Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
MiniReview
no
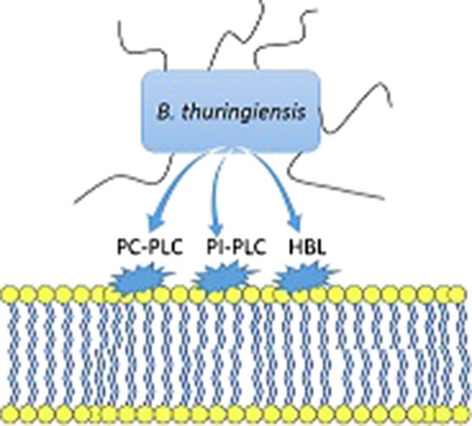
Bacillus thuringiensis membrane-damaging toxins acting on mammalian cells
- Pages: 95-103
- First Published: 03 October 2014
Genome Announcement
no
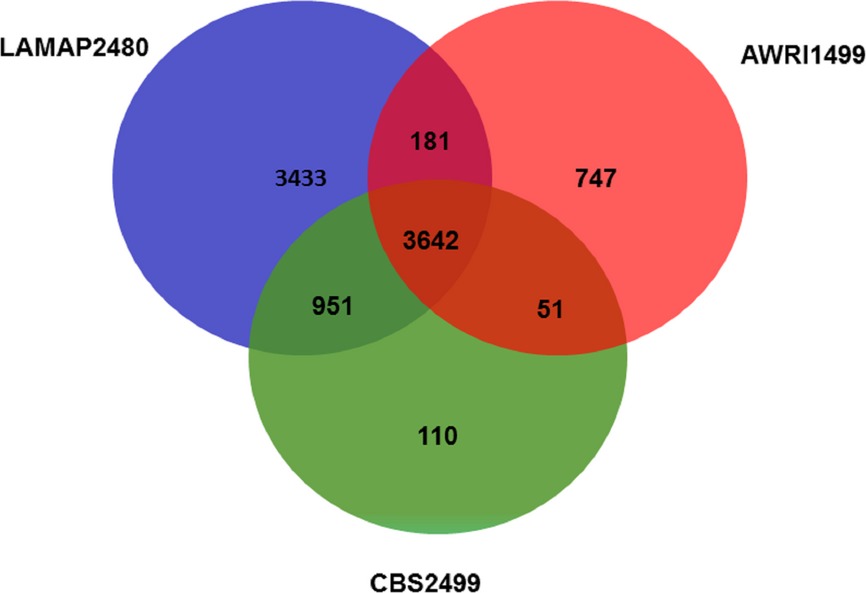
Draft genome sequence and transcriptome analysis of the wine spoilage yeast Dekkera bruxellensis LAMAP2480 provides insights into genetic diversity, metabolism and survival
- Pages: 104-106
- First Published: 18 October 2014
Research Letters
no
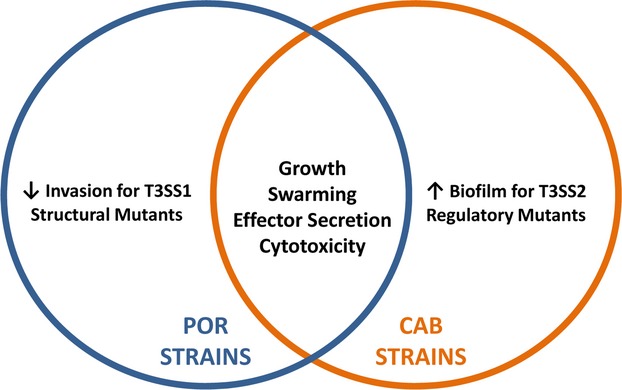
