Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
TRAPPopathies: An emerging set of disorders linked to variations in the genes encoding transport protein particle (TRAPP)-associated proteins
- Pages: 5-26
- First Published: 27 August 2018

Proteins associated with the human TRAPP complexes have been shown to function in cellular processes such as membrane traffic, autophagy, mitosis and protein glycosylation. Work dating back nearly two decades and particularly over the past few years has suggested that variants in these proteins lead to human disease. Here, we describe all known variants to date, review what is known about TRAPP function and suggest that the observed clinical phenotypes may be due to dysregulation of a specific function of the protein as opposed to dysfunction of the entire complex.
Lysosome: The metabolic signaling hub
- Pages: 27-38
- First Published: 10 October 2018
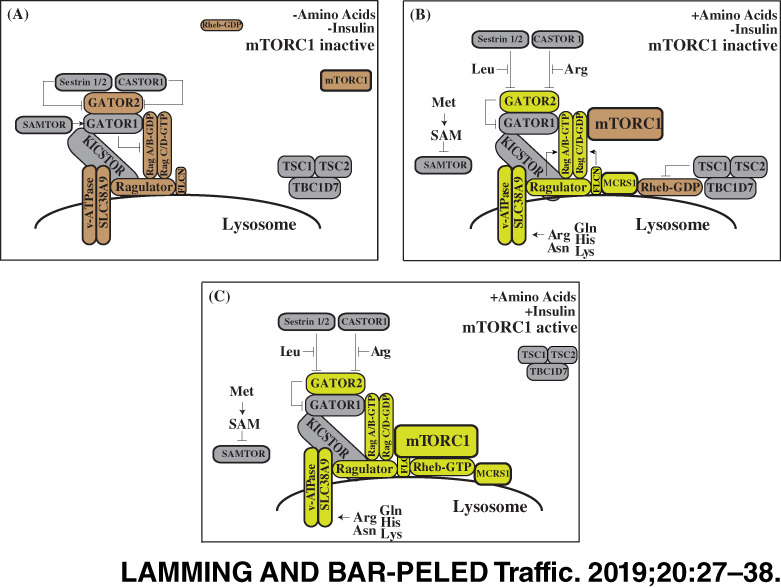
After decades of being known as just the cellular recycling center, the lysosome has recently emerged as a central hub for metabolic signaling. Signaling pathways that call the lysosome home connect this organelle to key anabolic and catabolic processes that control many facets of cellular metabolism. Metabolic signals emanating from the lysosome are contributors to multiple human diseases, emphasizing the key role of the lysosome as a cellular site for the regulation of human health.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Prominin-1 (CD133) modulates the architecture and dynamics of microvilli
- Pages: 39-60
- First Published: 17 October 2018
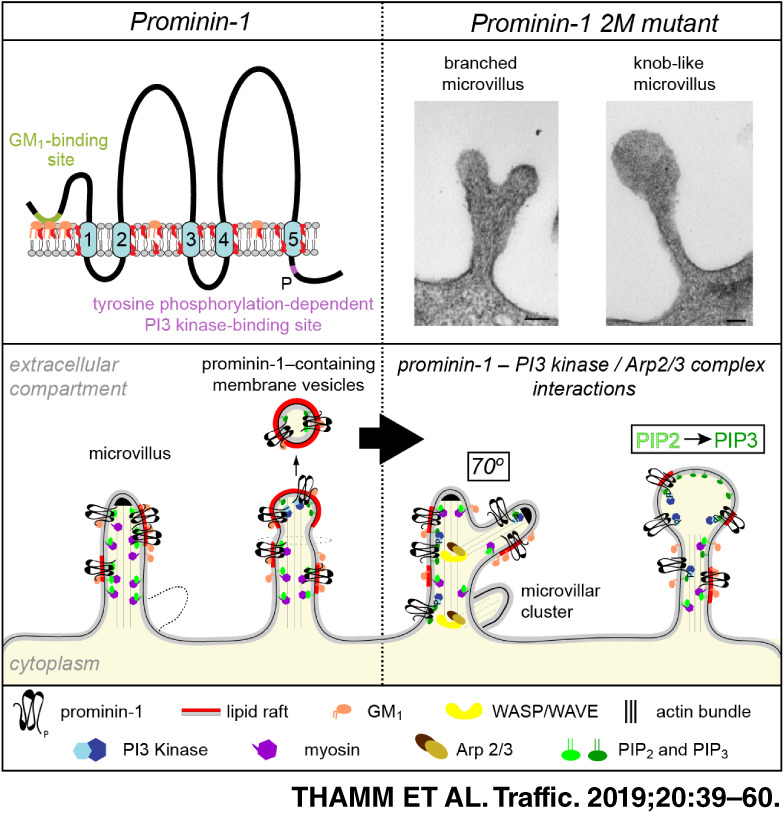
