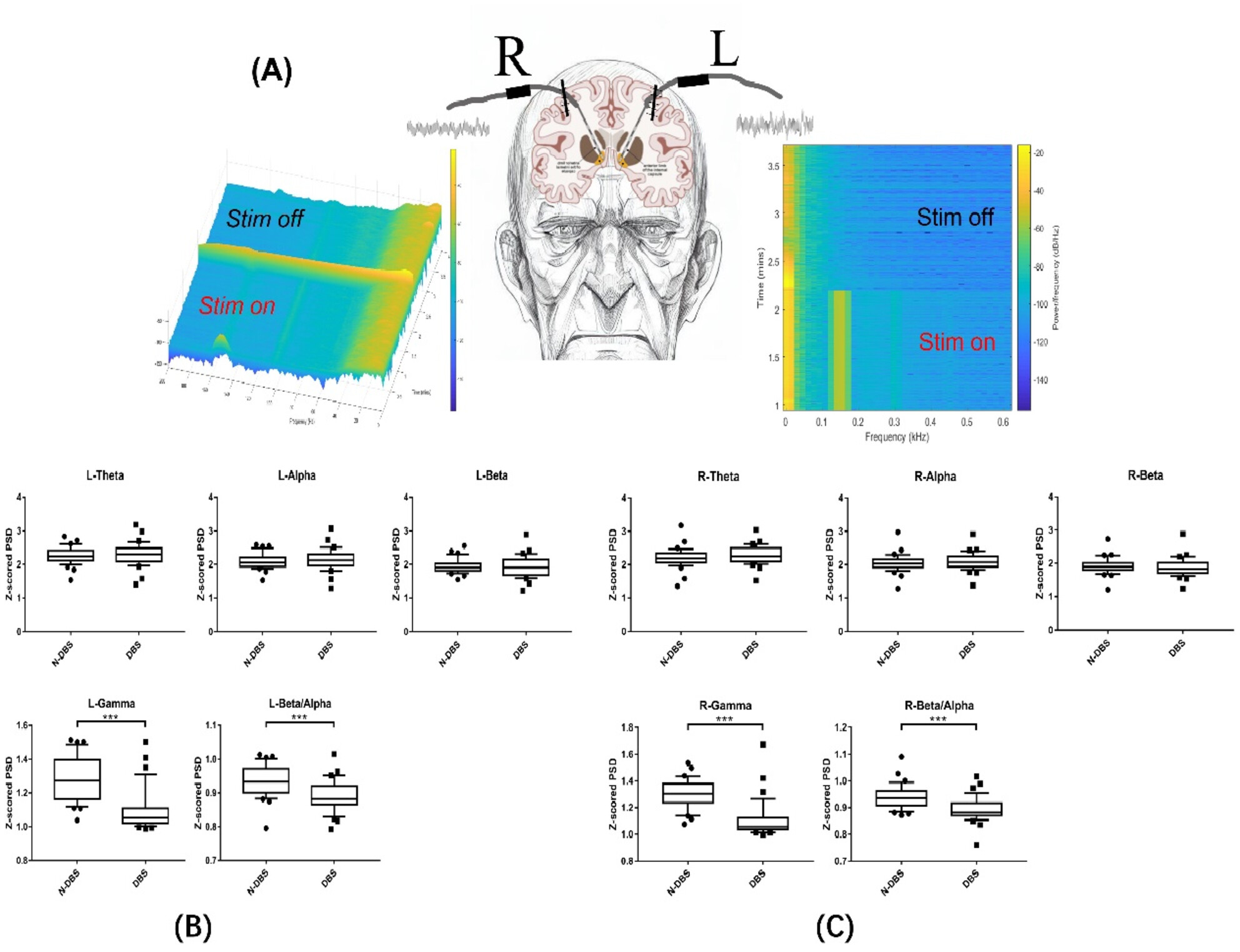
The guiding effect of local field potential during deep brain stimulation surgery for programming in Parkinson's disease patients
- First Published: 13 October 2023
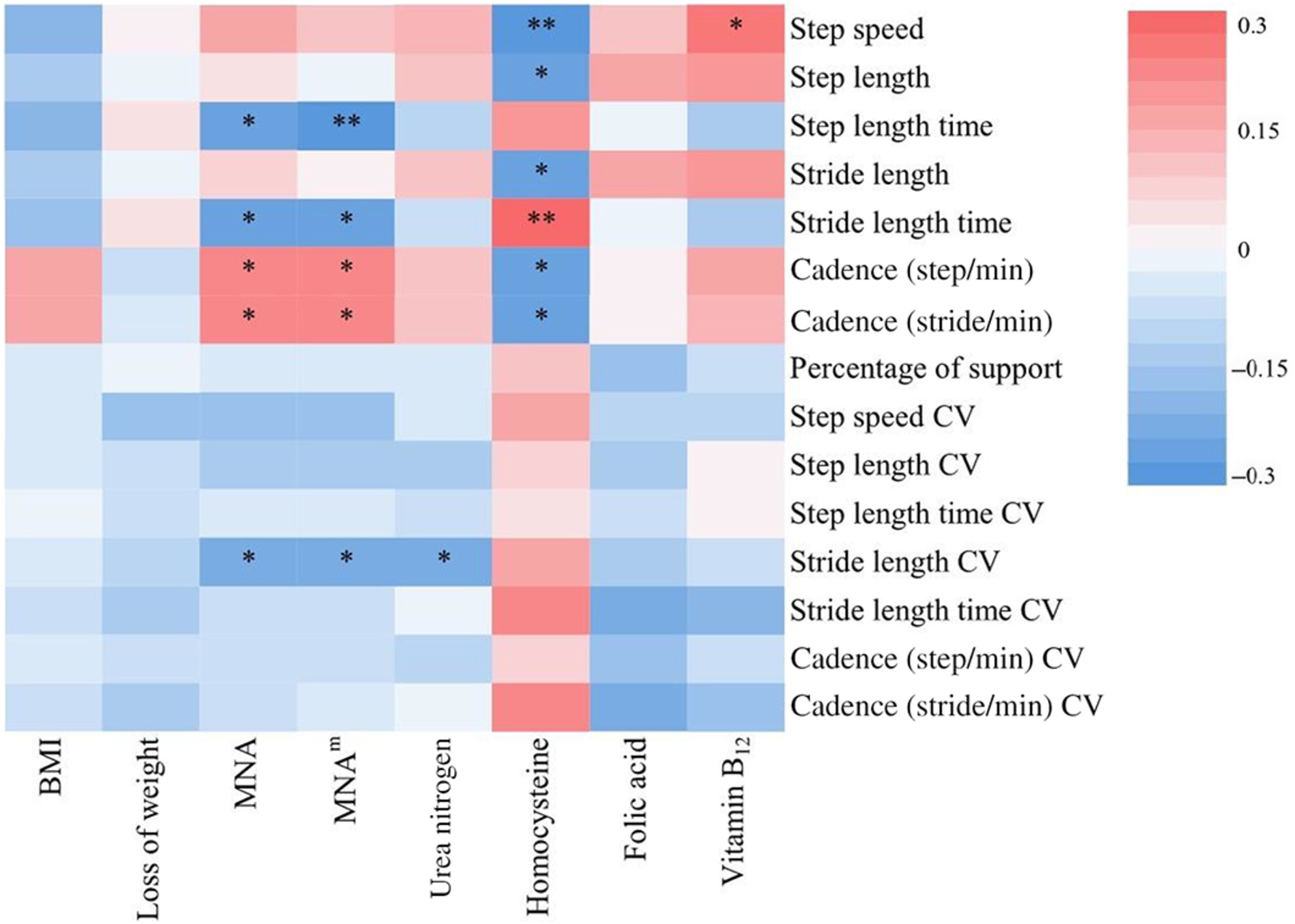
Association between nutritional status and gait performance in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 10 November 2023
Eomesodermin expression in CD4+T-cells associated with disease progression in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- First Published: 18 October 2023
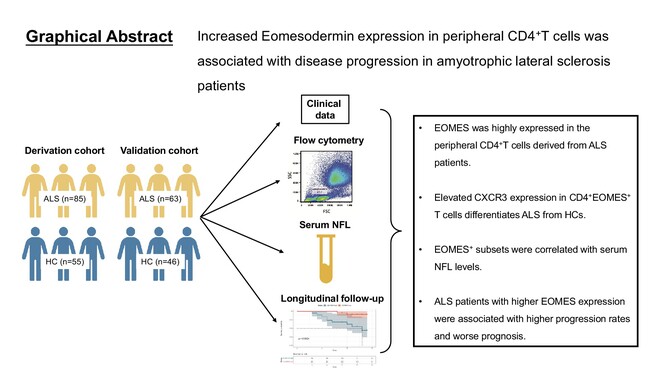
Eomesodermin was highly expressed in the peripheral CD4+T-cells derived from ALS patients. Elevated CXCR3 expression in CD4+EOMES+ T-cells differentiates ALS from HCs. EOMES+ subsets were correlated with serum NFL levels. ALS patients with higher EOMES expression were associated with higher progression rates and worse prognosis.
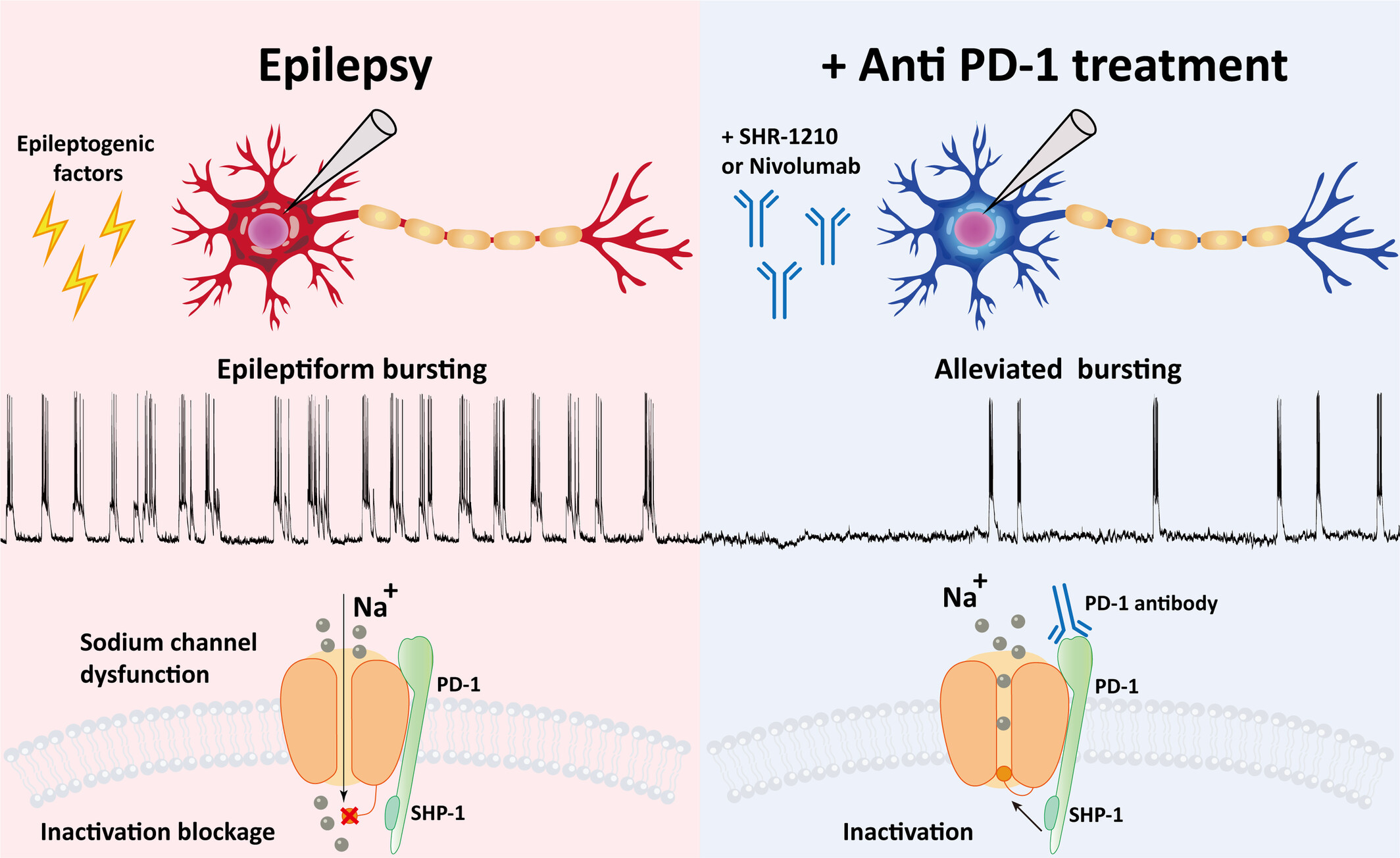
Anti-PD-1 treatment protects against seizure by suppressing sodium channel function
- First Published: 30 October 2023
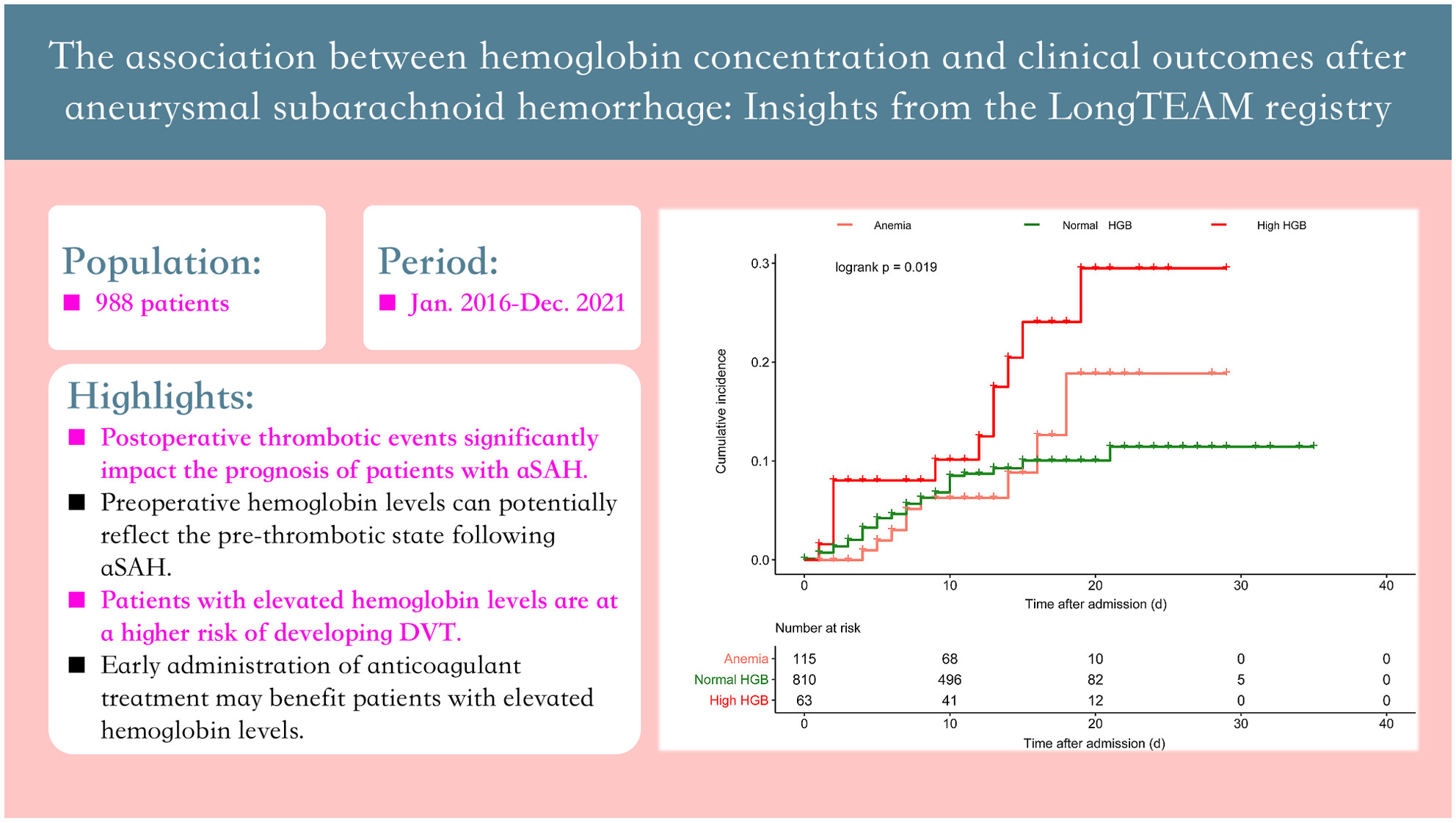
The association between hemoglobin concentration and clinical outcomes after aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage: Insights from the LongTEAM registry
- First Published: 17 October 2023
Nicotine suppresses crystalline silica-induced astrocyte activation and neuronal death by inhibiting NF-κB in the mouse hippocampus
- First Published: 21 October 2023
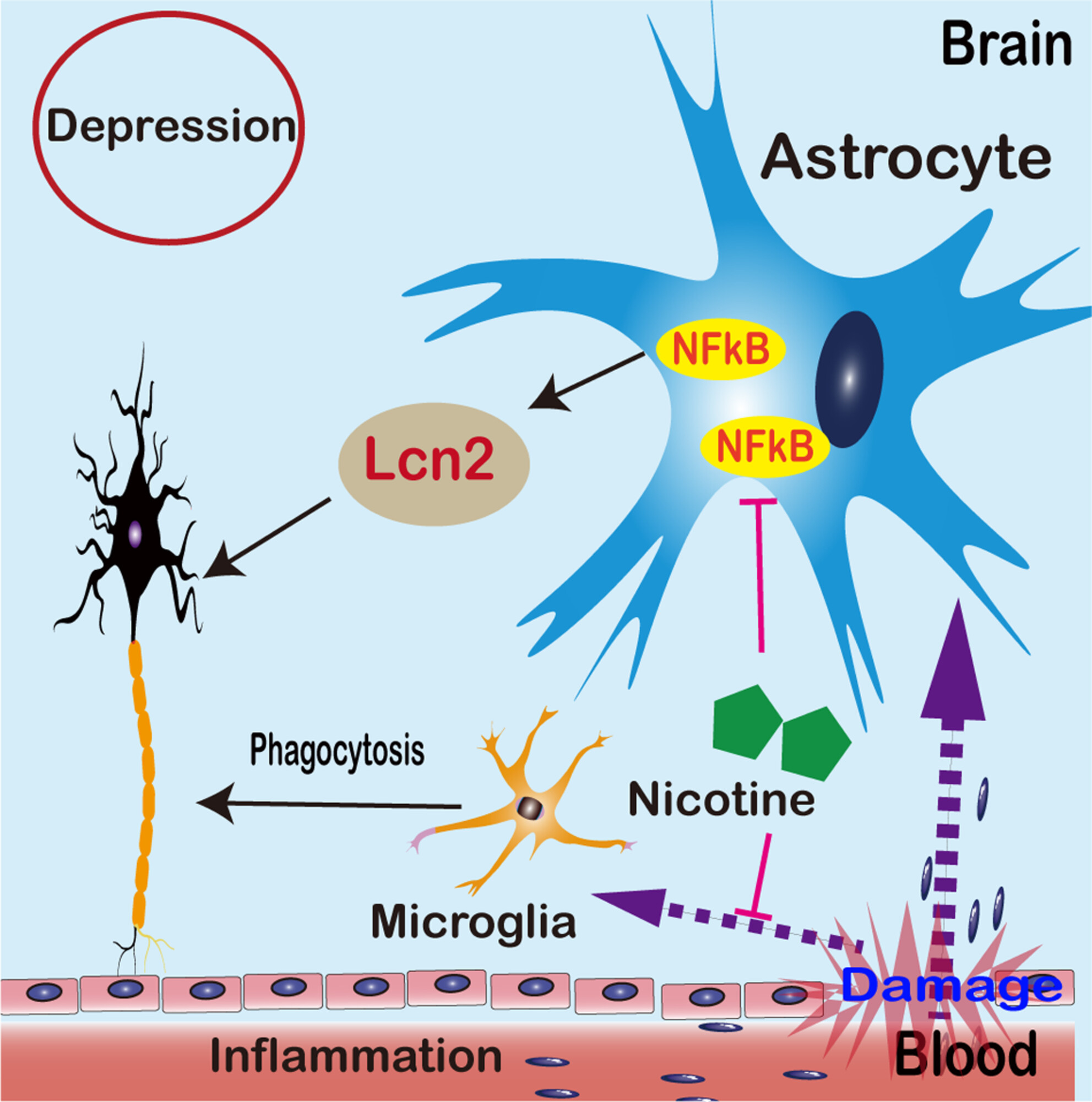
Pattern diagram illustrating the alleviation of depression induced by crystalline silica through nicotine intervention. Upon exposure to CS, the blood–brain barrier (BBB) in the hippocampus undergoes damage, leading to activation of astrocytes and microglia. The activated astrocytes facilitate the secretion of Lcn2 via the NF-κB pathway, ultimately resulting in neuronal death. However, nicotine mitigates the activation of astrocytes and microglia while safeguarding neurons against cell death.
Survivin enhances hippocampal neurogenesis and cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease mouse model
- First Published: 30 October 2023
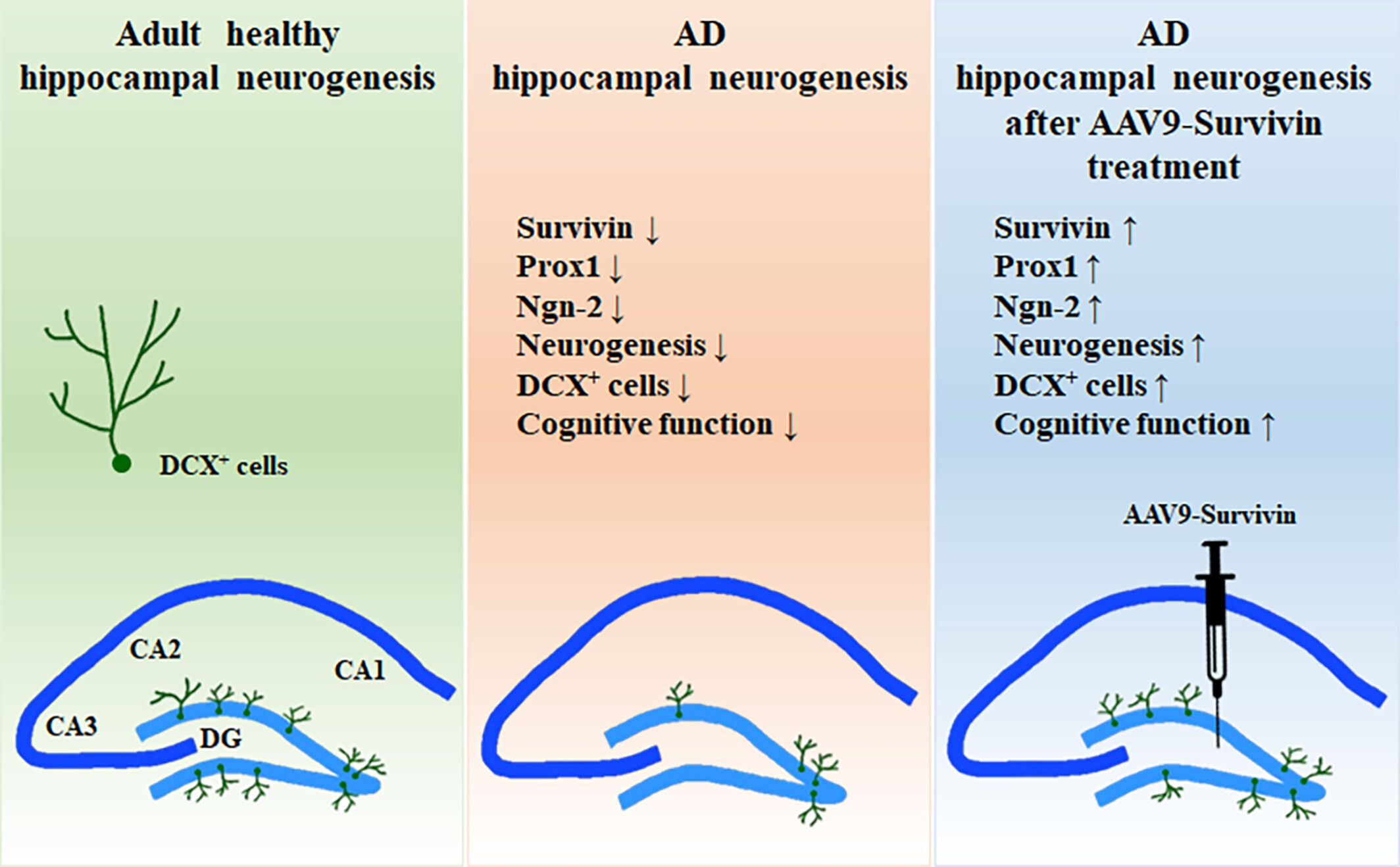
GA
Survivin is able to regulate neurogenesis in vitro and in vivo model. Our results demonstrate that therapeutic effects of survivin which improves cognitive function by enhancing neurogenesis in 5XFAD mouse. Survivin seems to be a good candidate for therapeutics to restore cognitive function in hippocampus of AD.
