Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2016
- Page: 617
- First Published: 02 March 2016

Front Cover: The polyrotaxane (PR) possesses outstanding stimuli-responsive properties resulting from the free movement of threaded α-CDs thereon. In this paper, the PRs can change from amorphous phase to crystalline phase by heating, UV radiation as well as polar solvent. Furthermore, it is more important that the mobility of α-CDs can definitely bring other new and interesting properties to PR, which is very worth researching in the future. Further details can be found in the article by Aiju Guo, Zhi Yan, Lin Ye,* Aiying Zhang, and Zengguo Fengon page 646.
Back Cover
Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2016
- Page: 721
- First Published: 02 March 2016

Back Cover: Well-defined triblock co- and terpolymers, which are difficult to be obtained by sequential monomer addition to anionic initiator, was precisely synthesized by the methodology combining the living anionic polymerization with a specially-designed linking reaction using a-phenylacrylate function. Further details can be found in the article by Yuri Matsuo,* Ryuji Konno, Raita Goseki, Takashi Ishizone, and Akira Hirao* on page 622.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Chem. Phys. 5/2016
- Pages: 619-621
- First Published: 02 March 2016
Full Papers
Tailored Synthesis of Triblock Co- and Terpolymers Composed of Synthetically Difficult Sequence Orders by Combining Living Anionic Polymerization with Specially Designed Linking Reaction
- Pages: 622-635
- First Published: 02 February 2016
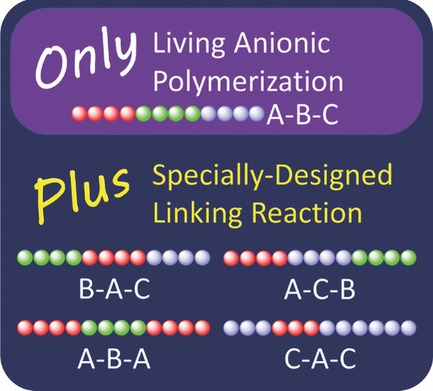
Well-defined triblock co- and terpolymers composed of polystyrene derivatives p-substituted with electron-withdrawing groups are successfully synthesized by the specially designed linking reaction between living polymer anion and the chain-end-(α-phenylacrylate)-functionalized polymers. The resulting triblock co- and terpolymers are well-controlled in chain length, composition, which are difficult to be obtained by sequential polymerization.
Heterofunctionalized Multiarm Star Polymers via Sequential Thiol-para-Fluoro and Thiol-Ene Double “Click” Reactions
- Pages: 636-645
- First Published: 20 January 2016
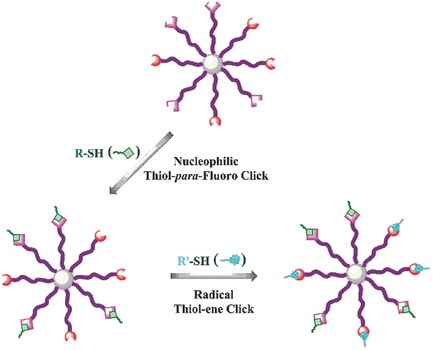
Multiarm star polystyrene (PS) with pentafluorophenyl and allyl moieties at the periphery is prepared through the cross-linking reaction of α-fluoro and α-allyl functionalized PS and divinyl benzene (DVB) yielding (fluoro-PS)m–polyDVB–(allyl-PS)m multiarm star polymer. Orthogonal thiol-para-fluoro and photoinduced radical thiol-ene double “click” reactions are successfully employed for the postfunctionalization of the obtained star polymer.
