Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2024
- Page: 1251
- First Published: 03 October 2024

Cover:
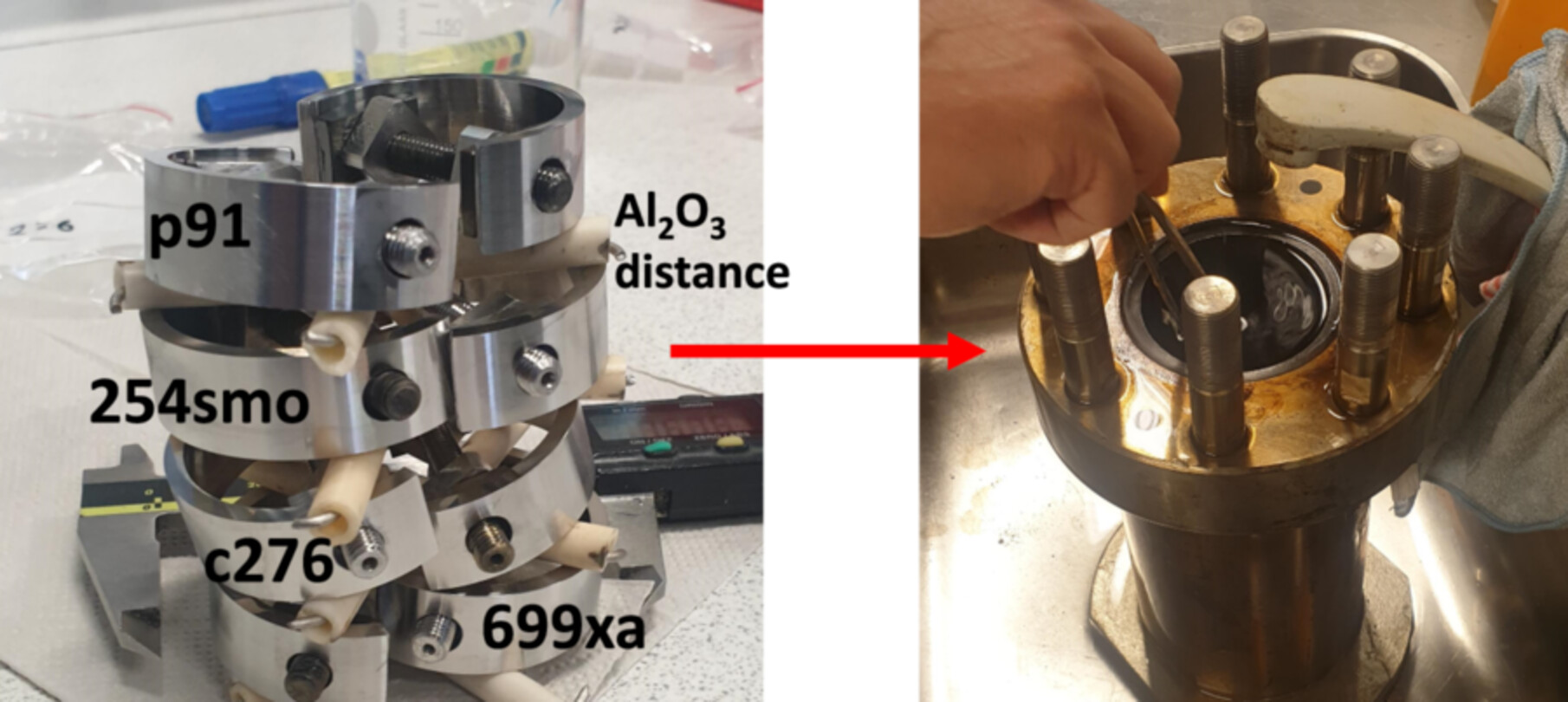
Optical microscopy images of as tested C-276 C-rings. Pitting corrosion was evident on the stressed inner edge of the C-rings and on the surface. A more detailed analysis showed that also intercrystalline corrosion had taken place with the loss of occasional grains because of the applied stress in combination with corrosion.
More detailed information can be found in: Daniel Blücher, Torstein Lange, Judit Sandquist, Inge Saanum, Mikko Uusitalo, Corrosion performance of different alloys exposed to HTL conditions—a screening study, Materials and Corrosion 2024, 75, 1258.