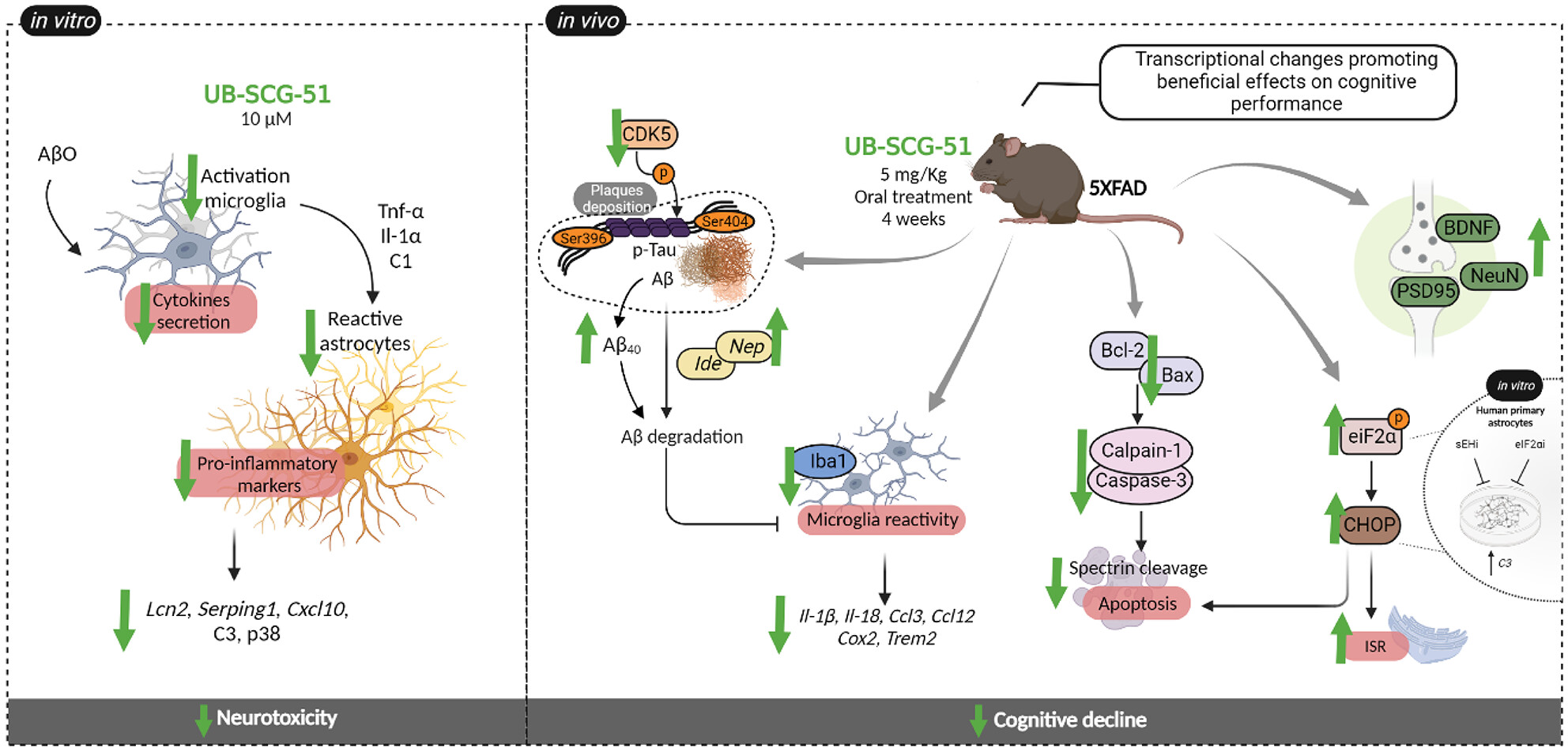
Novel molecular mechanism driving neuroprotection after soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibition: Insights for Alzheimer's disease therapeutics
- First Published: 31 October 2023
Circular RNA PTP4A2 regulates microglial polarization through STAT3 to promote neuroinflammation in ischemic stroke
- First Published: 23 October 2023
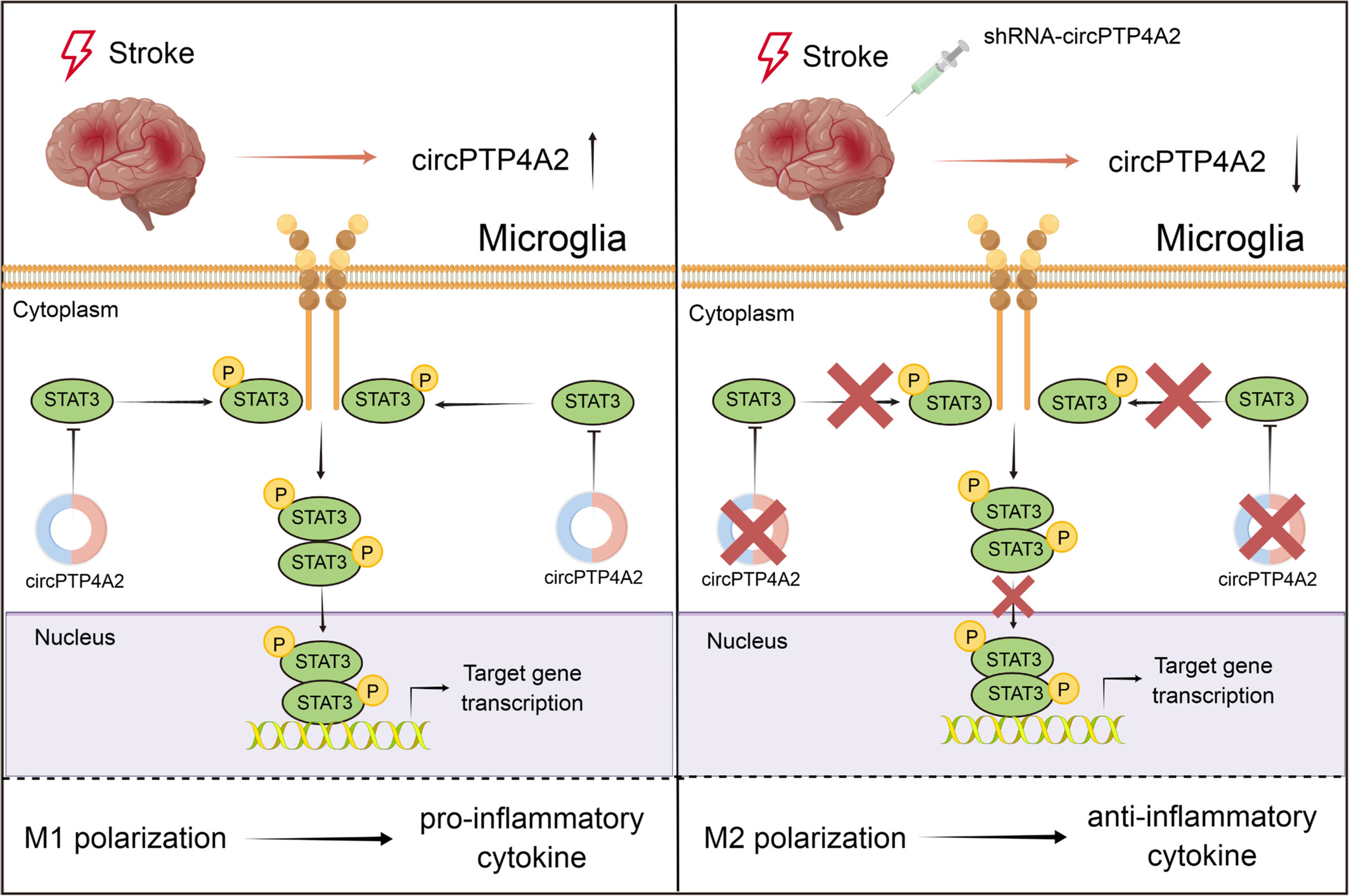
After cerebral ischemia, circPTP4A2 levels increased in peri-infarct cortex and the elevation of circPTP4A2 was mainly located in microglia. Upregulated circPTP4A2 directly binds to STAT3 and promoted STAT3 phosphorylation activation. The phosphorylated STAT3 dimer then enters the nucleus to modulate stroke-induced microglial polarization, which promotes neuroinflammation by driving M1 microglial polarization.
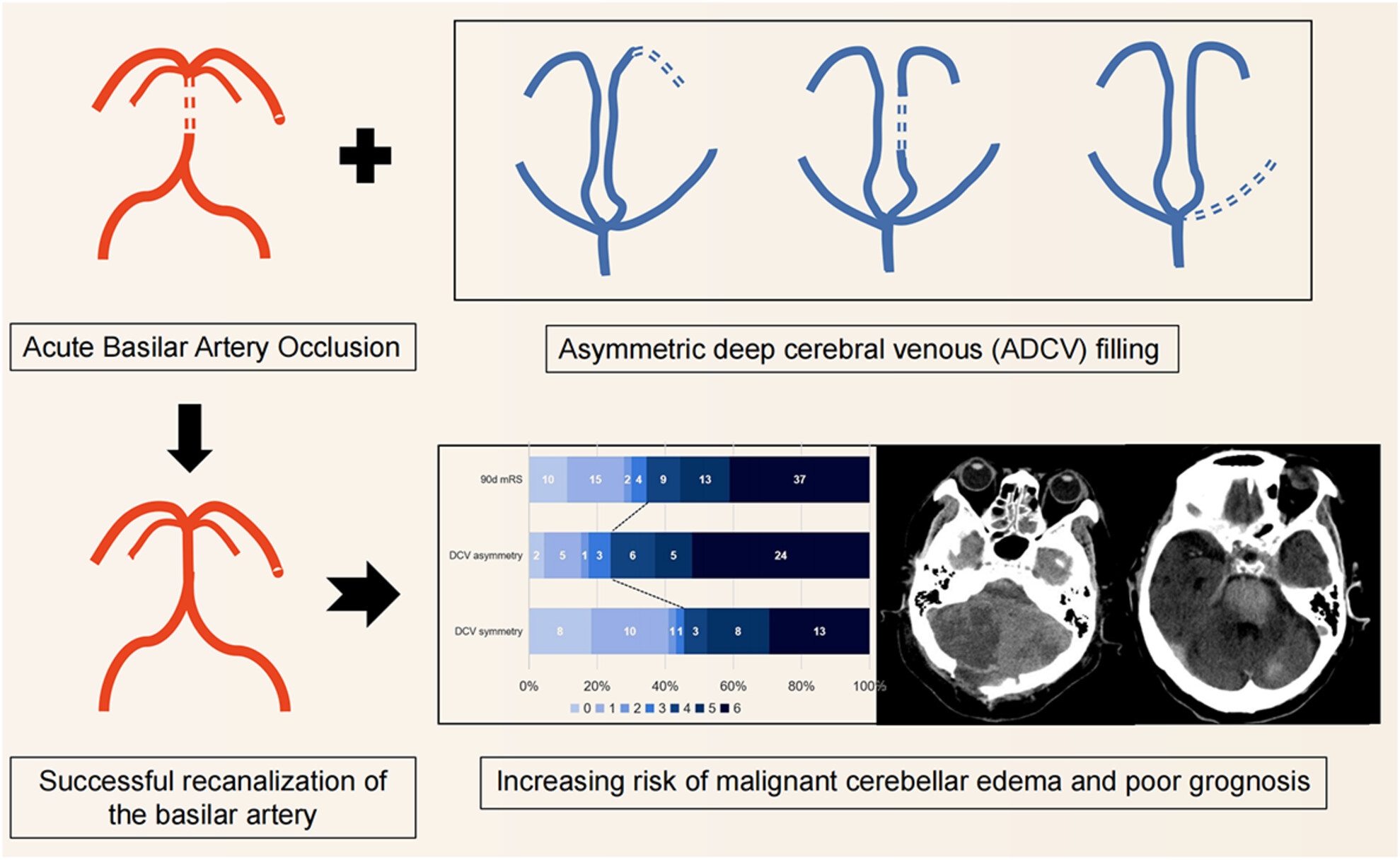
Asymmetric deep cerebral venous filling predicts poor outcome of acute basilar artery occlusion after endovascular treatment
- First Published: 12 November 2023
Emerging trends and hotspots of the itch research: A bibliometric and visualized analysis
- First Published: 30 October 2023
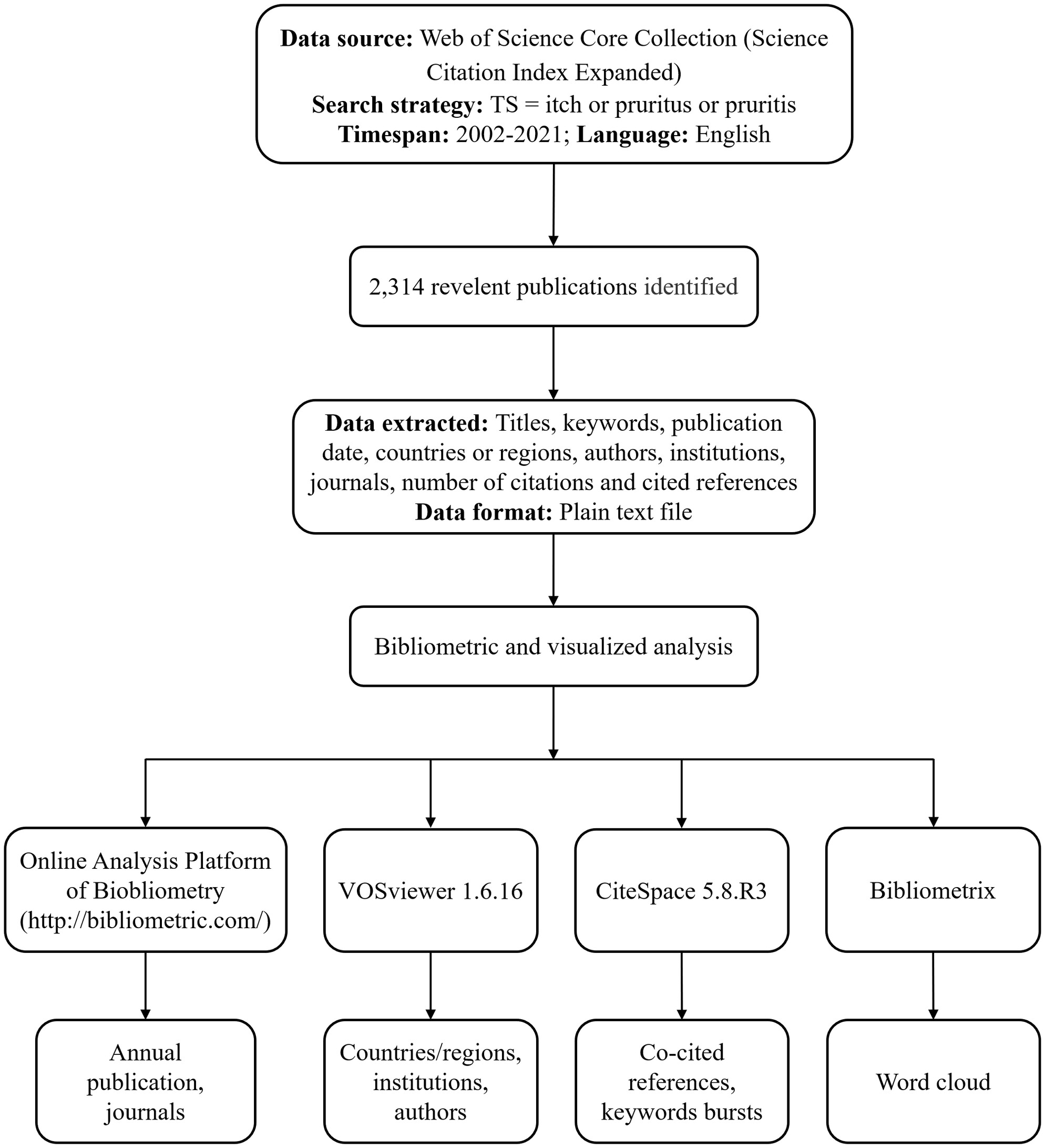
This study conducted a comprehensive bibliometric and visual analysis of itch research. 2314 papers closely related to itch research published between 2002 and 2021 were retrieved from the SCI-E of Web of Science Core Collection database. Full records and cited references were extracted from relevant publications. Then the data were imported into the Online Analysis Platform of Biobliometry, VOSviewer, CiteSpace software, and Bibliometrix to systematically evaluate publication trends in itch research and predict future research directions.
Carpesii fructus extract exhibits neuroprotective effects in cellular and Caenorhabditis elegans models of Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 31 October 2023
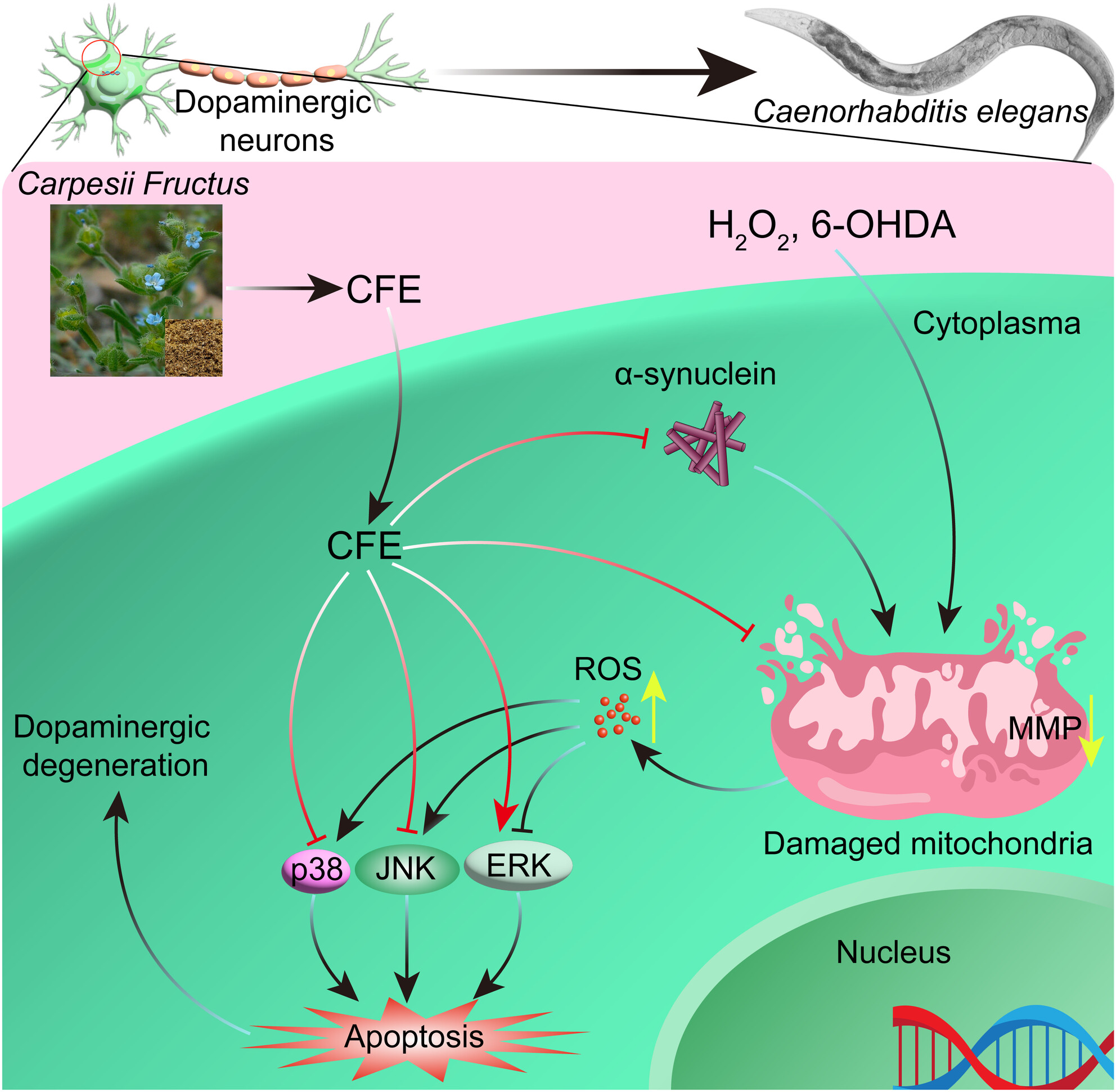
Carpesii fructus extract (CFE) attenuates H2O2- or 6-OHDA-induced toxicity and reduce α-synuclein to inhibit ROS production and restore MMP in PC-12 cells and Caenorhabditis elegans, resulting in the improvement of dopaminergic neurons and motor ability in PD. These effects are involved the regulation of MAPK signaling pathway.
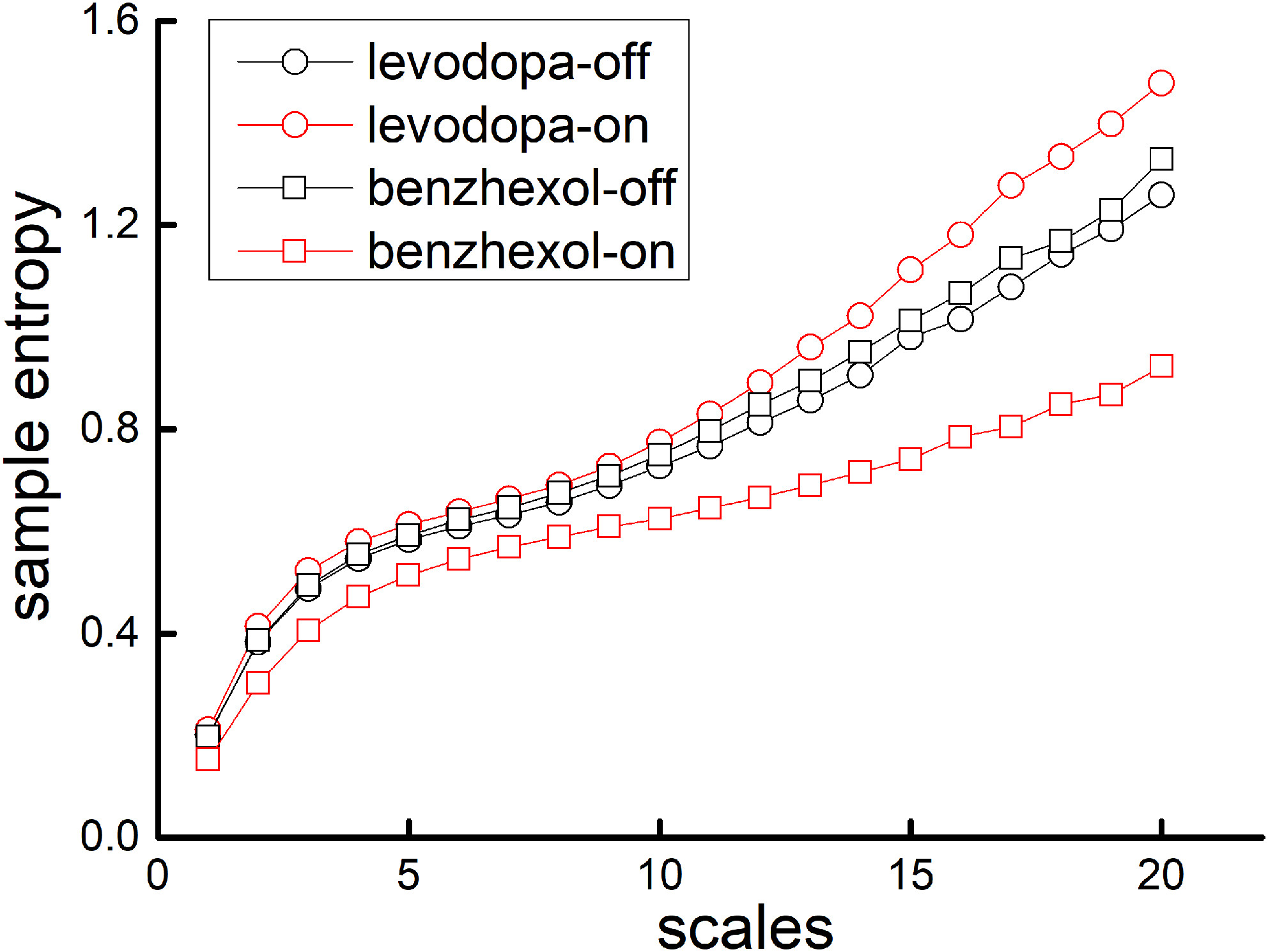
Dopaminergic versus anticholinergic treatment effects on physiologic complexity of hand tremor in Parkinson's disease: A randomized crossover study
- First Published: 31 October 2023
Amelioration of morphine withdrawal syndrome by systemic and intranasal administration of mesenchymal stem cell-derived secretome in preclinical models of morphine dependence
- First Published: 06 November 2023
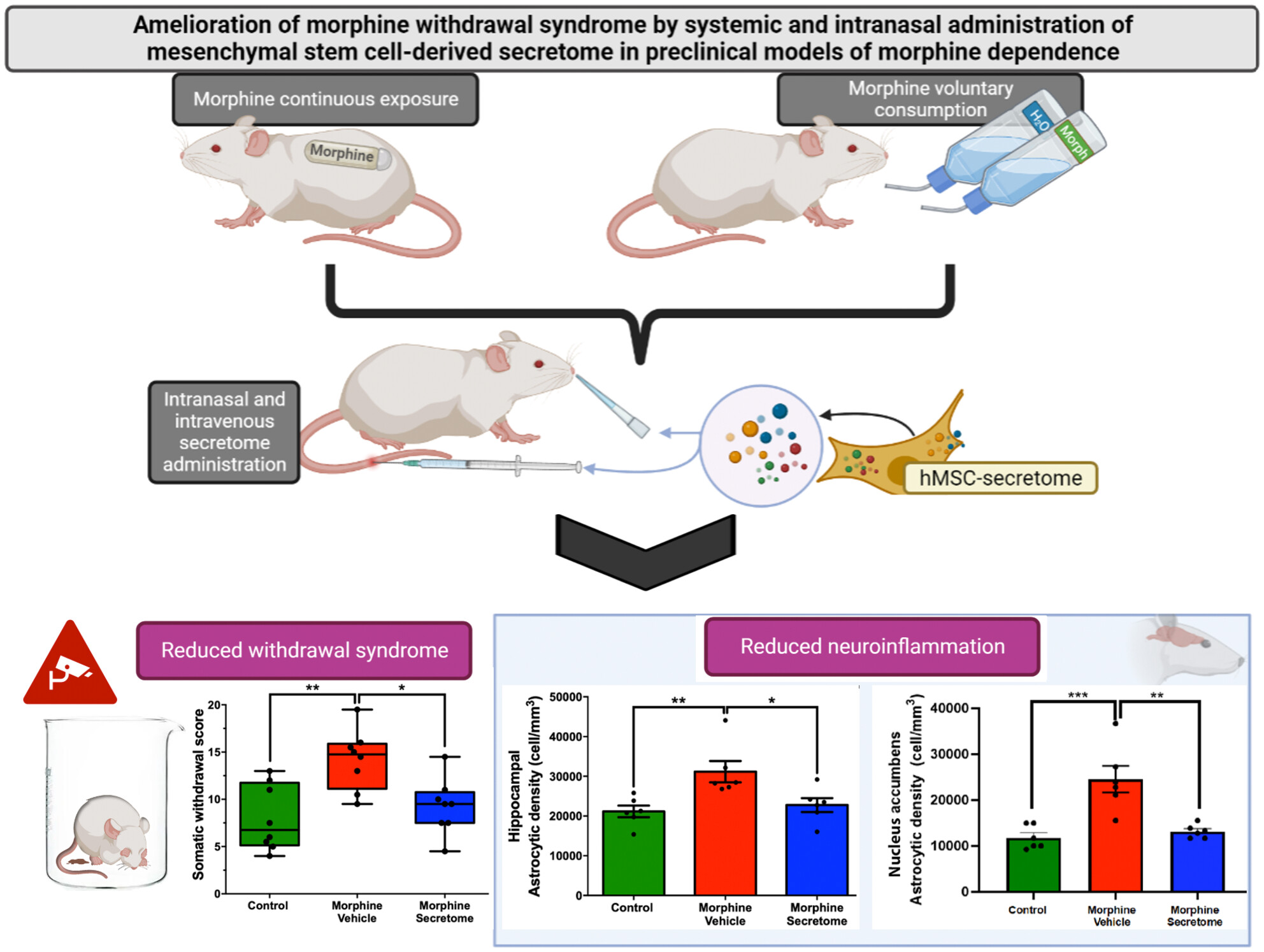
Overall, findings indicate the generation of therapeutic benefits through the simultaneous intravenous and intranasal administration of secretome derived from preconditioned human mesenchymal stem cells, which helps mitigate morphine-induced withdrawal syndrome in two relevant animal models of morphine dependence. These effects were associated with a reduction of morphine-induced neuroinflammation in the hippocampus and nucleus accumbens.
