Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cryo-Electron Microscopy: Cryo-EM-On-a-Chip: Custom-Designed Substrates for the 3D Analysis of Macromolecules (Small 21/2019)
- First Published: 24 May 2019

In article number 1900918, Deborah F. Kelly and co-workers develop a new cryo-electron microscopy (EM)-on-a-chip approach. This strategy enables researchers to directly visualize the “fault in our stars” regarding cancer proteins. The structural assemblies of p53 from brain cancer cells are determined for the first time using the microchip-based technique. Artistic rendition by Daryl N. Branford.
Inside Front Cover
Clay Materials: Clay Nanotubes Aligned with Shear Forces for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Patterning (Small 21/2019)
- First Published: 24 May 2019
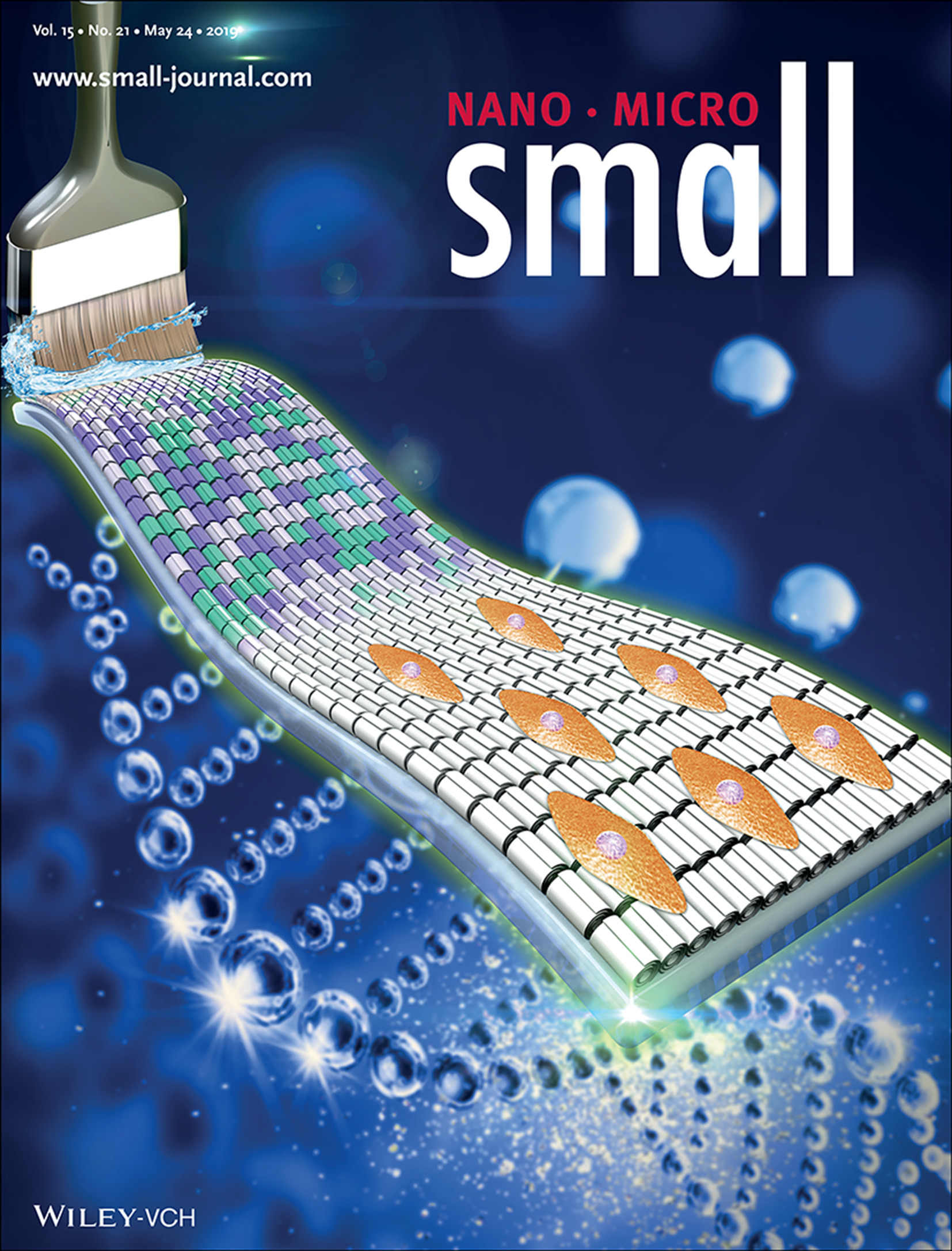
In article number 1900357, Yuri Lvov, Mingxian Liu, and co-workers report a simple method for preparing oriented clay nanotube architectures. The clay nanotubes are aligned by brush induced shear force into strip-like patterns on different substrates at elevated temperature. This clay pattern can induce stem cell orientation growth and is promising for surface modification in tissue engineering materials.