Prominin-1 is specifically associated with membrane protrusions. Despite its clinical relevance in the stem cell field and its impact on photoreceptor morphogenesis, its function remains elusive. We demonstrate that mutations in its ganglioside-binding site stimulate interactions with phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Arp2/3 complex, which in turn influence the architecture of microvilli of epithelial cells and other protrusions of non-epithelial cells. Thus, prominin-1 seems to organize cellular protrusions, possibly by driving the crosstalk between the outer and inner leaflet of the plasma membrane.
Pseudoginsenoside-F11 alleviates oligomeric β-amyloid-induced endosome-lysosome defects in microglia
- Pages: 61-70
- First Published: 29 October 2018
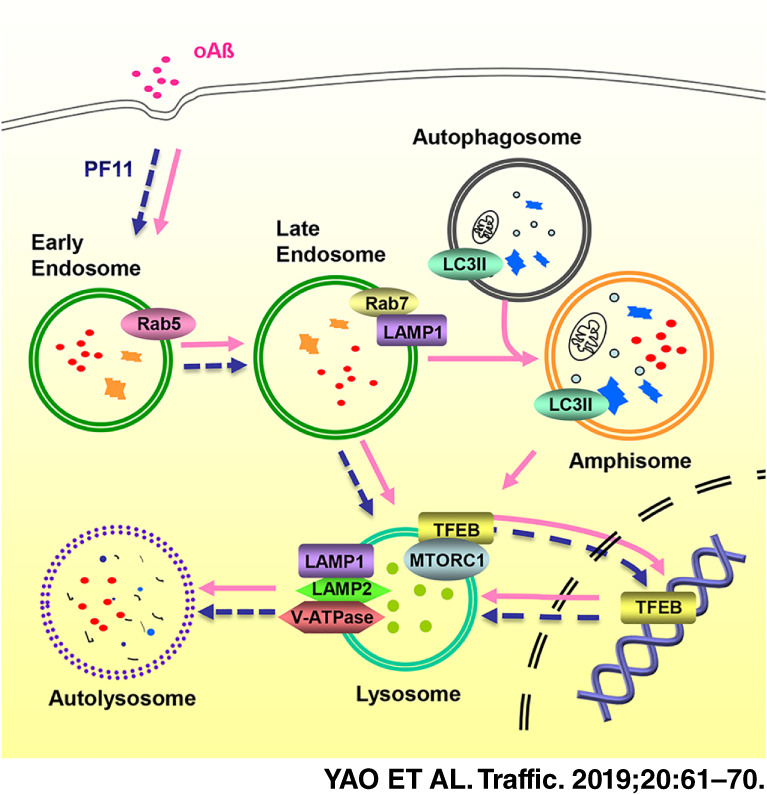
Amyloid beta (Aβ) is cleared by the endosomal-autophagy-lysosomal system, which is impaired in AD pathogenesis by an unknown mechanism. Oligomeric Aβ (oAβ) interrupted the autophagy-lysosomal degradative system by regulating the nuclear translocation of transcription factor EB. Conversion of Rab5 to Rab7 was also interrupted by high-concentration oAβ. Notably, pseudoginsenoside-F11 (PF11), a traditional medicine isolated from was isolated from leaves of Panax pseudoginseng that has been demonstrated to reduce Aβ levels in neurons, can reverse the dysfunction of the endosomal-lysosomal system induced by high-concentration oAβ in microglia, and this might be the main mechanism by which PF11 facilitates oAβ clearance. Orange structures: endocytosed material; Blue structures: cytosolic components.