Novel subsets of peripheral immune cells associated with promoting stroke recovery in mice
- First Published: 31 October 2023
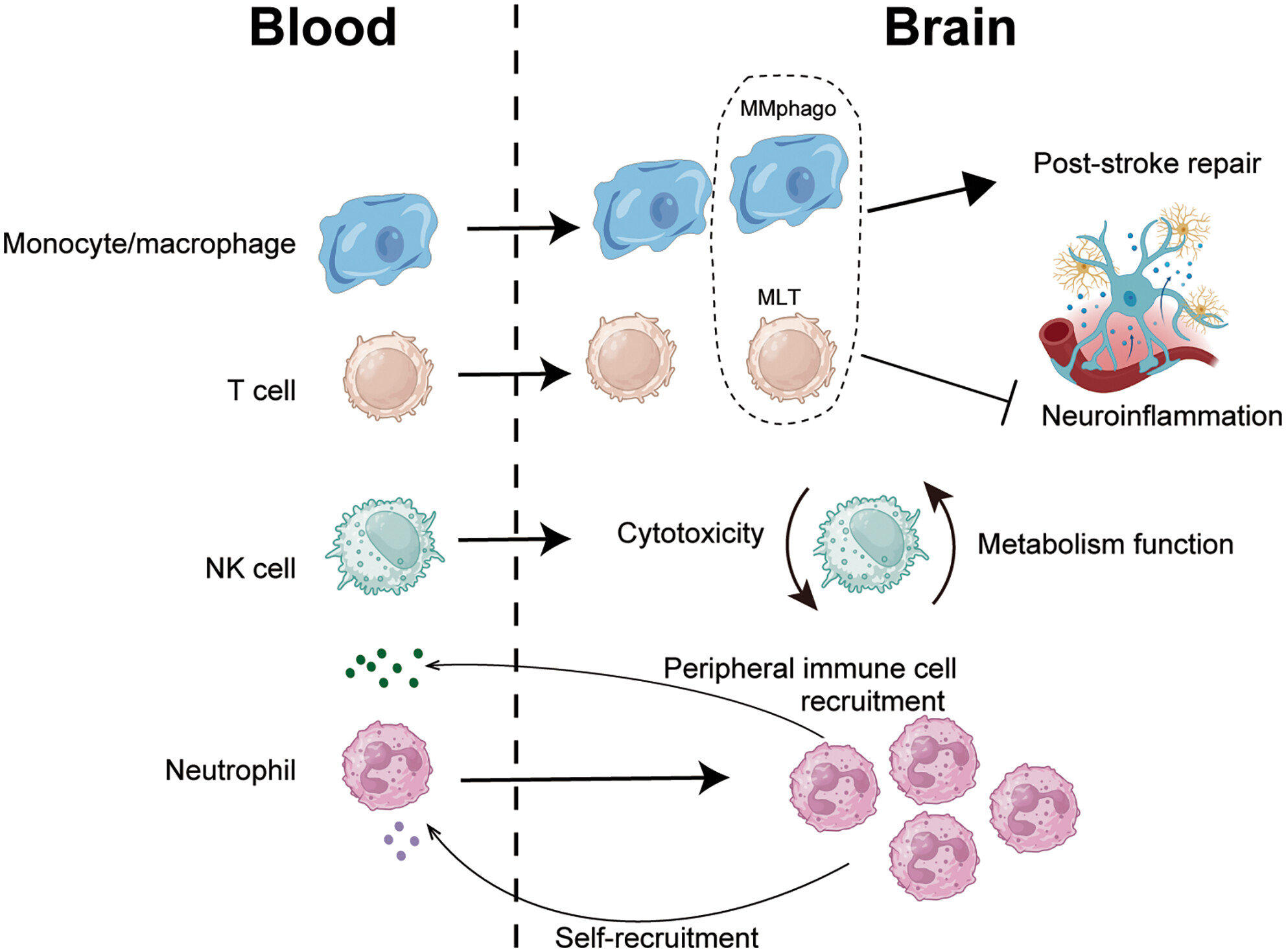
Brief abstract
The role of peripheral immune cells in stroke recovery remains unclear. Gu et al. report a phagocytic subset of macrophages and a macrophage-like subset of T cells enhancing brain repair, while natural killer cells decrease cytotoxicity and neutrophils keep cell recruitment. These identified immune components may provide potential therapeutic targets.
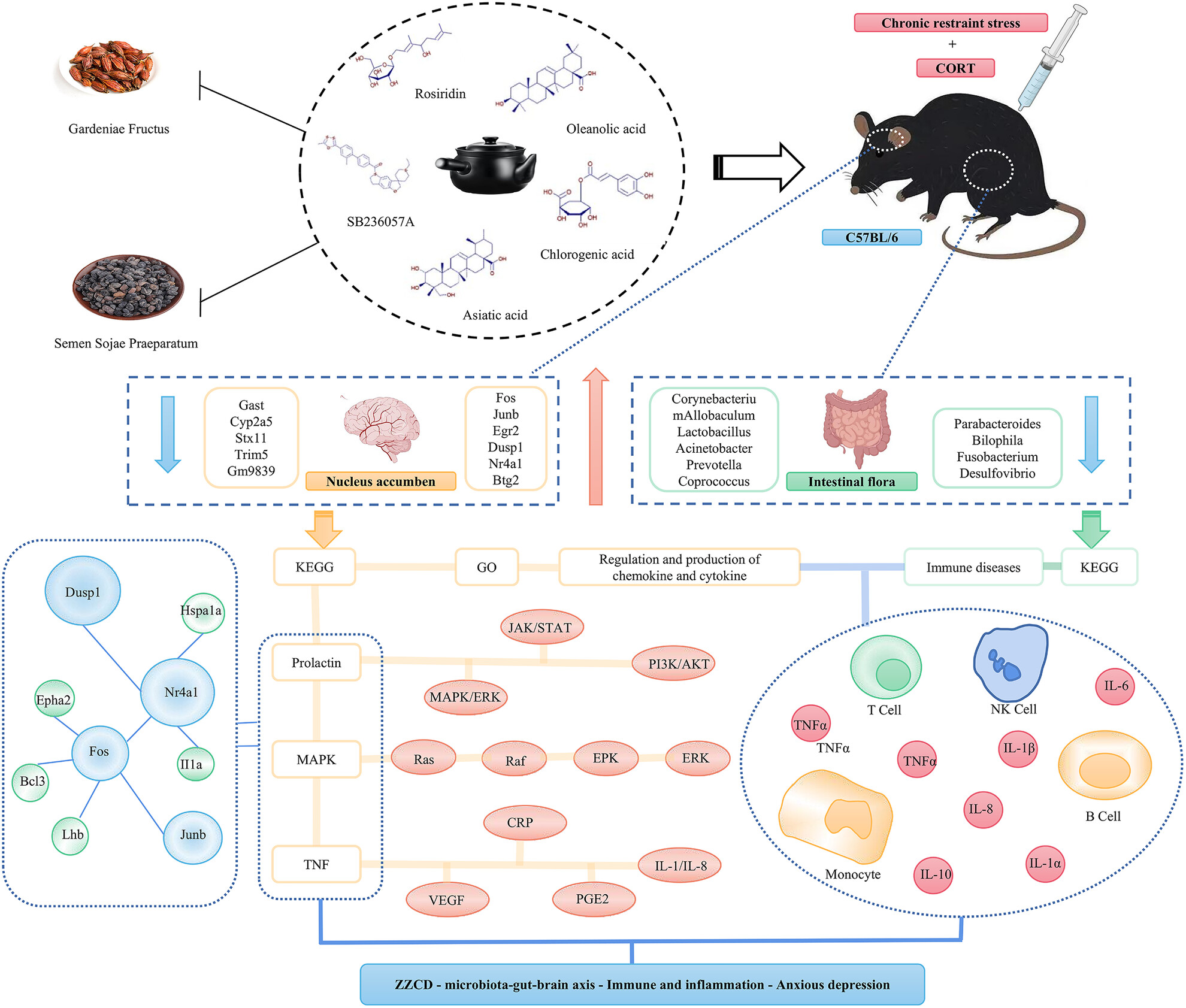
Zhi Zi Chi decoction (Gardeniae fructus and semen Sojae Praeparatum) attenuates anxious depression via modulating microbiota–gut–brain axis in corticosterone combined with chronic restraint stress-induced mice
- First Published: 31 October 2023
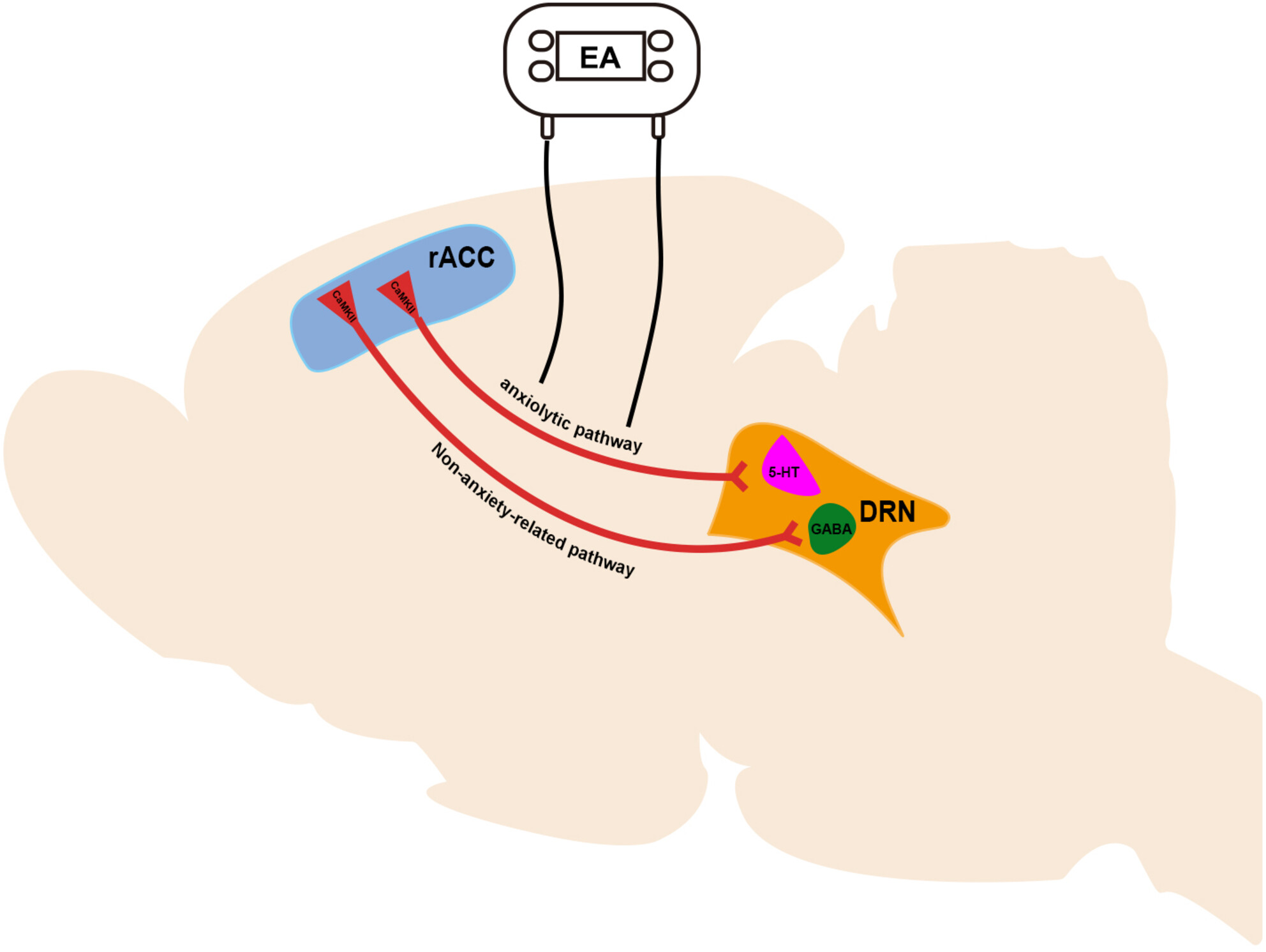
A neural circuit associated with anxiety-like behaviors induced by chronic inflammatory pain and the anxiolytic effects of electroacupuncture
- First Published: 29 November 2023
Psychiatric disorders associated with PCSK9 inhibitors: A real-world, pharmacovigilance study
- First Published: 10 November 2023
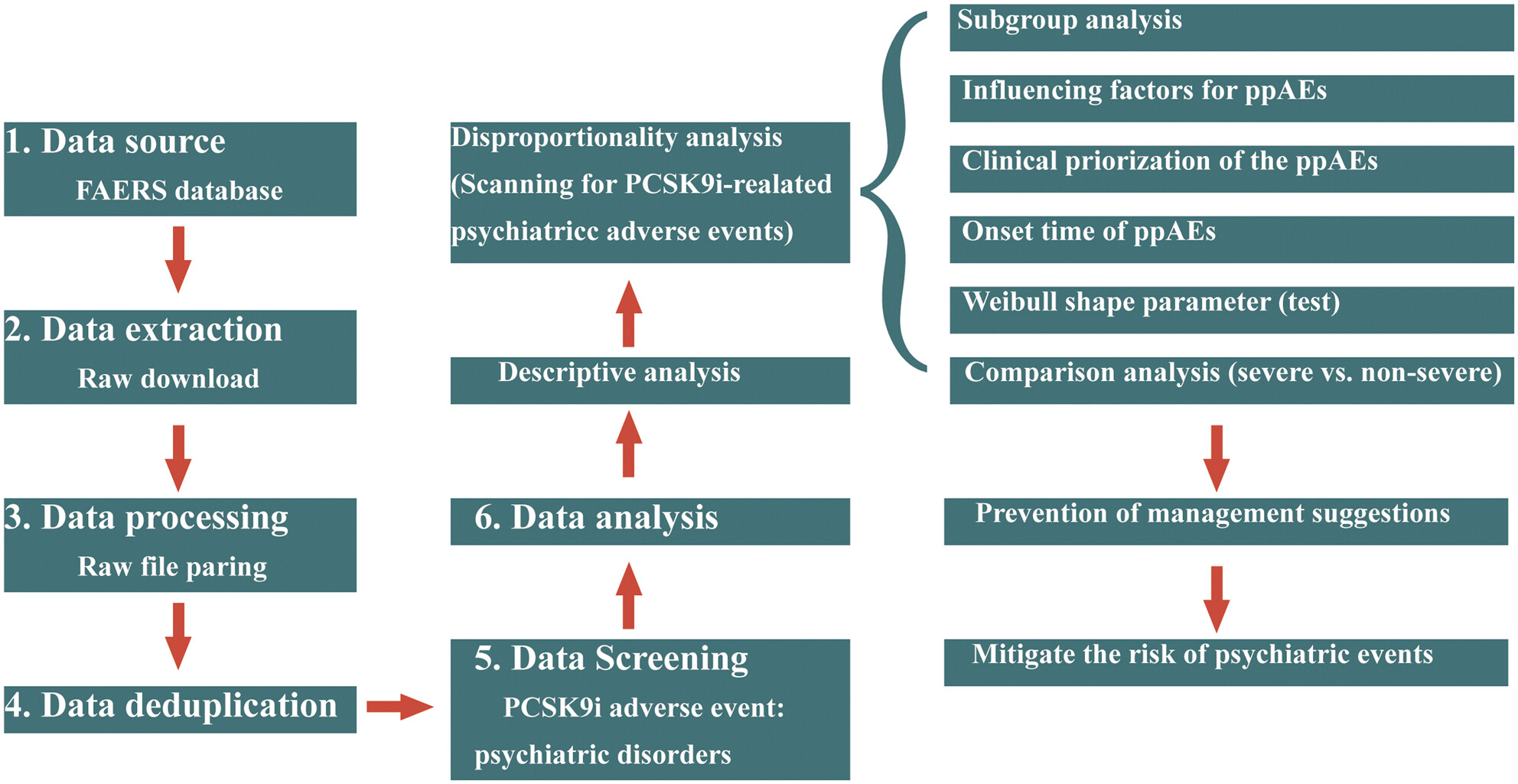
This pharmacovigilance study is based on real-world data from the FAERS database. Total AEs between the third quarter of 2015 and the first quarter of 2023 were obtained from FAERS. Psychiatric AEs were identified using disproportionality analysis and clinical prioritization of signals using a rating scale, followed by univariate logistic regression to explore factors influencing psychiatric AEs.
Abnormal regional activity in the prefrontal-limbic circuit at rest: Potential imaging markers and treatment predictors in drug-naive anxiety disorders
- First Published: 21 November 2023
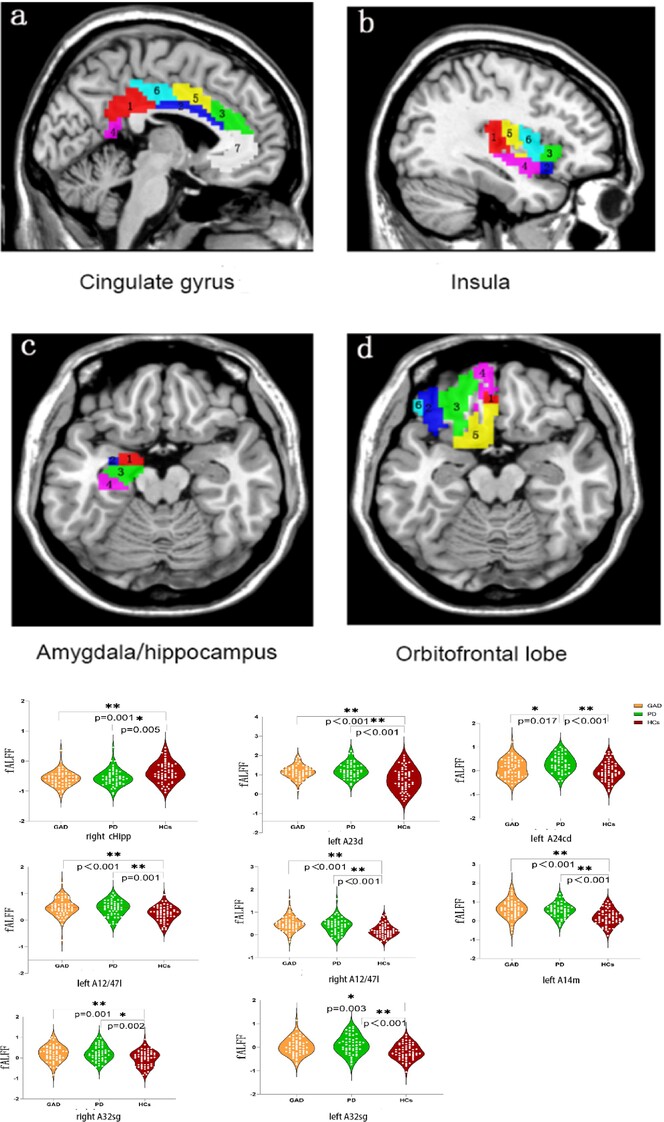
This study aims to explore the regional activity within the prefrontal-limbic circuit among drug-naive individuals diagnosed with GAD and panic disorder (PD) and to analyze changes following treatment. To our knowledge, this study is the first to explore the regional activity within the prefrontal-limbic system circuitry using a finely tuned Brainnetome atlas. A major strength of this study is that the abnormal regional activity in the right cHipp subregion of the hippocampus, left A23d and bilateral A32sg subregions of the cingulate, as well as the left A14m and bilateral A12/47L subregions of the orbitofrontal lobe, may be related to anxiety-induced state changes. In addition, high fALFF levels in the right A13 and right A24cd subregions could serve as predictors for individual responses to antipsychotic therapy.