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2024
- Page: 1253
- First Published: 03 October 2024
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2024
- Pages: 1254-1257
- First Published: 03 October 2024
ARTICLE
Corrosion performance of different alloys exposed to HTL conditions—A screening study
- Pages: 1258-1271
- First Published: 18 May 2024
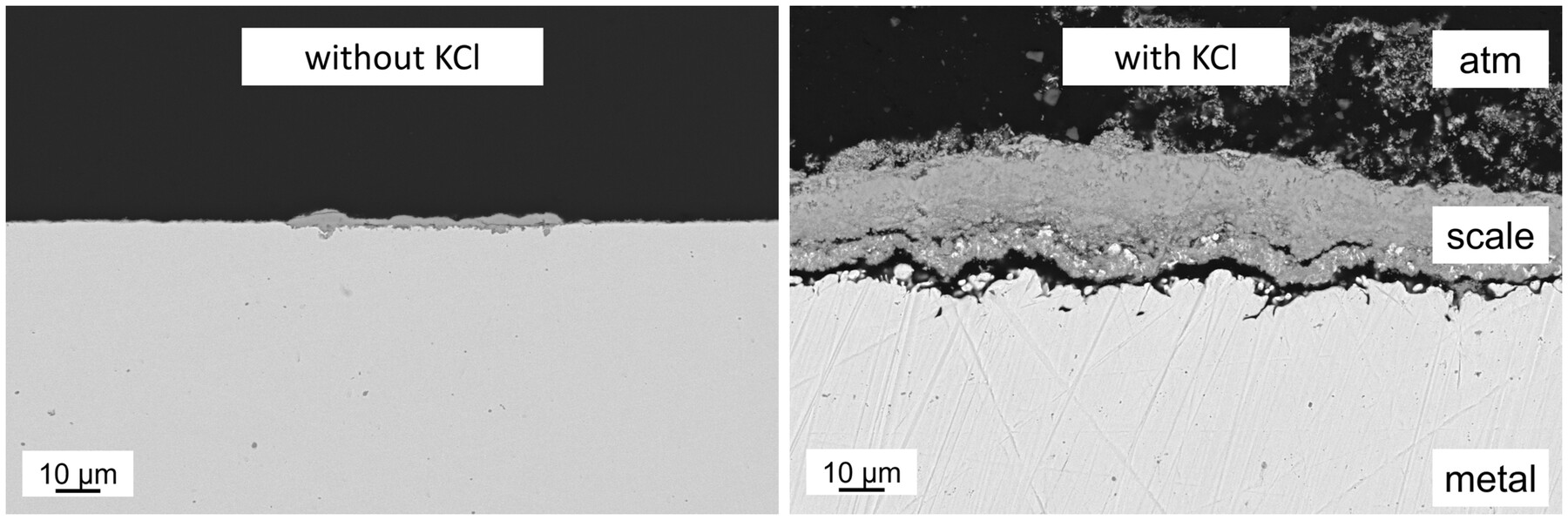
High-temperature KCl-induced corrosion of high Cr and Ni alloys investigated by in-situ diffraction
- Pages: 1272-1281
- First Published: 18 May 2024
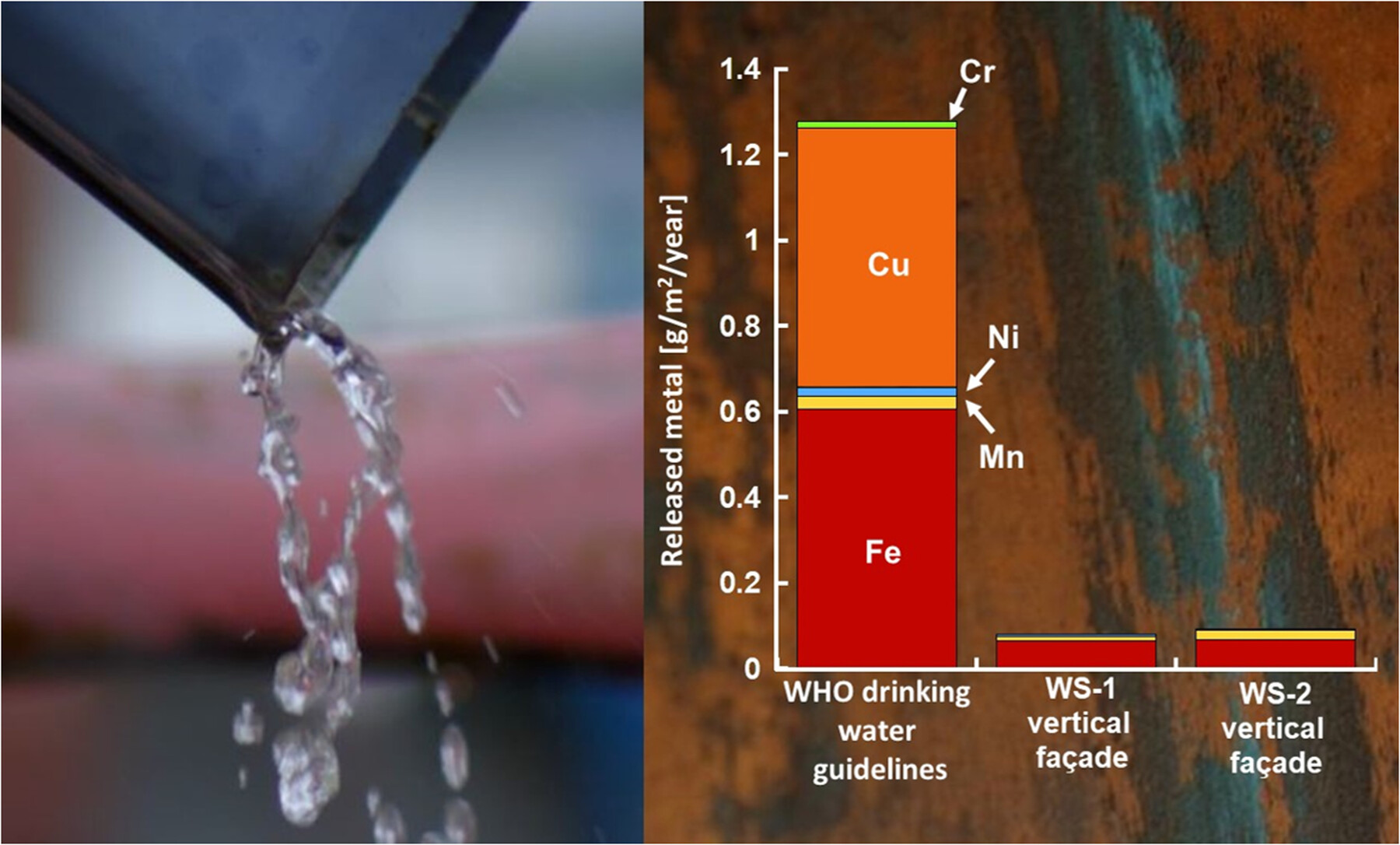
Patina formation and diffuse dispersion of alloying metals from weathering steels at urban atmospheric conditions—A combined laboratory and field investigation
