Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Cover Picture: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2019
- Page: 1737
- First Published: 06 October 2019
MASTHEAD
Masthead: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2019
- Page: 1739
- First Published: 06 October 2019
CONTENTS
Contents: Materials and Corrosion. 10/2019
- Pages: 1740-1744
- First Published: 06 October 2019
ARTICLES
Effect of passive film on the galvanic corrosion of titanium alloy Ti60 coupled to copper alloy H62
- Pages: 1745-1754
- First Published: 24 May 2019
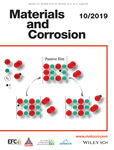
The role of the passive film on galvanic corrosion of Ti60-H62 galvanic coupling is studied. The conventional and in situ electrochemical results indicate that the galvanic corrosion is ignorable under the large potential difference. The results of polarization curves and M-S plots prove that low donor density of the passive film determines the slow electron charge transfer rate, resulting in the slow oxygen reduction rate at the metal/film interface, which plays an essential role in ignorable galvanic corrosion.
Corrosion and mechanical properties of age-hardened UNS N06625 forged bars for oil and gas applications
- Pages: 1755-1763
- First Published: 12 April 2019
Improvement on the pitting corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel via duplex passivation treatment
- Pages: 1764-1775
- First Published: 10 April 2019
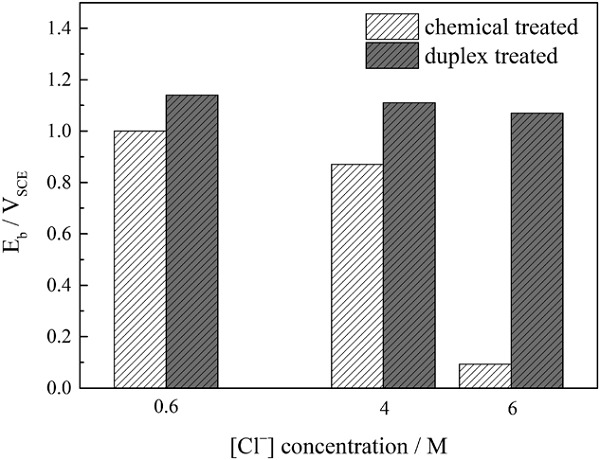
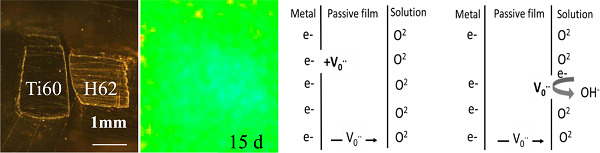
A remarkable improvement in the pitting corrosion resistance of 304 stainless steel was attempted using a novel duplex passivation treatment method. First, chemical passivation in nitric acid followed electrochemical passivation via potential polarization of step cycling in sodium nitrate electrolyte. The probable reason for the improvement on pitting resistance is discussed in detail.
Influence of grinding parameters on the corrosion behavior of austenitic stainless steel
- Pages: 1776-1787
- First Published: 15 April 2019
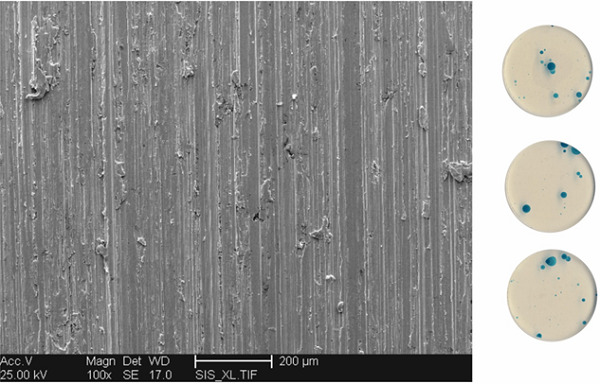
KorroPad tests, electrochemical potentiodynamic reactivation test based on a single loop test, and surface analytical methods were performed to investigate the influence of individual grinding parameters on the corrosion resistance of the austenitic stainless steel grade X5CrNi18-10. The results show a significant influence of the abrasive belt type. Granulate abrasive belts generated surfaces with a higher susceptibility to corrosion than single-coated grain.