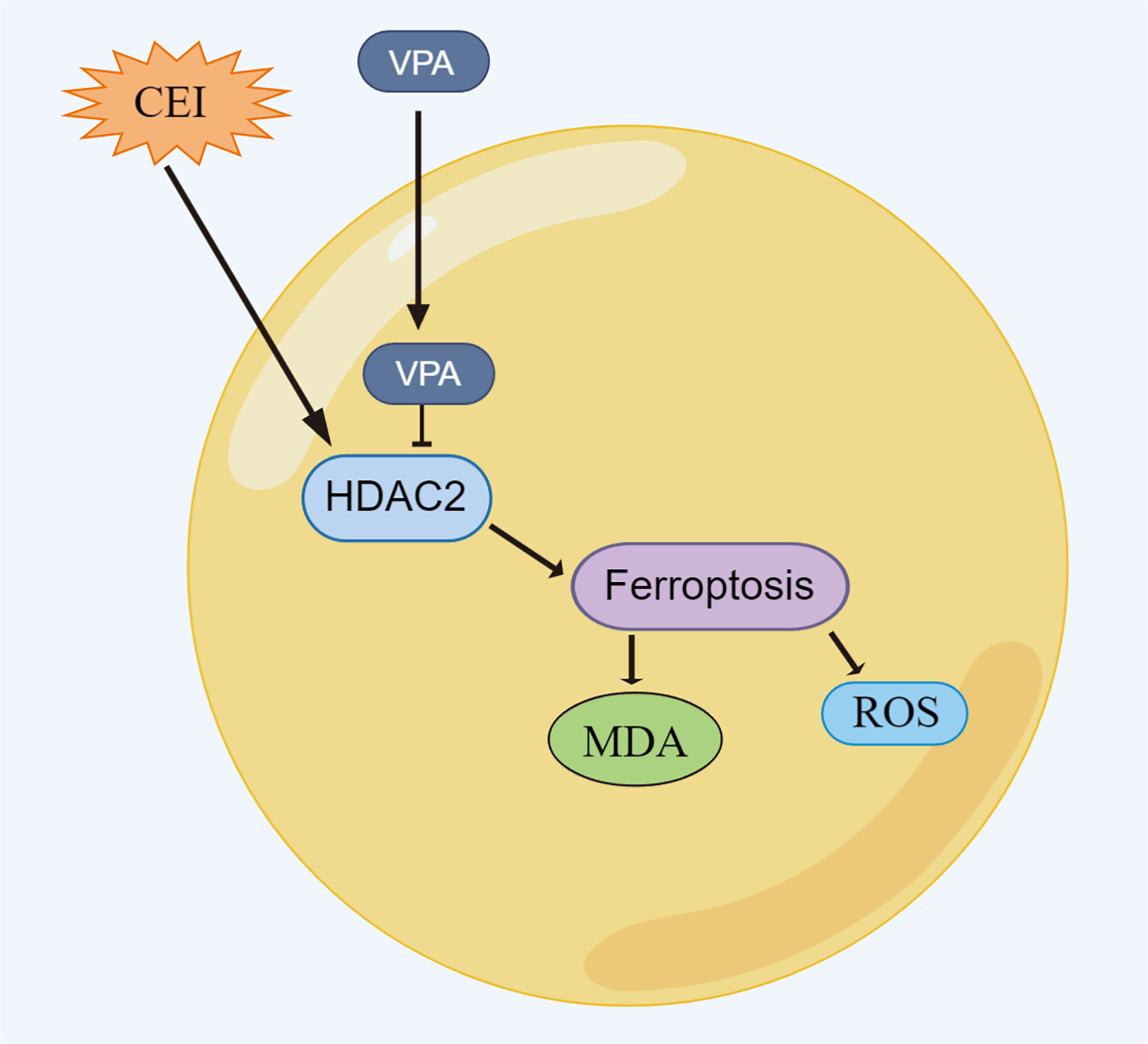
Valproic acid ameliorates cauda equina injury by suppressing HDAC2-mediated ferroptosis
- First Published: 17 December 2023
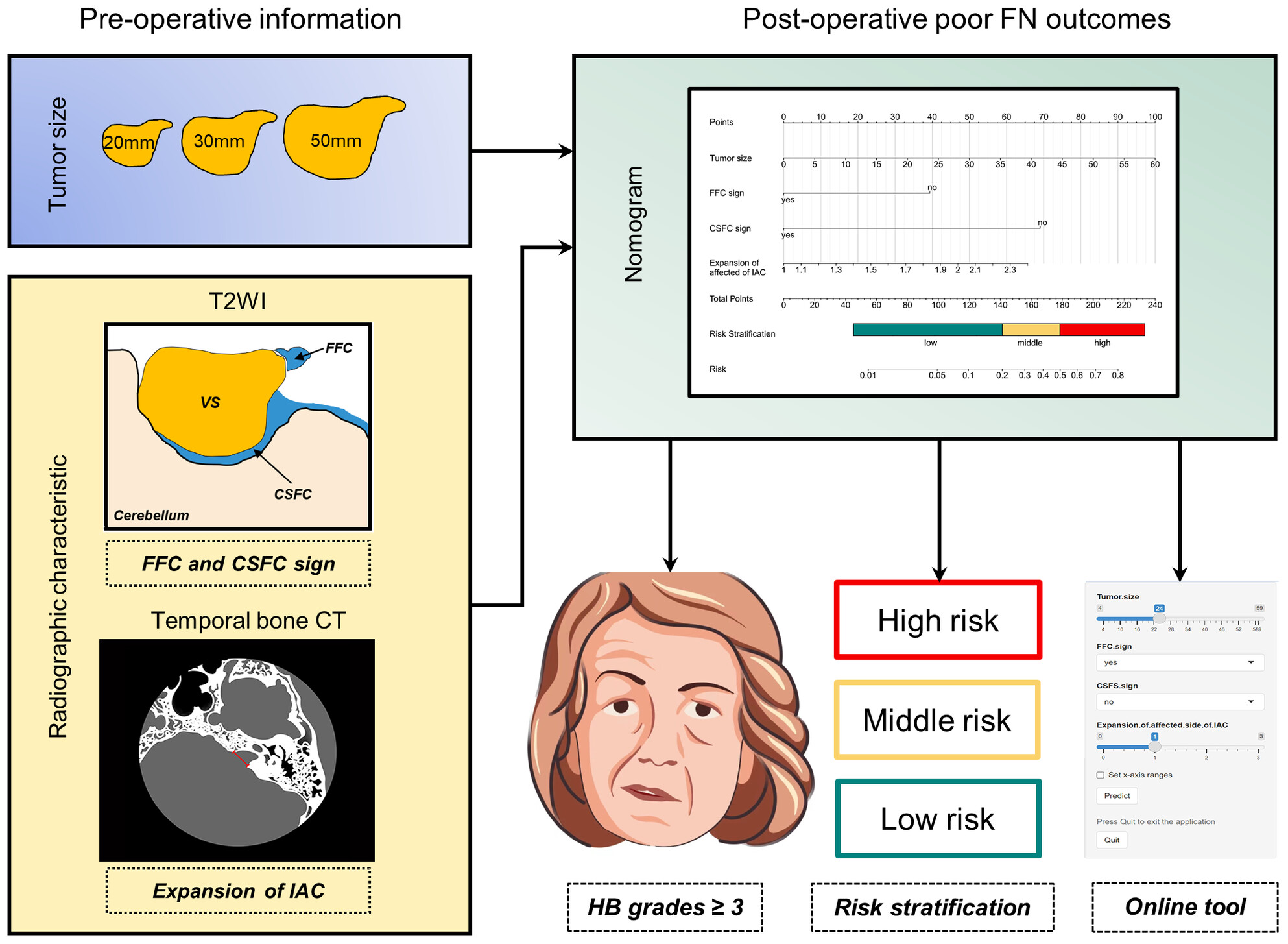
The value of radiographic features in predicting postoperative facial nerve function in vestibular schwannoma patients: A retrospective study and nomogram analysis
- First Published: 21 November 2023
Icaritin greatly attenuates β-amyloid-induced toxicity in vivo
- First Published: 21 November 2023
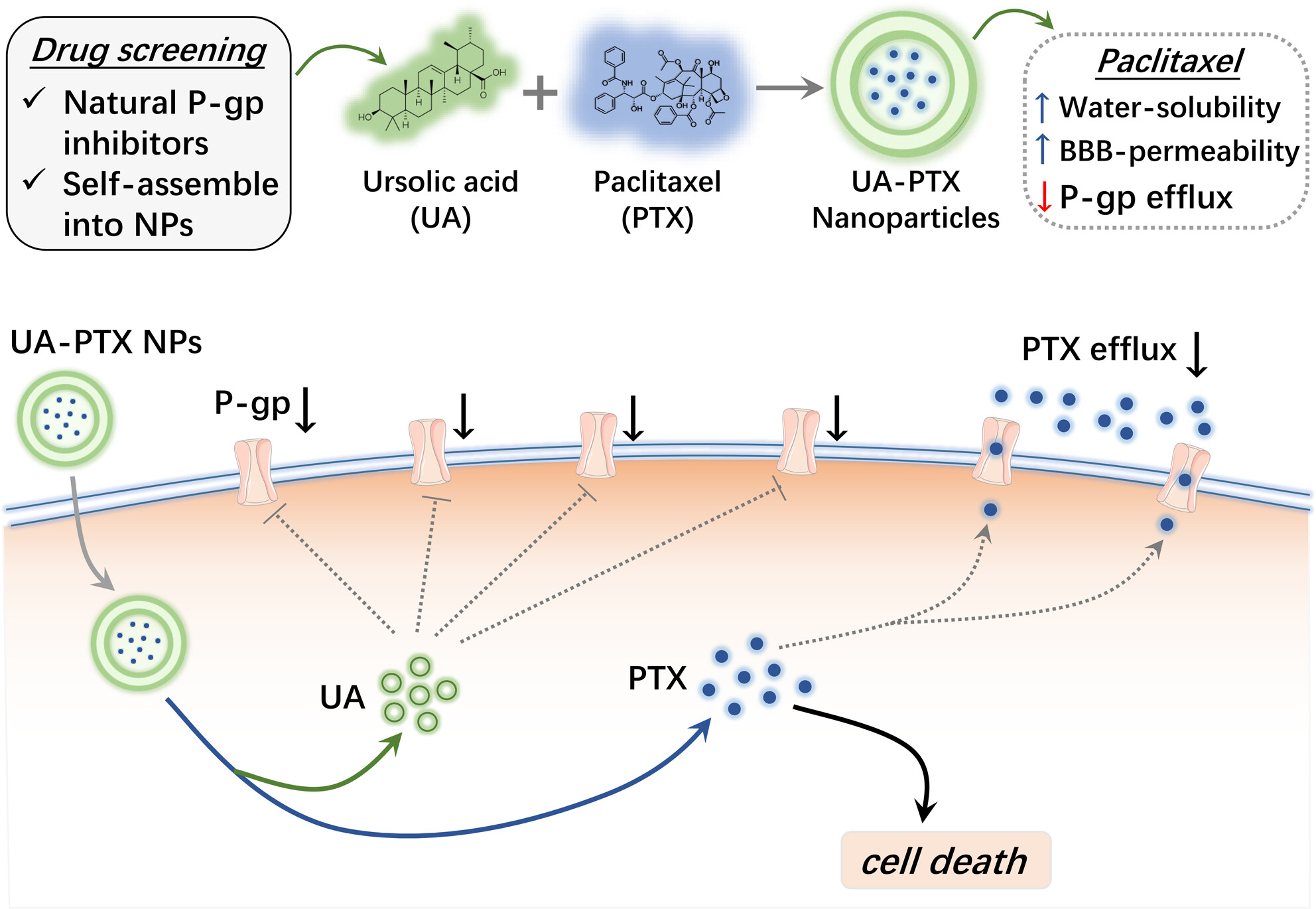
Self-Assembled nanoparticles of natural bioactive molecules enhance the delivery and efficacy of paclitaxel in glioblastoma
- First Published: 04 December 2023
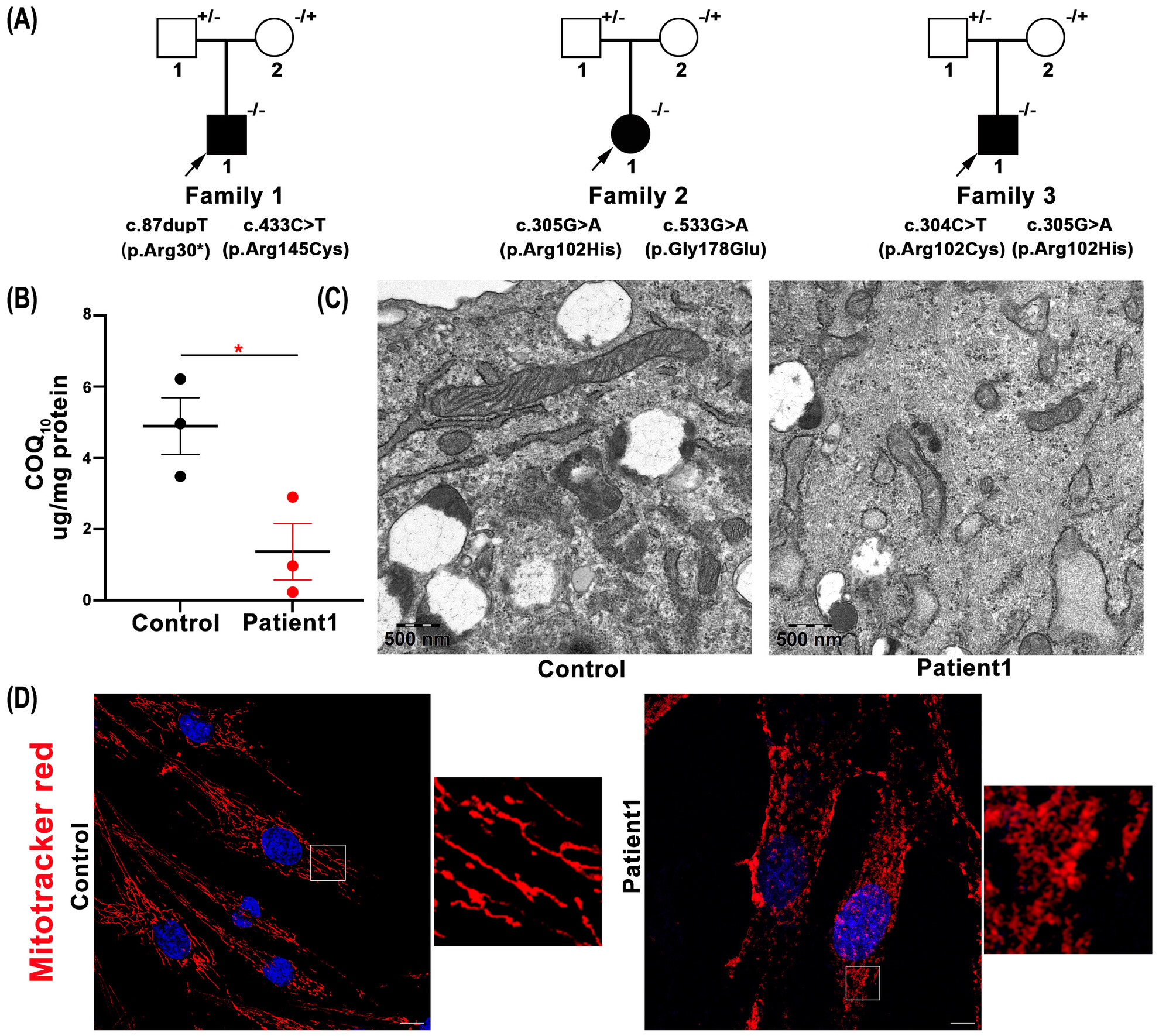
Biallelic variants in the COQ4 gene caused hereditary spastic paraplegia predominant phenotype
- First Published: 27 November 2023
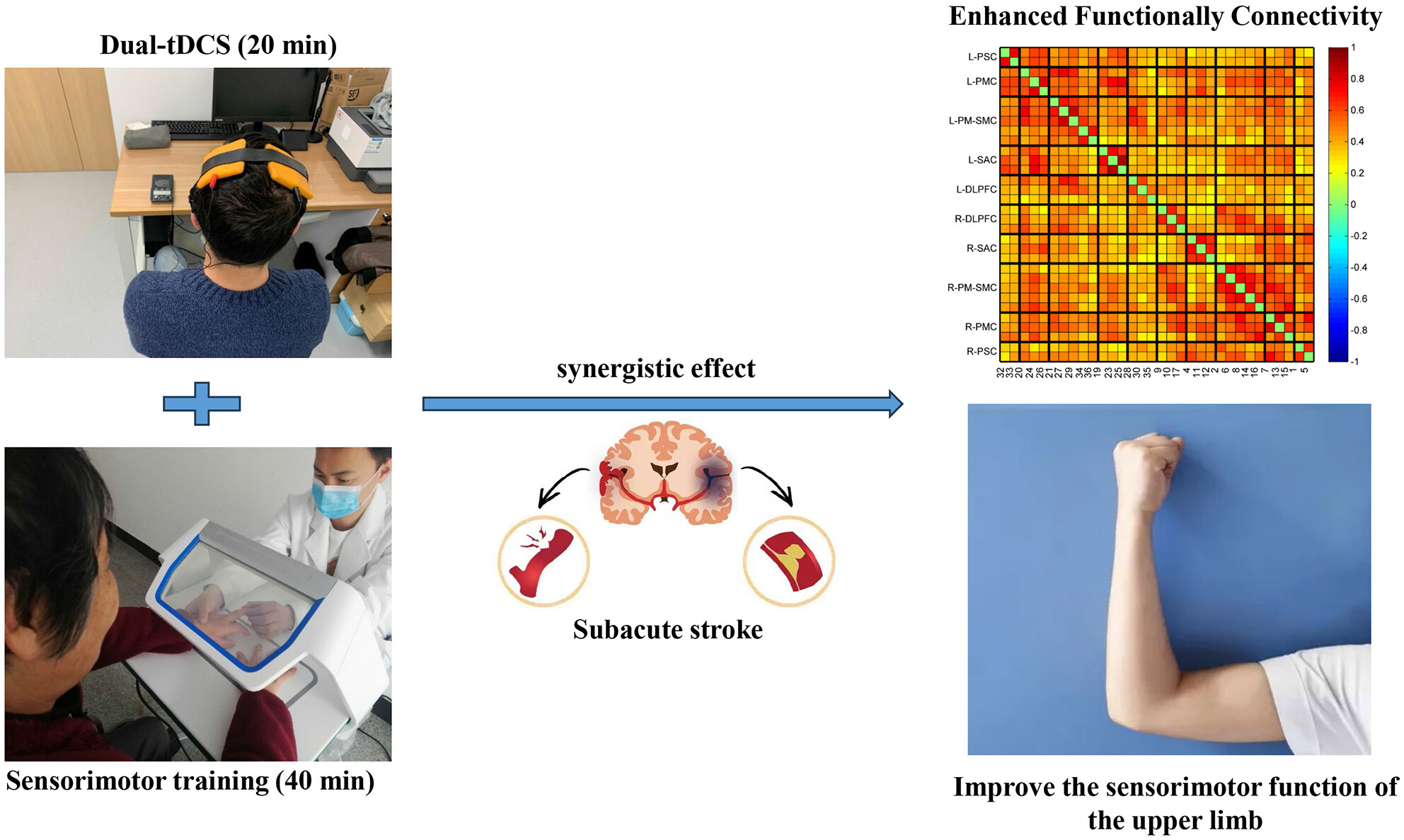
Dual-tDCS combined with sensorimotor training promotes upper limb function in subacute stroke patients: A randomized, double-blinded, sham-controlled study
- First Published: 23 November 2023
Comparison of the effectiveness, safety, and costs of anti-Parkinson drugs: A multiple-center retrospective study
- First Published: 20 November 2023
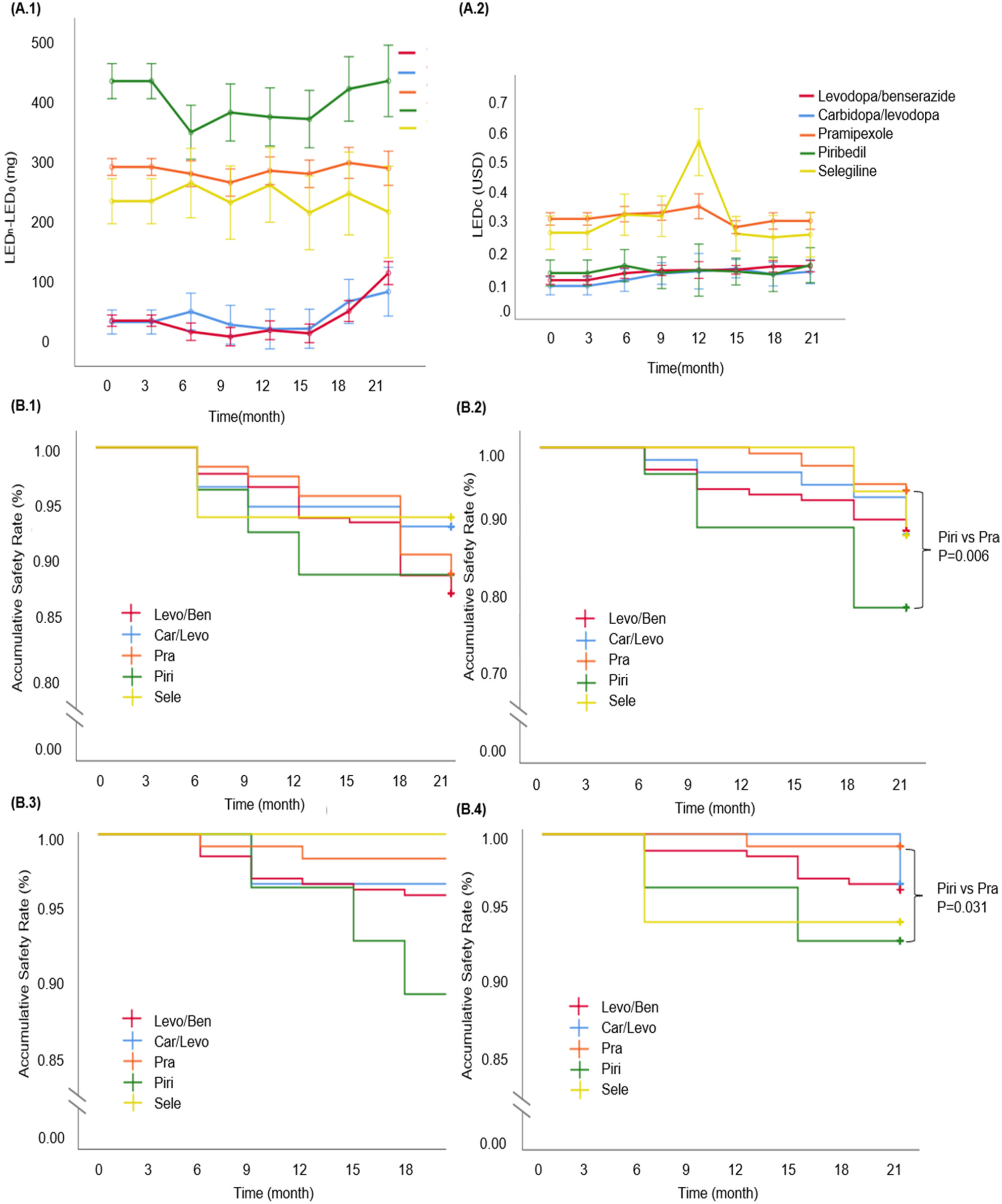
With a lack of comprehensive comparisons among anti-Parkinson drugs (APDs), this multi-center retrospective study systematically compared the effectiveness, safety, and costs of different APDs. Carbidopa/levodopa or levodopa/benserazide might exhibit better clinical improvement with less medical cost, while piribedil presented less clinical improvement but a higher risk in headache/dizziness, gastrointestinal, and neuropsychiatric symptoms.
Identification of mitophagy-associated proteins profile as potential plasma biomarkers of idiopathic Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 21 November 2023
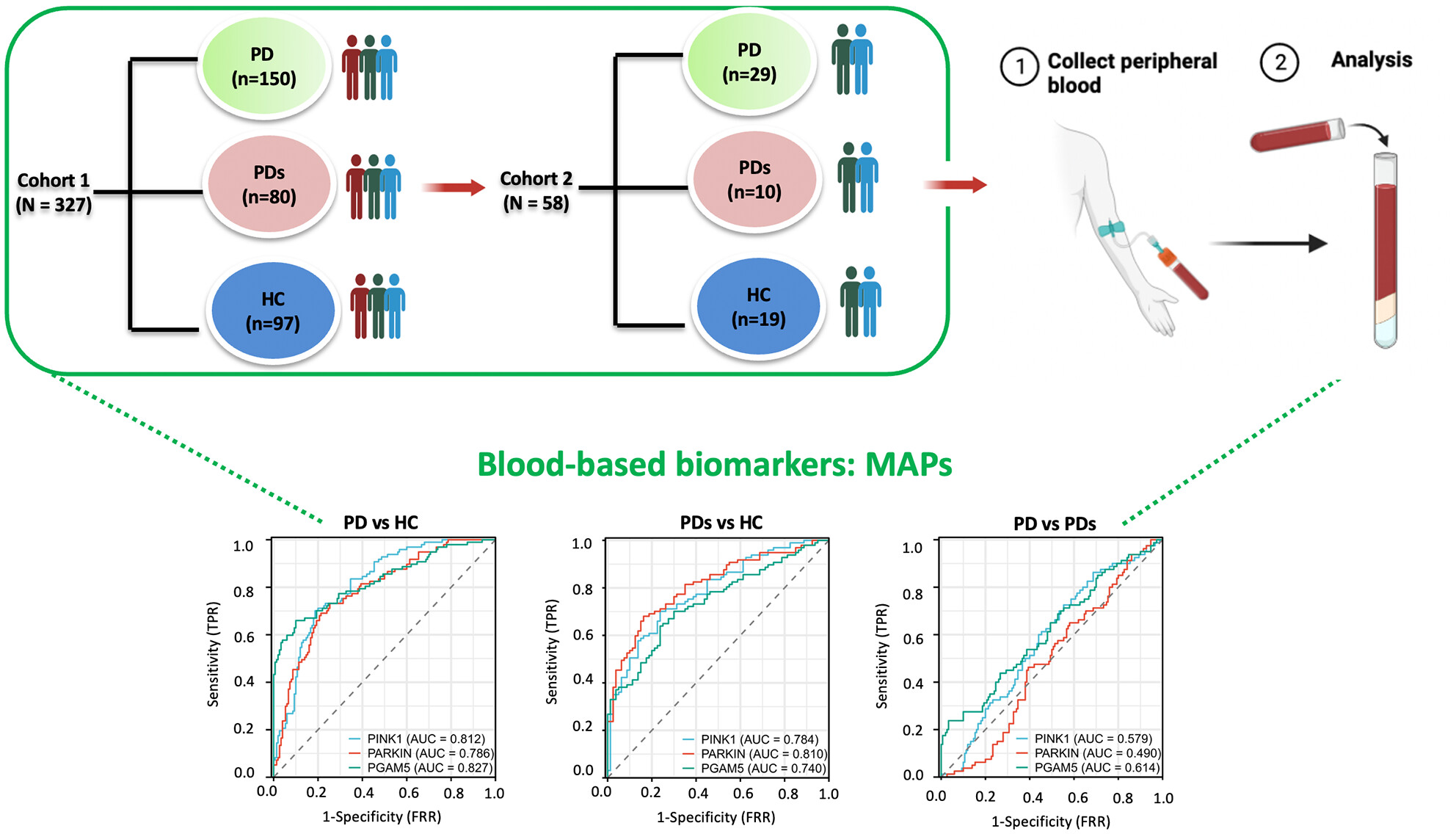
Subjects with Parkinson's disease (PD) or PDs exhibit higher mitophagy-associated protein (MAP) levels compared to the CN group, but the differences in values between PD and PDs did not reach significance. The AUCs of PINK1, PGAM5, and Parkin were ranked as the top three MAP candidates in diagnosis accuracy for PD from CN. Higher plasma PINK1-Parkin levels and prominent diagnostic accuracy in A-syn (+) subjects are higher than in A-syn (−) subjects.