- Pages: 1282-1296
- First Published: 18 May 2024
Electrochemical characterization of surfaces of galvanized steels under different exposure conditions using gel electrolytes
- Pages: 1297-1312
- First Published: 17 April 2024
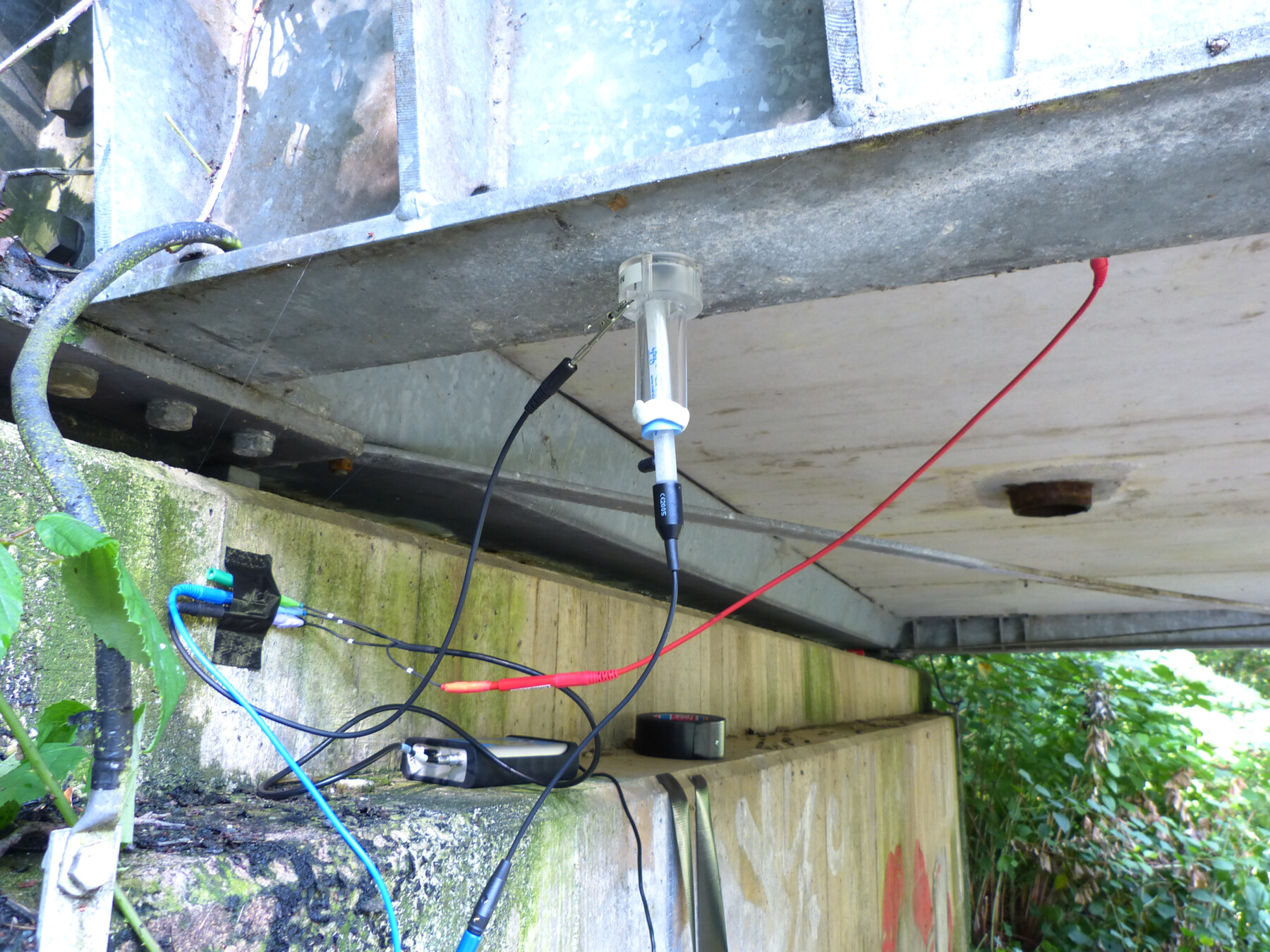

Electrochemical measurements on galvanized steel can be carried out more easily on practical components using gel electrolytes and show good agreement with laboratory measurements. The electrochemically determined cover layer resistance is a useful characteristic value for evaluating the current condition and further corrosion progression.