Structural and regulatory mutations in Vibrio parahaemolyticus type III secretion systems display variable effects on virulence
- Pages: 107-114
- First Published: 07 October 2014
no
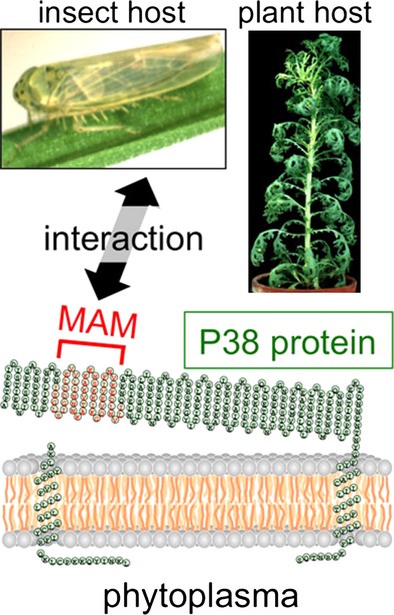
Onion yellow phytoplasma P38 protein plays a role in adhesion to the hosts
- Pages: 115-122
- First Published: 10 October 2014
no
Translational coupling of nasST expression in Azotobacter vinelandii prevents overexpression of the nasT gene
- Pages: 123-130
- First Published: 10 October 2014
no
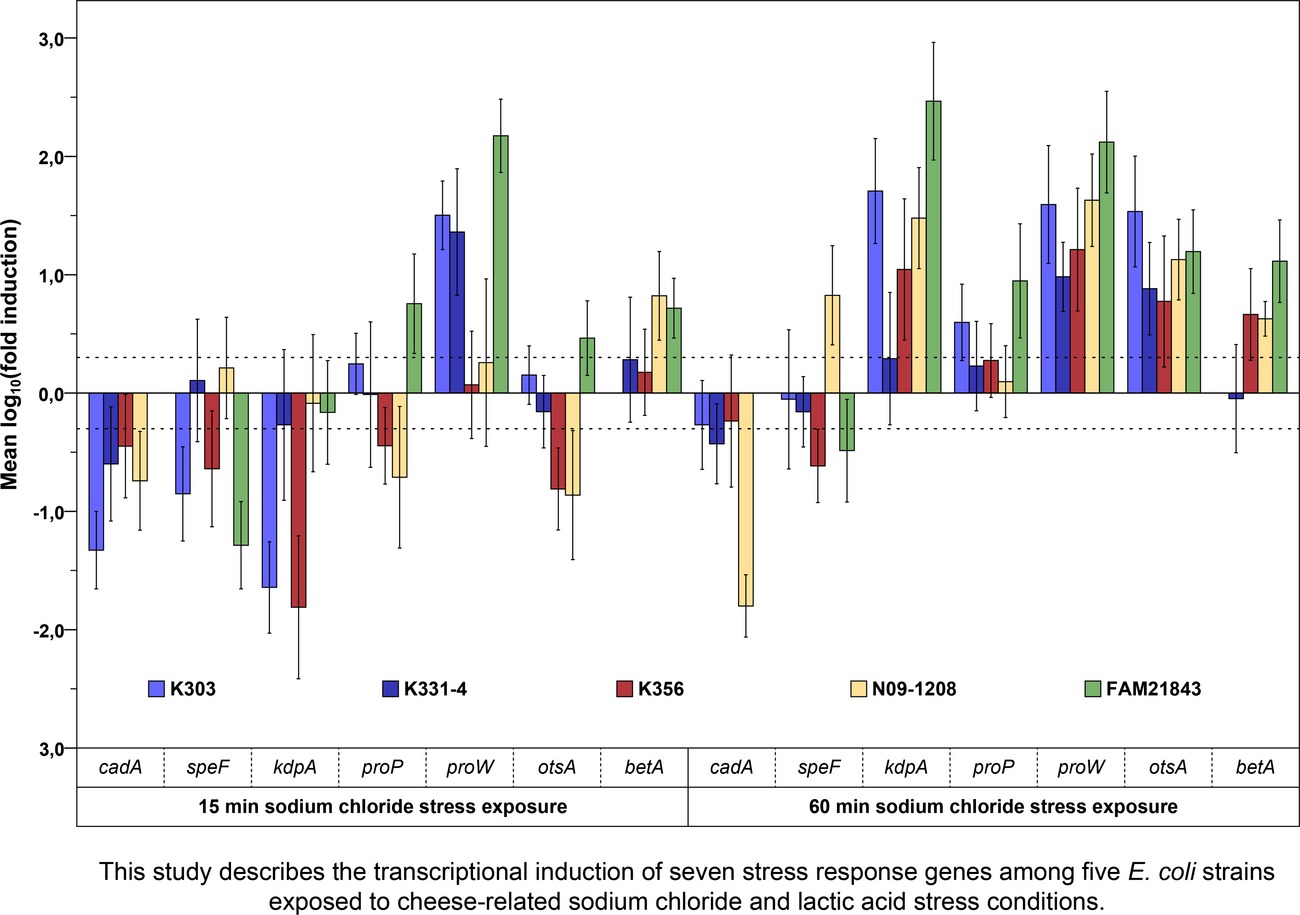
