Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Theory Simul. 7/2010
- First Published: 22 September 2010

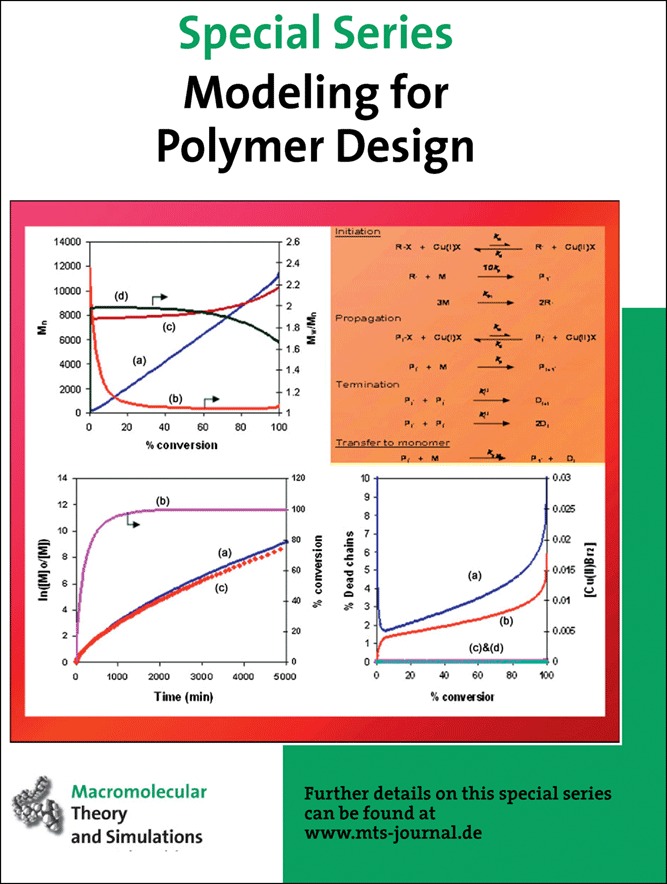
Cover: Accurate chain-length dependent termination and the persistent radical effect play and important role in the accurate and predictive modelling of living radical polymerizations. This will allow new insights into mechanistic pathways to be deduced. Further details can be found in the article by G. Johnston-Hall, M. J. Monteiro* on page 387.
Contents
Frontispiece
Special Article Series - Full Paper
Kinetic Simulations of Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization (ATRP) in Light of Chain Length Dependent Termination
- Pages: 387-393
- First Published: 01 September 2010
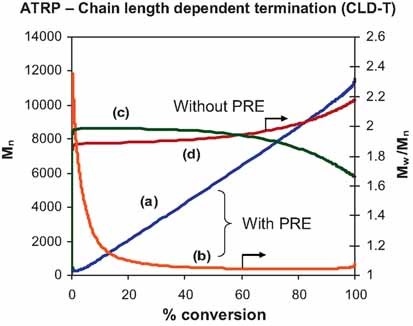
Kinetic simulations using the composite kt model allows a better understanding of the effects of the persistent radical affecting ATRP or for that matter any activation-deactivation system. It also provides a better fit to experimental data in either bulk or solution conditions for ATRP polymerizations carried out at 110°C. The PRE controls the molecular weight distribution, exemplified by a linear increase in 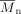 with conversion and a low PDI.
with conversion and a low PDI.
Communication
On the Scaling Behavior of the Force/Extension Relation of a Chain
- Pages: 394-398
- First Published: 26 August 2010
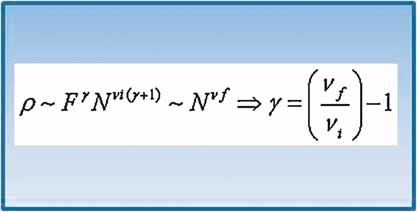
Assuming power law dependencies of the size ρ ∼ Nν of a chain on its length N at two different states, a scaling relationship is derived between the extending force F and the extension ρ of the chain. The exponent γ of the force/extension relation depends on both exponents νi and νf of the initial and the final states. The simplicity of the derivation permits the explanation of previous results and predicts some more.
