Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2/2018
- First Published: 19 January 2018

Front Cover: Atomic force microscopy topography (1 × 1 μm) and modulus map (125 × 125 nm) images reveal the rod-like morphology of hard domains in polycaprolactone-based segmented polyurethanes. The corresponding structural model shows these domains as parallel stacks of hard segments embedded in a soft polycaprolactone matrix. Further details can be found in article number 1700214 by Richard Chartoff* and co-workers.
Back Cover
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2/2018
- First Published: 19 January 2018

Back Cover: By a combination of Cu(0)- and Cu(II)-mediated homopolymerization of multivinyl monomers (MVMs) and thiol-ene click chemistry, amphiphilic multifunctional star polymers with high arm numbers are prepared by using single-chain cyclized/knotted nanoparticle (SCKPs) as the core. Further details can be found in article number 1700473 by Dezhong Zhou,* Guangfu Yin,* and co-workers.
Masthead
Editorial
Full Papers
Properties and Phase Structure of Polycaprolactone-Based Segmented Polyurethanes with Varying Hard and Soft Segments: Effects of Processing Conditions
- First Published: 16 November 2017
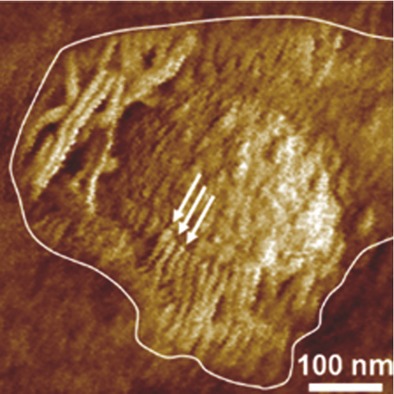
A series of polycaprolactone segmented polyurethanes (PUs) polymerized both in solution and bulk from blocked isocyanate prepolymers is the focus of this study. The effects of varying the chemical structure and processing of the PUs on their phase structure are evaluated. Differences in properties due to processing are related to morphology which includes rod-like nanocrystallites.
Effects of Different Unsaturated-Linker-Containing Donors on Electronic Properties of Benzobisthiadiazole-Based Copolymers
- First Published: 08 December 2017
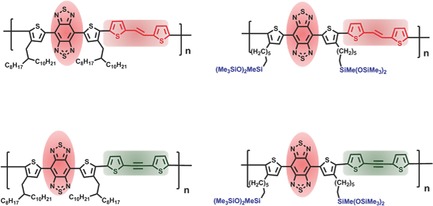
Benzobisthiadiazole-based copolymers with different unsaturated-linker-containing donors are synthesized, and their electronic properties are investigated. The strong electron-withdrawing benzobisthiadiazole units make these copolymers display very narrow bandgaps in the range of 0.75–1.26 eV. Bottom-gate and bottom-contact transistors based on these polymers exhibit p-type field-effect behavior with hole mobilities up to 1.17 × 10−3 cm2 V−1 s−1.
Sharp-pH-Sensitive Amphiphilic Polypeptide Micelles with Adjustable Triggered pHs by Salts via the Hofmeister Effect
- First Published: 08 December 2017
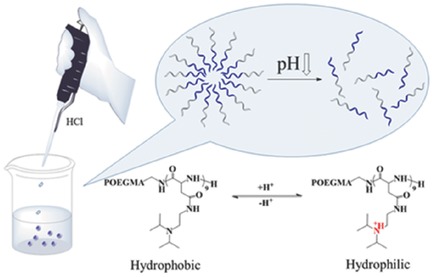
Amphiphilic polypeptide copolymers are synthesized and spontaneously assembled to micelles in aqueous solution. Protonation of the tertiary amine groups in the side-chain of the copolymer under weak acid in a sharp ΔpH causes the micelle disassembly, and the responsive pHs can be adjusted by adding salts according to the Hofmeister effect.
Smaller Counter Cation for Higher Transconductance in Anionic Conjugated Polyelectrolytes
- First Published: 11 December 2017
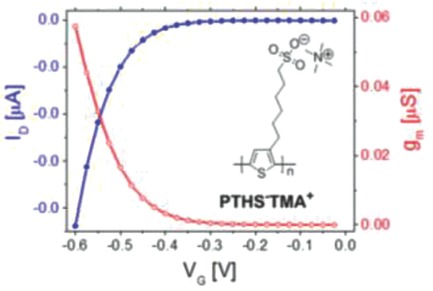
Anionic conjugated polyelectrolytes based on polythiophene carrying tetramethylammonium cation exhibit higher transconductance, drain current, and response time in organic electrochemical transistors compared to tetrabutylammonium and tetraethylammonium ions due to better aggregation, easy oxidation, and fast interdiffusion in aqueous media, high volumetric capacitance, and high charge carrier mobility.
Star Polymers from Single-Chain Cyclized/Knotted Nanoparticles as a Core
- First Published: 11 December 2017
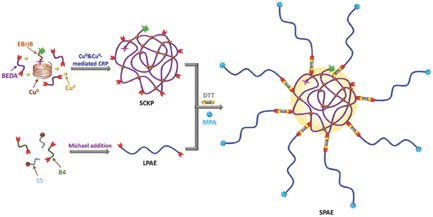
By using the Cu0&CuII-mediated controlled/living radical polymerization (CRP), polybisphenol A ethoxylate diacrylate (polyBEDA) single-chain cyclized/knotted nanoparticles (SCKPs) with multiple reactive pendant vinyl groups are synthesized. High number and high molecular weight linear-structured poly(β-amino ester) arms can be effectively conjugated to the polyBEDA SCKP cores via the grafting-onto strategy. This new approach opens new avenues for the synthesis of star polymers.
