Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
External validation of the GAP model in Chinese patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pages: 831-840
- First Published: 27 November 2022
Etiology and clinical features of children with bronchiectasis in China: A 10-year multicenter retrospective study
- Pages: 841-850
- First Published: 31 May 2023
Bronchiectasis patients usually suffer recurrent respiratory infections, and lung function is damaged progressively. It is not rare in China but is not well understood. Through the 10-year retrospective multicenter study, we initially found the etiology spectrum and clinical characteristics of bronchiectasis in Chinese children.
Effects of doxofylline as an adjuvant on severe exacerbation and long-term prognosis for COPD with different clinical subtypes
- Pages: 851-864
- First Published: 10 August 2023
Imaging and pathological characteristics, treatment, and prognosis of pulmonary sequestration—A retrospective study of 13 cases
- Pages: 865-873
- First Published: 02 August 2023
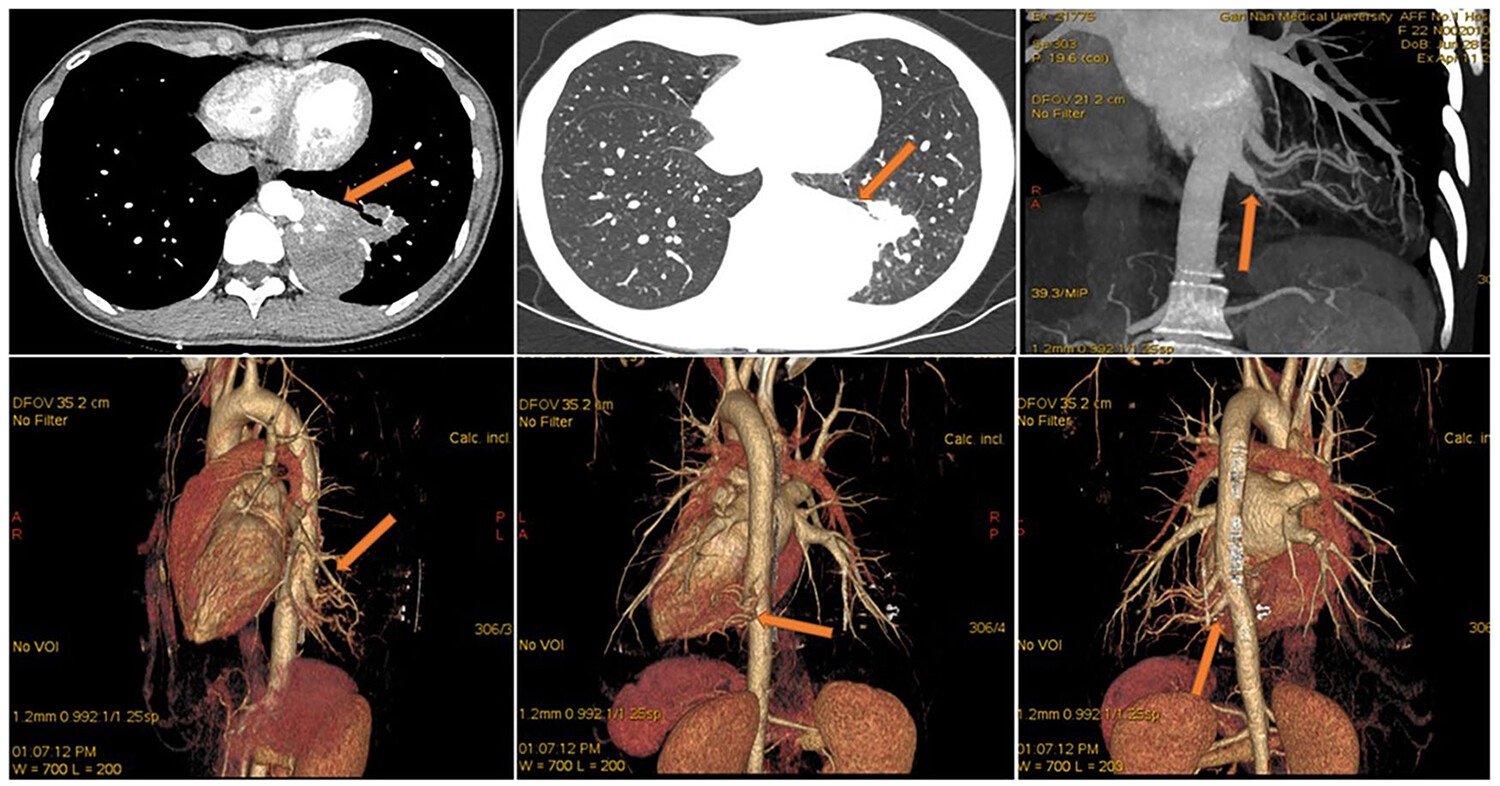
Thoracoscopic lobectomy, thoracoscopic wedge resection of the lesion, or thoracoscopic anatomical segmentectomy can be selected based on a comprehensive analysis of imaging results. Careful and reasonable treatment of the abnormal blood supply artery of the isolated lung is the key to the operation.