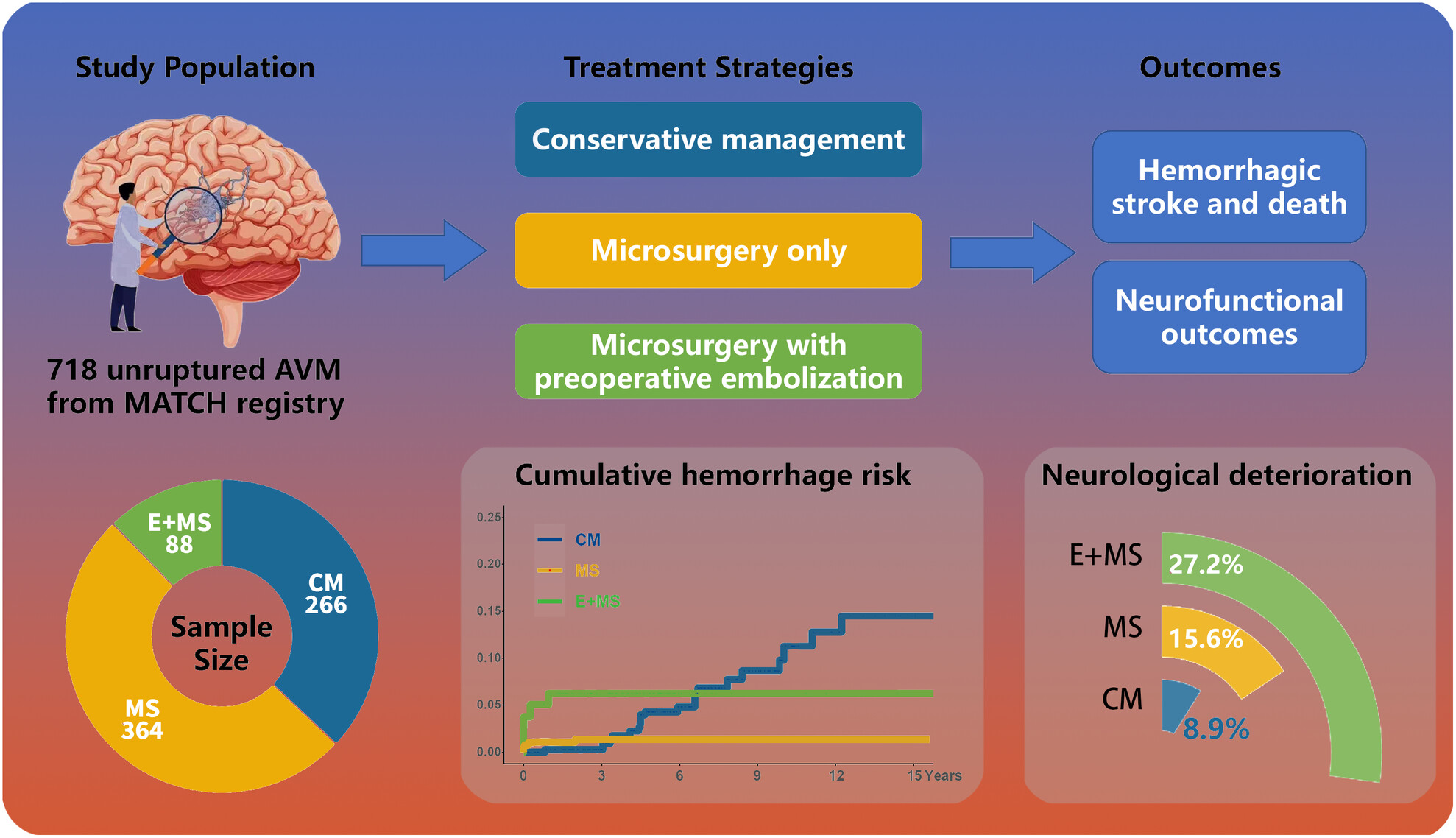
Comparison of conservative management, microsurgery only, and microsurgery with preoperative embolization for unruptured arteriovenous malformations: A propensity score weighted prospective cohort study
- First Published: 21 November 2023
Paraventricular thalamus-insular cortex circuit mediates colorectal visceral pain induced by neonatal colonic inflammation in mice
- First Published: 23 November 2023
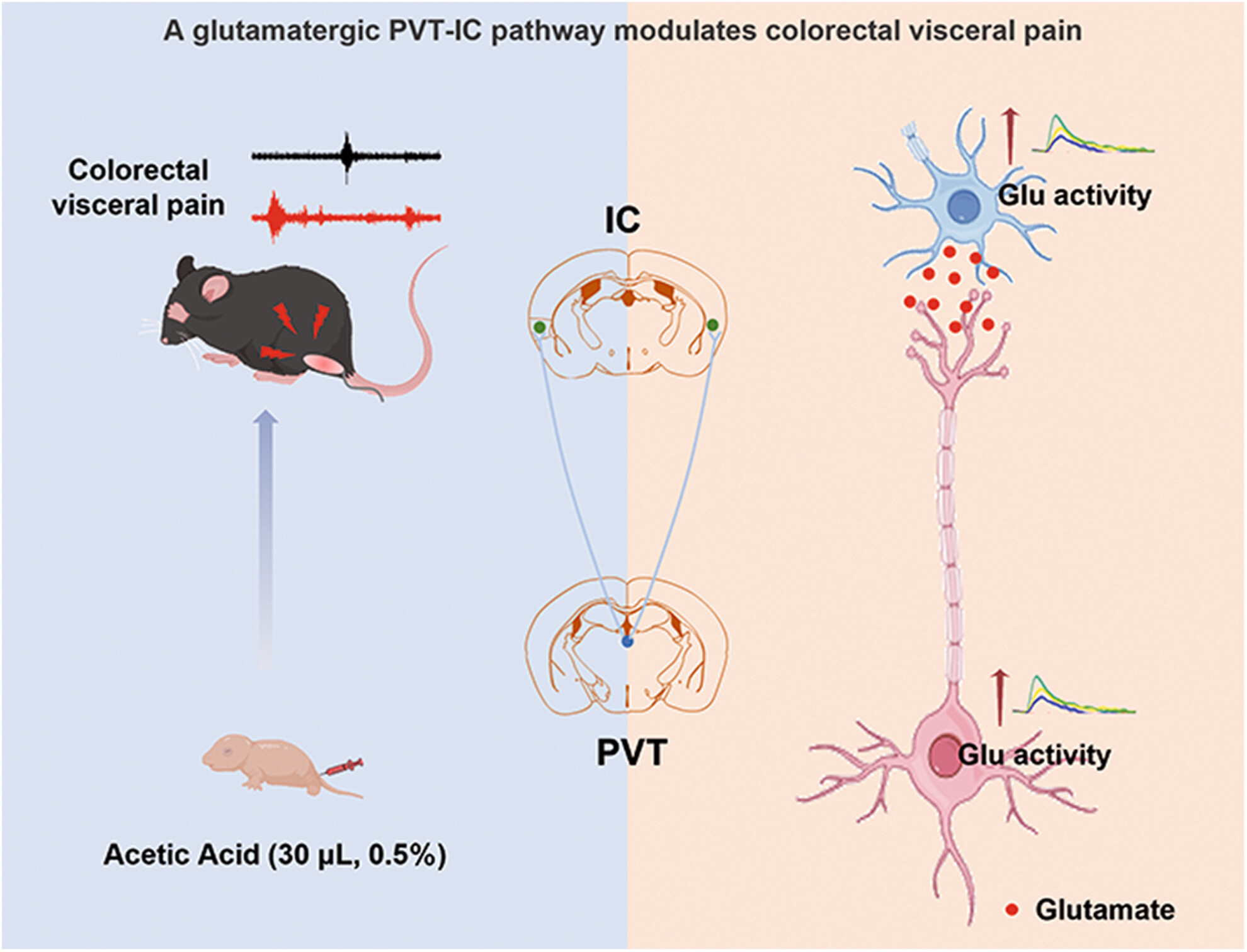
A direct PVT-IC glutamate neural circuit playing a critical role in visceral hypersensitivity in a mouse model of IBS. This work will strengthen fundamental research on the involvement of central nervous system in visceral hyperalgesia and provide potential therapeutic targets toward effective treatment.
Vof16-miR-185-5p-GAP43 network improves the outcomes following spinal cord injury via enhancing self-repair and promoting axonal growth
- First Published: 02 January 2024
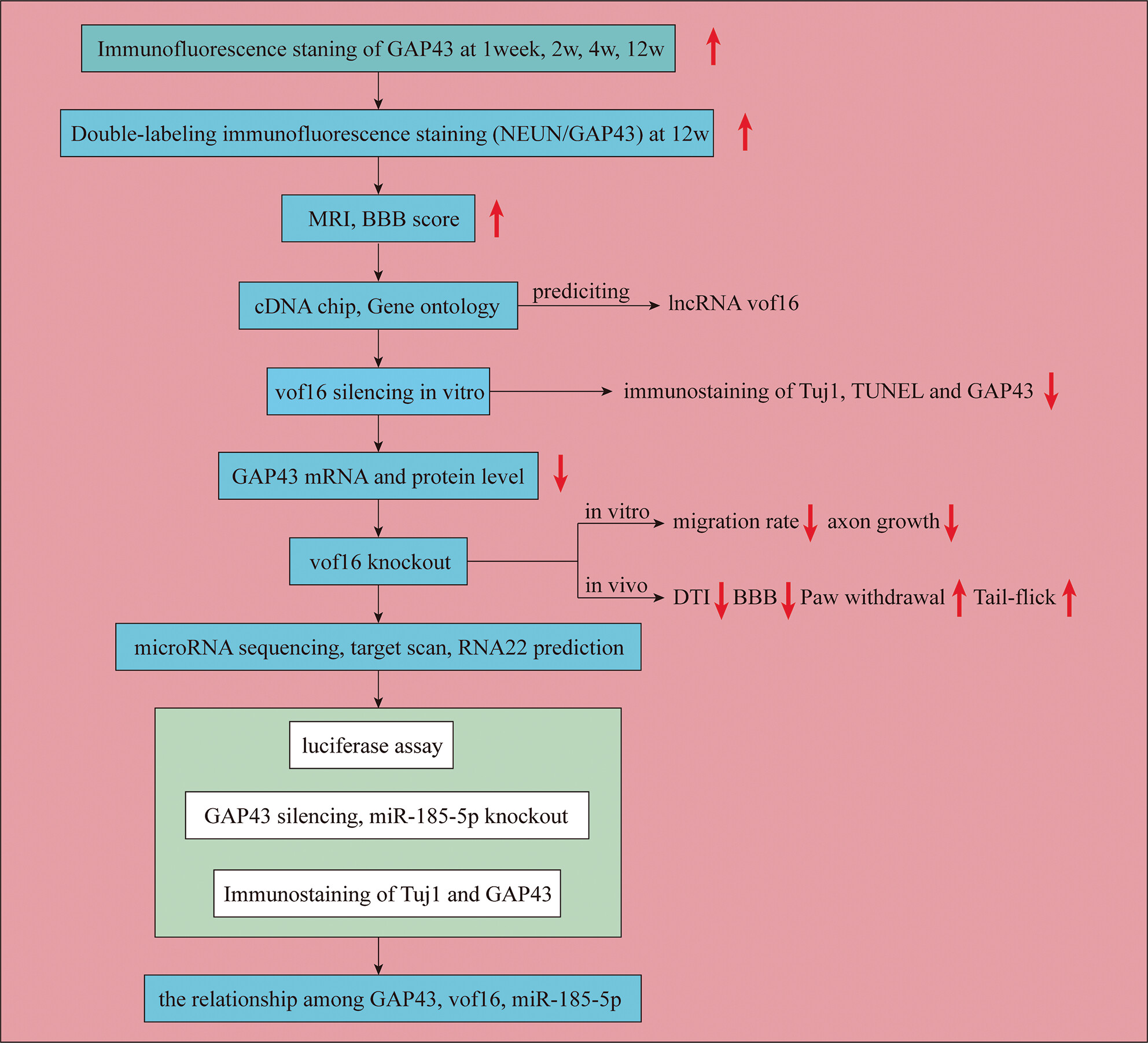
Here, we found that vof16-miR185-5p-GAP43 network is closely related to SCT self-repair, and simultaneously enhances motor and sensory function after SCT. Knocking out vof16 or GAP43 could inhibit the self-repair of spinal cord and neurite growth, while miR-185-5p knockout promoted the axonal growth after SCT. Furthermore, miR-185-5p can competitively bind the same regulatory region of vof16 and GAP43. Our study provides a novel regulatory network that functions via a miRNA competitive mechanism mediated by vof16 in SCT self-repair and axonal growth.
The phosphokinase activity of IRE1ɑ prevents the oxidative stress injury through miR-25/Nox4 pathway after ICH
- First Published: 23 November 2023
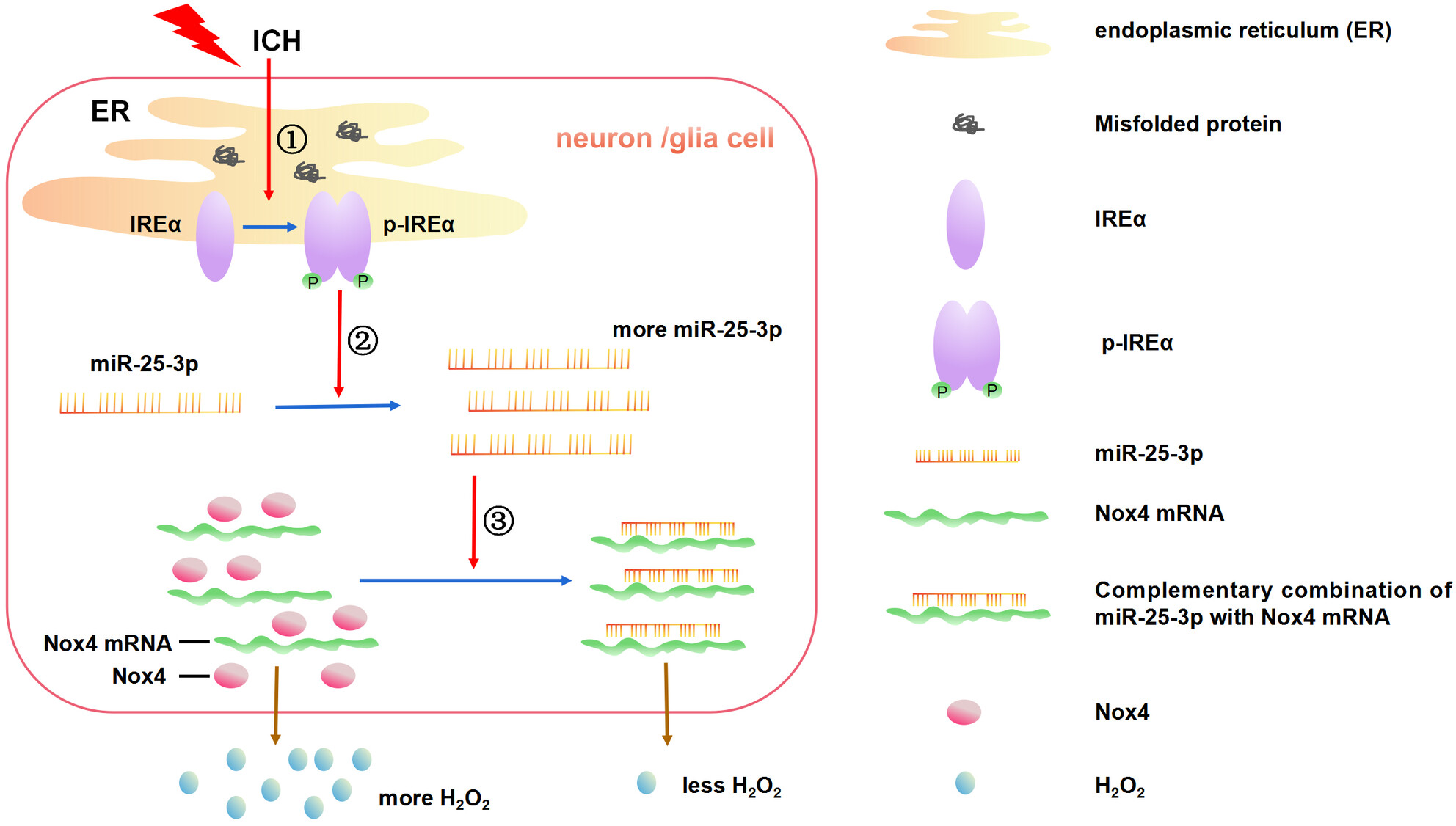
The proposed pathway by which IRE1α regulates the oxidative stress response via miR-25-3p/Nox4 after ICH. ① ICH induces ER stress and activates the phosphokinase activity of IRE1α. ② Self-phosphorylated IRE1ɑ increases the expression of miR-25-3p. ③ The complementary combination of miR-25-3p with Nox4 mRNA inhibits the translation of Nox4 mRNA and subsequently downregulated expression of Nox4, which leads to ROS production decrease, especially H2O2.
Multiparametric hippocampal signatures for early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease using 18F-FDG PET/MRI Radiomics
- First Published: 30 November 2023
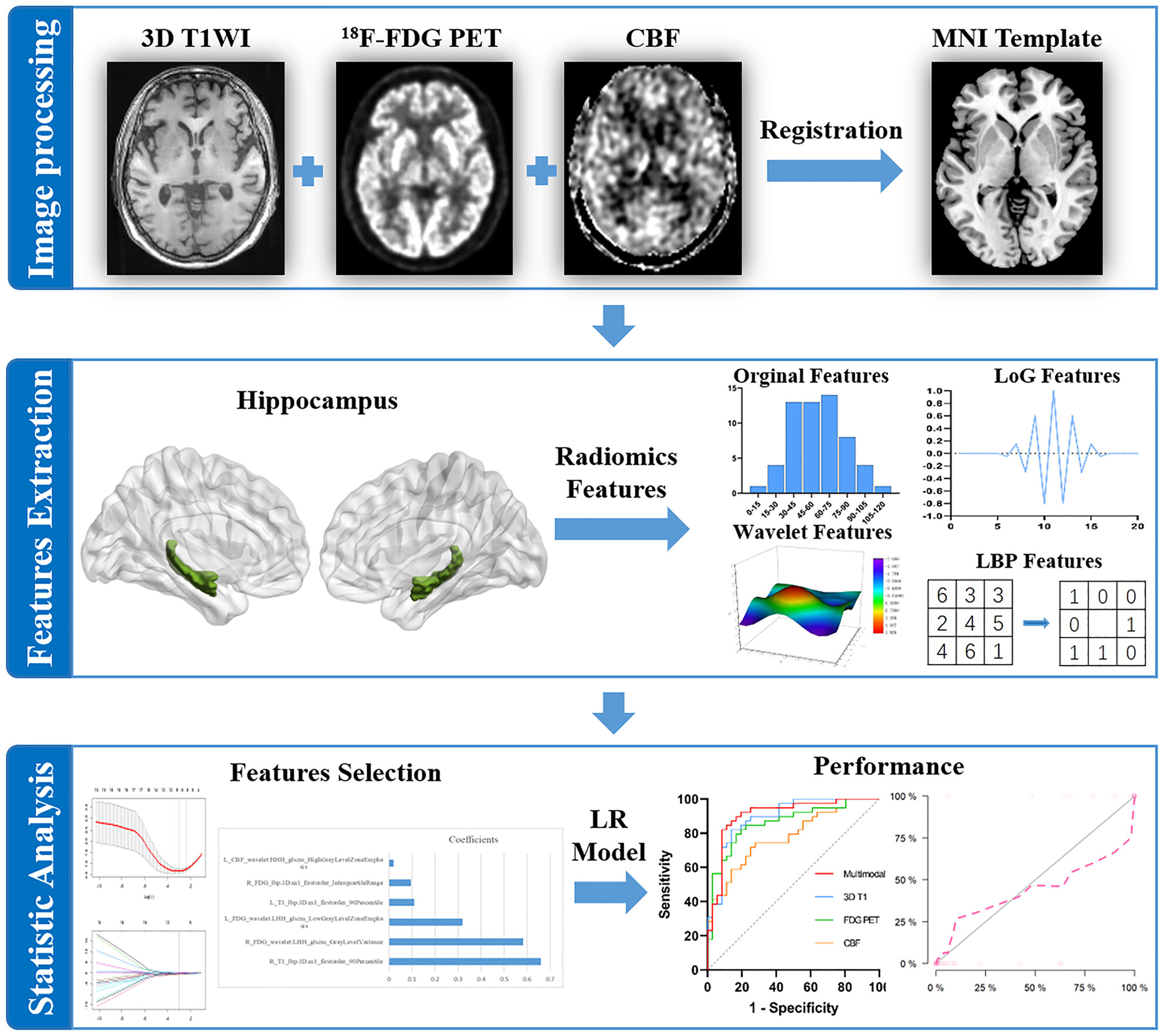
This study aimed to investigate multiparametric imaging of the hippocampal radiomics for early diagnosis of AD using simultaneous PET/MRI. Our findings demonstrated that multi-dimensional imaging of the hippocampal radiomics benefits the identification of early AD (aMCI especially) and may provide a potential biomarker for clinical applications in AD.
The effect of dopamine replacement therapy on cortical structure in Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 23 November 2023
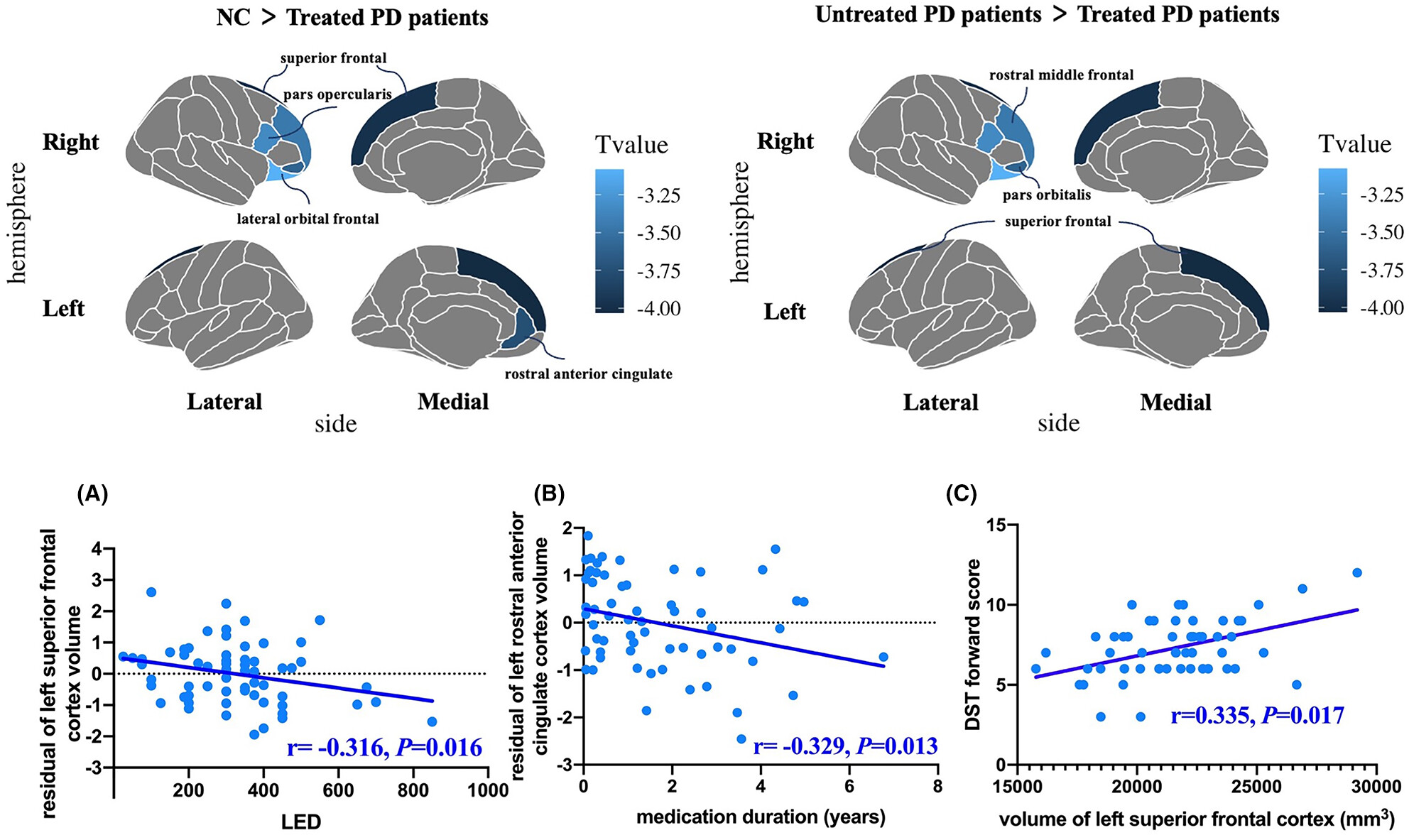
Significant cortical atrophy was primarily observed in the prefrontal cortex in DRT-treated patients, including bilateral superior frontal cortex (SFC) and left rostral anterior cingulate cortex (rACC). the left SFC volume was negatively correlated with levodopa equivalency dose (LED), as well as the left rACC volume and medication duration.