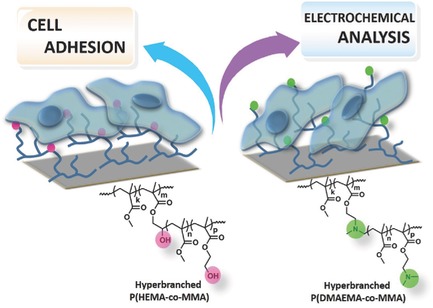
Functional Surfaces Constructed with Hyperbranched Copolymers as Optical Imaging and Electrochemical Cell Sensing Platforms
- First Published: 14 December 2017
Crystallization/Melting Kinetics and Morphological Analysis of Polyphenylene Sulfide
- First Published: 11 December 2017
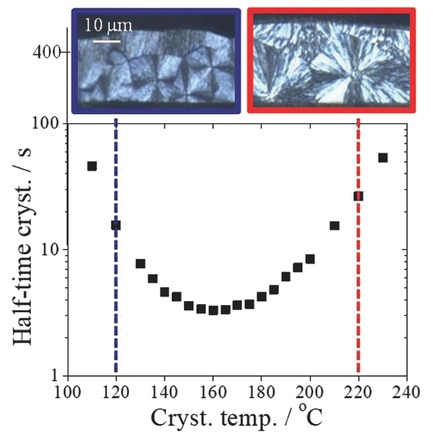
The temperature dependence of half-time crystallization of isothermally melt-crystallized polyphenylene sulfide shows a downward convex curve with a minimum at 160 °C. The minimum crystallization half-time is about 3 s. Transcrystalline surface morphology can be seen on the sample/gas surface at 120 °C. This is caused by the high density of nuclei on the surface.
CdS–Oleic Acid Quantum Dots as Long-Wavelength Photoinitiators in Organic Solvent and Preparation of Luminescent, Colloidal CdS/Polymer Nanocomposites
- First Published: 11 December 2017
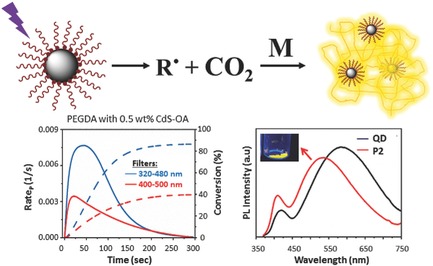
For the first time, quantum dots (QD) are shown as effective photoinitiators in a nonprotic solvent and in the absence of a coinitiator. Strongly luminescent PMMA/CdS nanoparticles are prepared in successful polymerizations initiated at 365 nm with oleic acid–CdS QDs. These QDs are also long-wavelength initiators, effectively starting polymerizations in the 400–500 nm range.
Photoresponsive Coumarin-Based Supramolecular Hydrogel for Controllable Dye Release
- First Published: 11 December 2017
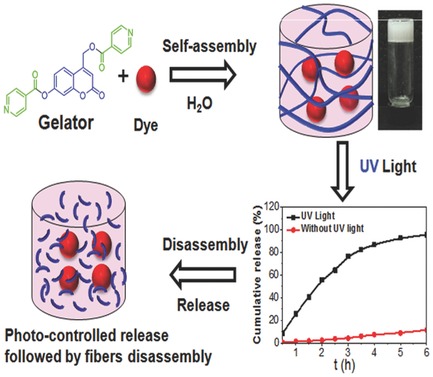
A new kind of coumarin-based photoresponsive supramolecular hydrogel without containing conventional gelation motif is designed and synthesized, which can be disintegrated and release the encapsulated agents under UV light irradiation. Such controllable disassembly of hydrogel networks holds great potential as promising delivery and release vehicles for anticancer drugs.
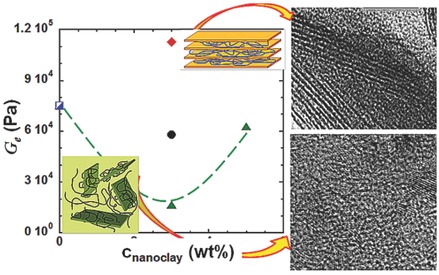
Viscoelasticity and Dynamics of Confined Polyelectrolyte/Layered Silicate Nanocomposites: The Influence of Intercalation and Exfoliation
- First Published: 11 December 2017
Temperature-Responsive Electrophoretic Deposition of Sulfone-Containing Nonionic Poly(N-isopropylacrylamide)
- First Published: 11 December 2017
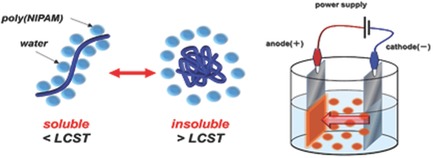
Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer radical copolymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide with a sulfone-containing methacrylate is performed. The nonionic sulfone-containing poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) showed electrophoresis above the lower critical solution temperature. This is the first example of temperature-responsive electrophoretic deposition (EPD). After EPD, adhesion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells on the deposited surfaces is demonstrated, aiming at the subsequent temperature-sensitive detachment.
Correction
Temperature-Induced Phase Transition Characterization of Responsive Polymer Brushes Grafted onto Nanoparticles
- First Published: 19 January 2018