Inside Back Cover
Cells at Wrinkled Interfaces: Laser-Assisted Strain Engineering of Thin Elastomer Films to Form Variable Wavy Substrates for Cell Culture (Small 21/2019)
- First Published: 24 May 2019
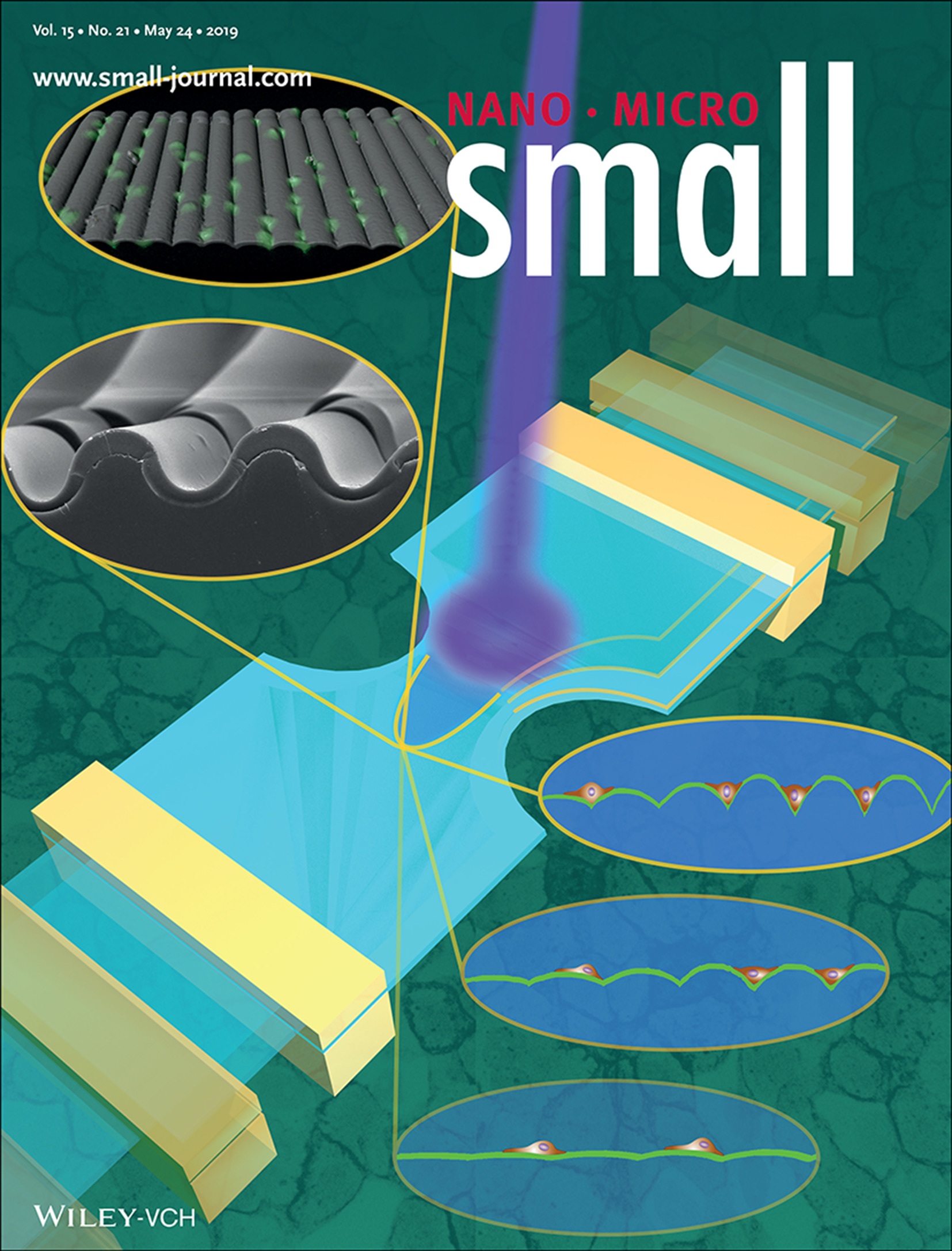
In article number 1900162, Caterina Tomba, Valeriy Luchnikov, and co-workers present a versatile approach to produce curved surfaces with dynamic and variable topographic parameters. Mid-infrared laser exposure allows for surface stiffening of an elastomer that is suitable as wavy substrate to grow cells on smooth and more realistic micro-environments. The wrinkled geometry is tuned by controlling the shape and stretching rate of the substrate and the irradiation parameters of the laser. This technique is easily accessible for further studies on cell migration and cell fate determination.
Back Cover
Ultrastable Perovskites: Strain-Mediated Phase Stabilization: A New Strategy for Ultrastable α-CsPbI3 Perovskite by Nanoconfined Growth (Small 21/2019)
- First Published: 24 May 2019
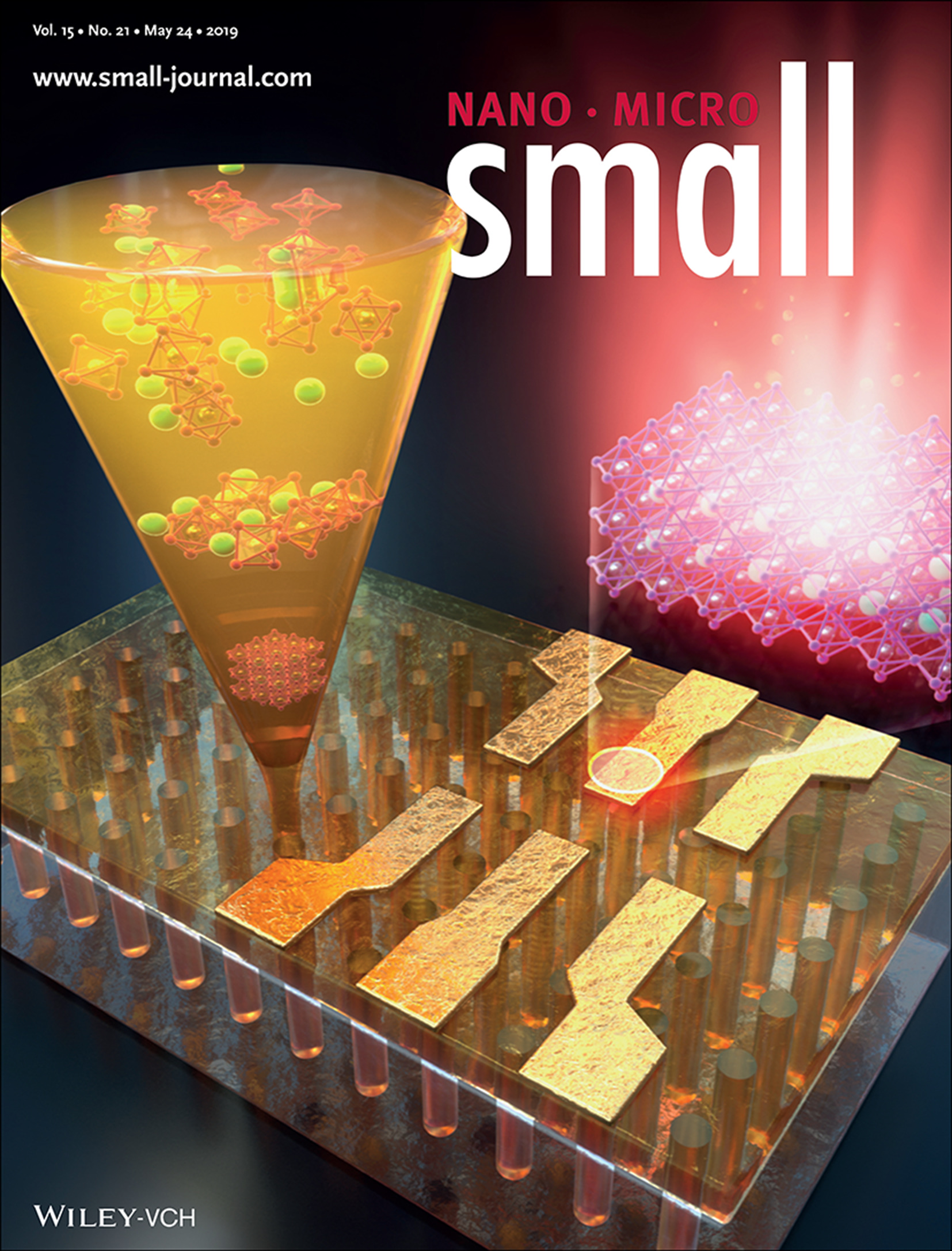