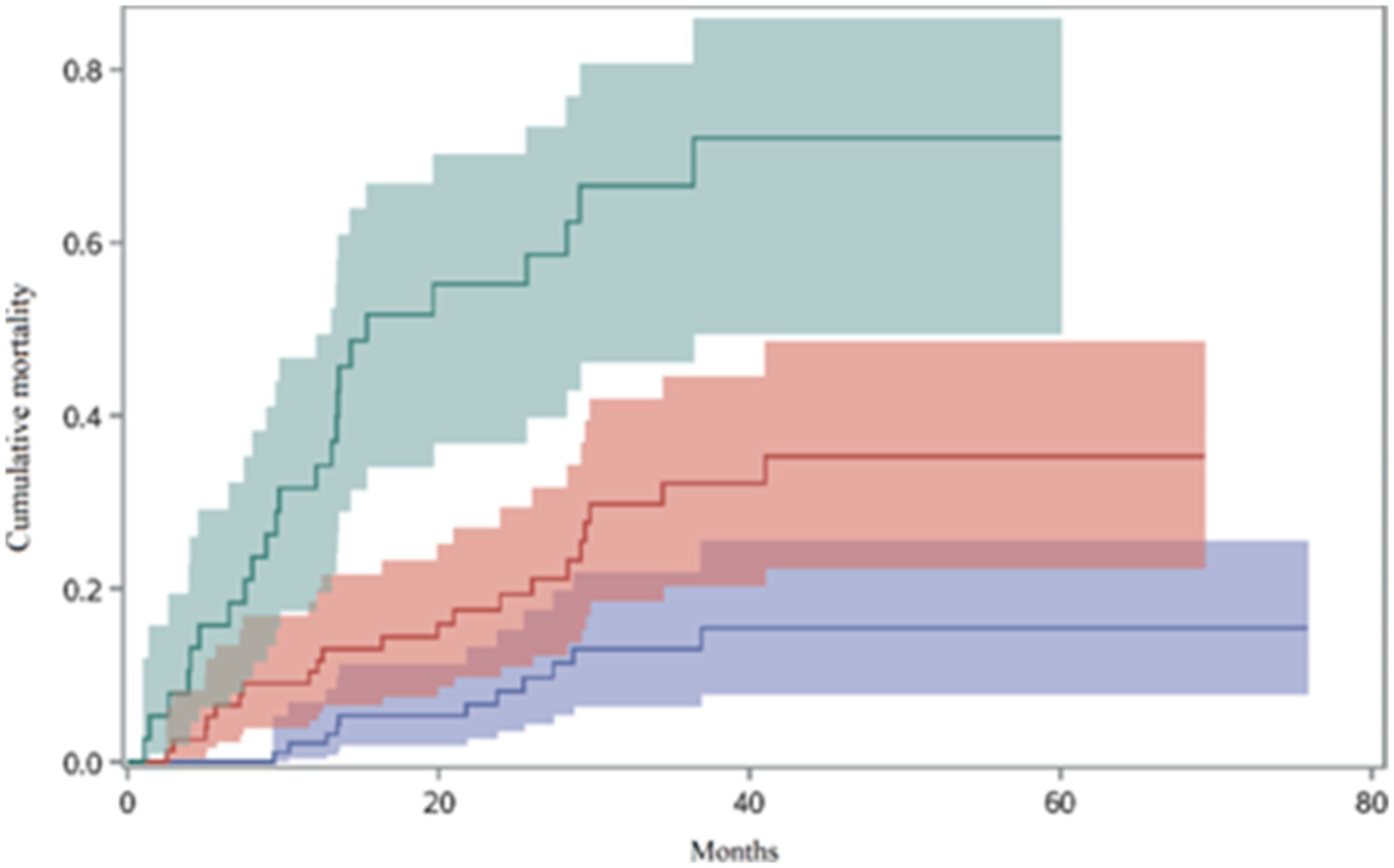
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation in immunocompromised patients with acute respiratory failure: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 874-883
- First Published: 27 August 2023
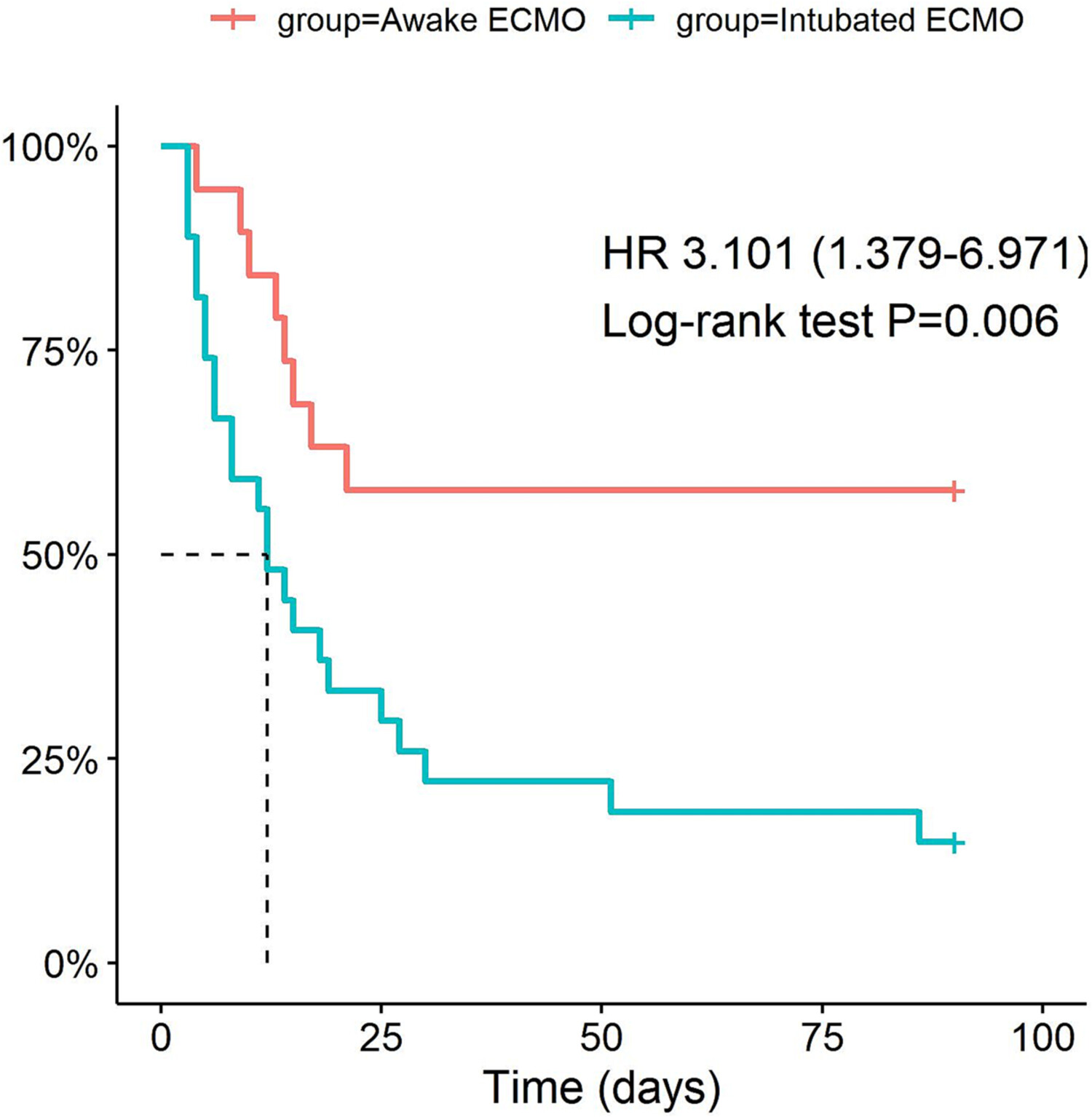
ECMO support for immunosuppressed patients remains controversial and challenging. This study provides detailed information on the clinical and laboratory features of these critical patients. Our findings provide insight into the in-hospital mortality has remained high in such patients. Interesting things are, a primarily awake ECMO strategy seems feasible in some selected patients and acute kidney injury requiring CRRT during ECMO treatment may predict ECMO failure in such patients.