Effects of retrogression and reaging heat treatment on the microstructure, exfoliation corrosion, electrical conductivity, and mechanical properties of AA7050
- Pages: 1788-1797
- First Published: 10 April 2019
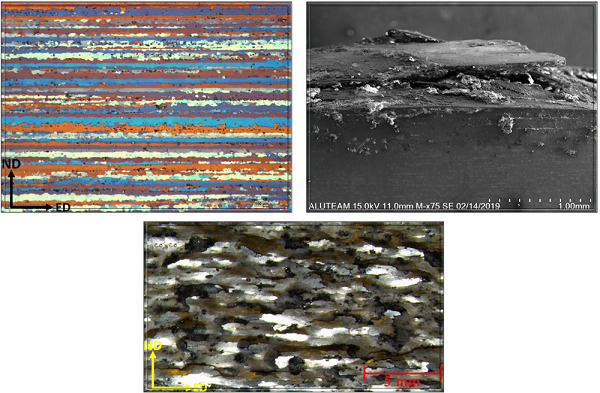
The effects of different retrogression times and temperatures on the microstructure, electrical conductivity, exfoliation corrosion (EXCO), and hardness of the 7050 aluminium alloy were compared with the T6 and T7451 condition. The results show that retrogression and reaging (RRA) times and temperatures have significant effects on AA7050 EXCO.
Mechanical properties, corrosion behavior, and microstructure of Sr modified Al–9.2Mg–0.7Mn alloys
- Pages: 1798-1807
- First Published: 18 April 2019
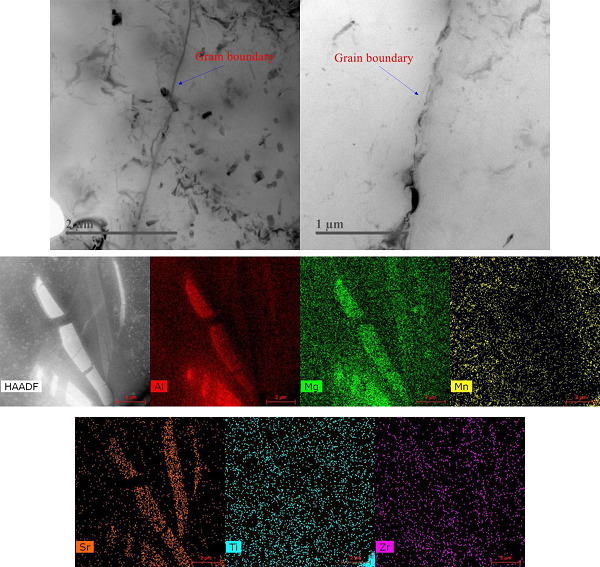
The effect of Sr additions in the form of Mg–Sr master alloys on the mechanical properties, corrosive nature, and microstructure of Al–9.2Mg–0.7Mn alloys is evaluated. There will be a new phase which might be (Al, Mg)17Sr2 formed in the as-cast microstructure. The Al–9.2Mg–0.7Mn alloy with 0.2 wt% addition exhibits the best combined mechanical properties and intergranular corrosion resistance.
Effect of the T6 heat treatment on corrosion behavior of additive manufactured and gravity cast AlSi10Mg alloy
- Pages: 1808-1816
- First Published: 08 April 2019
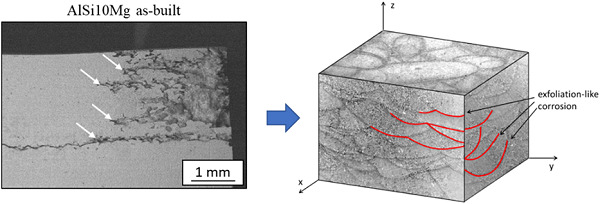
Immersion corrosion tests on samples with sharp edges of AlSi10Mg alloy produced by additive manufacturing allowed indentifying a deleterious corrosion mechanism in as-built condition. Electrochemical tests were not adequate to reveal this behavior. Due to the microstructural evolution after T6 heat treatment, samples exhibited a lower mass loss in heat-treated conditions than in as-built condition.