Distinct alterations of retinal structure between thalamic and extra-thalamic subcortical infarction patients: A cross-sectional and longitudinal study
- First Published: 29 November 2023
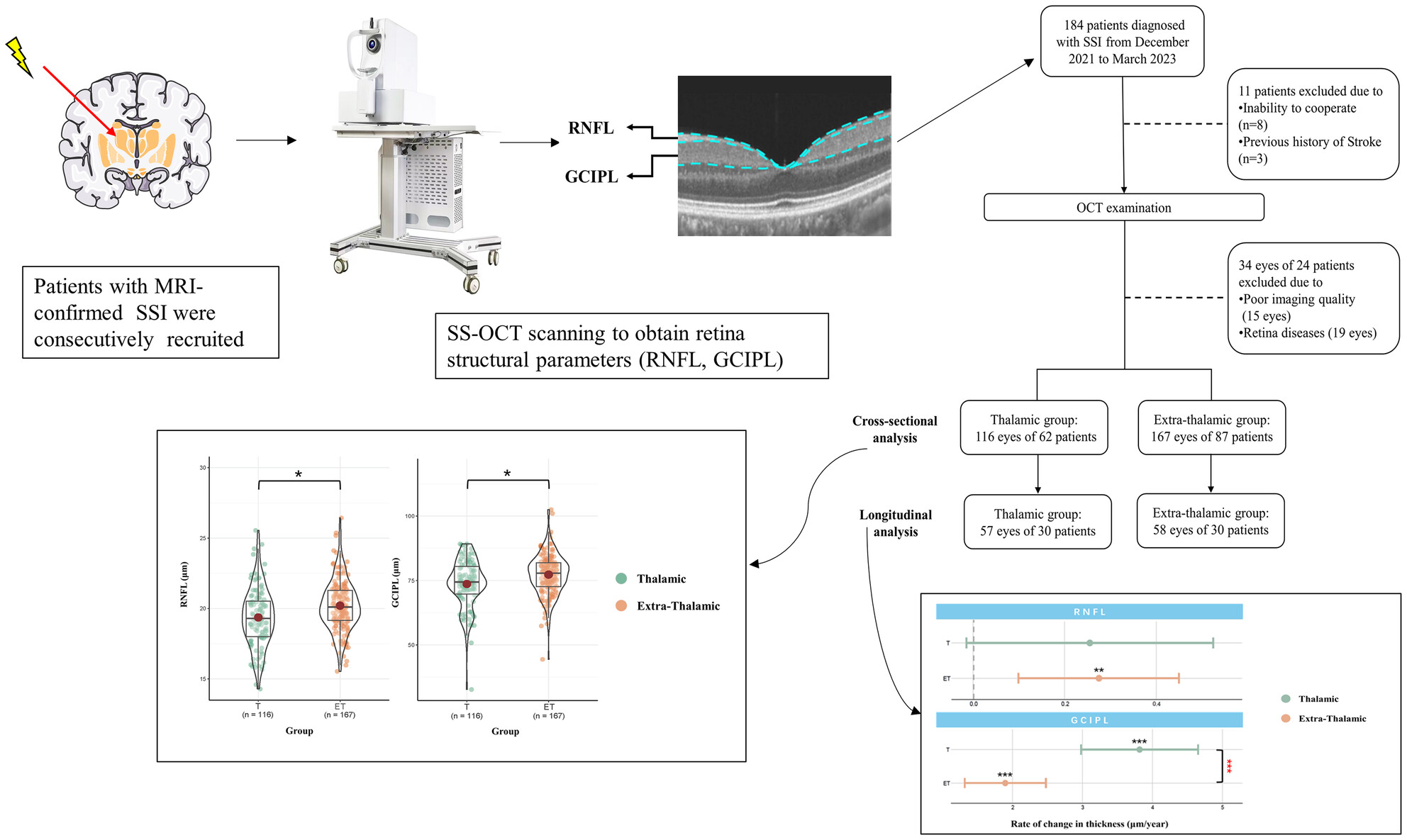
We explored the cross-sectional and longitudinal retinal structural thicknesses in SSI patients based on their location. We showed at the baseline that thalamic infarction patients had thinner RNFL and GCIPL thicknesses compared with extra-thalamic stroke patients. Longitudinal analysis showed the thinning rate in GCIPL of the thalamic infarction group was significantly higher than that in the extra-thalamic infarction group.
Disrupted topological organization of the default mode network in mild cognitive impairment with subsyndromal depression: A graph theoretical analysis
- First Published: 17 December 2023

The global efficiency and nodal efficiency were significantly lower in mild cognitive impairment with SSD (MCID), and the accuracy of the support vector machine model was 0.83 for distinguishing MCID from MCIND. MCID is correlated to the greatest disrupted topological organization, which may serve as biomarkers of different MCI subgroups.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Familial Mediterranean fever concurrent with autoimmune glial fibrillary acidic protein astrocytopathy in a young adult
- First Published: 23 November 2023
Childhood stroke associated with protein C and S deficiency
- First Published: 21 September 2023
Carotid artery stiffness induced by the fine particulate matter PM2.5 could be alleviated by exercise
- First Published: 07 October 2023
Co-housing with Alzheimer's disease mice induces changes in gut microbiota and impairment of learning and memory in control mice
- First Published: 03 October 2023
CORRIGENDUM
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Automatic sleep–wake classification and Parkinson's disease recognition using multifeature fusion with support vector machine
- First Published: 11 April 2024
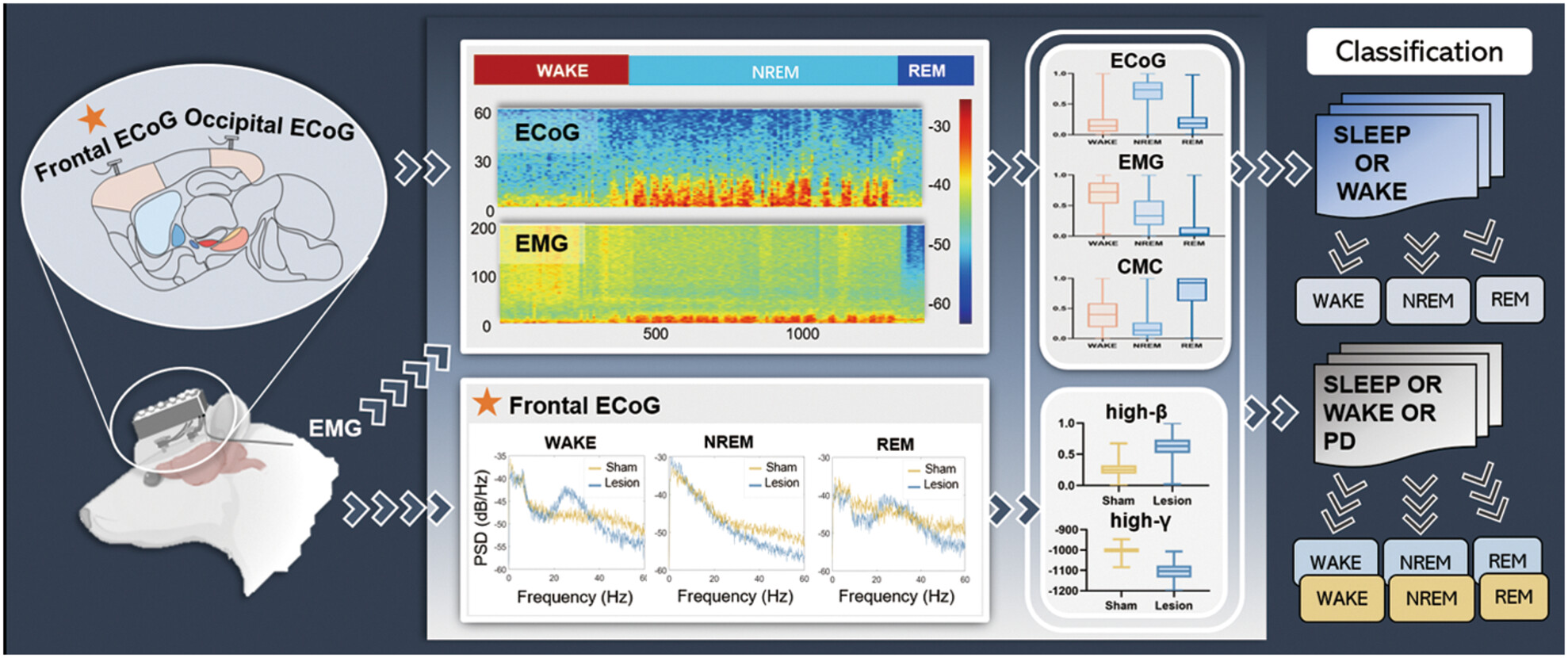
This study utilized electrocorticographic (ECoG) power, electromyogram (EMG) amplitude, and corticomuscular coherence (CMC) values to construct sleep–wake scoring and Parkinson's disease (PD) prediction models based on the support vector machine (SVM) algorithm. The models enable precise classification and identification of sleep–wake states and exhibit robust performance across different rats.
Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein facilitates glioblastoma progression and radioresistance by regulating the ANXA2/STAT3 axis
- First Published: 11 April 2024
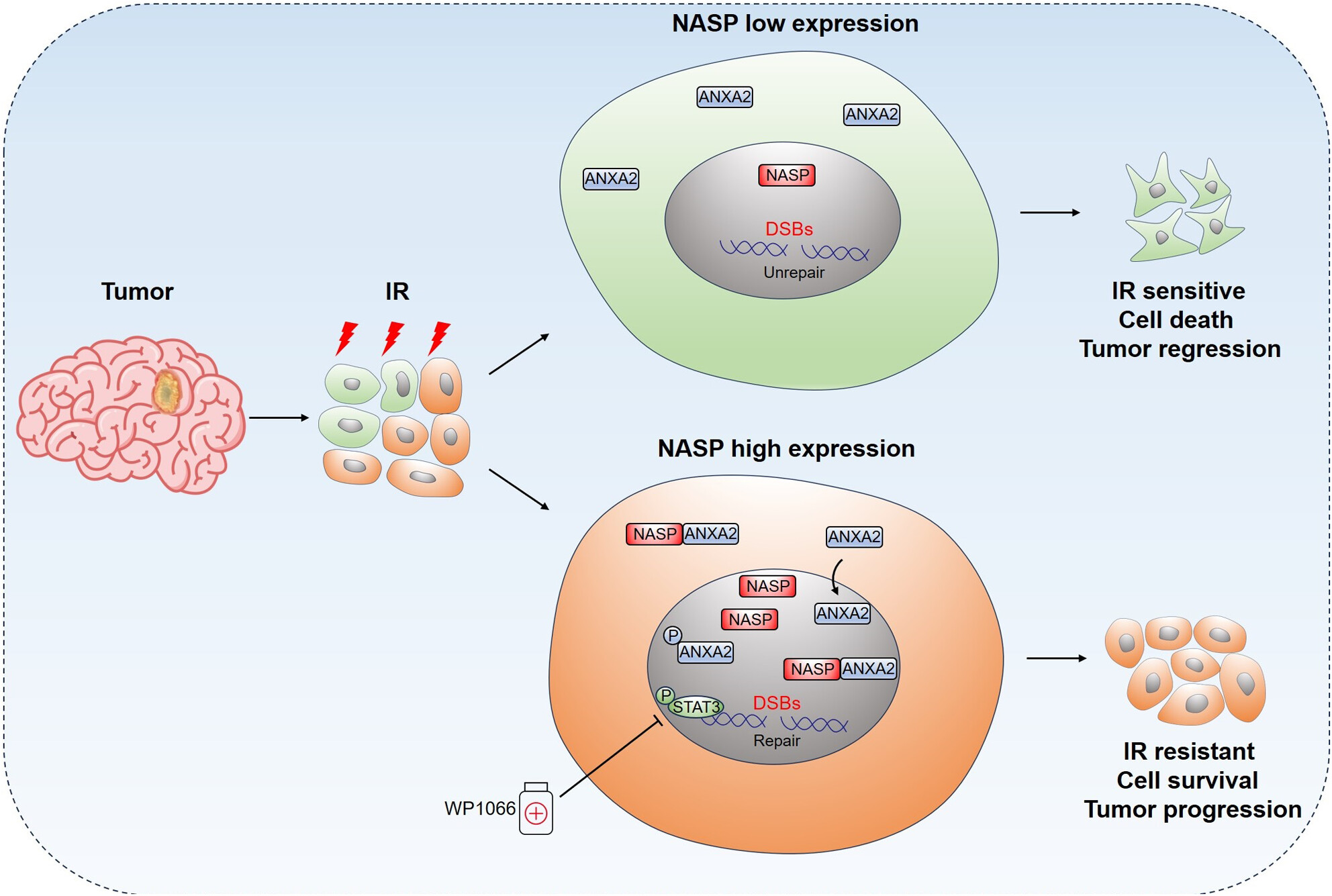
Nuclear autoantigenic sperm protein (NASP) plays a crucial role in glioblastoma progression and radioresistance, promotes DNA repair, and activates the STAT3 signaling pathway through ANXA2. The NASP/ANXA2/STAT3 axis is a potential therapeutic target for improving the prognosis of patients with GBM.