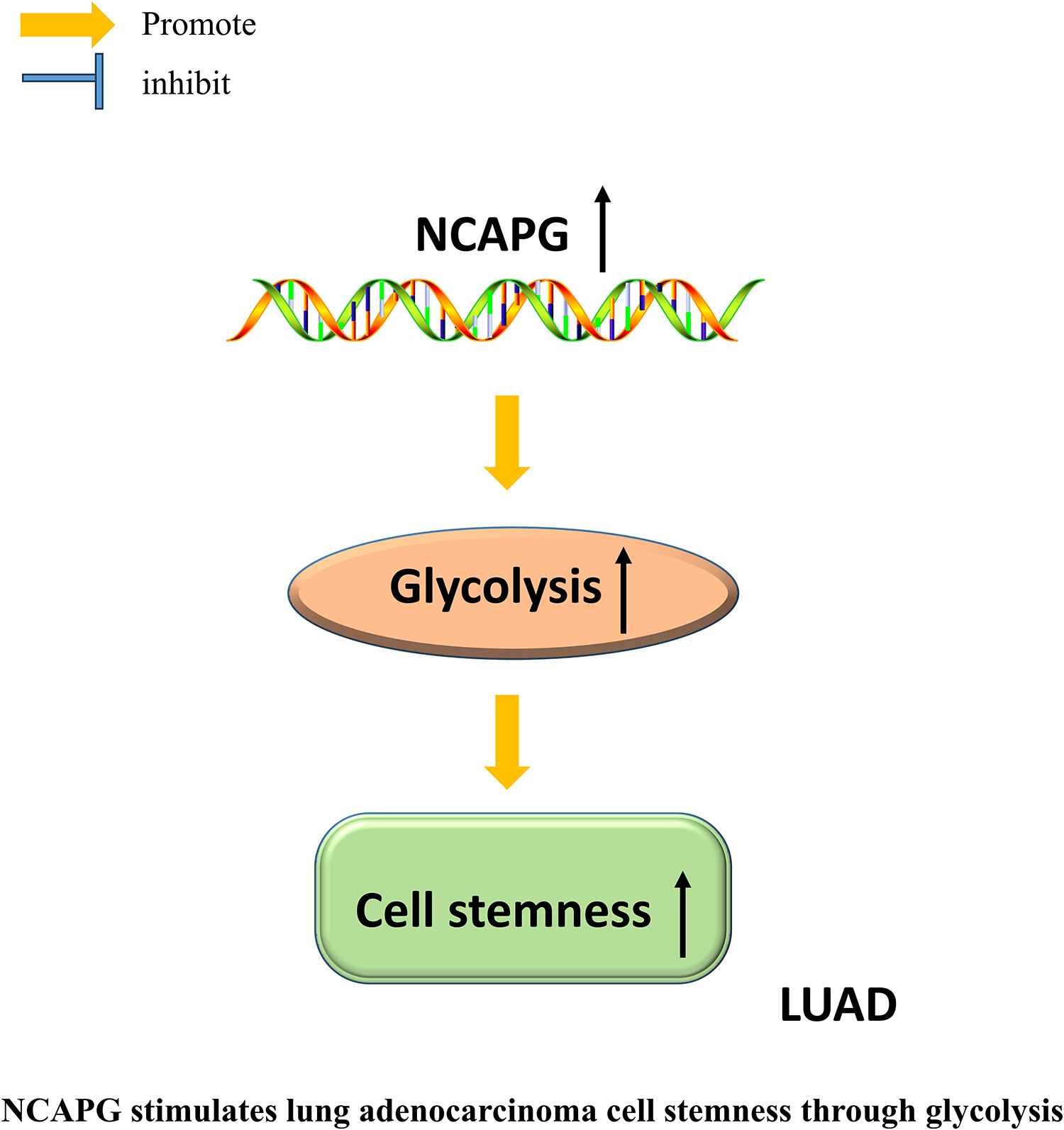
NCAPG stimulates lung adenocarcinoma cell stemness through aerobic glycolysis
- Pages: 884-892
- First Published: 08 August 2023
Serum iron levels in tuberculosis patients and household contacts and its association with natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 1 polymorphism and expression
- Pages: 893-904
- First Published: 22 August 2023
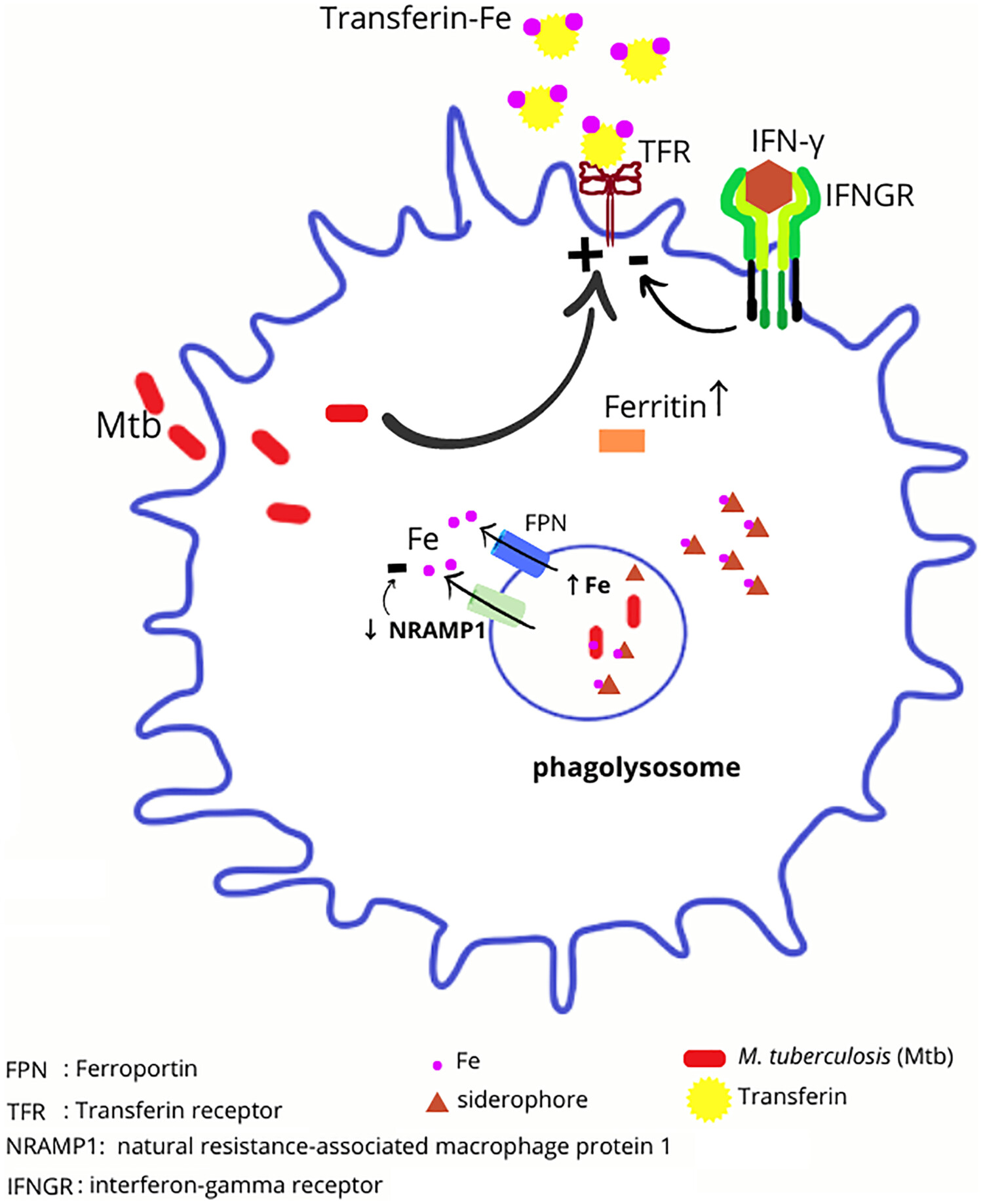
M. tuberculosis needs to obtain iron to survive and grow inside its host. M.tuberculosis suppresses ferroportin expression, which increases Fe levels in the phagosome. It also obtains Fe by increasing transferrin receptor (TFR) expression. These conditions cause a decrease in Fe in the blood, and thus anemia occurs. Besides, IFN-gamma, which releases upon immune activation, downregulates the expression of TFR. The ability of NRAMP1 and FPN1 to remove iron from the phagolysosome limits the availability of intracellular iron to intracellular bacteria. Alteration in the NRAMP1 gene may result in a nonfunctional protein or decrease the expression of NRAMP1, leading to more active replication of the bacteria in lung alveolar macrophage. This study demonstrated that TB was associated with decreased NRAMP1 gene, NRAMP1 gene expression was correlated to Fe levels, and TB was associated with low Fe levels. This finding would suggest that TB can lower Fe levels by downregulating NRAMP1 expression.