Development of potentiostatically deposited cerium conversion coating for Mg alloys
- Pages: 1313-1330
- First Published: 15 May 2024
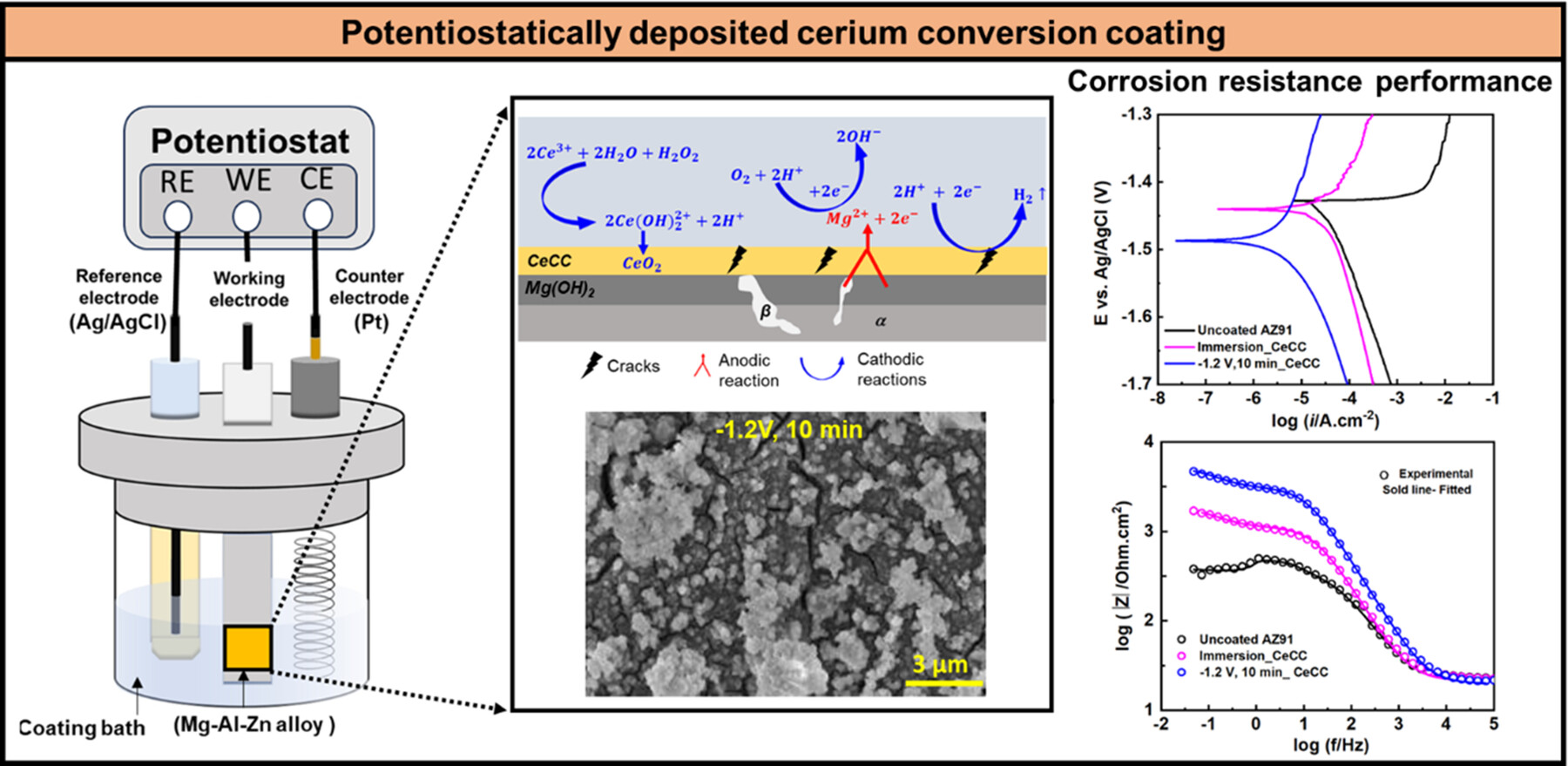
This study investigated a novel potentiostatic polarization method for cerium conversion coating (CeCC), comparing it to the conventional immersion method. Potentiostatic deposition conditions (−1.2 V, 10 min) resulted in crack-free surface with denser and larger deposits. Potentiostatically deposited CeCC showed significantly lower corrosion current density and higher charge transfer resistance compared to immersion_CeCC. It exhibited five times higher charge transfer resistance and twice lower corrosion rate than uncoated specimens.