The effect of temperature on corrosion behavior of AA5083 in brackish water and seawater
- Pages: 1817-1825
- First Published: 24 May 2019
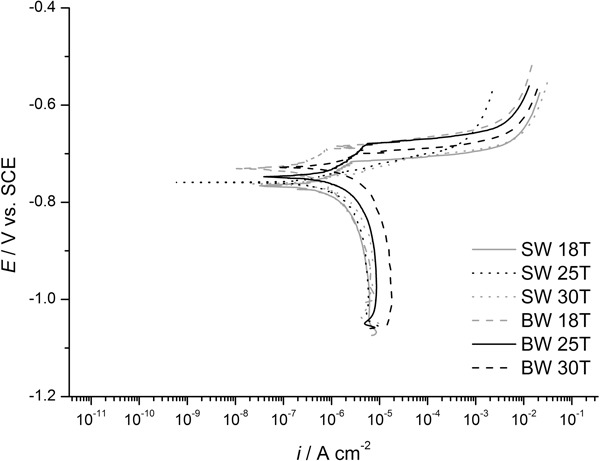
Determination of corrosion behavior of AA5083 in brackish and seawater has been investigated and compared at 18, 25, and at 30°C. Obtained results have shown that an increase in temperature leads to an increase in corrosion activity of AA5083 in both electrolytes, while microscopic examination reveals that the dominant type of corrosion is pitting.
Development of microbially influenced corrosion on carbon steel in a simulated water injection system
- Pages: 1826-1836
- First Published: 12 April 2019

A continuously fed biofilm simulating the water injection process was operated to investigate the influence of biofilm development on microbially influenced corrosion (MIC) behavior in the early phase of corrosion development. The development of the corrosion product film and biofilm was monitored for 5 months with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, linear polarization resistance, scanning electron microscopy, 3D optical profiling, and direct weight measurement. MIC development was found to comprise three phases: initialization, transition, and stabilization.
Characterization of corrosion morphologies from deteriorated underground cast iron water pipes
- Pages: 1837-1851
- First Published: 12 April 2019
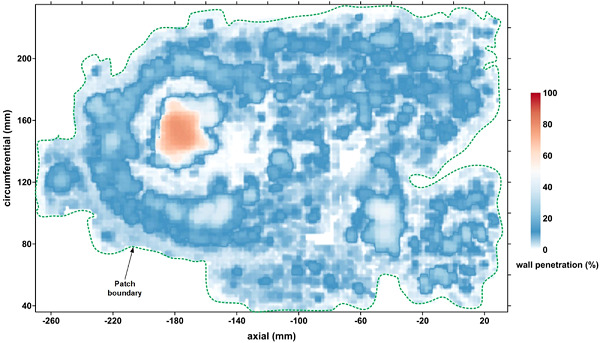
We defined a corrosion patch as a cluster of individual defects within or less than the one-wall-thickness distance of each other and conducted a morphometric study on patches from several deteriorated cast iron pipes. It was found that the size parameters, viz., the patch length, width, area, and volume potentially attain steady-state progression over long-term deterioration and are consistent with current understanding in underground corrosion.
The corrosion behavior and mechanism of X65 steel induced by iron-oxidizing bacteria in the seawater environment
- Pages: 1852-1861
- First Published: 23 April 2019

The corrosion behavior and mechanism of iron-oxidizing bacteria (IOB) on X65 steel in seawater are investigated. The results reveal that IOB increases the corrosion damage degree of steel. Micrometer-scale pittings are observed in the presence of the bacterial medium. The synergies in corrosion between the metal surface, abiotic corrosion products, and bacterial cells, and the pitting corrosion mechanism of X65 steel are discussed.