High-flow nasal cannula oxygen therapy for the treatment of acute respiratory failure secondary to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia out of ICU
- Pages: 905-914
- First Published: 04 August 2023
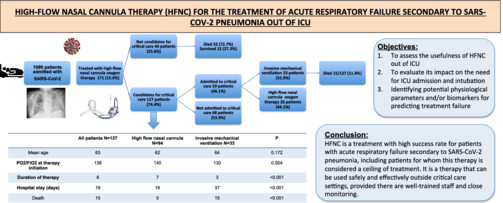
High-flow nasal cannula is a treatment with high success rate for patients with acute respiratory failure secondary to SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia. This therapy reduces the rates of intubation and mechanical ventilation. It can be used effectively in a conventional hospital ward. In patients not candidates for critical care may also be a suitable treatment option.
Clinical features and outcome of eight patients with Chlamydia psittaci pneumonia diagnosed by targeted next generation sequencing
- Pages: 915-930
- First Published: 08 August 2023
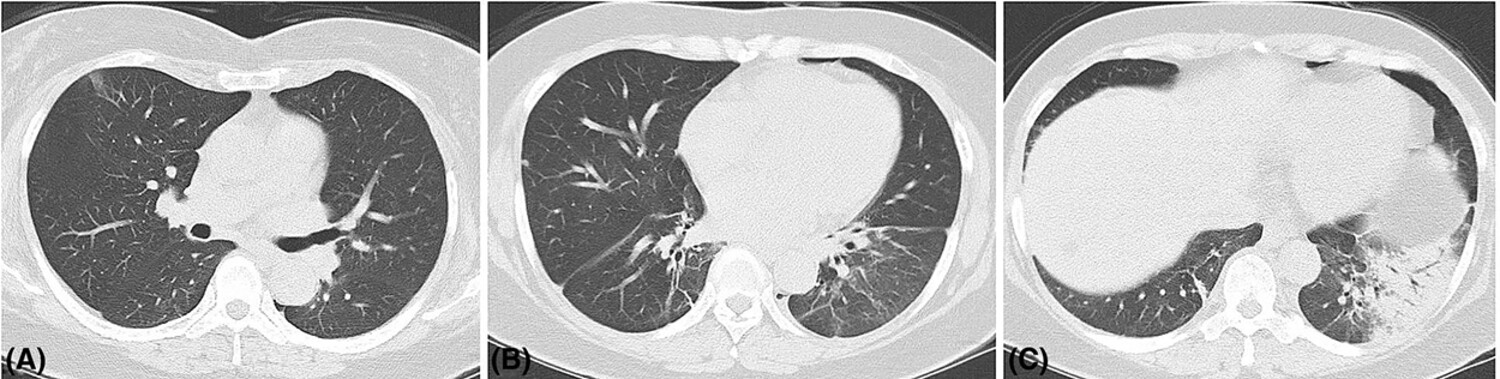
The tNGS technique is of great value in the diagnosis and management of C. psittaci pneumonia. A poultry or bird contact history, typical flu-like symptoms, radiographic characteristics such as patchy consolidation, ground-glass density shadow and air bronchogram may contribute to the diagnosis of C. psittaci pneumonia. Moxifloxacin and minocycline are effective in the management of C. psittaci pneumonia.
