Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Synergistic Double-Layer Mechanochromic Polymers for Enhanced Strain Sensing and Emission Control
- First Published: 22 June 2025
Front Cover: A double-layer polymer system shows mechanochromic fluorescence enhancement under strain. The synergy between a pyrene-based emissive layer and a perylene pigment optical filter enables strain sensing via light emission modulation. More details can be found in article 2500060 by Andrea Pucci, Marco Carlotti, and co-workers.
Issue Information
Review
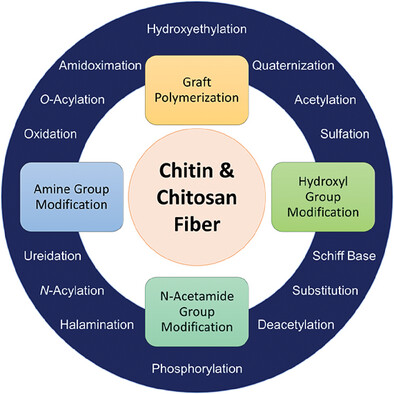
Chemical Modifications of Chitin and Chitosan Fibers and Filaments: A Review
- First Published: 03 March 2025
Harnessing Crystallization-Driven Self-Assembly (CDSA) of Semicrystalline Block Copolymers for Functional 2D Architectures and Their Applications
- First Published: 02 February 2025
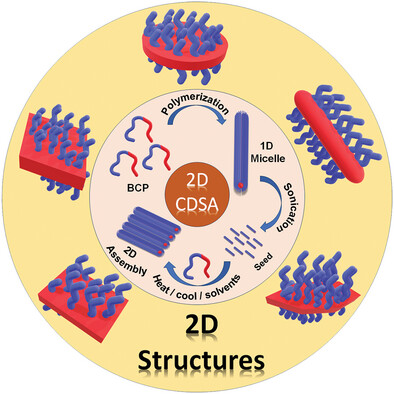
This review article discusses Crystallization-Driven Self-Assemblies (CDSA) of semicrystalline block co-polymers (BCP) to 2D nanostructures, their application, and influencing factors like a solvent, unimer-to-seed ratio, temperature, and counterion. It also discusses the synthesis procedure of BCPs used for CDSA, their application in various areas, and future opportunities.
Stimuli-Responsive Functional Polymeric Materials: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives
- First Published: 27 January 2025
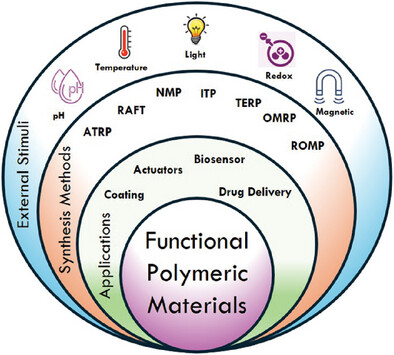
This review explores the latest advances in stimuli-responsive macromolecular architectures, emphasizing their innovative design and synthesis. It highlights their transformative applications in smart materials, environmental remediation, and biomedicine. The manuscript provides a forward-looking perspective on these adaptable systems, underscoring their potential for interdisciplinary breakthroughs and practical implementations.
Research Article
Synergistic Double-Layer Mechanochromic Polymers for Enhanced Strain Sensing and Emission Control
- First Published: 08 April 2025
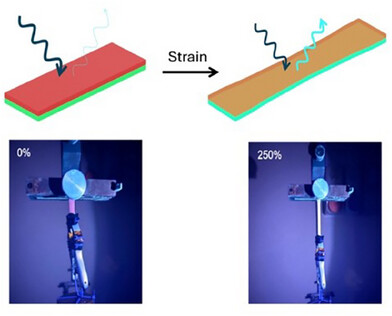
The study presents a double-layer mechanochromic polymer system composed of a pyrene-based emissive layer and a perylene bisimide-derived optical filter. Upon stretching, the system shows a synergistic increase in fluorescence intensity, reaching 120% at 250% strain. The design demonstrates cost-effective fabrication, high sensitivity to strain, and strong potential for wearable sensors and structural monitoring applications.