In article number 1900219, Donghwa Lee, Jooho Moon, and co-workers develop an approach to stabilize α-CsPbI3 perovskite through strain engineering, whereby CsPbI3 perovskite is confined by a vertically aligned nanoporous template. By imposing a strain on the perovskite lattice, the ultra-stable black α-CsPbI3 with its desirable optoelectrical properties is obtained. This universally applicable template-based stabilization strategy provides in-depth insights on the strain-mediated phase transition mechanism in all-inorganic perovskite.
Masthead
Correction
Aligned Heterointerface-Induced 1T-MoS2 Monolayer with Near-Ideal Gibbs Free Energy for Stable Hydrogen Evolution Reaction
- First Published: 24 May 2019
Reviews
Recent Progress in Molecular Design of Fused Ring Electron Acceptors for Organic Solar Cells
- First Published: 16 April 2019
Remarkable advancement has been made in the efficiency of organic solar cells (OSCs) in recent times, mostly due to novel fused ring electron acceptors (FREAs). Here, structural evolution of FREAs to enhance efficiency is comprehensively discussed. Moreover, recent progress in polymer design, semi-transparent OSCs, ternary, and tandem OSCs is provided. The challenges and future development of FREAs are briefly addressed.
Development of Dip-Pen Nanolithography (DPN) and Its Derivatives
- First Published: 12 April 2019
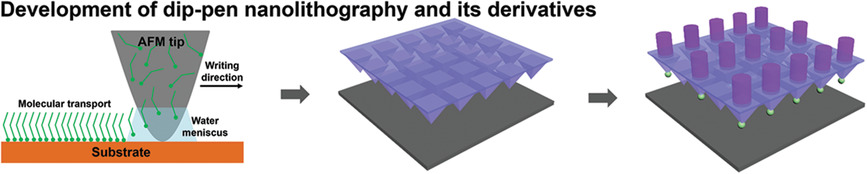
Dip-pen nanolithography (DPN) is a unique nanofabrication tool that can directly write a variety of molecular patterns on a surface with high resolution and excellent registration using a scanning tip. DPN has experienced a tremendous evolution since its invention in 1999. This work reviews the technical development of DPN and its derivative technologies over the past 20 years.
Communications
Cryo-EM-On-a-Chip: Custom-Designed Substrates for the 3D Analysis of Macromolecules
- First Published: 08 April 2019
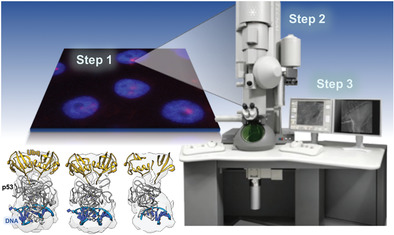
Interest in the cryo-electron microscopy (EM) field has recently skyrocketed, presenting new opportunities to study molecular systems. Here, new cryo-EM techniques are developed through the use of custom-designed substrates (Cryo-Chips). These substrates enable structural studies of native tumor suppressors that are mutated in human cancer. Cryo-Chip may be broadly used to study entities for both materials and life sciences applications.