Effect of DBSA-doped PANI on the corrosion protection performance of GO/epoxy coatings
- Pages: 1331-1347
- First Published: 18 May 2024
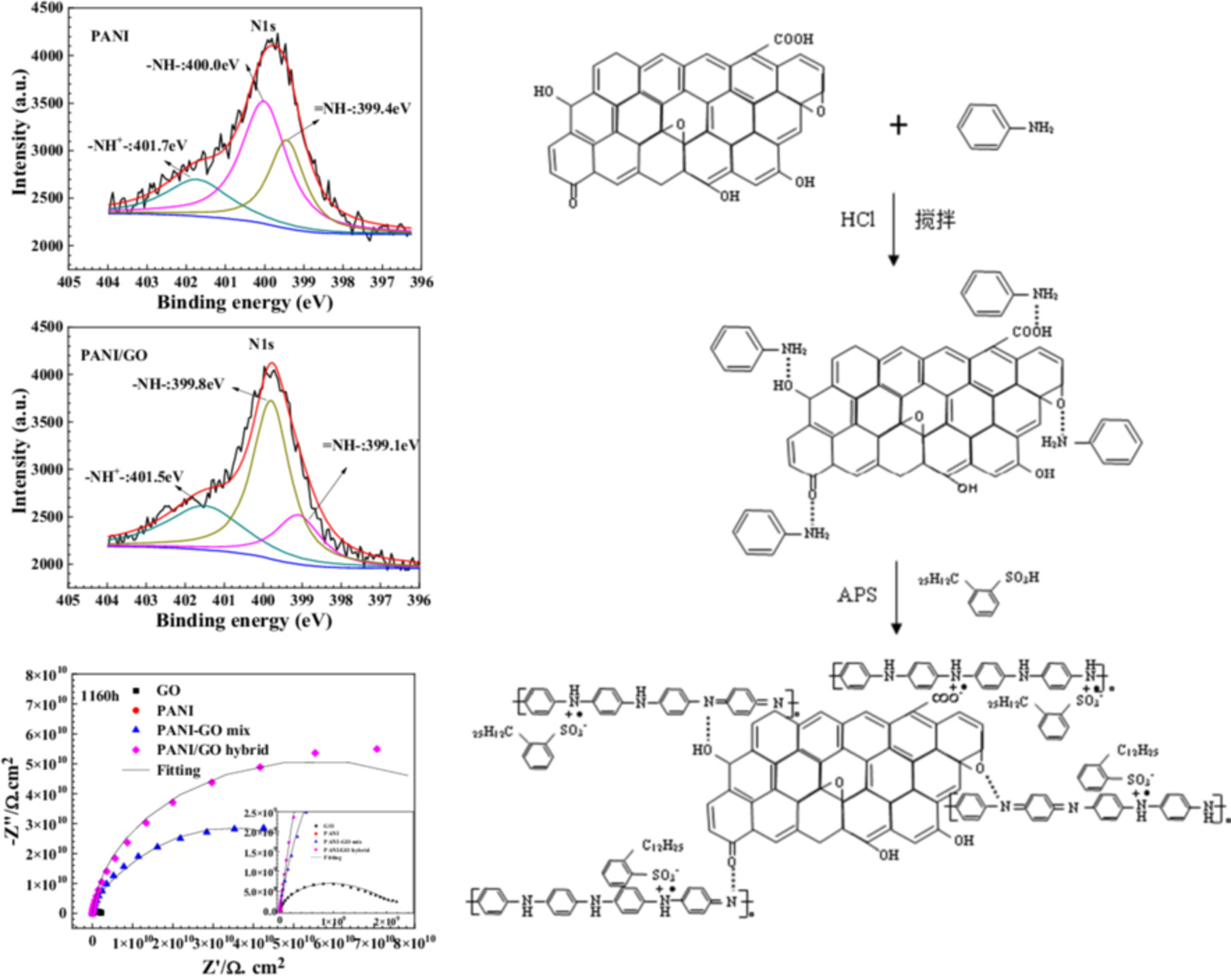
PANI/GO hybrid with dodecylbenzene sulfonic acid as a dopant is synthesized using the in-situ emulsion polymerization method. This synthesis prompts a significant rearrangement of electron clouds within both the GO and PANI molecular structures, resembling the process of acid doping. Finally, the corrosion resistance property of the GO/epoxy coating is improved.
