Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Mesoporous Nanoparticles: Facile Synthesis of Yolk–Shell-Structured Triple-Hybridized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for Biomedicine (Small 26/2016)
- Page: 3473
- First Published: 07 July 2016

On page 3550, G. Lu, L. Wang, and co-workers report yolk–shell structured periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) nanoparticles simultaneously incorporated with ethane, thioether, and benzene moieties. The unique yolk–shell structure is formed via hydrothermal treatment of triple-hybridized PMOs synthesized using a surfactant-directed sol–gel process. Excellent biobehaviors, bioimaging properties, and high anticancer drug loading capacity endowed by the triple-hybridized groups are demonstrated.
Inside Front Cover
Energy Storage: Nitrogen-Doped Ordered Mesoporous Anatase TiO2 Nanofibers as Anode Materials for High Performance Sodium-Ion Batteries (Small 26/2016)
- Page: 3474
- First Published: 07 July 2016

On page 3522, Y. Yu and co-workers fabricate nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous TiO2 nanofibers (denoted as N-MTO) by electrospinning and subsequent nitridation treatment. Nitrogen atoms are successfully doped into the TiO2 lattice, accompanied by the formation of Ti3+ and oxygen vacancies, contributing to the improvement of electronic conductivity of TiO2. When used as an anode for a sodium-ion battery, the N-MTO demonstrates excellent rate capability and superior long cycling performance.
Back Cover
Silica Nanospheres: Hollow Structure Improved Anti-Cancer Immunity of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres In Vivo (Small 26/2016)
- Page: 3602
- First Published: 07 July 2016

Hollow and non-hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres are synthesized and used for cancer vaccine adjuvants by X. Wang, A. Ito, N. M. Tsuji, and co-workers on page 3510. The hollow structure of mesoporous silica nanospheres significantly promotes cellular uptake of a model cancer antigen by macrophage-like cells in vitro, improves anti-cancer immunity, and increases CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations in splenocytes of mice in vivo.
Masthead
Contents
Reviews
Black Phosphorus Nanosheets: Synthesis, Characterization and Applications
- Pages: 3480-3502
- First Published: 25 May 2016
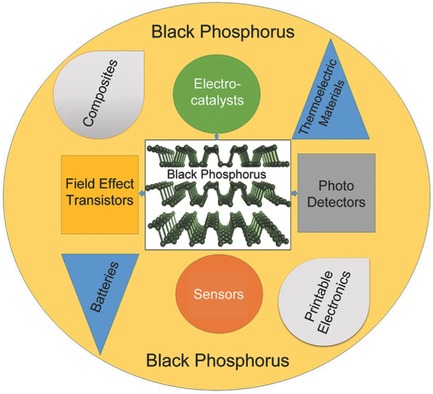
Black phosphorus (BP) exhibits extraordinary performance, both in electronics and wide range optoelectronic devices due to its suitable bandgap. The unconventional anisotropy in BP arises from its puckered structure, which makes it an anisotropic material at large magnitude. It also has potential applications in gas sensing at ultralow level detection towards various gases, energy storage devices and thermoelectric applications.
Communications
Study of the Mechanical Behavior of Radially Grown Fivefold Twinned Nanowires on the Atomic Scale
- Pages: 3503-3509
- First Published: 27 May 2016
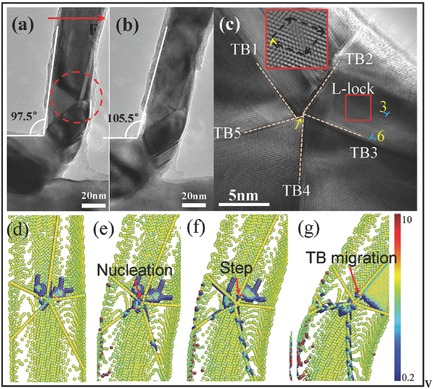
In situ bending tests and dynamic modeling simulations are for the first time revealing the mechanical behavior of copper nanowires (NW) with radially grown fivefold twin structures on the atomic scale. Combining the simulations with the experimental results it is shown that both the twin boundaries (TBs) and the twin center act as dislocation sources. TB migration and L-locks are readily observed in these types of radially grown fivefold-twin structures.
Hollow Structure Improved Anti-Cancer Immunity of Mesoporous Silica Nanospheres In Vivo
- Pages: 3510-3515
- First Published: 18 May 2016
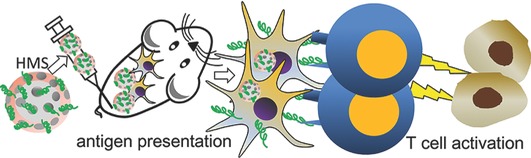
Hollow and non-hollow mesoporous silica nanospheres are synthesized and used for cancer vaccine adjuvants. The hollow structure of mesoporous silica nanospheres significantly promote cellular uptake of a model cancer antigen by macrophage-like cells in vitro, improve anti-cancer immunity, CD4+ and CD8+ T cell populations in splenocytes of mice in vivo.