Self-Healing, Adhesive, and Highly Stretchable Ionogel as a Strain Sensor for Extremely Large Deformation
- First Published: 16 April 2019
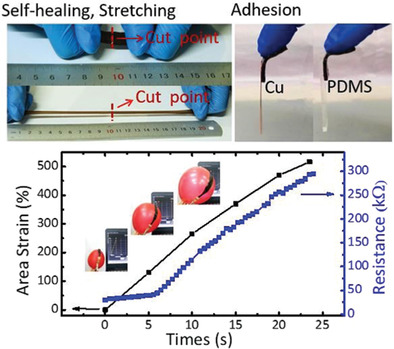
An ionogel nanocomposite with the combined features of excellent autonomous self-healing, strong adhesion, high stretchability, and strain sensitivity is fabricated. A conformal strain sensor based on the nanocomposite is demonstrated by changing electrical resistance with special distortion, like arbitrary curved and moving surfaces of a balloon with large inflation. The proof-of-concept strain sensor holds great potential for exploring various conformal mechanical sensor systems.
Temperature Gradients Drive Bulk Flow Within Microchannel Lined by Fluid–Fluid Interfaces
- First Published: 16 April 2019
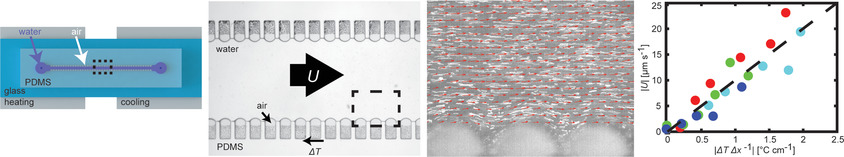
A micropump that exploits surface tension gradients induced by temperature changes is developed. The micropump is demonstrated in a lab-on-a-chip device for blood diagnosis. Due to its low energy consumption, it can operate with absorption of solar irradiation. The device has the potential to replace bulky syringe pumps and be implemented in low-resource settings with limited electricity.
Responsive Porous Microcarriers With Controllable Oxygen Delivery for Wound Healing
- First Published: 17 April 2019
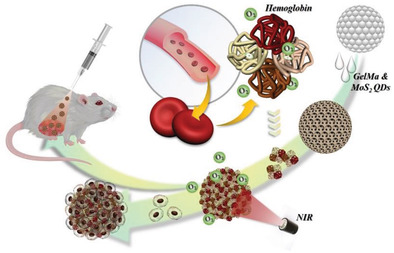
Responsive porous microcarriers are derived from GelMa inverse opal particles integrated with oxygen-carrying protein hemoglobin and molybdenum disulfide quantum dots. These designed microcarriers can deliver oxygen photo-controllably through near-infrared radiation, and they are demonstrated to be able to maintain cell survival in a hypoxic environment and promote wound healing successfully.
Ultraflexible Transparent Bio-Based Polymer Conductive Films Based on Ag Nanowires
- First Published: 23 April 2019
Flexible transparent conductive films (TCFs) based on silver nanowires and bio-based poly(ethylene-co-1,4-cyclohexanedimethylene 2,5-furandicarboxylate)s with a low sheet resistance (23.8 Ω sq−1 at 84.6% transmittance) and superior mechanical properties are fabricated. The relationship between the mechanism behind the bending behavior and the electrical properties, which is important for improving the mechanical stability of flexible TCFs, is explored.