Transcriptional analysis of different stress response genes in Escherichia coli strains subjected to sodium chloride and lactic acid stress
- Pages: 131-137
- First Published: 13 October 2014
no
Selenate reductase activity in Escherichia coli requires Isc iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis genes
- Pages: 138-143
- First Published: 13 October 2014
no
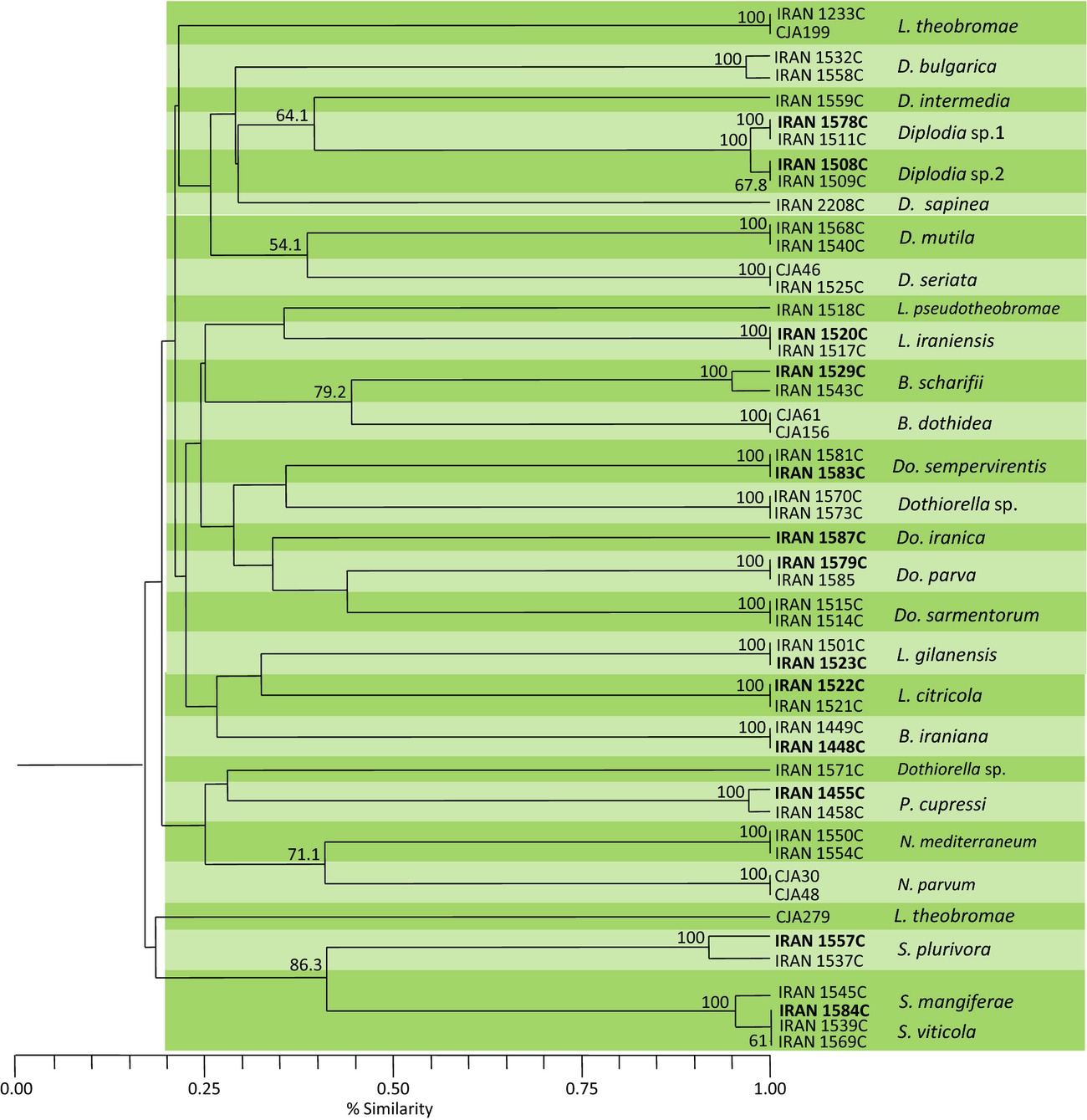
Efficiency of rep-PCR fingerprinting as a useful technique for molecular typing of plant pathogenic fungal species: Botryosphaeriaceae species as a case study
- Pages: 144-157