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9-mediated kif15 mutations accelerate axonal outgrowth during neuronal development and regeneration in zebrafish
- Pages: 71-81
- First Published: 08 November 2018
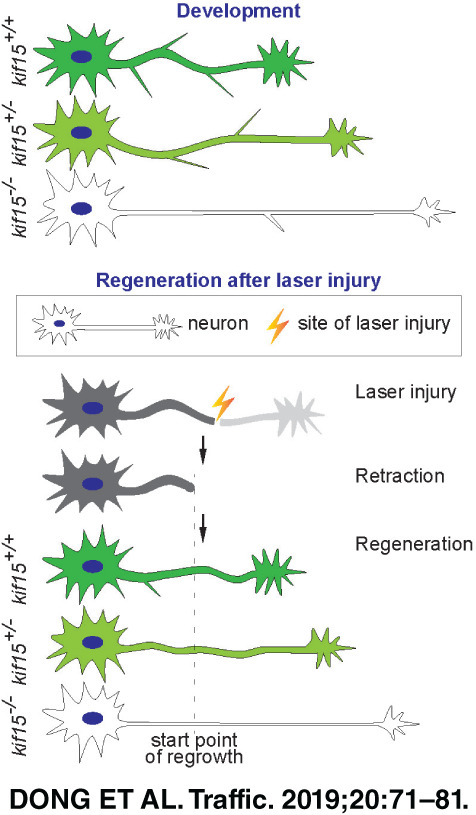

KIF15, a microtubule-associated motor protein, was reported previously impacting axonal growth, navigation and branching in cultured rat neurons. To elucidate kif15 function in vivo, we employed CRISPR/Cas9-based knockout technology to create kif15 mutants in zebrafish. By comparing the homozygotic and heterozygotic mutants with their wildtype siblings, the effects of kif15 depletion were ascertained during axon development and regeneration. That is, a disuse of kif15 renders axons fast-growing, smooth and slender, and also with greater regenerative velocity after axonal laser injury.
Phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate on Rab7-positive autophagosomes revealed by the freeze-fracture replica labeling
- Pages: 82-95
- First Published: 13 November 2018
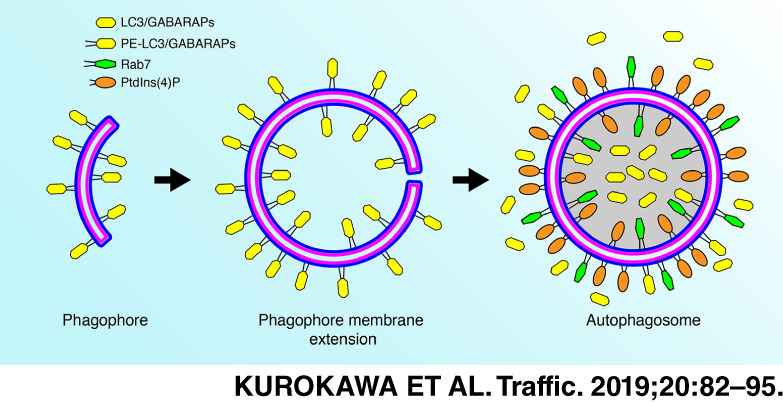
Quick-freezing and freeze-fracture replica labeling method revealed that phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate (PtdIns(4)P) was localized on the cytoplasmic leaflet in the inner and outer membranes of the autophagosome in the Torin1-treated autophagy-induced Huh7 cells. PtdIns(4)P was colocalized with Rab7, but not LC3B, GABARAP, GABARAPL1 or GABARAPL2 on the autophagosomal membranes. Rab7 was reported to play essential roles for the maturation of autophagosome formation, suggesting that PtdIns(4)P appears with Rab7 at the later and mature stages of autophagosome formation.