Smart Microcapsules with Molecular Polarity- and Temperature-Dependent Permeability
- First Published: 17 April 2019
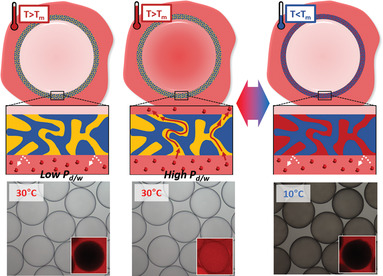
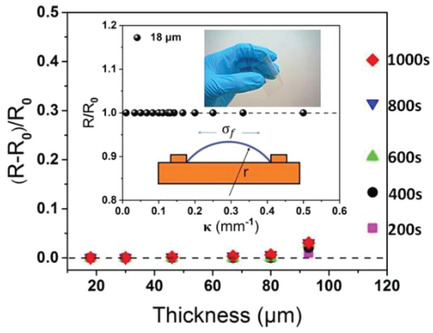
Smart microcapsules are designed to have molecular polarity- and temperature-dependent permeability using microfluidic technology. The shell is composed of a polymeric framework whose void is filled with phase change material (PCM). This enables the selective permeation of molecules that are soluble in the molten PCM and the rate of permeation is adjustable with partition coefficient and temperature.
Frontispiece
Antioxidants: Stimulus-Responsive Anti-Oxidizing Drug Crystals and their Ecological Implication (Small 21/2019)
- First Published: 24 May 2019
In article number 1900765, Jonghwi Lee, Young Jun Kim, Hyunjoon Kong, and co-workers assemble a new drug-delivery system prepared with stimulus-responsive crystallized catechin–an antioxidant found in green tea and fruit–that can dissolve when the hydrogen peroxide level increases abnormally and restore the heart rate of water fleas.
Full Papers
Stimulus-Responsive Anti-Oxidizing Drug Crystals and their Ecological Implication
- First Published: 05 April 2019
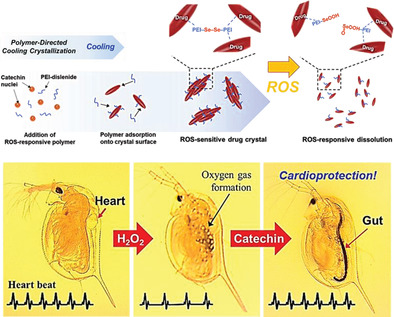
H2O2-responsive, anti-oxidizing drug crystals are assembled by polymer-directed recrystallization of catechin, for the first time. The catechin crystals exhibit constant dissolution for 7 days and also display accelerated dissolution in the oxidative media. The crystals can lower the intracellular oxidative stress of cells and protect the hearts of Daphnia from oxidative stress.
Clay Nanotubes Aligned with Shear Forces for Mesenchymal Stem Cell Patterning
- First Published: 08 April 2019
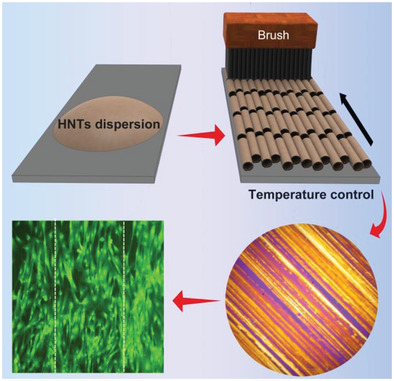
Aligned halloysite clay patterns on solid substrates are fabricated by shearing force provided by commercial brushes. These nanotubes can direct mesenchymal stems cell orientation and promote osteogenic differentiation without growth factors. This simple method for preparing oriented nanoparticle patterns is promising for surface modification of biomaterials and functional device fabrication.
Laser-Assisted Strain Engineering of Thin Elastomer Films to Form Variable Wavy Substrates for Cell Culture
- First Published: 05 April 2019
Cell growth is studied on elastic wavy substrates made by mid-infrared irradiation. The wrinkle wavelength is controlled by the laser power, the scan velocity of the beam, and the scan number, while the amplitude is also controlled by the film prestrain. It is shown that cells adapt to substrate curvature (curvotaxis) and stretching, from single cell to multicellular scale.