- First Published: 13 October 2014
no
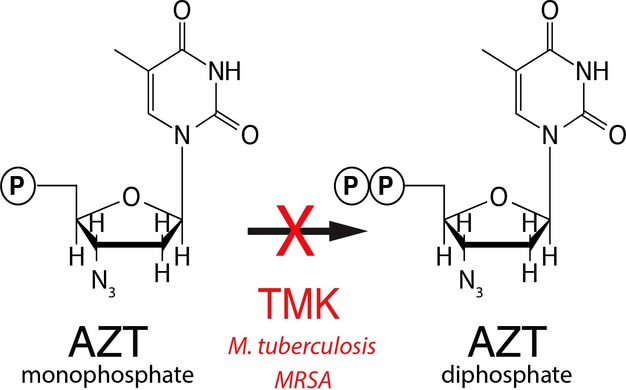
The thymidylate kinase genes from Mycobacterium tuberculosis and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus confer 3′-azido-3′-deoxythymidine resistance to Escherichia coli
- Pages: 158-165
- First Published: 14 October 2014
no
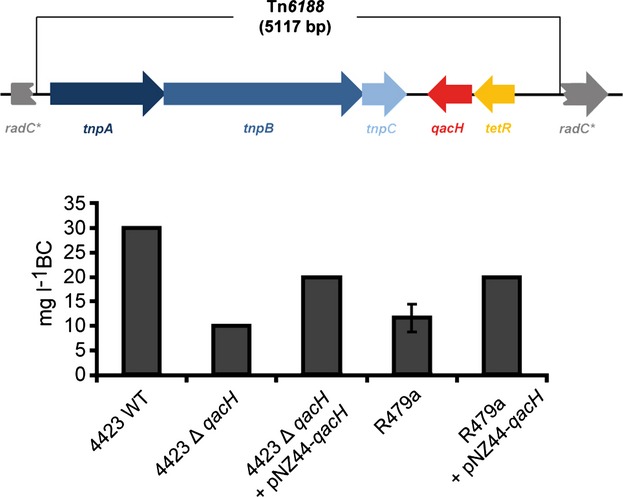
The Listeria monocytogenes transposon Tn6188 provides increased tolerance to various quaternary ammonium compounds and ethidium bromide
- Pages: 166-173
- First Published: 14 October 2014
no
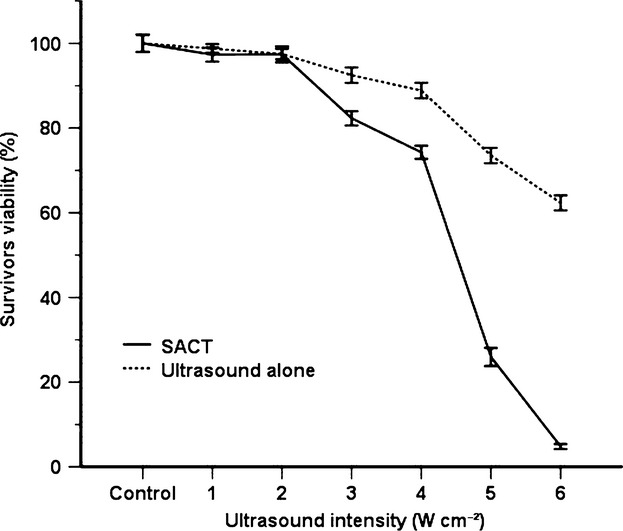