Nomogram to diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnoea-hypopnoea syndrome in high-risk Chinese adult patients
- Pages: 931-940
- First Published: 02 August 2023
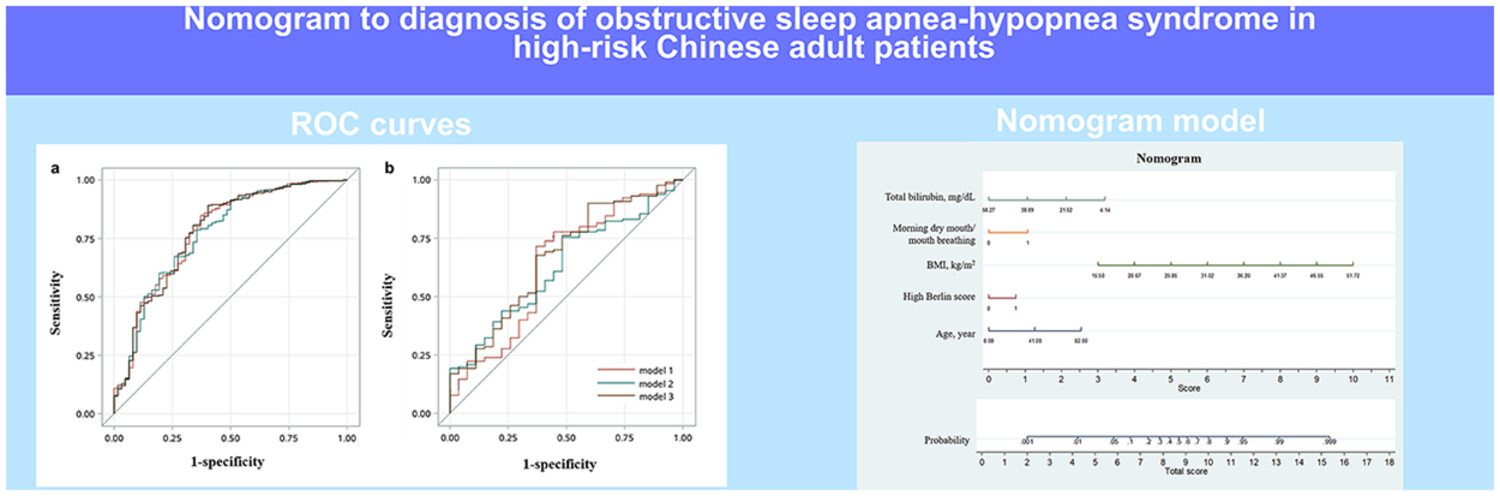
This cross-sectional study was to develop and validate an efficient and simple clinical diagnostic model to help screen patients at risk of OSAHS. Totally 34 potential predictors were evaluated. The final model has been built with five factors: age, BMI, total bilirubin levels, high Berlin score, and symptom of morning dry mouth or mouth breathing.
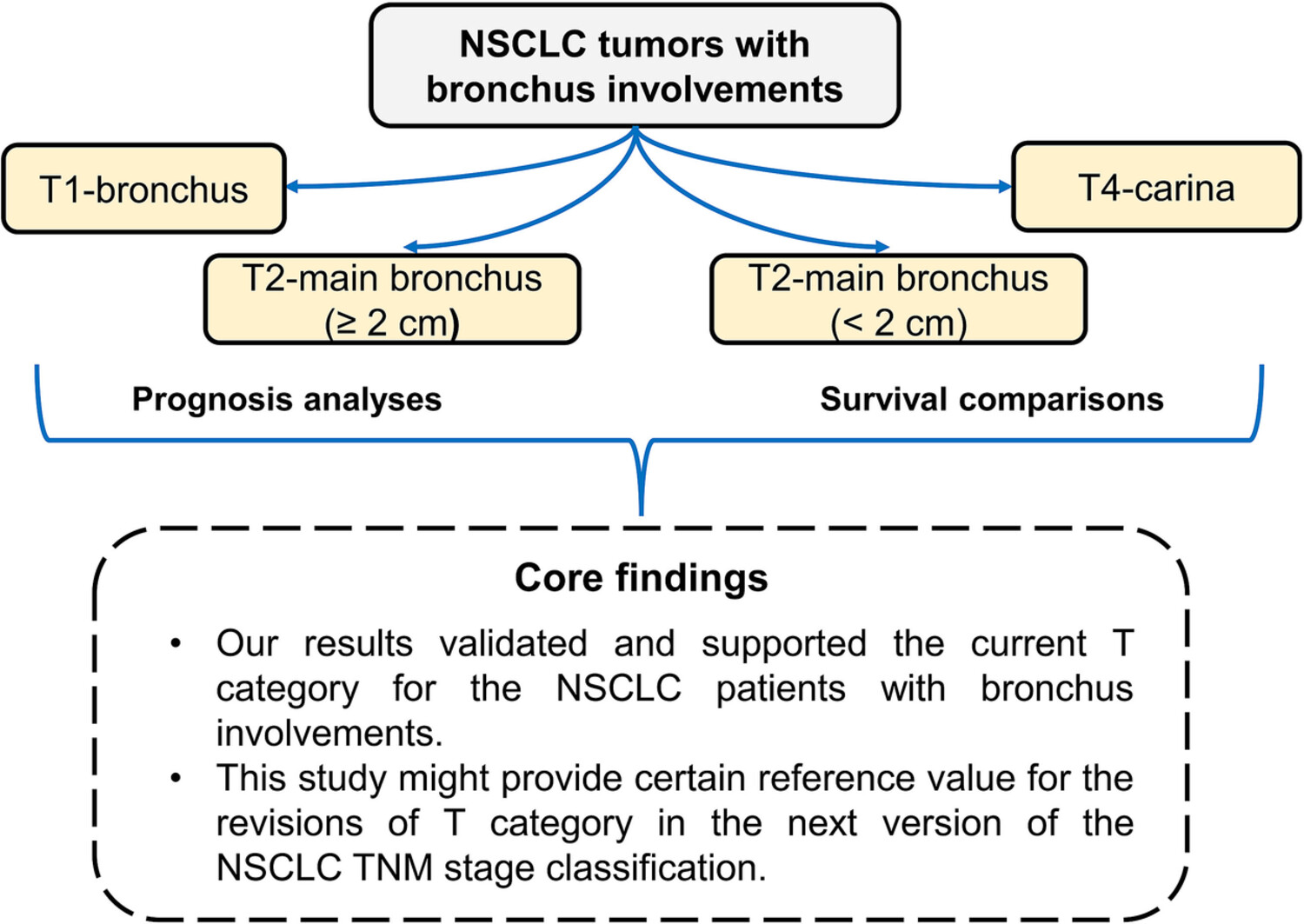
Investigation of the non-small cell lung cancer patients with bronchus involvements: A population-based study