Increase corrosion resistance of mild steel in sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid solutions by metoclopramide tablet
- Pages: 1862-1871
- First Published: 14 April 2019
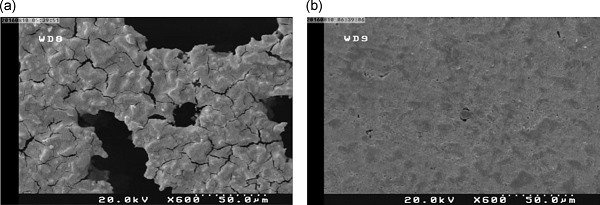
Scanning electron micrographs were used to evaluate the conditions of the mild steel surface in contact with a sulfuric acid solution in the absence and presence of metoclopramide. The images show that surface corrosion of alloy decreased noticeably in the presence of metoclopramide tablet. There are less pits and cracks observed in the inhibited surface.
Influence of Cu on nanostructure of Fe3O 4 particles
- Pages: 1872-1877
- First Published: 26 April 2019
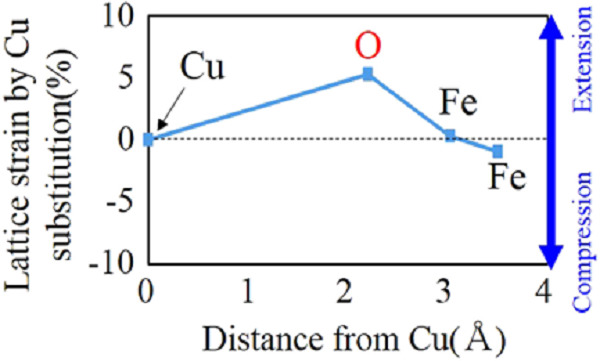
The influence of Cu on the nanostructure of Fe3O4 particles was investigated through a detailed analysis of the characteristics of the artificially synthesized Fe3O4 particles formed with Cu2+. X-ray absorption fine structure (XAFS) analysis showed that Cu is substituted for octahedral Fe in Fe3O4. The first-principle calculation showed that lattice strain resulted around the substituted Cu. It is suggested that this lattice strain around substituted Cu inhibited the lattice growth of Fe3O4 particles.
Dissolution corrosion of 4H-SiC in lead-bismuth eutectic at 550°C
- Pages: 1878-1883
- First Published: 24 May 2019
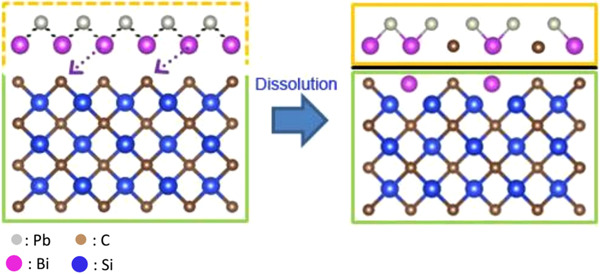
The corrosion behavior of 4H-SiC in lead-bismuth (Pb-Bi) eutectic (LBE) at 550°C was investigated. To clarify the effect of irradiation damage on corrosion, samples with and without Si 5+ ion irradiation were contrastively evaluated. The main results show that dissolution corrosion occurs in both unirradiated and irradiated samples, while the irradiation damage can accelerate the corrosion rate.