Stereoselective Ring-Opening Polymerization of Racemic Lactide by Racemic Organo-Catalyst at Room Temperature: Direct Access to Stereocomplex Polylactides
- First Published: 18 October 2024
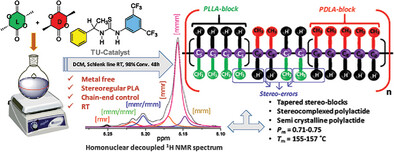
This study presents the design of a cost-effective thiourea-based racemic organocatalyst for stereoselective ring-opening polymerization of racemic lactides. The synthesized polylactides showed moderate tacticity, with a Pm value ranging from 0.71 to 0.78. The bulk structure of the synthesized polylactides revealed that the PLA synthesized from rac-lactide and [(rac-TU)Me] catalysts resulted in a tapered stereoblock structure exhibiting stereocomplex characteristics.
A Comprehensive Study on the Antimicrobial Activity of Polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) Film Incorporated with Gallic Acid and Potassium Sorbate
- First Published: 22 February 2025
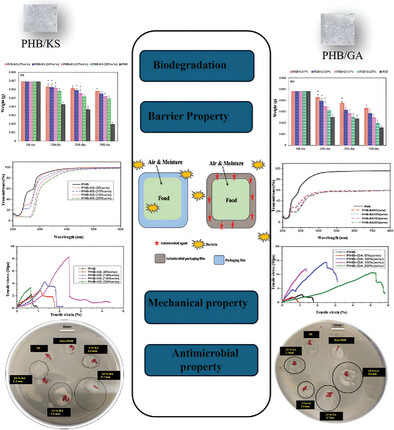
This study investigates the development of biodegradable PHB/KS composites with enhanced barrier, mechanical, and antimicrobial properties for food packaging applications. The composites demonstrate improved performance by reducing microbial contamination, maintaining food freshness, and exhibiting superior tensile strength and degradation profiles. The findings offer a sustainable alternative to traditional packaging materials, addressing environmental concerns and food safety challenges.
Variations in Packing as a Function of Side Chains in Random Copolymers and its Impact on Charge Carrier Mobility
- First Published: 10 October 2024
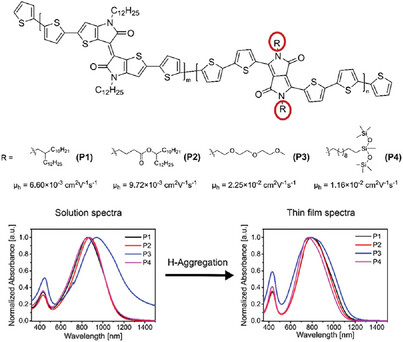
Various side chains (hydrophilic and hydrophobic) affect molecular packing of random polymers which ultimately affects its thin film morphology and semiconducting performances. Linear chains provide better interchain packing by π–π stacking compared to bulky branched side chains. The incorporation of heteroatoms and polar groups into the side chain further enhances the interchain interactions.
Understanding the Supramolecular Chemistry of Lutein with Gelatin, Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Starch Polymers in Simulated Gastro-Intestinal Buffers: A Molecular Dynamics Study
- First Published: 20 December 2024
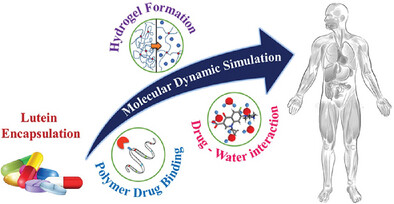
Molecular dynamics simulations explore polymer membranes, revealing detailed drug binding sites and interaction mechanisms with pharmaceutical compounds. These studies provide insights into drug release, transport, and stability within gastro-intestinal buffers, advancing drug delivery system design and optimization.
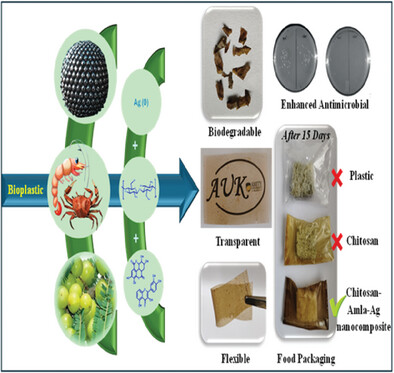
Enhanced Antimicrobial and Degradable Properties of Silver Nanoparticles-Reinforced Chitosan-Indian Gooseberry Films for Sustainable Food Packaging
- First Published: 14 October 2024
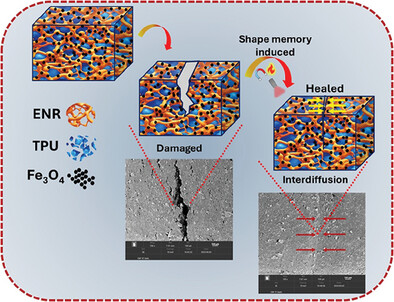
Construction and Characterization of Multi-Stimuli Responsive Shape Memory Assisted Self-Healing Thermoplastic Elastomeric Materials Based on TPU/ENR/Fe3O4 Blends
- First Published: 13 January 2025
Charge Regulation Stabilizes the Formation of Ionic Liquid-Based Amphiphilic Oligomer Droplet Interface Bilayers
- First Published: 08 April 2025
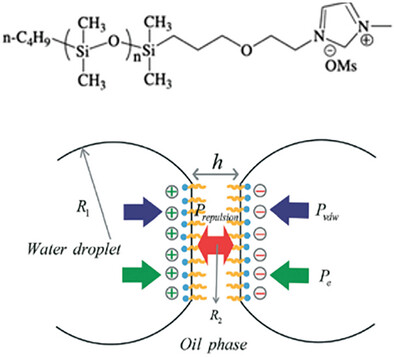
Amphiphilic charged oligomers (oligodimethylsiloxane – methylimidazolium cation, ODMS-MIM(+)), assemble into bilayers using the droplet interface bilayer (DIB) platform, possess similar size and functionality as phospholipid bilayers, but exhibit increased stability. Charge regulation stabilizes the formation of ordered, molecularly close-packed brush phases, which results in highly insulating, stable DIB membranes.
Cellulose Based Aerogels Derived From Rice Agro Wastes with Enhanced Antifungal Activity for Topical Management of Vulvovaginal Candidiasis
- First Published: 17 February 2025
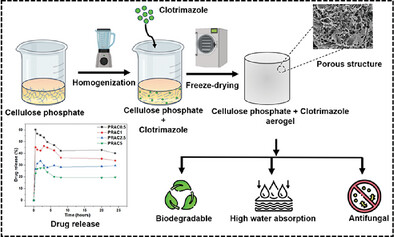
The present study presents the upcycling of rice straws into a valuable all-cellulose-based aerogel through phosphorylation, serving as an alternative to traditional absorbent layers in sanitary pads. The aerogels produced demonstrate impressive water absorption, thermal stability, porosity, and biodegradability. The aerogels also demonstrate a prolonged storage and release profile of clotrimazole, demonstrating a synergistically strong antifungal effect against Candida species.
Impact of Tuning the Hydrophobicity in ABA-Type Amphiphilic Polythiourethane on the Dye Loading and Stability of Formed Polymersomes Using Pendant Aromatic Groups
- First Published: 07 January 2025
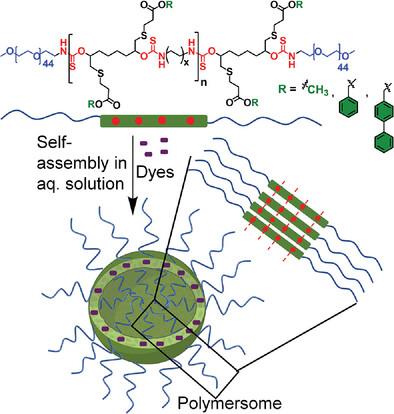
Here the one-pot synthesis and self-assembly of polyethylene-glycol-based amphiphilic polythiourethanes consisting of a pendant methyl or aromatic ester are reported. Introducing an aromatic pendant group enhances the stability and dye-loading ability of the polymersomes. This phenomenon is unraveled studying the evolution of fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) by encapsulating donor–acceptor chromophore.