- Pages: 941-950
- First Published: 07 August 2023
Exploration of the minimal clinically important difference value of the 3-min simulated pedal motion in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A self-controlled prospective clinical trial
- Pages: 951-961
- First Published: 16 August 2023
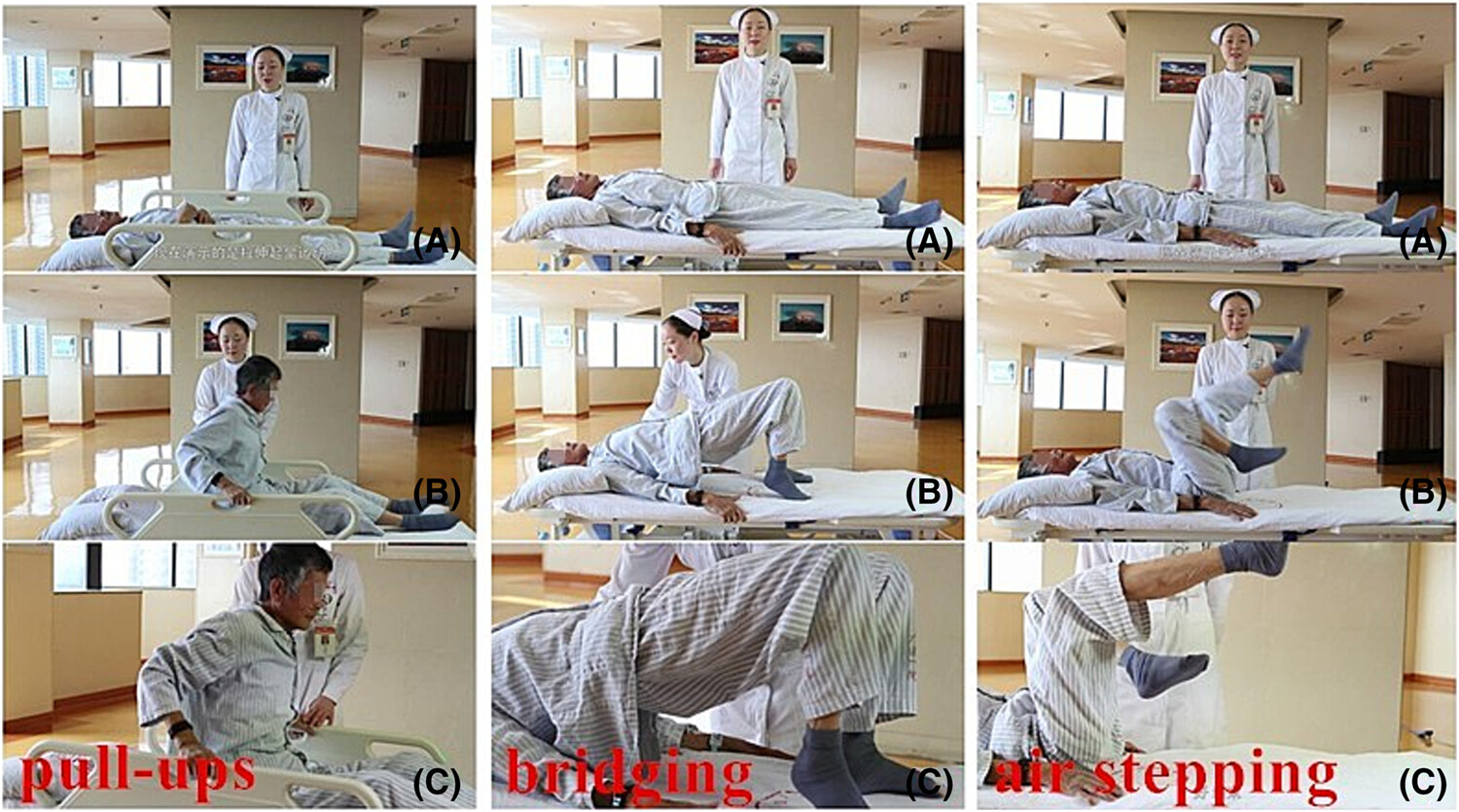
Our results indicate based on the regression equation, 3MSPM can predict 6MWD, and it can be used as a simple exercise endurance method to evaluate patients with safety hazards in underground activities or who cannot complete the 6MWD test. The minimum clinically important difference value is increased by 23.