Effects of external corrosion defect growth on wall pipeline under internal pressure and various defect sizes with mechano-electrochemical interaction
- Pages: 1348-1358
- First Published: 12 April 2024
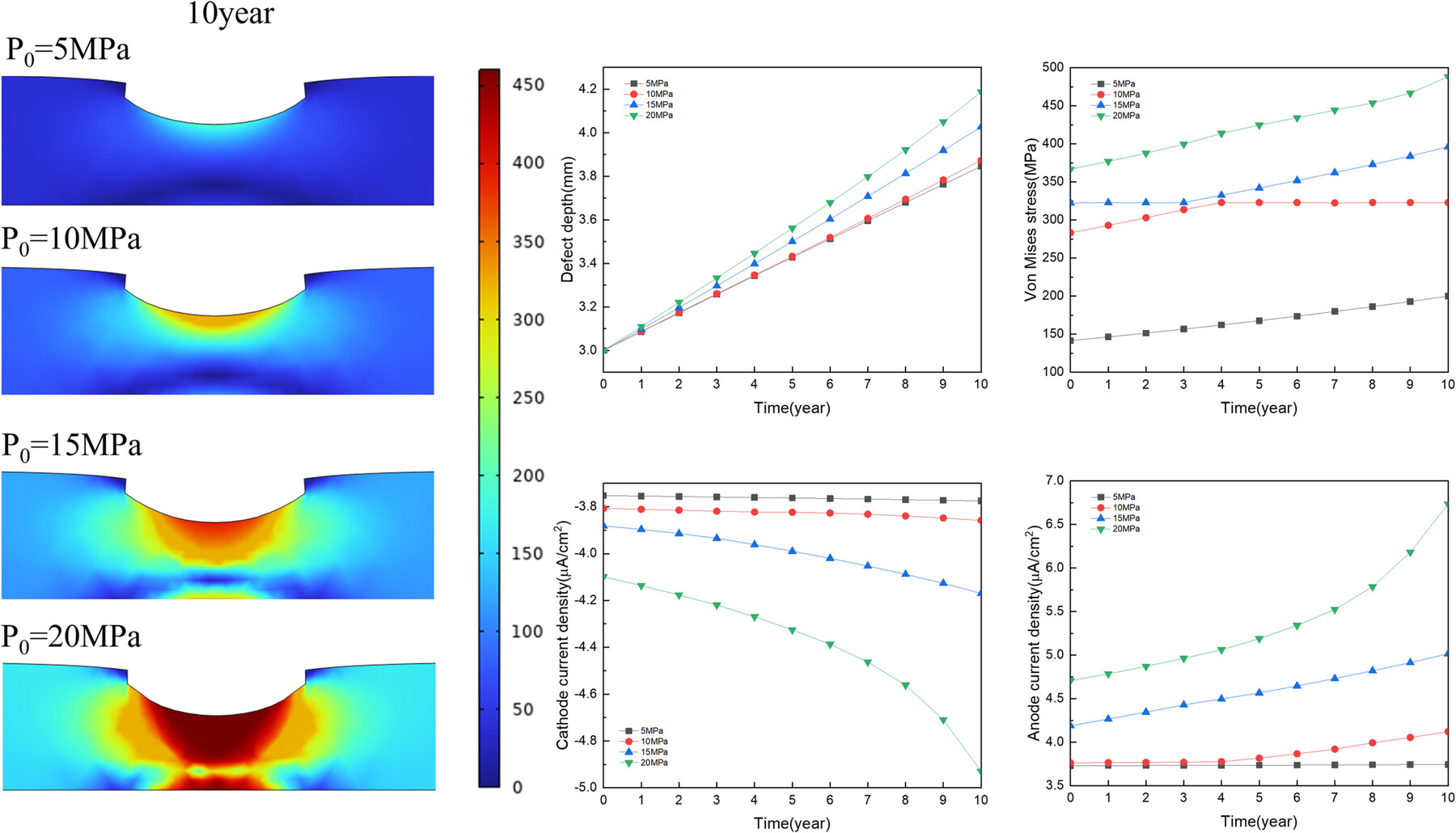
The corrosion defects increase with time. As the pressure increases, the failure pressure of the pipeline gradually decreases. The increase in internal pressure causes local plastic deformation and anodic current density concentration at the inner edge of the defect and in the adjacent areas of the defect. The influence of defect depth on the corrosion rate at the defect is greater than that of defect width.