Strain-Mediated Phase Stabilization: A New Strategy for Ultrastable α-CsPbI3 Perovskite by Nanoconfined Growth
- First Published: 04 April 2019
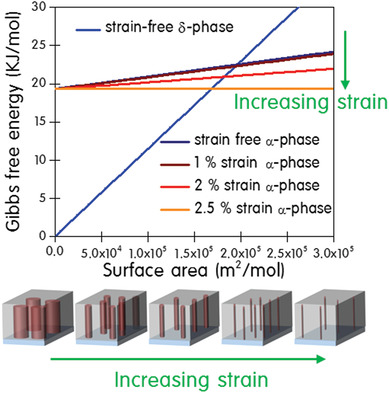
A novel approach to stabilize α-CsPbI3 perovskite through strain engineering, whereby CsPbI3 perovskite is confined by a vertically aligned nanoporous template, is developed. By imposing a strain on the perovskite lattice, the ultrastable black α-CsPbI3 with its desirable optoelectrical properties is obtained. The density functional theory calculations on the formation energy confirm that the strain-mediated phase stabilization is thermodynamically allowed.
α-Fe2O3 Nanoparticles Decorated C@MoS2 Nanosheet Arrays with Expanded Spacing of (002) Plane for Ultrafast and High Li/Na-Ion Storage
- First Published: 16 April 2019
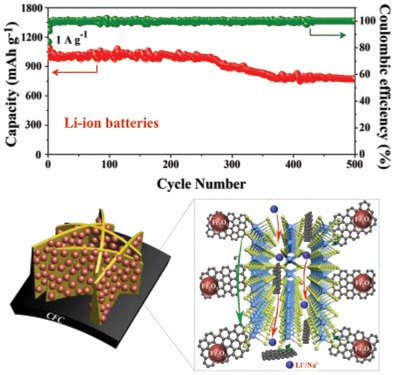
The design of vertically grown MoS2 nanosheet arrays with expanded spacing of (002) plane, decorated with graphite carbon and Fe2O3 nanoparticles, on flexible carbon fiber cloth is reported. Due to the unique 3D ordered Fe2O3@C@MoS2 array-type nanostructures, these electrodes manifest an outstanding electrochemical performance for lithium-ion and sodium-ion batteries.
Strong Charge Transfer at 2H–1T Phase Boundary of MoS2 for Superb High-Performance Energy Storage
- First Published: 24 April 2019
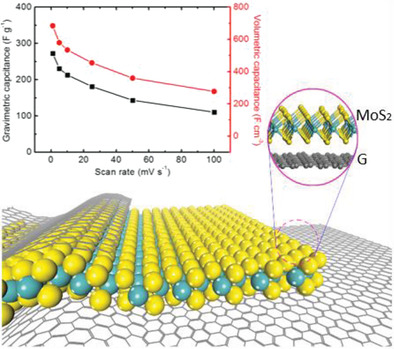
A strong charge transfer ability at the phase boundary of MoS2 is demonstrated. Through modulating the phase composition of MoS2 contacted with graphene, a promoted supercapacitive performance is achieved in MoS2/graphene nanohybrid films. The strategy detailed in the present study reveals that heterophase engineering could be a promising avenue to develop an efficient energy storage device.
Highly Reproducible Physiological Asymmetric Membrane with Freely Diffusing Embedded Proteins in a 3D-Printed Microfluidic Setup
- First Published: 12 April 2019
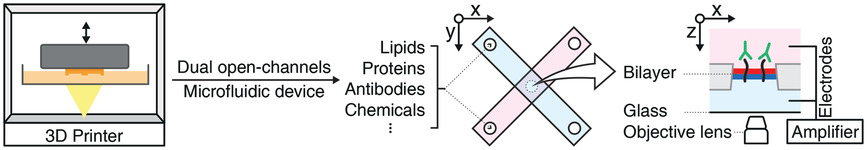
Horizontal free-standing membrane having a physiological lipid composition is reconstituted in a 3D-printing-based microfluidic chip. Simultaneous monitoring of the membrane processes with a microscope and patch-clamp amplifier reveals that the membrane is free-standing, horizontal, fully fluid, stable, flat, and large enough. Dual open-channels adjacent to the bilayer are freely used to alter each lipid monolayer composition and oriented protein insertion.