BRIEF REPORTS
Pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula due to pulmonary infection caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis in a patient with periodontitis
- Pages: 962-965
- First Published: 13 August 2023
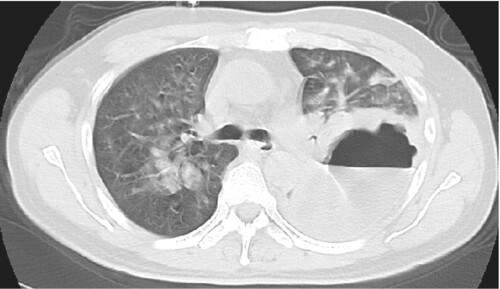
Pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula is a rare complication of lung infection. We herein report a case of pyopneumothorax with bronchopleural fistula caused by Porphyromonas gingivalis infection, a common pathogenic pathogen of periodontitis, in a 49-year-old man with periodontitis. The patient was admitted with respiratory failure. Pleural puncture yielded a lot of gas continually and foul-smelling light brown pus, which was found to be caused due to infection with P. gingivalis by the next generation sequencing (NGS) and anaerobic culture.
A systematic review of psychological interventions in adults with pulmonary hypertension: Is the evidence-base disproportionate to the problem?
- Pages: 966-972
- First Published: 15 August 2023
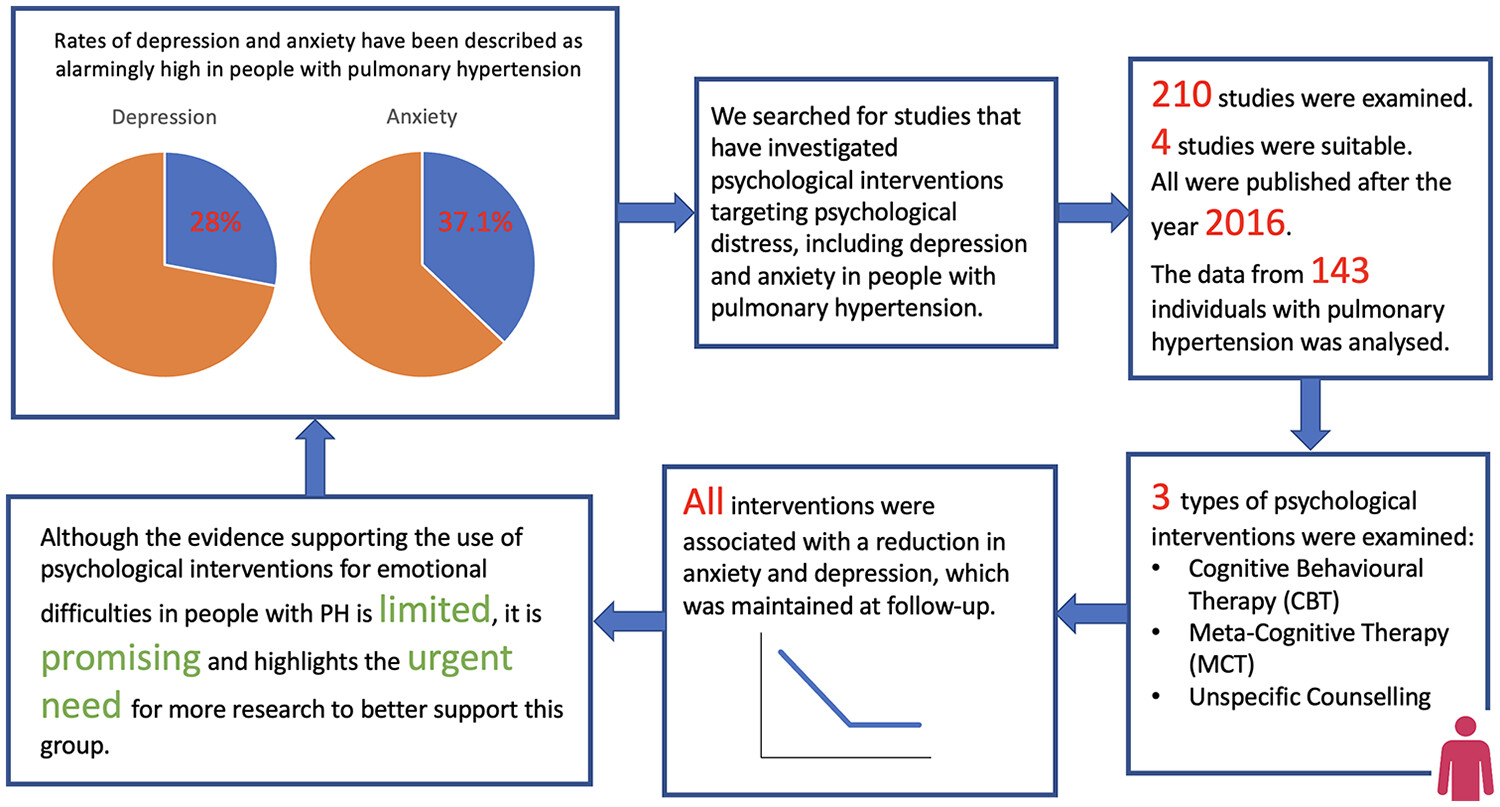
Our understanding of the psychological impact of living with pulmonary hypertension (PH) is growing. Evidence exists for the use of psychological interventions in chronic lung conditions; however, trials involving adults with PH have not been subject to a systematic review. We show that although the evidence is limited, the findings are promising and there is a need for more research.