Durable Antibacterial and Nonfouling Cotton Textiles with Enhanced Comfort via Zwitterionic Sulfopropylbetaine Coating
- Pages: 3516-3521
- First Published: 23 May 2016
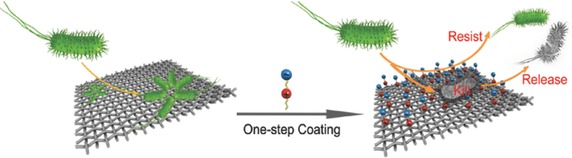
A rapid, environment-friendly, and cost-effective finishing method has been developed for cotton textiles by using zwitterionic NCO-sulfopropylbetaine as the antibacterial finishing agent through covalent bond. The sulfopropylbetaine-finished cotton textile exhibits durable broad-spectrum antibacterial and nonfouling activity, improved mechanical properties, and enhanced comfort.
Nitrogen-Doped Ordered Mesoporous Anatase TiO2 Nanofibers as Anode Materials for High Performance Sodium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 3522-3529
- First Published: 17 May 2016
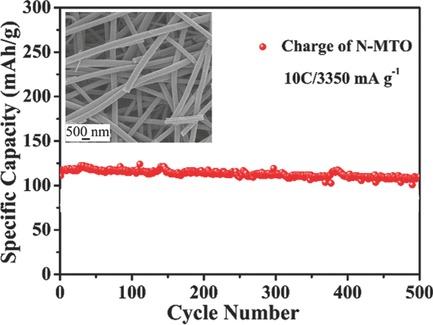
Nitrogen-doped ordered mesoporous TiO2 nanofibers (N-MTO) have been fabricated by electrospinning and subsequent nitridation treatment. The N-doping in TiO2 leads to the formation of Ti3+, resulting in the improved electron conductivity of TiO2. In addition, one-dimensional (1D) N-MTO nanostructure possesses very short diffusion length of Na+/e− in N-MTO, easy access of electrolyte, and high conductivity transport of electrons along the percolating fibers. The N-MTO shows excellent sodium storage performance.
Synthesis of Ultrasmall Cu2O Nanocubes and Octahedra with Tunable Sizes for Facet-Dependent Optical Property Examination
- Pages: 3530-3534
- First Published: 24 May 2016
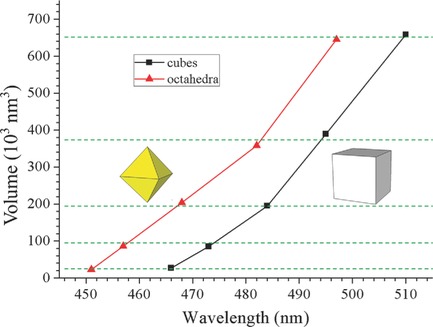
Size-tunable small to ultrasmall Cu2O nanocubes and octahedra are synthesized in aqueous solution without the introduction of any surfactant. These nanocrystals provide strong evidence of the existence of facet-dependent optical absorption properties of Cu2O nanoparticles, showing nanocubes always have a more redshifted absorption band than that of octahedra having a similar volume by about 15 nm.
Full Papers
Graphene-Analogues Boron Nitride Nanosheets Confining Ionic Liquids: A High-Performance Quasi-Liquid Solid Electrolyte
- Pages: 3535-3542
- First Published: 25 May 2016
Self-Sensitized Carbon Nitride Microspheres for Long-Lasting Visible-Light-Driven Hydrogen Generation
- Pages: 3543-3549
- First Published: 25 May 2016
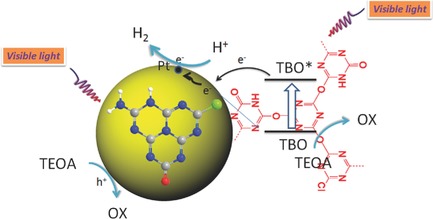
Self-sensitized carbon nitride microspheres, possessing a microsphere core of oxygen-containing carbon nitride and self-sensitized surfaces by covalently linked 1,3,5-triazine based oligomer, exhibit high visible-light activities for H2 generation with excellent stability. This new type of highly stable self-sensitized metal-free semiconductor opens a new direction of future development of low-cost photocatalysts for efficient and stable solar fuels production.