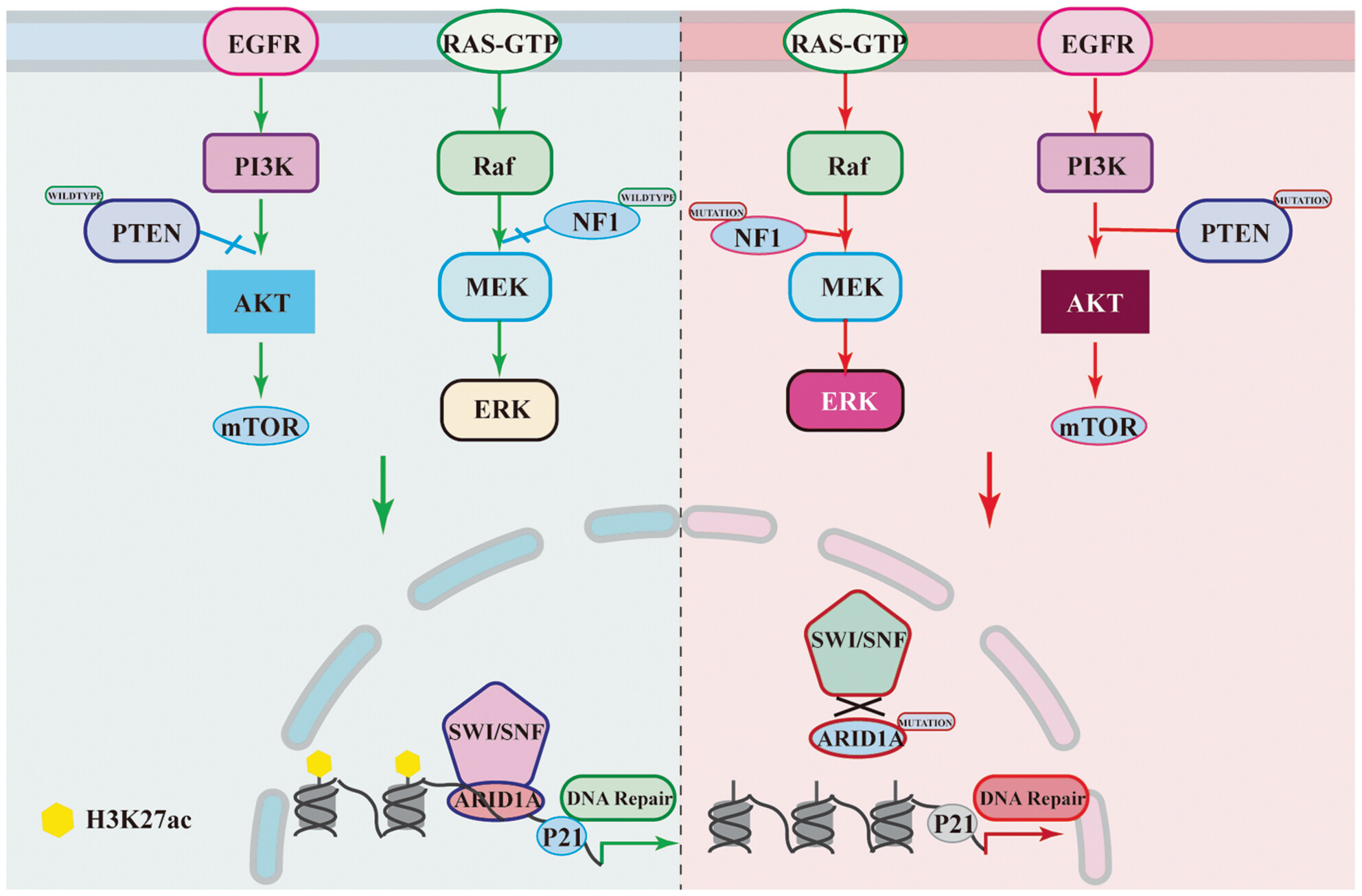
Deep-targeted gene sequencing reveals ARID1A mutation as an important driver of glioblastoma
- First Published: 11 April 2024
REVIEWS
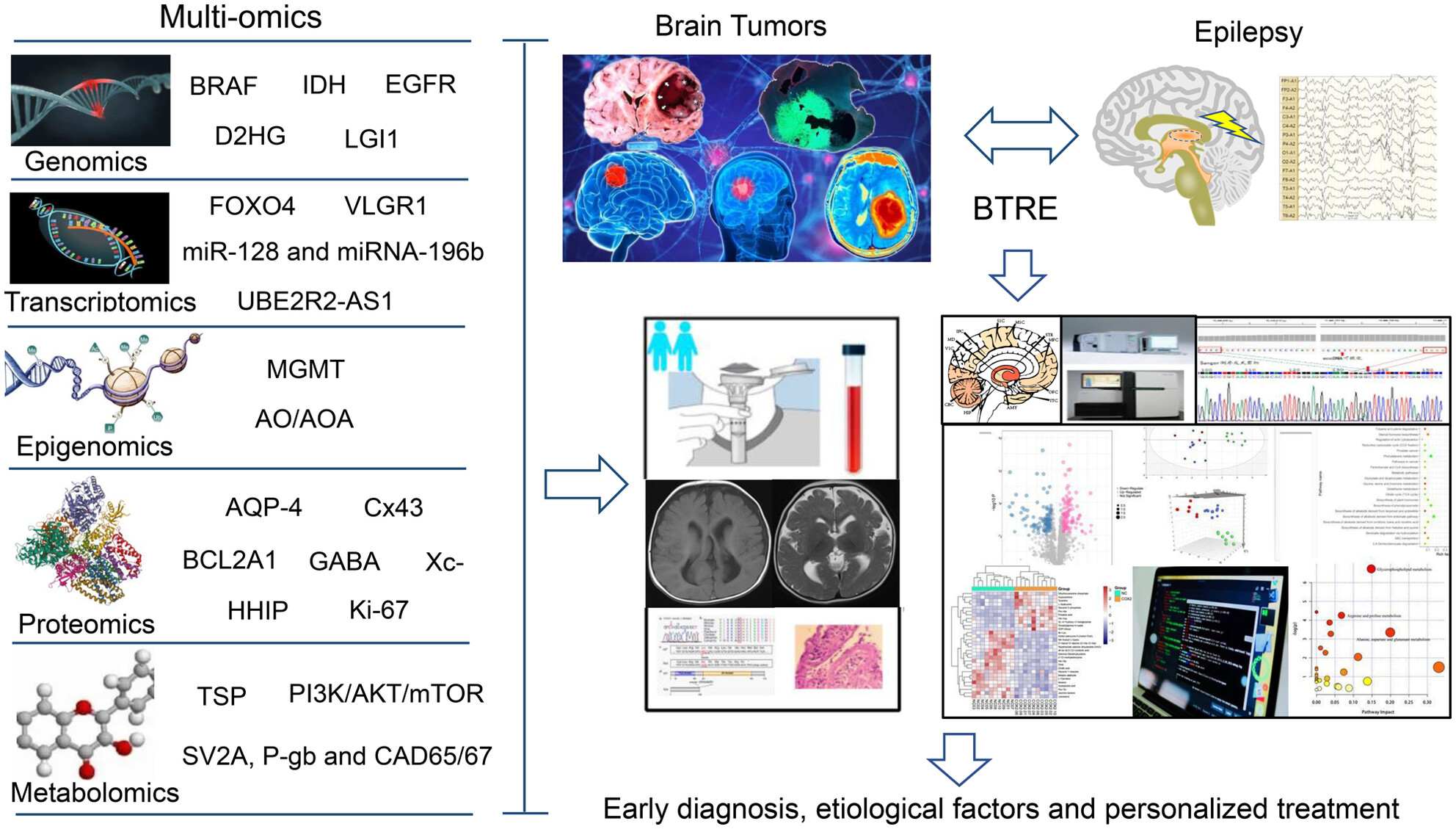
Multi-omics technologies and molecular biomarkers in brain tumor-related epilepsy
- First Published: 20 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
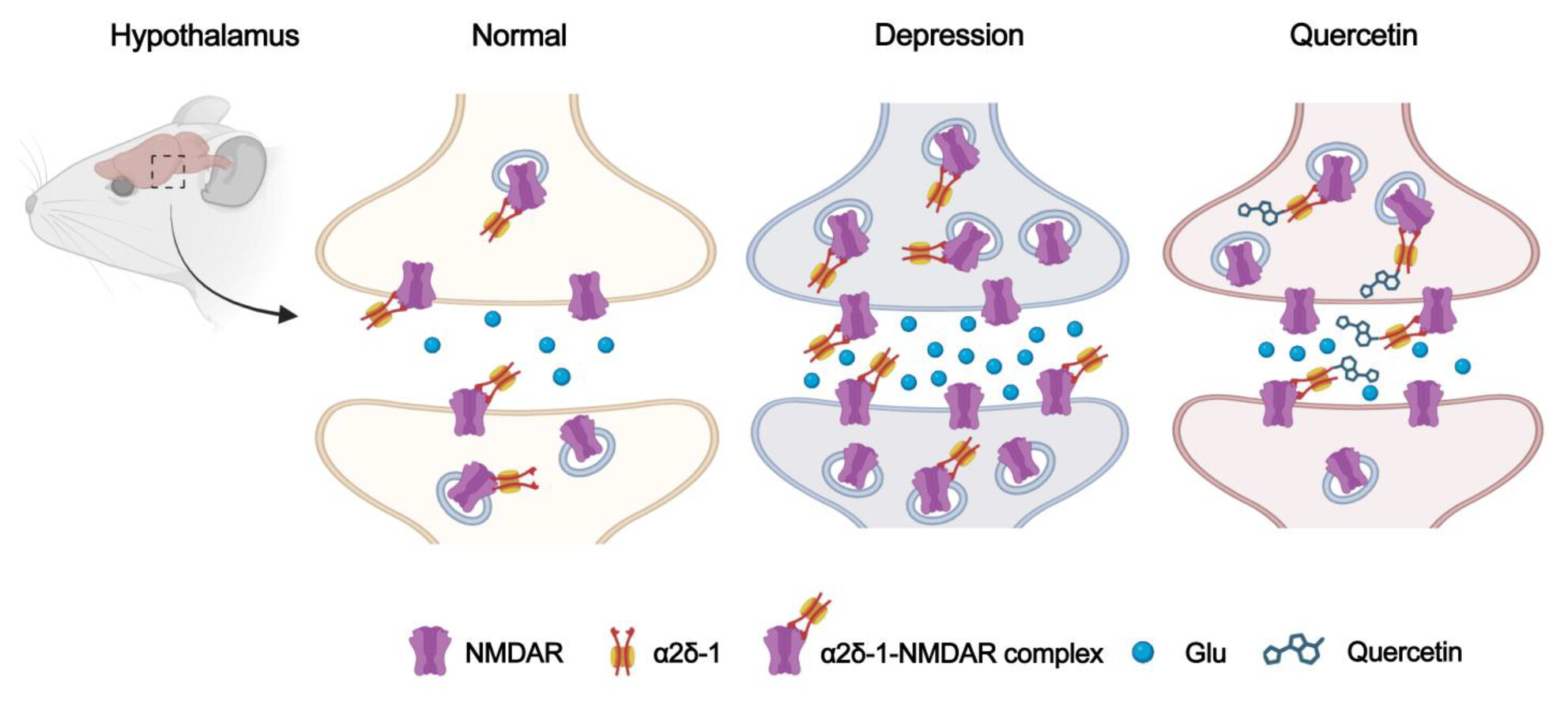
Quercetin alleviates chronic unpredictable mild stress-induced depression-like behavior by inhibiting NMDAR1 with α2δ-1 in rats
- First Published: 14 April 2024
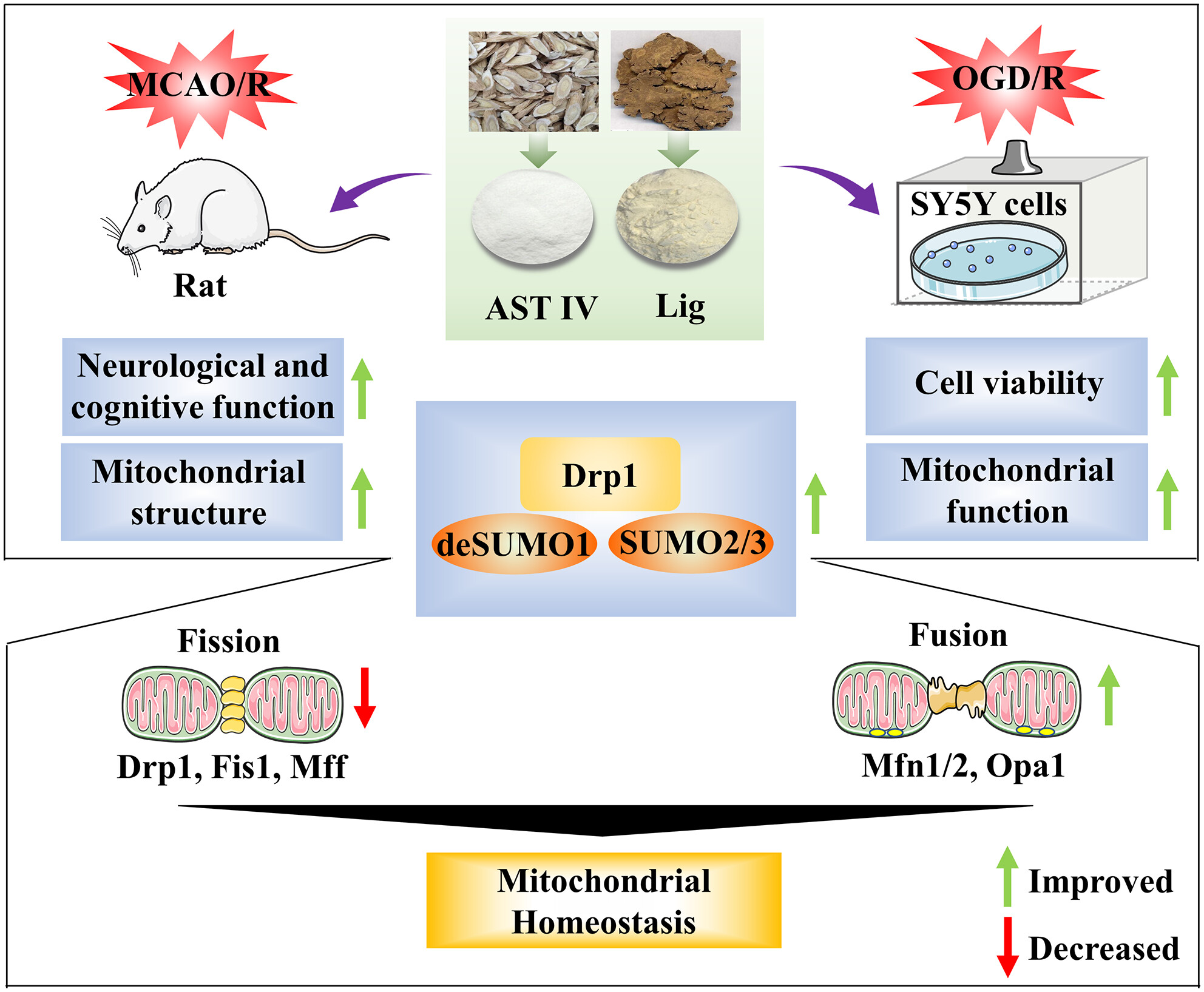
Astragaloside IV combined with ligustrazine ameliorates abnormal mitochondrial dynamics via Drp1 SUMO/deSUMOylation in cerebral ischemia–reperfusion injury
- First Published: 14 April 2024
The promotion-like effect of the M1-STN hyperdirect pathway induced by ccPAS enhanced balance performances: From the perspective of brain connectivity
- First Published: 14 April 2024
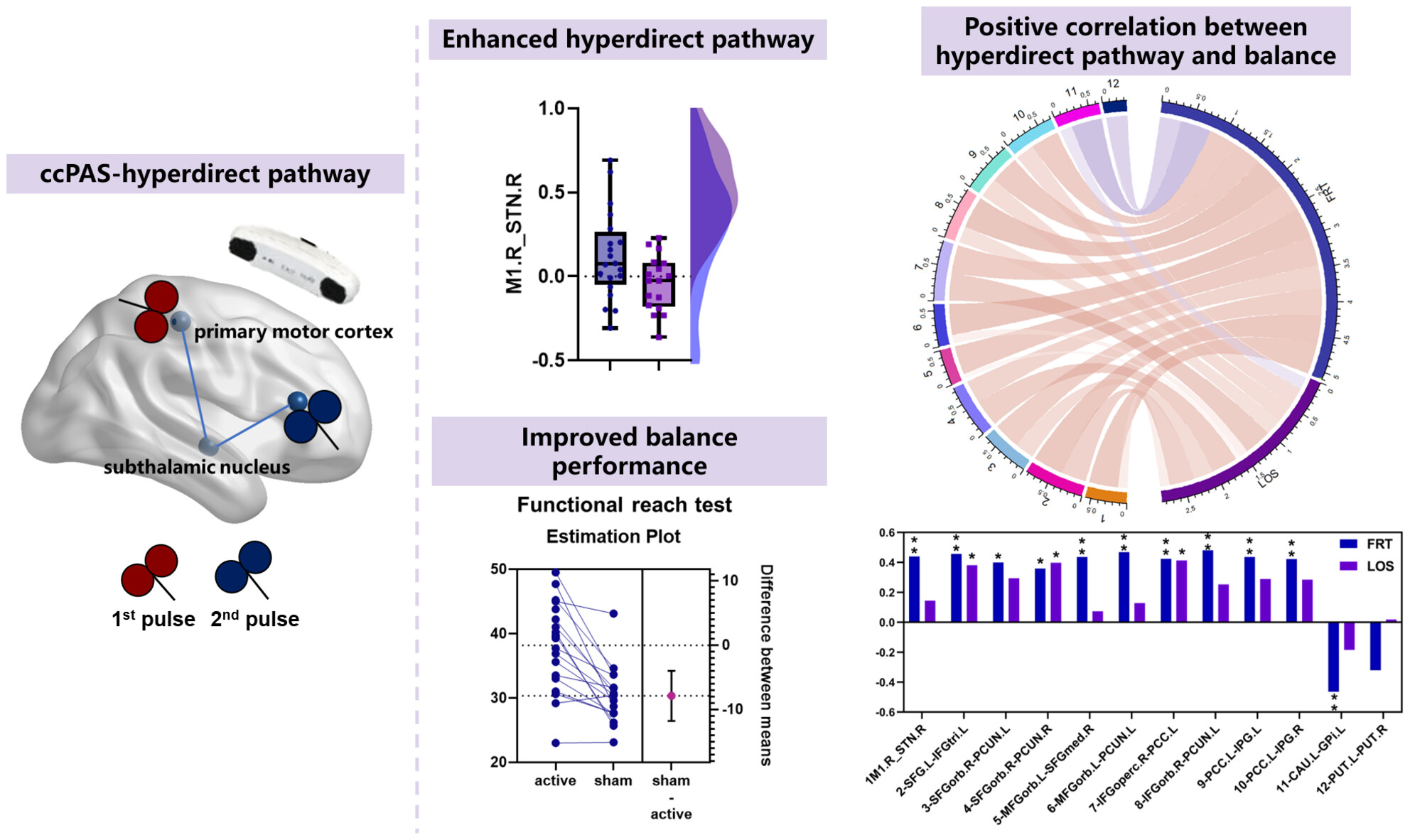
The targeted stimulation of the hyperdirect pathway (M1-STN connectivity) with ccPAS enhanced the functional connectivity between the M1 and STN and subsequently enhanced the balance performance, highlighting the capability and efficacy of ccPAS in regulating brain connectivity associated with functional impairments.
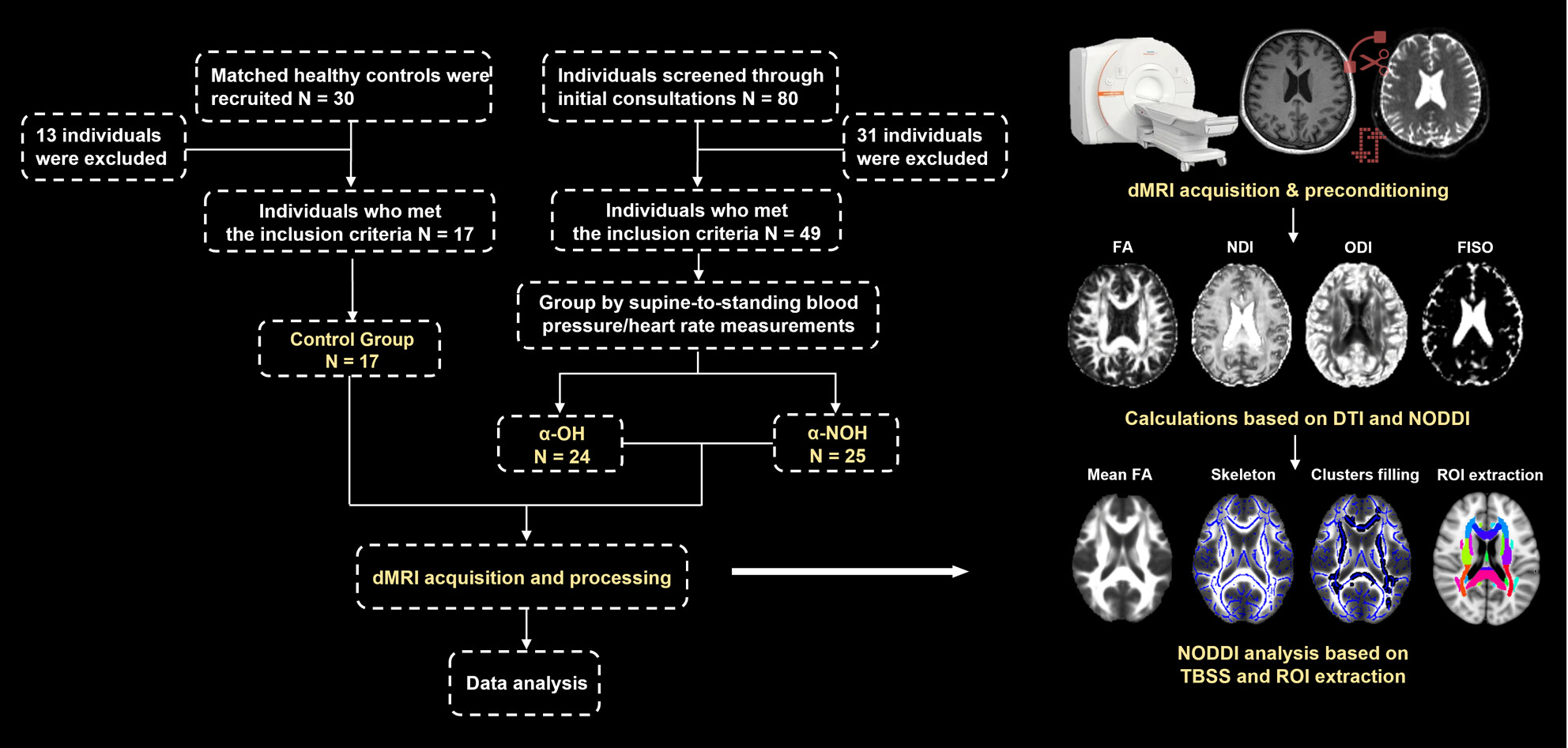
Brain white matter changes and their associations with non-motor dysfunction in orthostatic hypotension in α-synucleinopathy: A NODDI study
- First Published: 14 April 2024
Novel α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazole-propionic acid receptor (AMPAR) potentiator LT-102: A promising therapeutic agent for treating cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia
- First Published: 14 April 2024
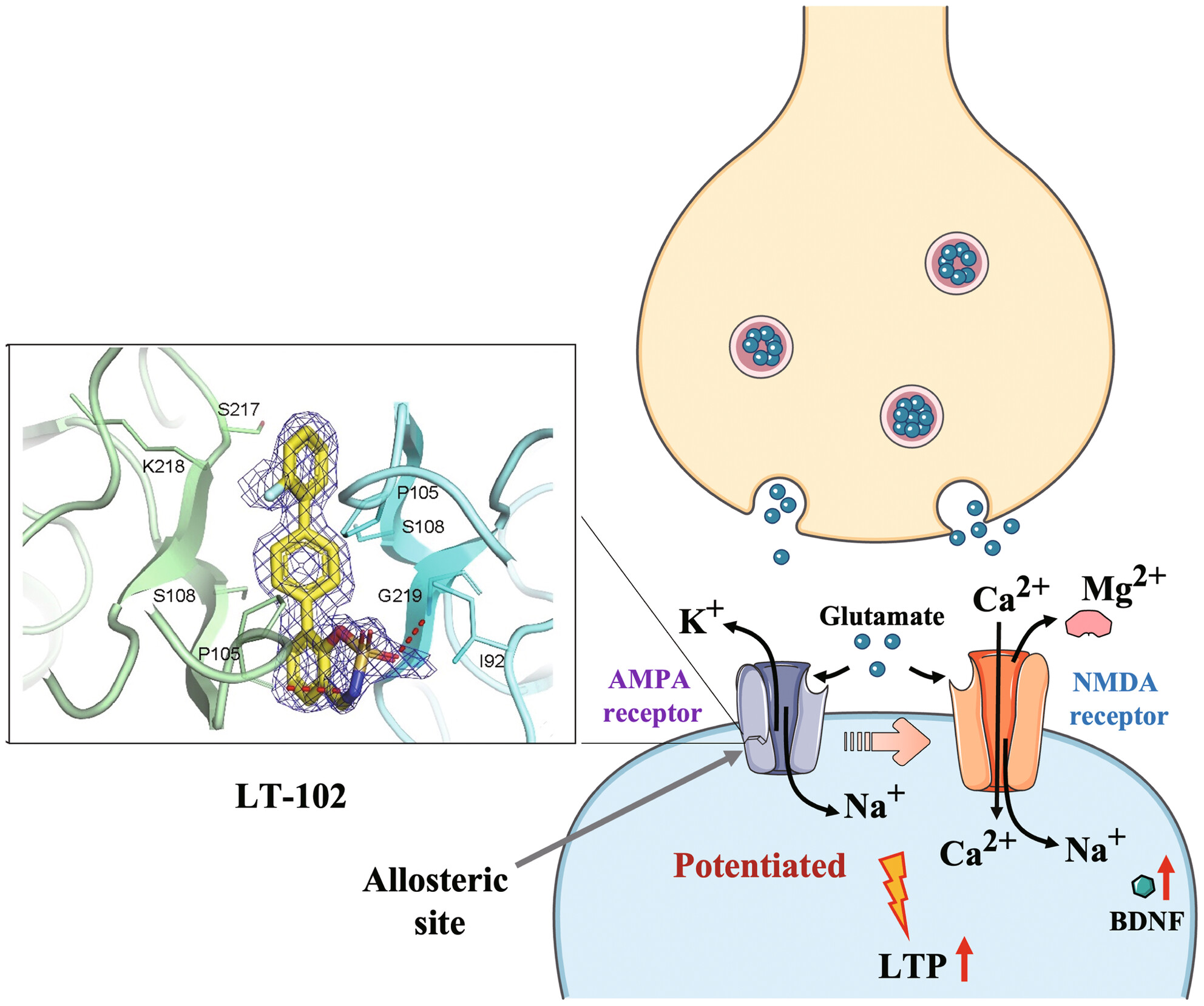
The challenge of improving cognitive impairment associated with schizophrenia (CIAS) persists due to the limited availability of novel treatment options and drugs. Our study introduces a novel AMPAR potentiator, LT-102, which could be a potential therapeutic candidate for CIAS by modifying synaptic plasticity and glutamate signaling.
Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid reveals candidate diagnostic biomarkers to distinguish between spinal muscular atrophy type II and type III
- First Published: 14 April 2024
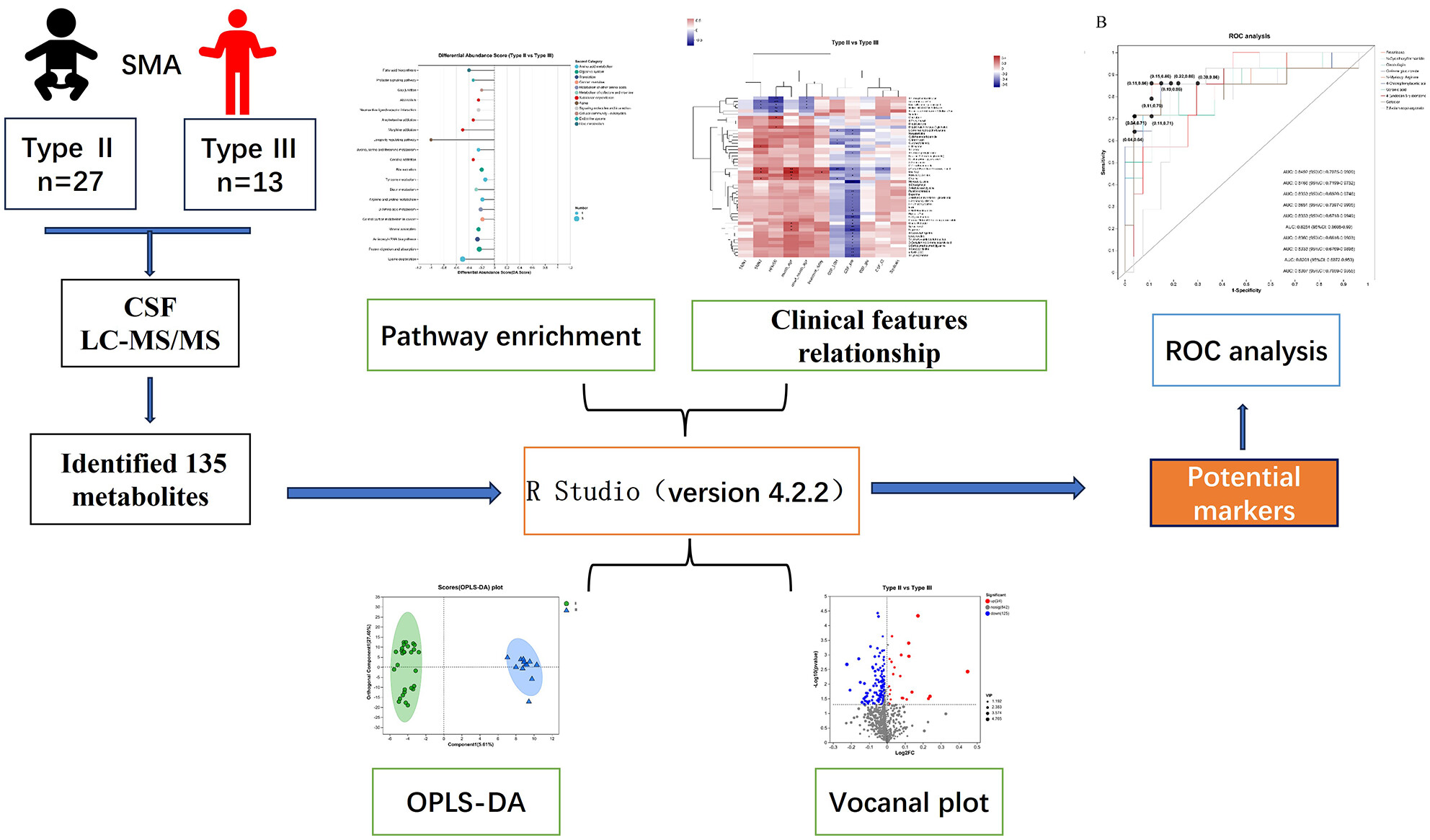
We have demonstrated metabolic markers in CSF associated with the classification of SMA in children, including 4-chlorophenylacetic acid, sodium dodecyl benzenesulfonate, and cinobufagin. We also identified the metabolic pathways associated with the severity of SMA, including lysine degradation, arginine metabolism, and tyrosine metabolism.