Incorporation of silica nanocontainers and its impact on a waterborne polyurethane coating
- Pages: 1884-1899
- First Published: 12 April 2019
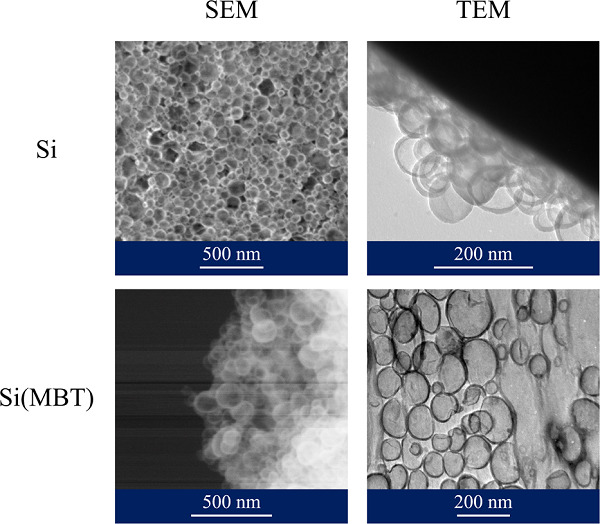
The development and characterization of a versatile smart coating containing an encapsulated inhibitor is described. This includes the synthesis and characterization of hollow spherical nanocapsules with diameters ranging from 180 to 200 nm. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy highlighted a negative effect of the capsules’ addition to the polyurethane network, affecting the coating's barrier properties.
Influence of electric current on the corrosion behavior of Cu for the electric contact in the isolation switch
- Pages: 1900-1906
- First Published: 12 April 2019
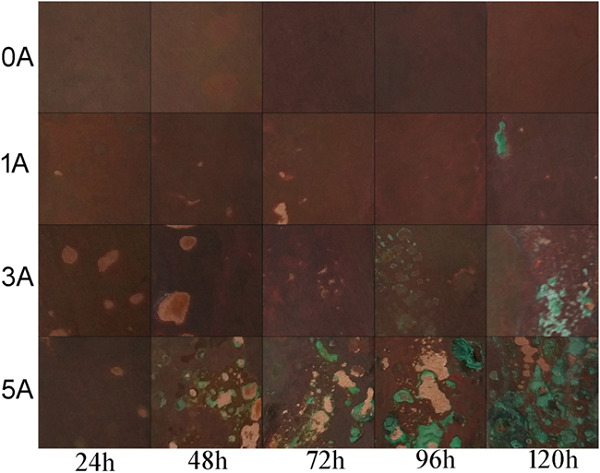
It is very important to improve the stability of power transmission systems. High voltage disconnectors used outdoors will be corroded in the atmosphere, but the influence of electric current on the corrosion behavior has not been well studied yet. In this paper, the effect of electric current on corrosion behavior is studied by means of a self-made device.
Synthesis and evaluation of hexamethylenetetramine quaternary ammonium salt as corrosion inhibitor
- Pages: 1907-1916
- First Published: 27 May 2019
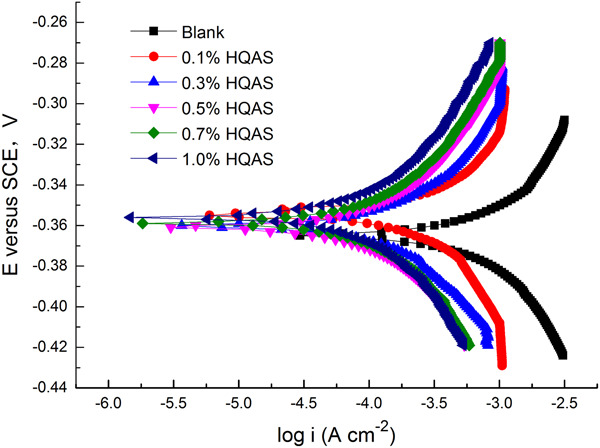
A novel corrosion inhibitor, hexamethylenetetramine (HMTA) quaternary ammonium salt, is synthesized using HMTA and bromohexane as main reactants. The inhibitive action of HQAS on QT800-2 steel in hydrochloric acid medium is evaluated by weight-loss method, electrochemical method, and quantum chemical calculation.