Full Papers
Phase-Field Simulation of Long-Wavelength Line Edge Roughness in Diblock Copolymer Resists†
- Pages: 399-406
- First Published: 27 July 2010
Investigation of the Crossover From Simple Liquid-Like to a Polymer-Like Behavior of Polyisoprene by Means of MD Simulations
- Pages: 407-413
- First Published: 20 July 2010
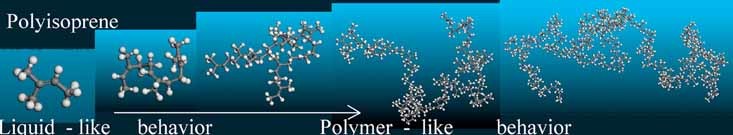
Using MD simulations, it is demonstrated that the transition from liquid-like behavior characteristic for small molecules to Rouse dynamics characteristic for polymers, in a series of polyisoprenes with molecular weights M = 70–6 802 g · mol−1 is a smooth function of molecular weight. The results show that the Rouse behavior establish at molecular weights of about 1 000 g · mol−1, which roughly corresponds to ≈14 monomer units in the chain.
Effect of Finite Extensibility on the Equilibrium Chain Size
- Pages: 414-420
- First Published: 02 July 2010
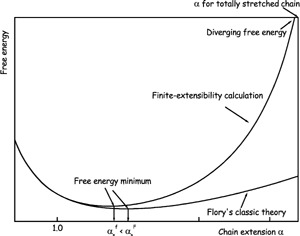
A simple theory of the finite-extensibility effect on the equilibrium size of a single polymer chain is developed in this paper. Compared to the result from Flory's classic theory, the finite extensibility decreases the equilibrium chain size systematically. This effect is important and necessary to be taken into account for a chain with a short contour length and/or with strong repulsions between monomers. The highly charged and highly crosslinked hydrogel is a typical system where the finite extensibility plays an important role.
RIS Model of the Helix-Kink Conformation of Erythro Diisotactic Polynobornene
- Pages: 421-431
- First Published: 16 August 2010

An RIS model for the erythro diisotactic isomer of PNB was developed that reflects the observed helix-kink morphology. MC simulations indicate that the origin of the kink is the reversal of the helical symmetry, which occurs in approximately 0.2% of the monomeric units. These kinks can form or be destroyed at the polymer ends, and each one of these kinks adds approximately 4kcal·mol−1 to the energy of the helical structure. The basic format of the RIS model developed here may be applicable to other polymers as well.
Crystalline/Crystalline Phase Transitions in Polymer Systems Consisting of Finite-Size Crystals in Each Crystalline Phase: Generalized Gibbs-Thomson Equation
- Pages: 432-439
- First Published: 16 August 2010
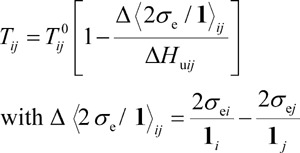
A generalized Gibbs-Thomson equation is derived for one-component polymer systems with two crystalline phases. Its application to the PT phase diagram of polyethylene is demonstrated. Comparison with experimental data leads to estimates for the structural characteristics such as the ratio of the surface free energy to crystal length of the polymer crystal for the respective crystalline phases.
Conformational and Dynamical Properties of the Isolated, Three-Dimensional Single- and Double-Tethered Polymer Chain on an Infinite Surface
- Pages: 440-448
- First Published: 27 July 2010
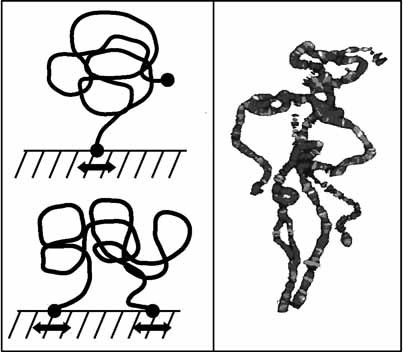
By Monte Carlo simulations we provide insight into the isolated single- and double-tethered polymer chain attached to an impenetrable surface to elucidate open theoretical questions and to guide future experiments investigating the impact of tethering on the packaging of the genome by concurrent visualisation of multiple loci along the chromosome(s) in eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms.