Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Efficient Stabilization and Directional-Controlled Release of Vitamin C in Disaccharide/Megasaccharide Composite Xerogels
- First Published: 21 October 2024

Front Cover: The combination of disaccharide trehalose and magasaccharide sacran in composite xerogel films effectively preserves vitamin C in a dry state. The cross-section FE-SEM images confirmed the presence of intercalated layered structures, supporting the existence of a striped structure with numerous lines along the longitudinal axis. Upon immersion in water, they exhibit anisotropic swelling behavior, releasing vitamin C preferentially from the edges, aiding dynamic control in sustained delivery systems. More details can be found in article 2400125 by Thapakorn Tree-Udom and co-workers.
Masthead
Research Article
Correlation Between Side-Chain Arrangement and Main-Chain Helix Conformation in Liquid Crystalline Syndiotactic Poly(Substituted Methylene)s Bearing Cyanobiphenyl Mesogens
- First Published: 22 July 2024
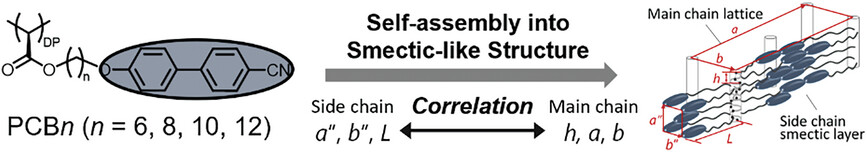
Syndiotactic poly(substituted methylene)s bearing 4-cyanobiphenyl (CB) moieties at the side-chain end, designated as PCBn, form smectic structures by assembling side-chain CBs into layers with short-range positional ordering. The main-chain carbon atom positions along the helical chain contour correlate with the side-chain positions.
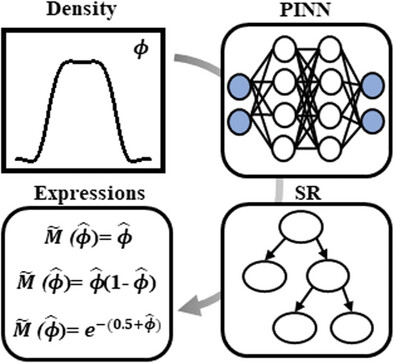
Inference of Constitutive Relation of Phase-Separated Polymers by Integrating Physics-Informed Neural Networks and Symbolic Regression
- First Published: 24 July 2024
Preparation and Third-Order Nonlinear Optical Properties of Novel Axial Fullerenol-Substituted Phthalocyanines
- First Published: 30 July 2024
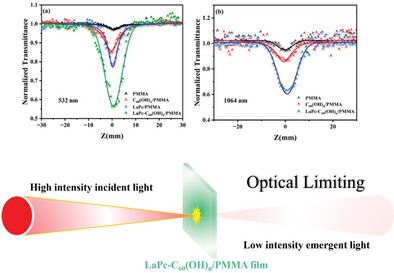
The study explores LaPc-C60(OH)n, a D-A compound combining lanthanide phthalocyanine and fullerenol for enhanced optical limiting. The nonlinear optical response in its solution and in PMMA films is enhanced due to efficient intramolecular electron transfer. It shows strong nonlinear optical responses at 532 and 1064 nm, with significant optical limiting effects.
Polymerization-Induced Emission and Specific Detection to Cu2+ Ions of Polyacrylates with Morpholine Structure
- First Published: 30 July 2024
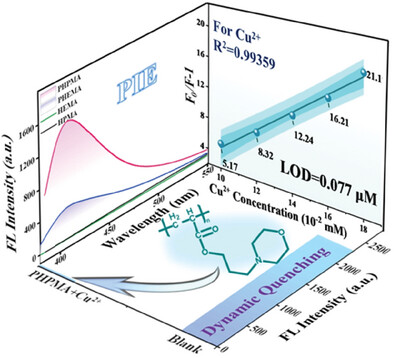
The fluorescent poly(N-hydroxyethyl morpholine acrylate) (PHPMA) with PIE effect is prepared and applied as the probes for the specific detection of Cu2+ ions. PHPMA specifically detects Cu2+ ions by the dynamic quenching even in the presence of 16 common metal ions and 6 anions with an LOD of 0.077 µM.
Efficient Stabilization and Directional-Controlled Release of Vitamin C in Disaccharide/Megasaccharide Composite Xerogels
- First Published: 03 August 2024
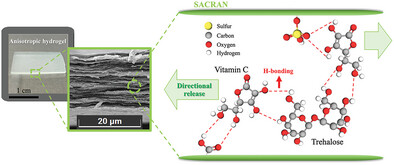
The combination of disaccharide trehalose and magasaccharide sacran in composite xerogel films effectively preserves vitamin C in a dry state. Upon immersion in water, they exhibit anisotropic swelling behavior, releasing vitamin C preferentially from the edges, aiding dynamic control in sustained delivery systems. These offer an excellent versatile platform for loading and controlling the release of sensitive substances.
Compositional Influence of Cross-linked Polyion Hydrogels from Poly(L-Lysine) and Poly(L-Glutamic Acid) on Their Properties for Potential Skin Applications
- First Published: 06 August 2024
Characterization and Properties of Polylactic Acid/Cottonseed Protein Bioplastics
- First Published: 13 August 2024
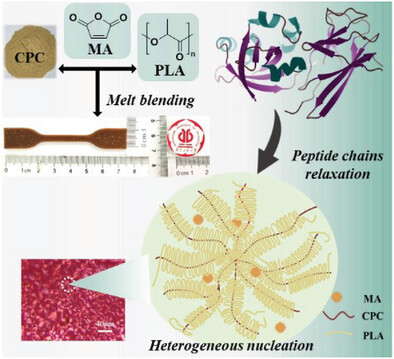
Oilseed cottonseed protein is applied as a biomass nucleating agent to regulate PLA crystallization behavior. The protein-inducing heterogeneous crystallization and maleic anhydride-inducing interfacial compatibility contribute to the enhancement of mechanical properties, water resistance, and thermal stability of the PLA/cottonseed protein biocomposites.
Orientation of Chitin Nanofibers Dispersed in a Thermoplastic Polymer Matrix Through Dry Thermal Stretching
- First Published: 18 August 2024

This study investigates the orientation of chitinous nanofibers within a thermoplastic polymer matrix composed of poly(N-vinylpyrrolidone) and glycerol through dry thermal stretching. The results demonstrate that varying interactions between nanofibers and the polymer matrix, controlled by surface functional groups, significantly influence stretchability and orientation, promising advancements in bioactive applications.