Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Theory Simul. 6/2010
- First Published: 23 August 2010

Cover: The chain length distribution in ideal controlled radical copolymerization of vinyl/divinyl monomers was predicted using population balance equations of generating functions. Multimodal chain length distributions are predicted. Each peak corresponds to a specific count of crosslinks, the one with lowest molecular weight being the linear polymer fraction (zero crosslinks). Calculations have been carried out both before and after gelation. Further details can be found in the article by R. C. S. Dias* and M. R. P. F. N. Costa on page 323.
Contents
Full Papers
Conformational Behavior of Bottle-Brush Polyelectrolytes with Charged and Neutral Side Chains
- Pages: 298-308
- First Published: 23 August 2010
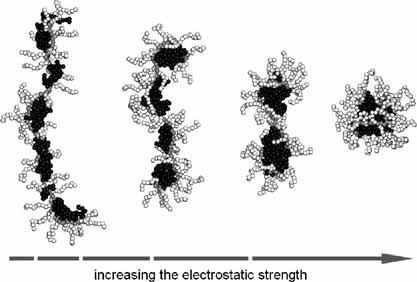
The conformational transition of a single bottle-brush polyelectrolyte with charged and neutral side chains is studied through molecular dynamics simulations. In the case of neutral side chains in a poor solvent, as the electrostatic strength between monomers in charged side chains increases, the neutral side chains can condense into clusters with variable size.
Multiscale Modeling of Branch Length in Butyl Acrylate Solution Polymerization
- Pages: 309-322
- First Published: 23 August 2010
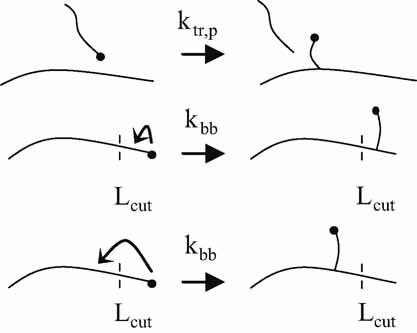
The formation of short- and long-chain branches from both backbiting and intermolecular chain transfer to polymer is studied using a combination of rate-equation and lattice models in comparison to experimental data. Backbiting is shown to be responsible for nearly all branching in this system, and to be capable of producing long-chain branches.
Calculation of CLD Using Population Balance Equations of Generating Functions: Linear and Non-Linear Ideal Controlled Radical Polymerization
- Pages: 323-341
- First Published: 23 August 2010
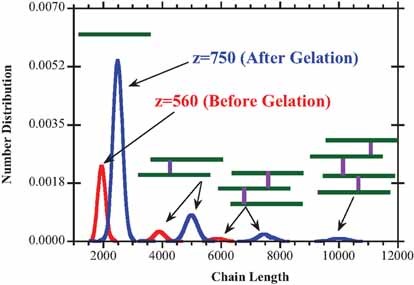
Calculated chain length distribution in ideal controlled radical copolymerization of vinyl/divinyl monomers. Multimodal chain length distributions are predicted. Each peak of the distribution is correspondent to a different number of crosslinks between primary chains. Calculations are possible before and after gelation.
Mathematical Modeling of Bivariate Polymer Property Distributions Using 2D Probability Generating Functions, 1 – Numerical Inversion Methods
- Pages: 342-359
- First Published: 23 August 2010
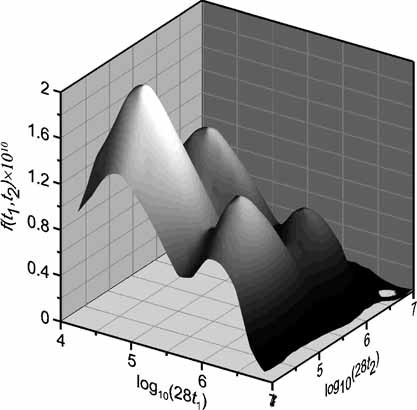
The 2D pgf transform method is a powerful tool for modeling bivariate distributions of polymer properties in systems described by population mass balances. In order to apply this technique, accurate inversion methods are required. In this work, two numerical inversion methods of 2D pgf transforms are proposed and validated using distributions as complex as the one shown in the figure.
Analysis of the Adequacy of the Representation of Entanglement Effects by Chain Loops
- Pages: 360-369
- First Published: 23 August 2010
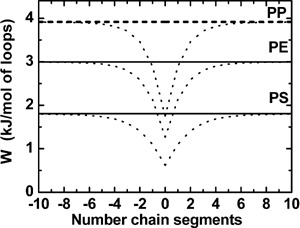
Entanglements are usually represented with the looping picture, but it is commonly accepted that this picture is a poor representation. The figure shows values of the interaction potential energy between a loop and a chain at its centre at the molten state (200 °C). It is shown that because these values are lower than the thermal energy of the melt, the representation of entanglements by chain loops and the use of this construction to draw models for explaining properties assigned to entanglements must be seriously reconsidered.
Size-Dependent Interfacial Tension of Polymer Blends with Broad Composition Polydispersity
- Pages: 370-377
- First Published: 23 August 2010
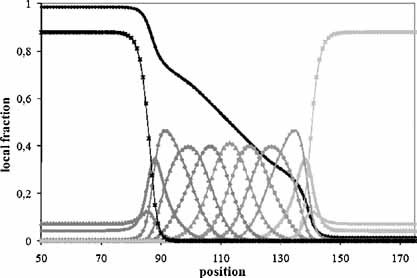
A large class of commercial blends that are manufactured by Ziegler-Natta catalysis exhibit a large polydispersity in chemical composition per polymer chain. The addition of such statistical copolymers with a large chemical polydispersity to a polymer blend leads to a rich structure of the interface. Interfaces that are compatibilized with such mixtures can attain widths of several hundred nanometers. In this paper the effect on interfacial tension of such dramatically wide interfacial zones is studied via a self-consistent field simulation.