Sonodynamic effects of hematoporphyrin monomethyl ether on Staphylococcus aureus in vitro
- Pages: 174-180
- First Published: 15 October 2014
no
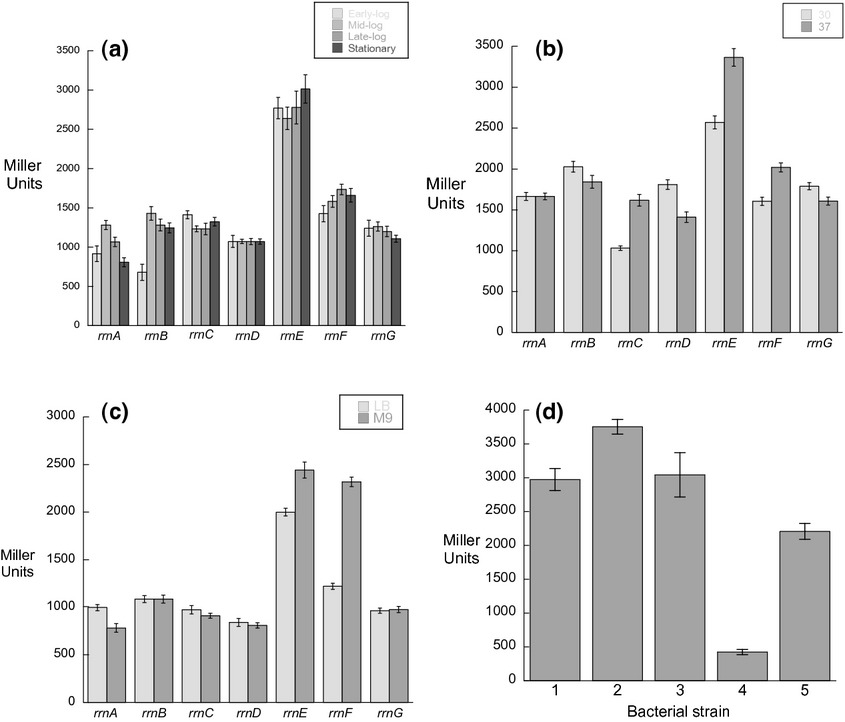
Differential expression of the seven rRNA operon promoters from the plant growth-promoting bacterium Pseudomonas sp. UW4
- Pages: 181-189
- First Published: 18 October 2014
no
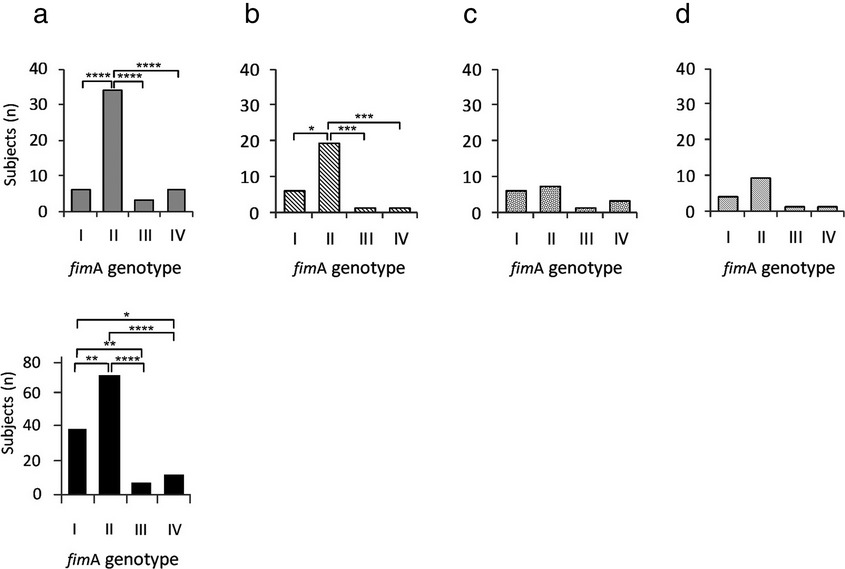
The profile of Porphyromonas gingivalis kgp biotype and fimA genotype mosaic in subgingival plaque samples
- Pages: 190-194
- First Published: 29 October 2014