The Synthesis and Characterization of Spacer-Free Liquid Crystal Polyrotaxane by Virtue of the Mobility of Threaded α-Cyclodextrins
- Pages: 646-653
- First Published: 22 January 2016
Development of Charge-Transfer Complex Hybrid Films as Polymer Electrolyte Membrane for High Temperature PEFC Operation
- Pages: 654-663
- First Published: 22 January 2016
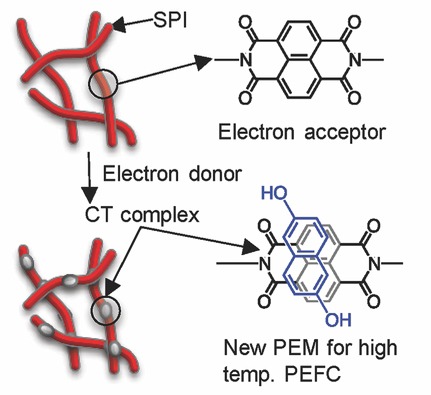
In order to develop a novel polymer electrolyte membrane for high temperature operation of polymer electrolyte fuel cell, charge-transfer (CT) complex hybrid films composed of sulfonated polyimide and 2,6-dihydroxynaphthalene are developed, and the effect of the CT complex formation on the polymer properties is evaluated. The CT complex hybrid films show comparable proton conductivity to Nafion 115 under high-temperature operational conditions (100–120 °C).
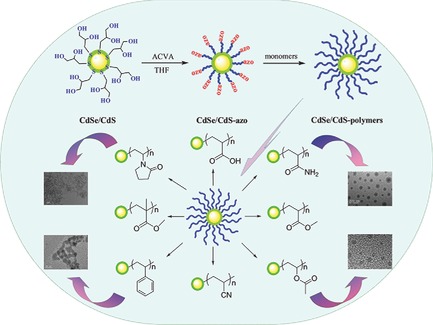
A Versatile Synthetic Approach to Covalent Binding of Polymer Brushes on CdSe/CdS Quantum Dots Surface: Multitype Modification of Nanocrystals
- Pages: 664-671
- First Published: 19 January 2016
The Synthesis of Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) Containing Polymers via Step-Growth Click Coupling Reaction for CO2 Separation
- Pages: 672-682
- First Published: 22 December 2015
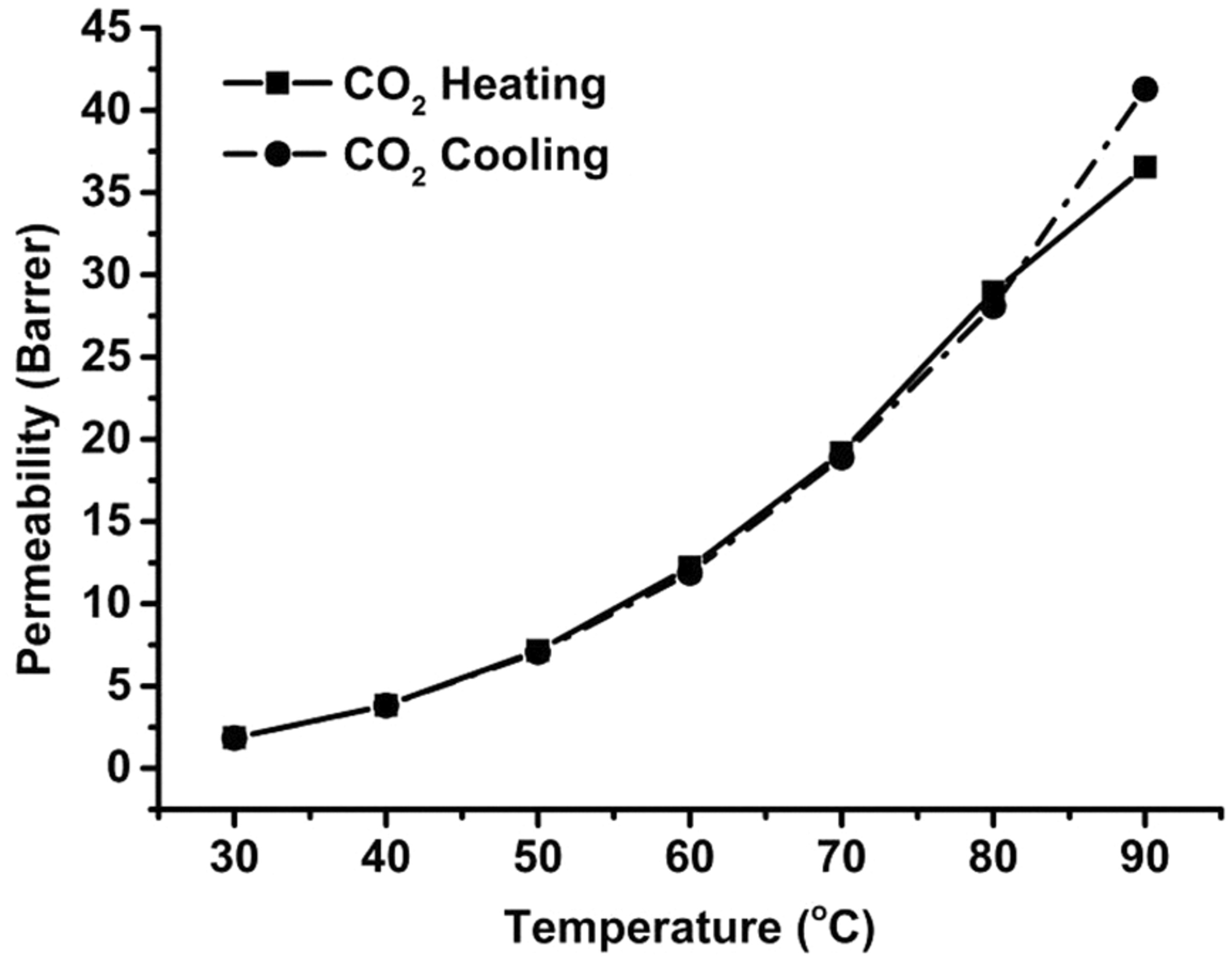
Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) containing polymers are very effective as membrane material, especially for CO2 separation from other gases. In this study, for the first time, a PEG-containing polymer synthesized via step-growth click coupling reaction is studied for CO2 separation. This demonstrates the potential of step-growth click coupling polymerization as a useful synthetic strategy to new polymer materials for membrane applications.