Synergistic Effect of MgO/ZnO on β-Phase Crystallization in PVDF: A Comparative Study of Mode of Nanofiller Additions for Piezoelectric Applications
- First Published: 27 January 2025
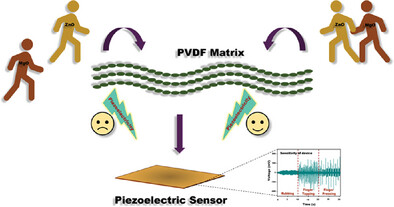
The graphical abstract depicts importance of mode of nanofiller additions for an enhanced piezoelectric property of the PVDF matrix. The novel approach of ZMx Nanocomposite filler additions brings out better piezoelectric behavior at material-device levels in comparison to conventional Z/Mx Hybrid fillers in polymer. The possibility of using of ZMx Nanocomposite-Polymer nanocomposite films for potential sensing applications is further explored.
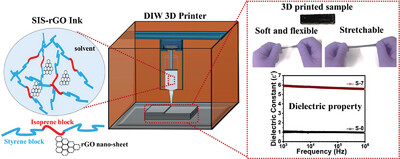
Additive Manufacturing of Styrene-Isoprene-Styrene Block Copolymer Based Soft Thermoplastic Elastomeric Nanocomposites: Influence of Reduced Graphene Oxide on Microstructural, Mechanical and Functional Properties
- First Published: 24 February 2025
Synthesis of Poly(vinyl acetate)-Based Block Copolymers for Highly Stretchable Film by Troponoid-Mediated Radical Emulsion Polymerization
- First Published: 07 April 2025
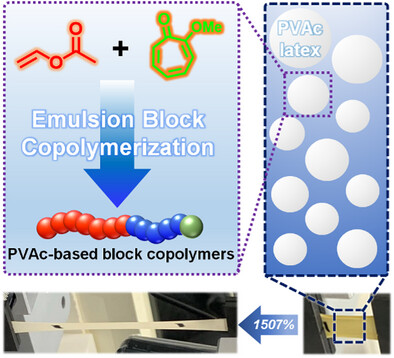
Highly stretchable poly(vinyl acetate)-block-poly(methyl acrylate) film is synthesized via troponoid-mediated radical emulsion polymerization. The polymerization demonstrates the features of reversible-deactivation radical polymerization and provides the latexes with narrow particle size distributions. This method offers a sustainable and scalable approach for producing advanced poly(vinyl acetate)-based materials with potential applications in flexible coatings, adhesives, and other high-performance materials.
Thermo-Mechanical Processing of Chitosan Using Cyclic Carbonates as Green Plasticizers
- First Published: 26 March 2025
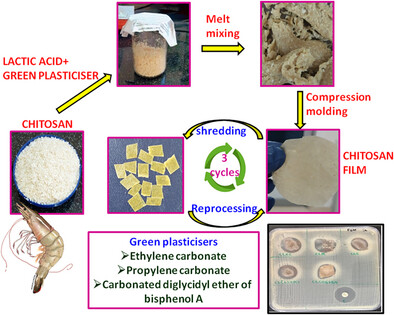
Thermo-mechanical processing of chitosan provides an industrially viable alternative to solvent casting technique. Using cyclic carbonates as green plasticizers improves the tensile strength and antimicrobial properties of plasticized chitosan films with good reprocessability without lessening the tensile and tear properties.