Quantifying intergranular corrosion susceptibility in AA2098-T351 weldments through friction stir welding
- Pages: 1359-1372
- First Published: 10 June 2024
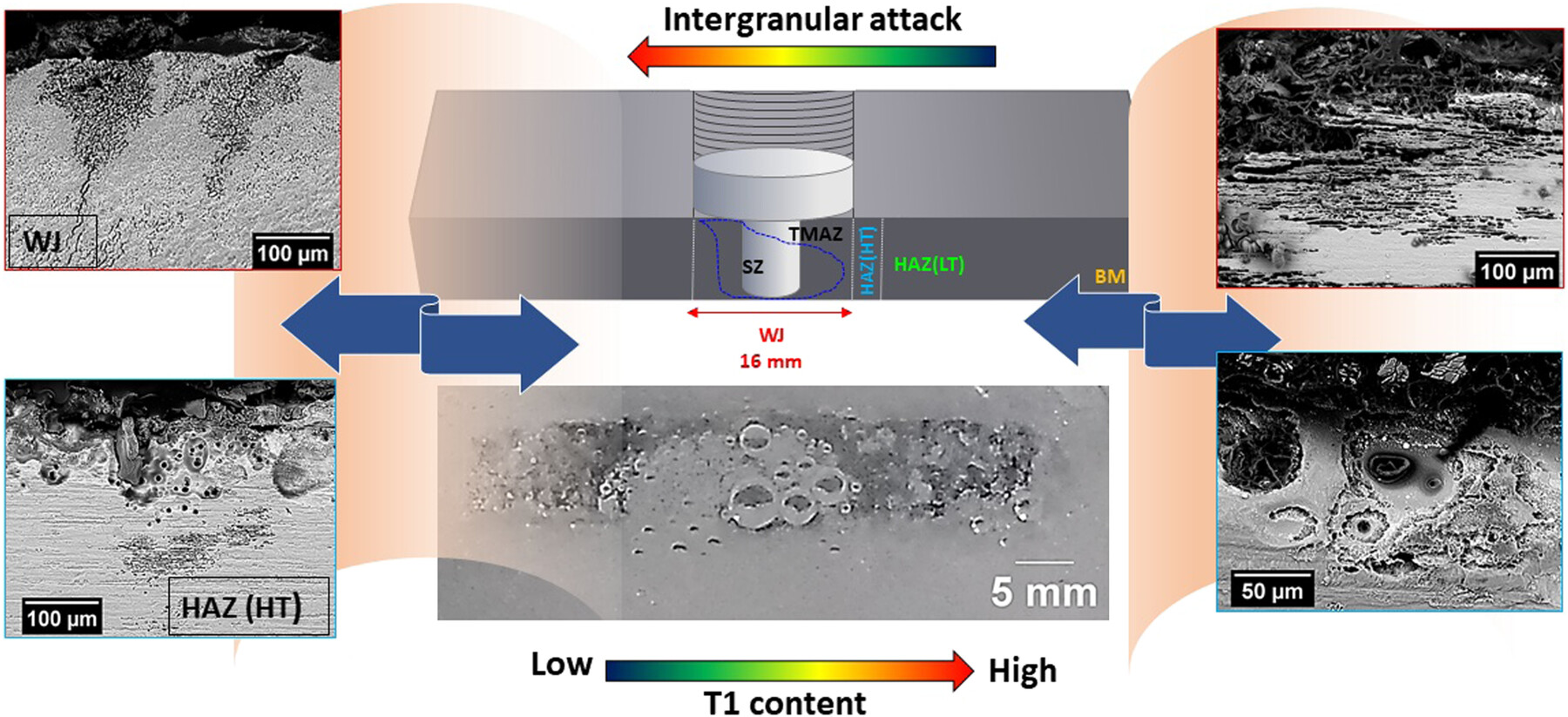
This study explored friction stir welding (FSW) impact on AA2098-T351 welds, focusing on microstructural changes and intergranular corrosion susceptibility. Electrochemical impedance measurements and ASTM G110-92 were employed, revealing FSW-induced microstructural alterations significantly affecting intergranular corrosion (IGC) susceptibility. The ASTM G110-92 test differentiated heat-affected zone segments, influencing diverse zone susceptibilities to IGC.