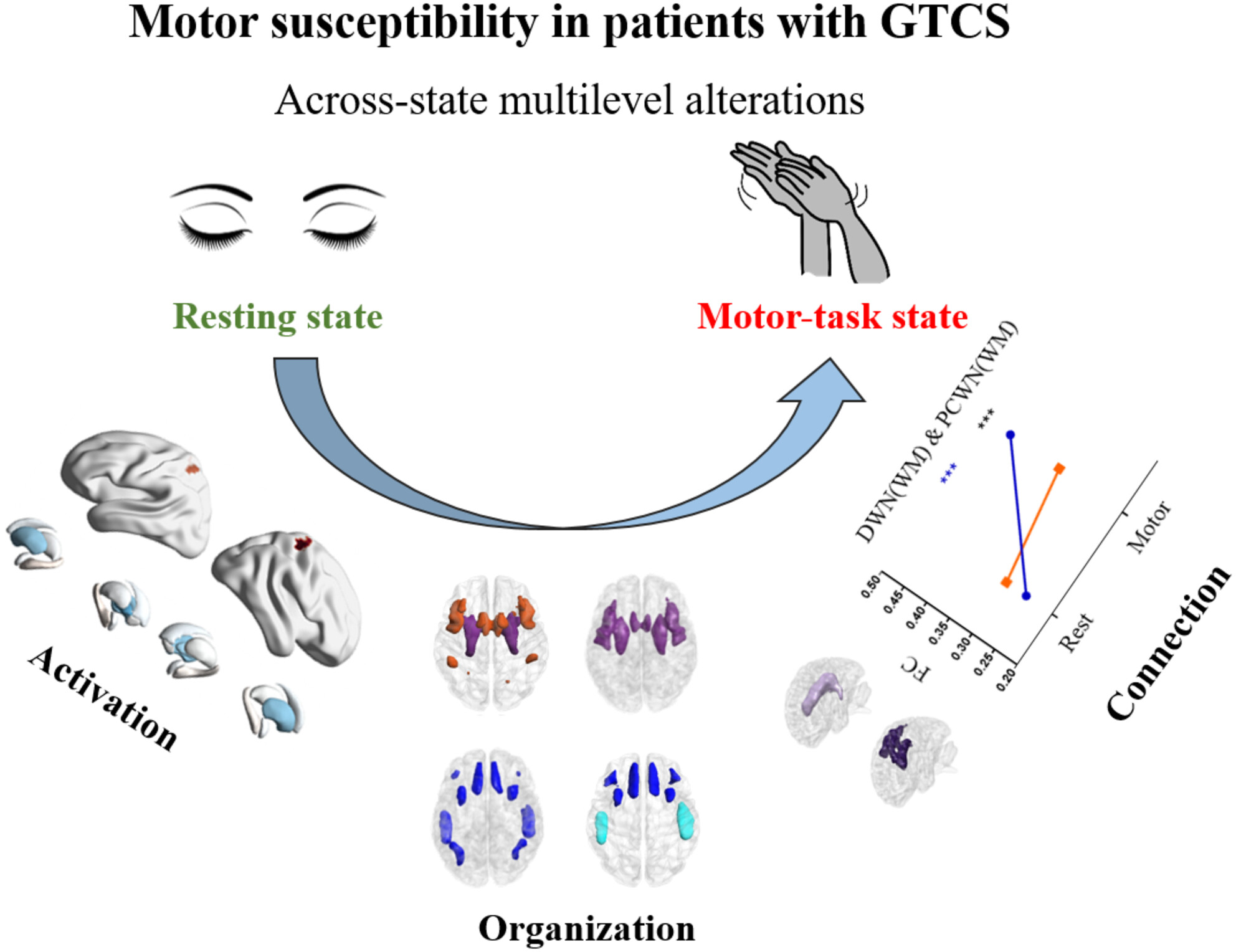
Brain activation and connection across resting and motor-task states in patients with generalized tonic–clonic seizures
- First Published: 21 April 2024
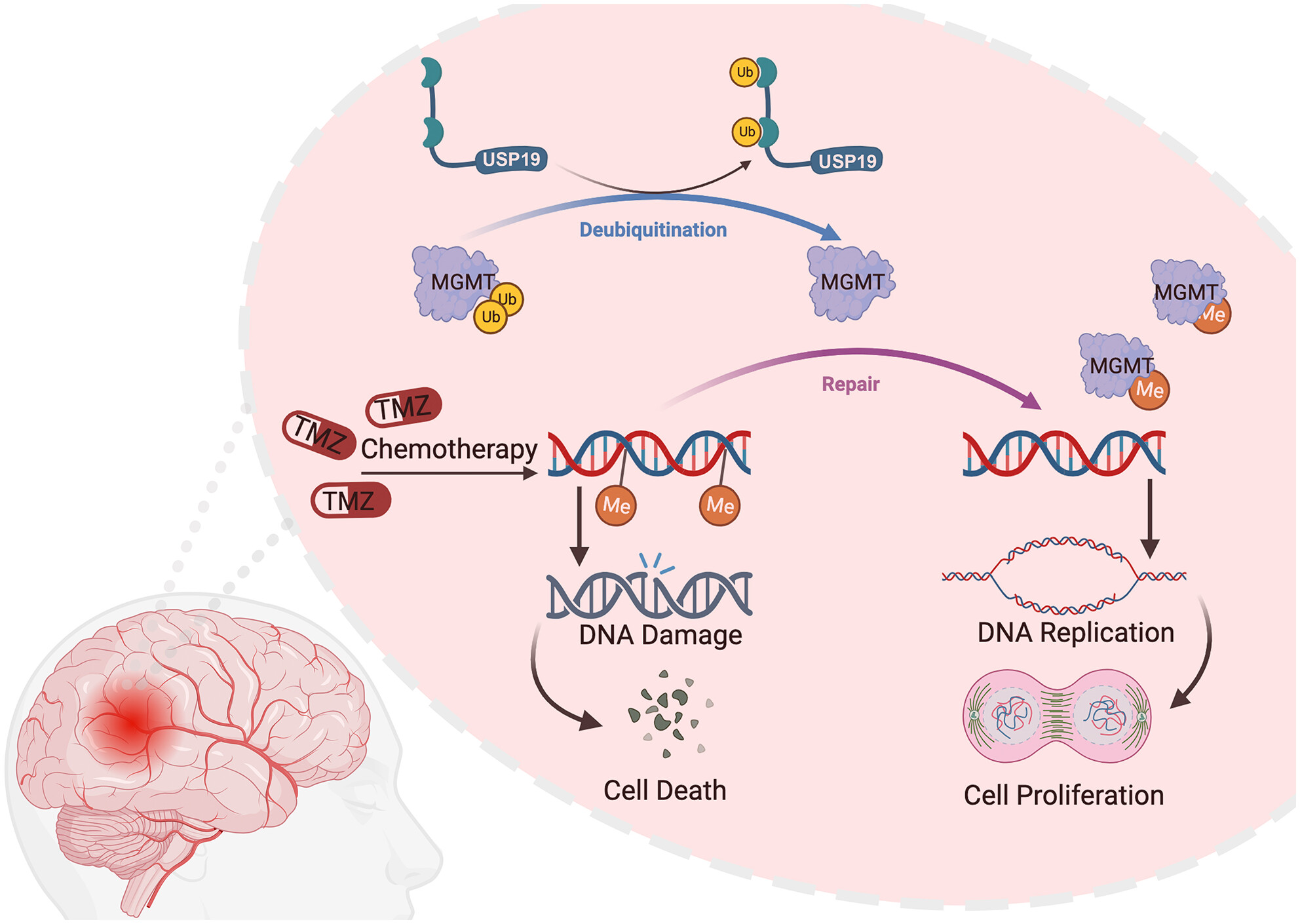
USP19 regulates DNA methylation damage repair and confers temozolomide resistance through MGMT stabilization
- First Published: 21 April 2024
REVIEWS
C/EBPβ: A transcription factor associated with the irreversible progression of Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 21 April 2024
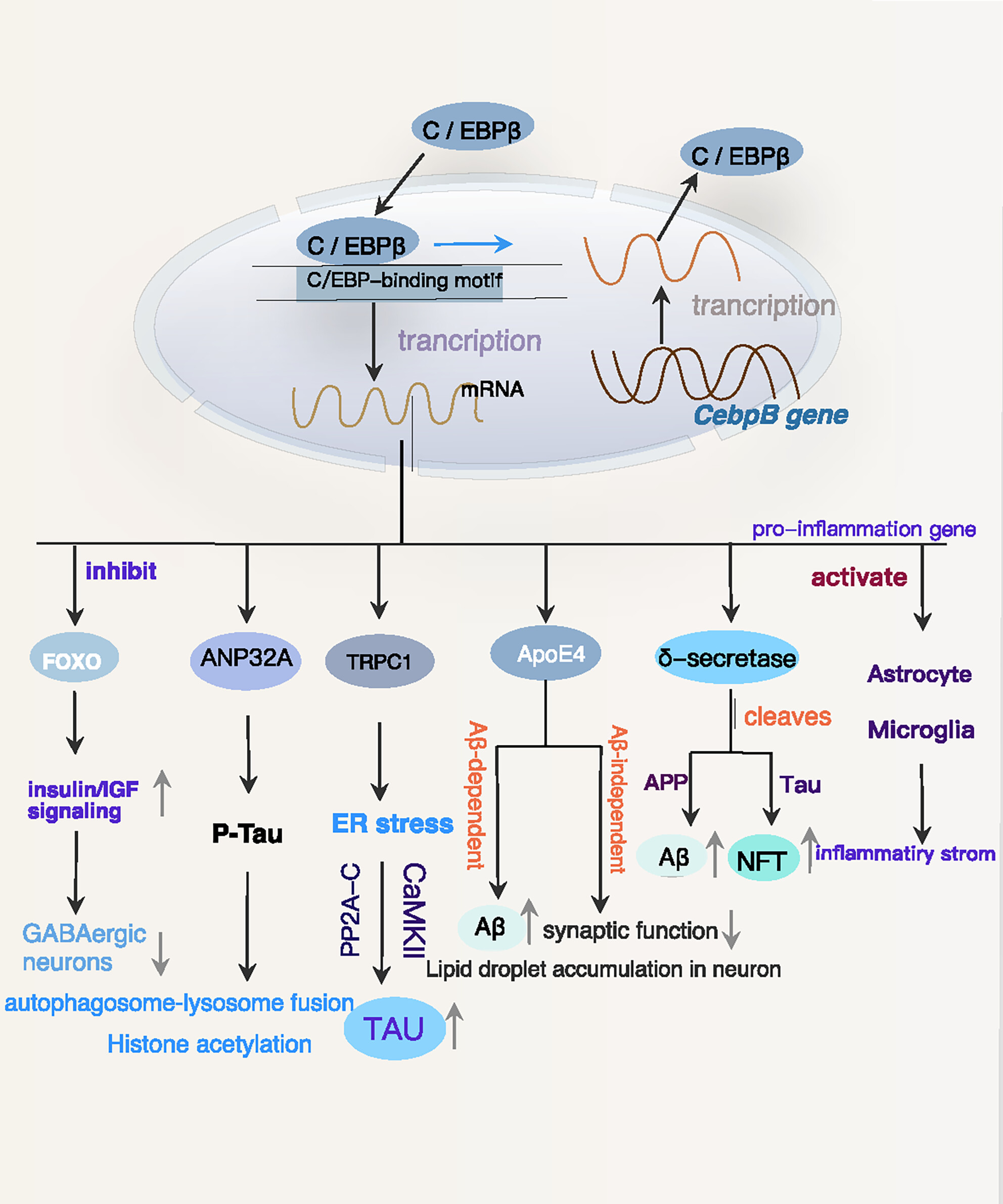
C/EBPβ overexpression exacerbates the pathologic progression of AD, primarily by promoting neuroinflammation and mediating transcriptional regulation of several disease-associated proteins, such as δ-secretase and APOE4. Additionally, C/EBPβ stimulates the upregulation of ANP32A and TRPC1, leading to elevated levels of phosphorylated Tau, while inhibiting the expression of FOXO, which is associated with genes involved in longevity. The in-depth research of the pathway through which C/EBPβ regulates the development of AD also reveals multiple vicious cycle pathways between C/EBPβ overexpression and the pathological progression of AD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Radiotherapy plus temozolomide with or without anlotinib in H3K27M-mutant diffuse midline glioma: A retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 21 April 2024
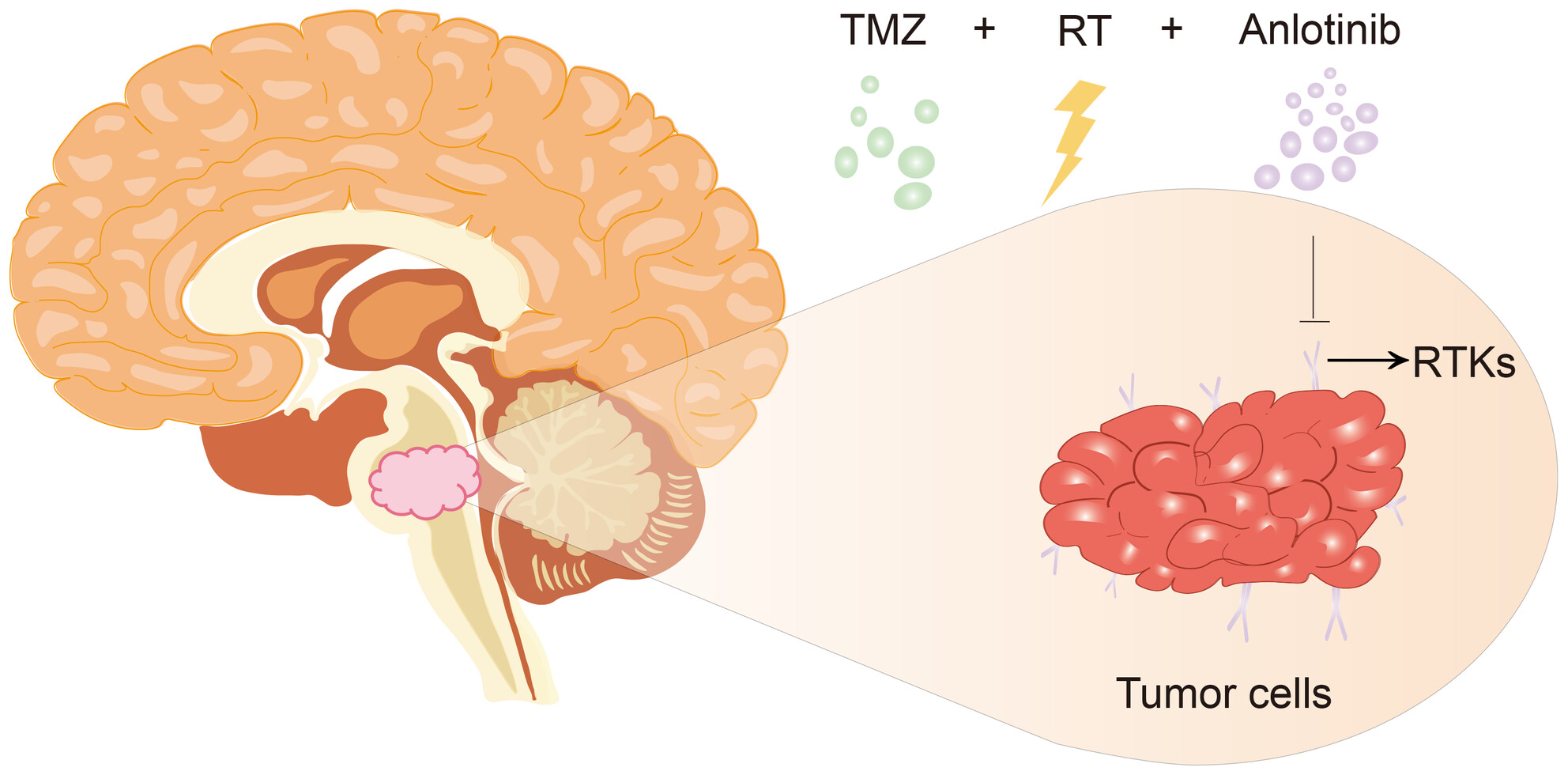
This retrospective cohort study investigated the tolerability and efficacy of Anlotinib combined with the Stupp regimen for patients with H3K27M mutant diffuse midline glioma (DMG). Beyond establishing the safety profile, our study also identified encouraging benefits associated with Anlotinib treatment, particularly for patients with infratentorial DMG. These findings suggest that Anlotinib may represent a promising treatment option for H3K27M mutant DMG in the clinical setting.
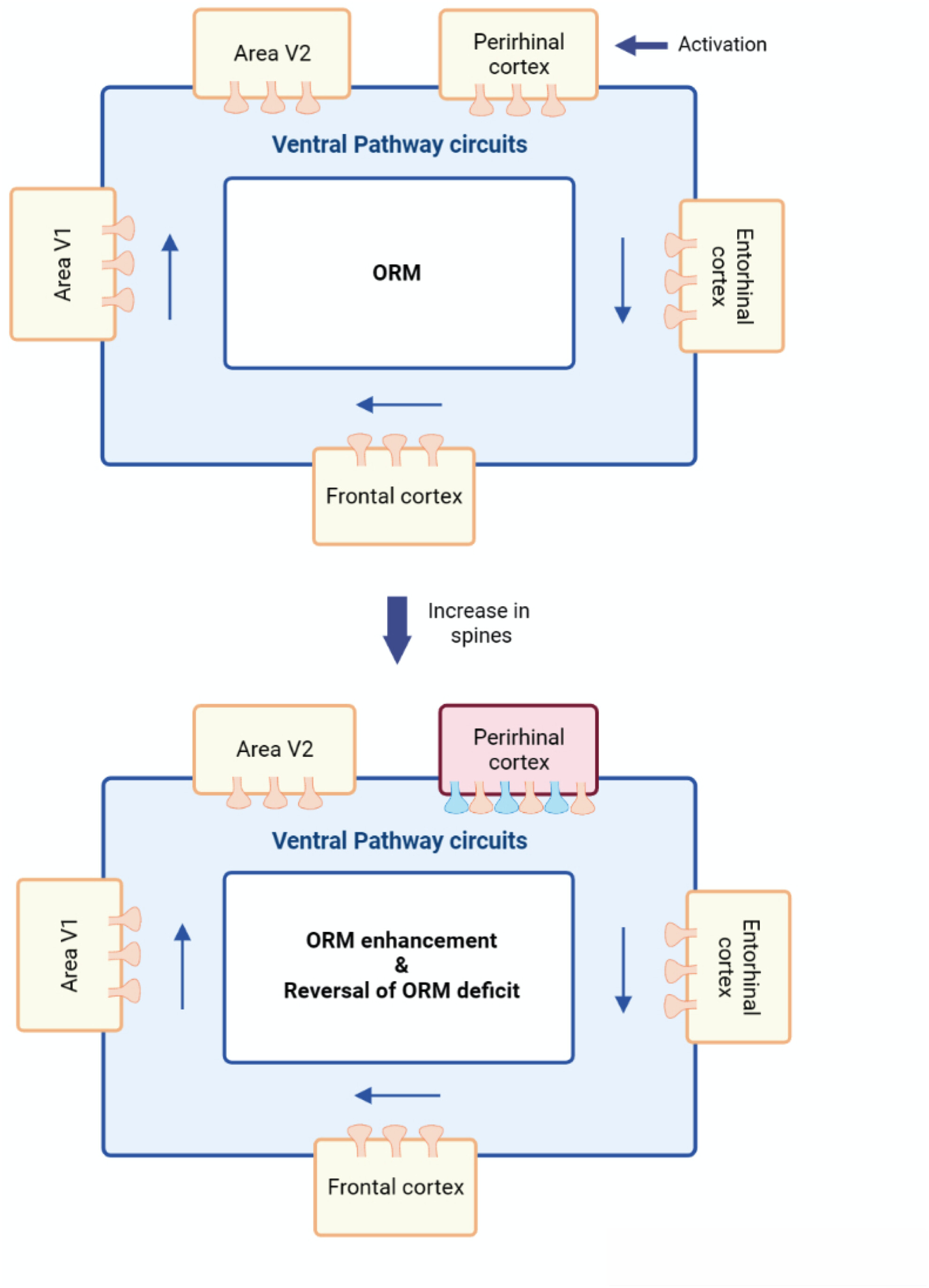
Brain areas interconnected to ventral pathway circuits are independently able to induce enhancement in object recognition memory and cause reversal in object recognition memory deficit
- First Published: 21 April 2024
Peripheral inflammation triggering central anxiety through the hippocampal glutamate metabolized receptor 1
- First Published: 26 April 2024
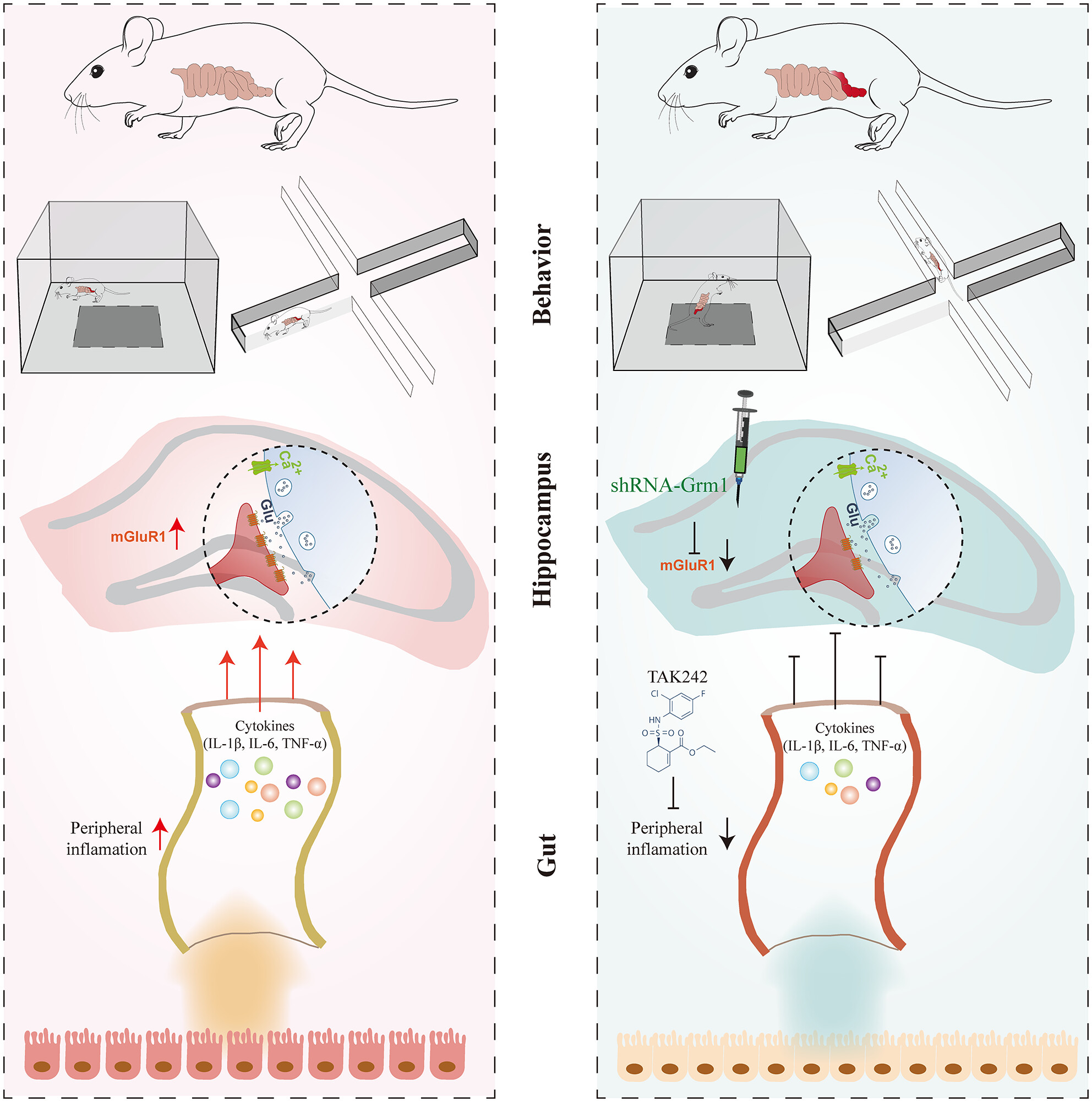
Anxious behavior in mice with colitis was associated with an imbalance in hippocampal excitatory inhibition due to the overactivation of glutamate synapses. Peripheral suppression of colon inflammation or downregulation of GRM1 expression by AAV virus interference can significantly improve anxiety-like behavior.
REVIEWS
CircRNA-associated ceRNA regulatory networks as emerging mechanisms governing the development and biophysiopathology of epilepsy
- First Published: 26 April 2024
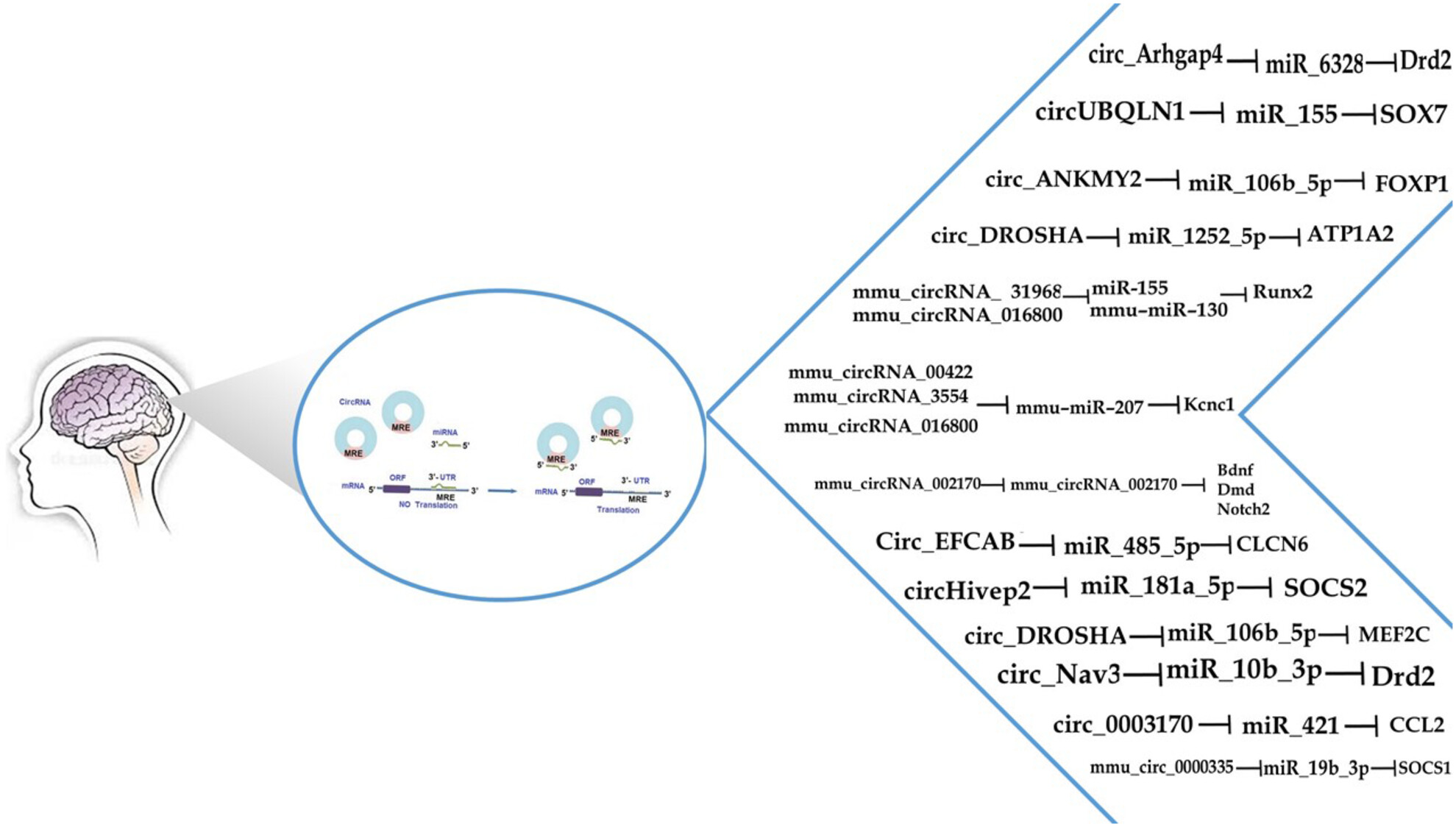
CircRNA–miRNA–mRNA networks in epilepsy. CirRNAs can bind to microRNA response elements through sponging and regulate their expression downstream according to the competitive endogenous RNA hypothesis (ceRNA). The circRNA–miRNA–mRNA axes hold potential as valuable tools for comprehending the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of epilepsy. We summarize the possible regulatory networks of circRNA–miRNA–mRNA in epilepsy.