Enhancing the Colloidal Stability and Electrical Conductivity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotubes Dispersed in Water
- Pages: 683-700
- First Published: 22 December 2015
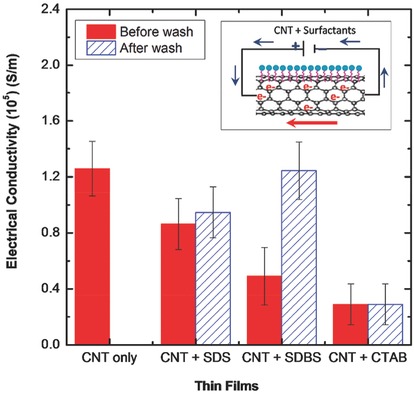
The amphiphilicity, concentration, and surfactant charge determine their surface coverage on the single-walled carbon nanotube and simultaneously increase electrostatic and steric repulsion and decreases surface chemical heterogeneity. Not surprisingly, the surfactants with the highest surface coverage on the nanotube result in dispersions with high colloidal stability and films with enhanced electrical conductivities.
3D Damage Micromechanisms in Polyamide 6 Ahead of a Severe Notch Studied by In Situ Synchrotron Laminography
- Pages: 701-715
- First Published: 20 January 2016
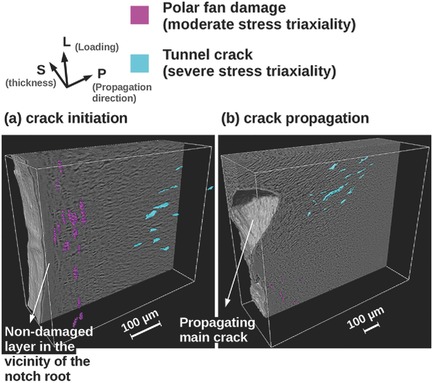
The in situ microdamage mechanisms in semicrystalline polyamide 6 are examined in 3D by X-ray imaging for crack initiation and propagation in a large flat specimen. The characteristic sizes of the damage features are quantified. Distinct damage zones are found well distributed ahead of the initial notch, and characterized as a function of stress states. The formation of tunnel cracks during crack propagation and the effect of notch defect are discussed.
Correction
Influence of H-Bonding on Self Assembly and Tunable Dual-Emission of Carbazole-Based Zn(II)-Terpyridine Metallocycles
- Page: 716
- First Published: 10 February 2016