Insight into the crevice corrosion mechanism of AA7075-T651 high-strength aluminum alloys in neutral nitrate solution: The effect of Cl−
- Pages: 1373-1388
- First Published: 18 May 2024
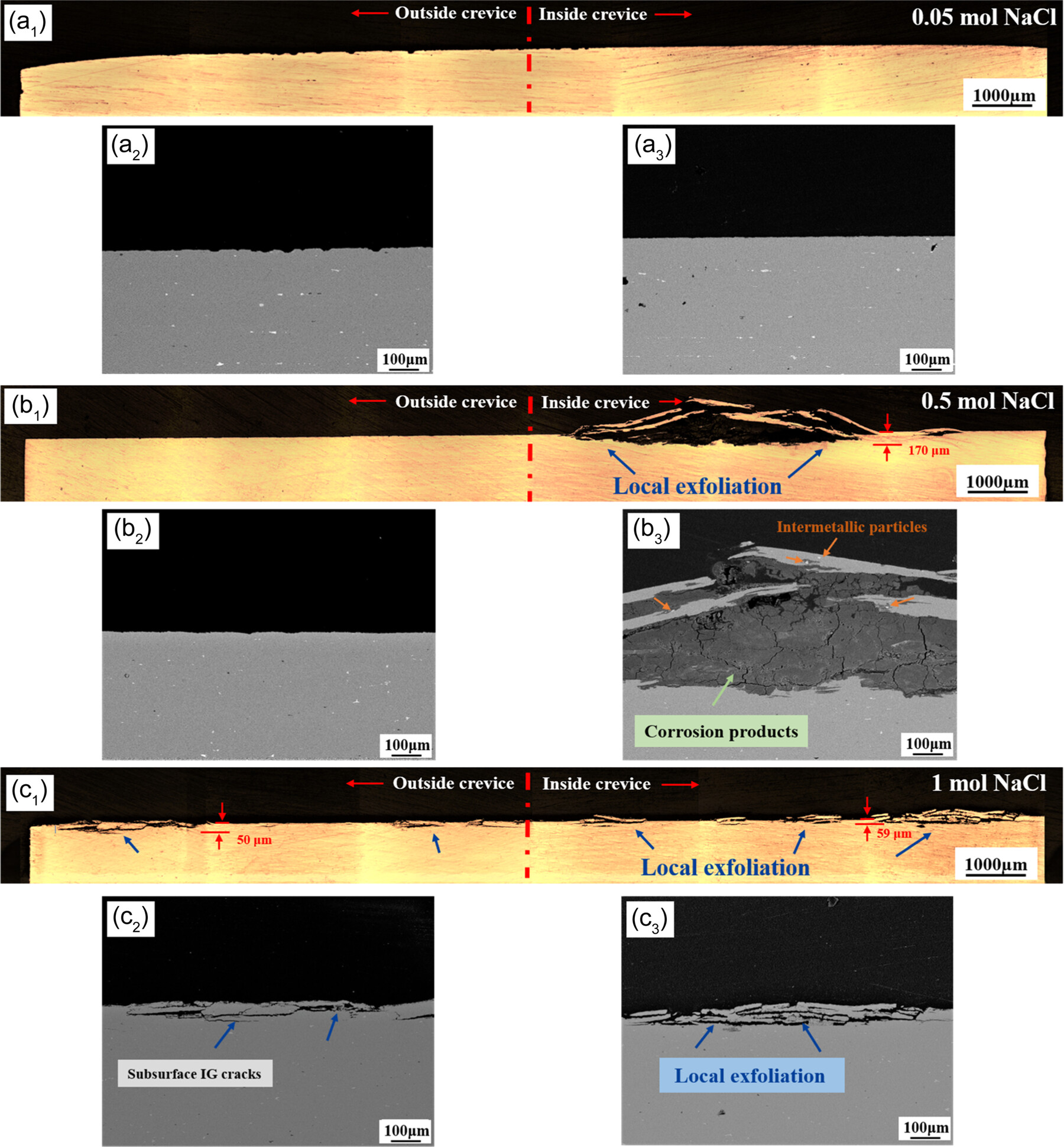
The crevice corrosion of high-strength Al alloy shows a complicated behavior in solution with different contents of NaCl. The crevice corrosion was more pronounced in the 0.5 M NaCl solution compared to 0.05 and 1 M NaCl solution. The rapid dissolution of the anodic phase resulted in the increased Cl− inside the crevice, while the cathodic phase enhanced the localized dissolution through micro-galvanic corrosion. This synergistic effect significantly facilitated the development of crevice corrosion.