Facile Synthesis of Yolk–Shell-Structured Triple-Hybridized Periodic Mesoporous Organosilica Nanoparticles for Biomedicine
- Pages: 3550-3558
- First Published: 17 May 2016
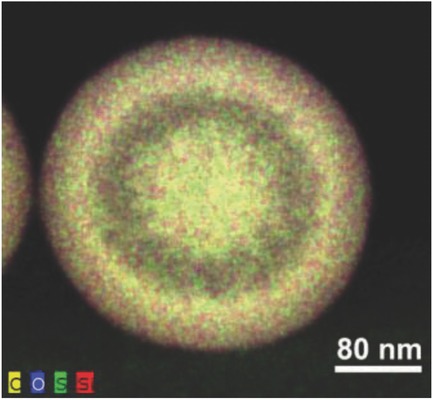
Yolk–shell-structured periodic mesoporous organosilica (PMO) nanoparticles simultaneously incorporated with ethane-, thioether-, and benzene-bridged moieties are successfully synthesized for the first time. The PMO nanoparticles have uniform and controllable diameter, large surface area, accessible mesochannels, large pore volume, and excellent biocompatibility. By using the incorporated organic groups, fluorescence imaging probes and stimuli-responsive drug carriers are successfully prepared.
The Age of Cortical Neural Networks Affects Their Interactions with Magnetic Nanoparticles
- Pages: 3559-3567
- First Published: 27 May 2016
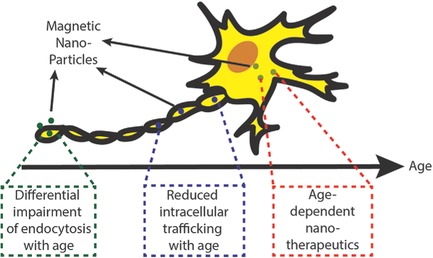
The age of neurons (either induced with chemokine CCL11 or cultured for up to 3 weeks) affects the endocytic uptake of chitosan-coated magnetic nanoparticles, with impairment of clathrin-mediated endocytosis increasing with age. The neuro-protective effects of chitosan coatings on magnetic nanoparticles are also age-dependent due to reduced intracellular trafficking of magnetic nanoparticles with age.
An Experimental and Computational Approach to the Development of ZnO Nanoparticles that are Safe by Design
- Pages: 3568-3577
- First Published: 11 May 2016
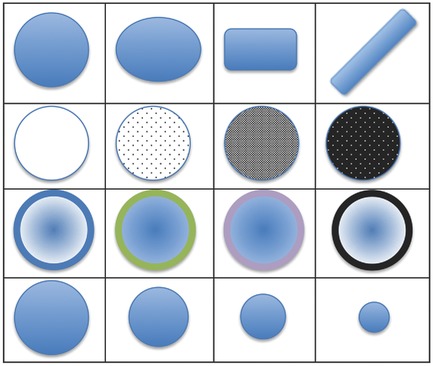
Modifying the surfaces of ZnO nanoparticles can reduce potential cell toxicity of these widely used particles. The relationship is elucidated between surface chemistry and toxicity by screening 45 modified ZnO nanoparticles for cell toxicity and generating quantitative, predictive computational models. The models can be used to design functional nanomaterials with lower adverse impacts than unmodified nanoparticles.
Somatostatin Receptor-Mediated Tumor-Targeting Nanocarriers Based on Octreotide-PEG Conjugated Nanographene Oxide for Combined Chemo and Photothermal Therapy
- Pages: 3578-3590
- First Published: 31 May 2016
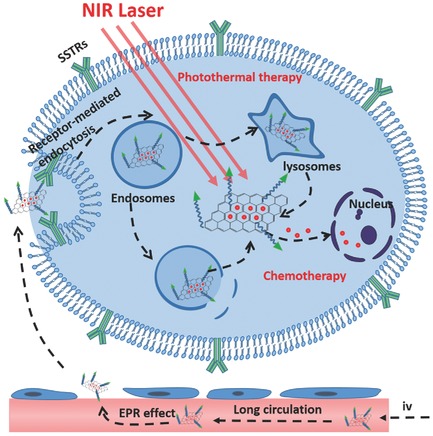
Efficient biotarget molecule octreotide conjugated nanographene oxide delivers somatostatin receptor-mediated tumor-specific targeting effect as tumor therapy agent. This active targeting offers a remarkably improved cancer-cell-specific cellular uptake, chemo-cytotoxicity, and decreased systemic toxicity, which also enables combined chemo and photothermal therapeutic effect against cancer cells.
High-Performance Upconversion Nanoprobes for Multimodal MR Imaging of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Pages: 3591-3600
- First Published: 24 May 2016
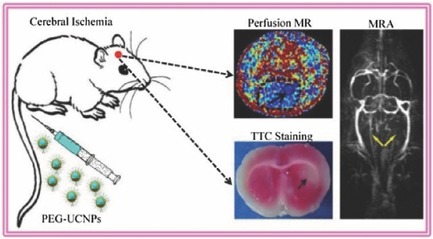
High-performance polyethylene glycol (PEG)-ylated upconversion nanoprobes (PEG-UCNP nanoprobes) synthesized through the typical thermal decomposition method are successfully used for multimodal magnetic resonance (MR) imaging including MR angiography and MR perfusion imaging, which possess distinctive advantages compared with clinical Magnevist on the vascular system imaging and the diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke.