Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Characterization of Immune Landscape Based on Homologous Recombination Deficiency Associated Signatures and Identification of Knockdown of ERCC6L to Promote Radiosensitivity in Breast Cancer
- First Published: 23 February 2025
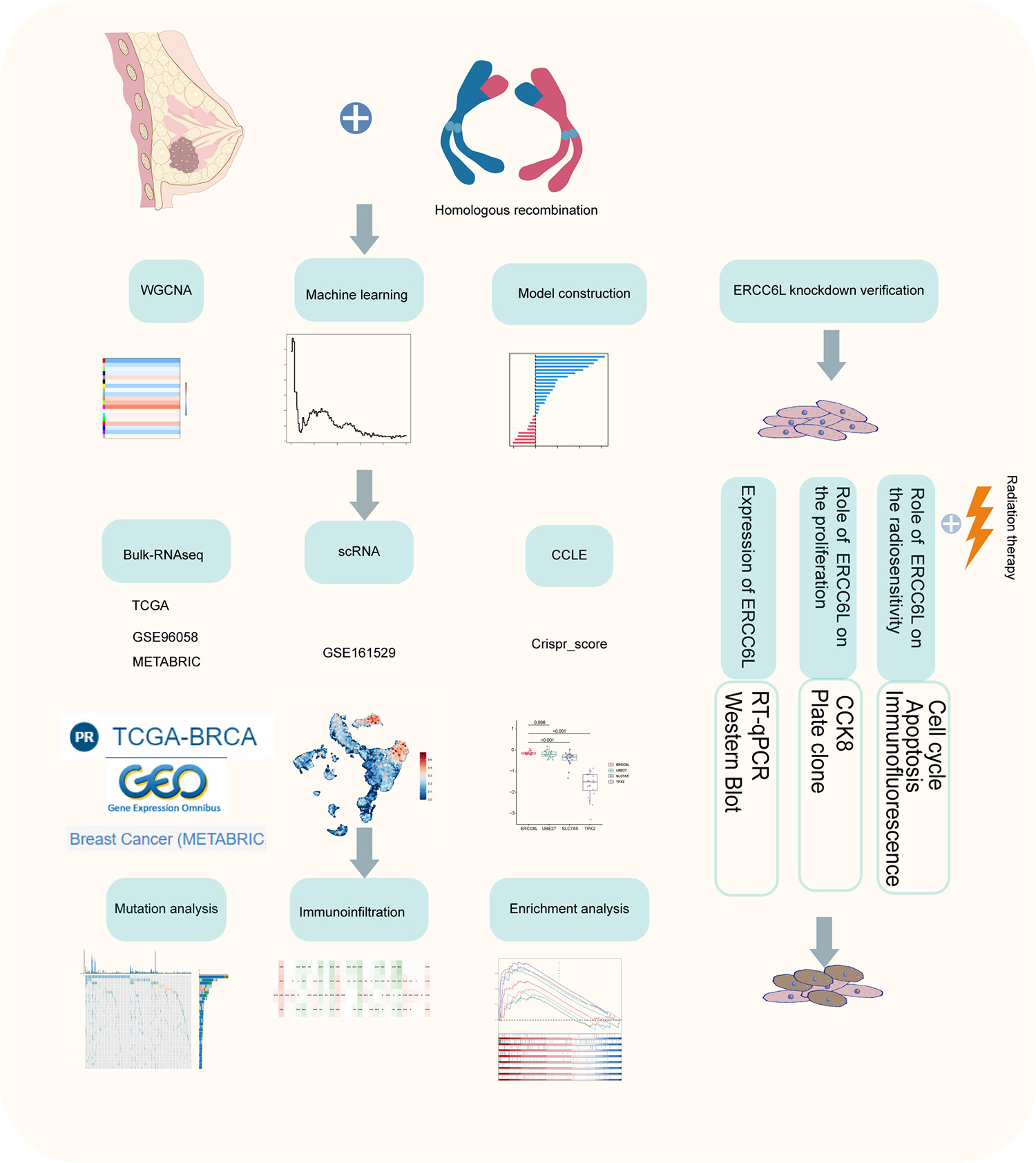
The illustrational workflow of this study. The article revolves around identifying markers associated with homologous recombination deficiency (HRD) for the development of prognostic model for breast cancer. Through various machine learning methods to construct the most predictive HRD-associated signatures on the prognosis and the efficacy of immunotherapy and radiotherapy and to reflect the immune microenvironment. Experiments elucidated the role of ERCC6L in enhancing radiation-induced apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and DNA damage to sensitizing cancer cells to radiotherapy.
REVIEW ARTICLE
The Mechanisms, Research Status, and Future Prospects of m6A Modification in Breast Cancer
- First Published: 19 February 2025
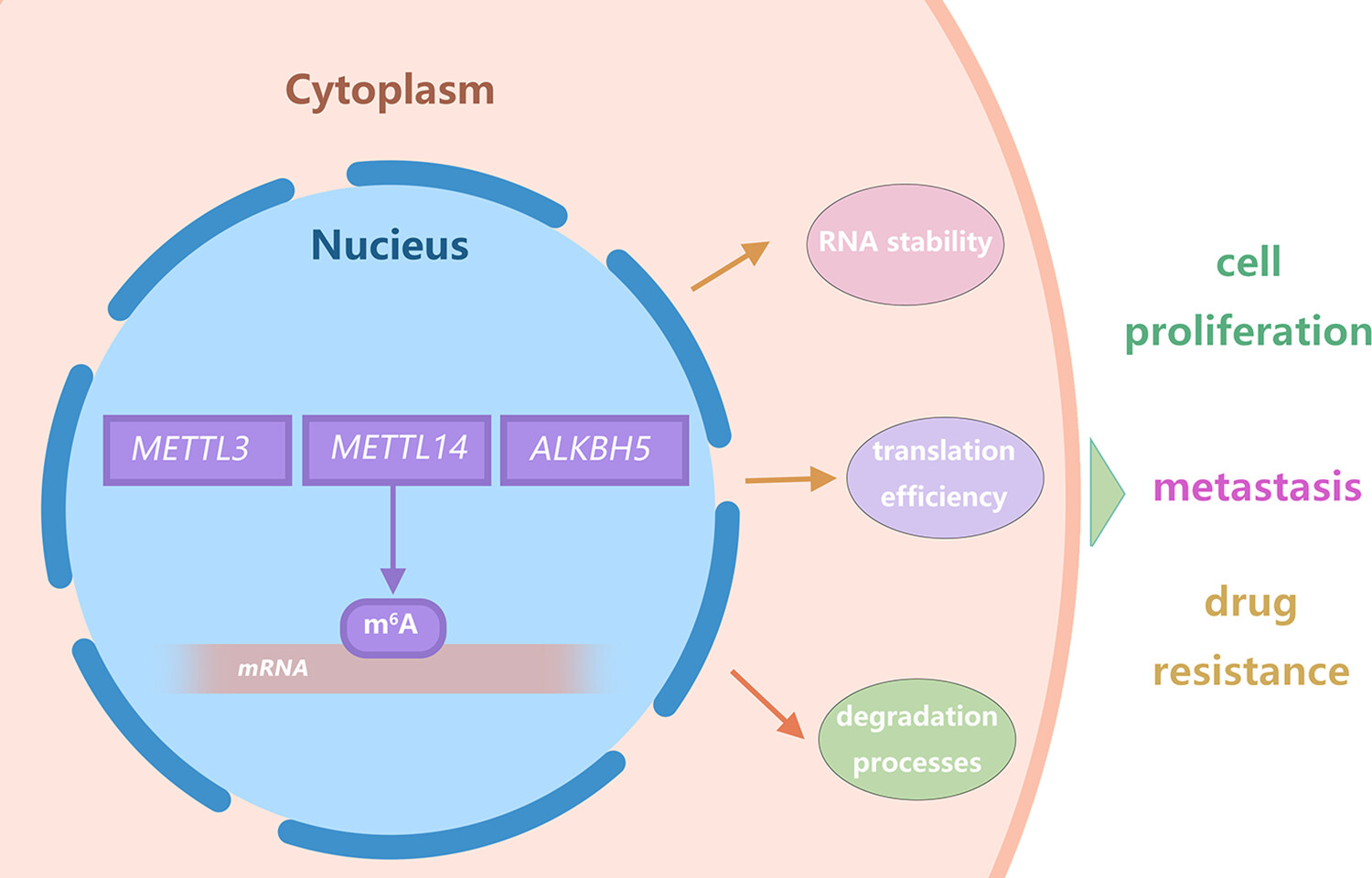
N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification in eukaryotic RNAs has drawn much attention in breast cancer research recently. It impacts breast cancer's onset, progression, and prognosis via regulating RNA-related processes. m6A regulatory factors play key roles. Also, its interactions with non-coding RNAs and in the tumor microenvironment are of interest. Despite some known dual roles, its mechanisms need further study. This article summarizes the research to aid future research and clinical applications.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
RNA Interference Targeting Small Heat Shock Protein B8 Failed to Improve Distal Hereditary Motor Neuropathy in the Mouse Model
- First Published: 19 February 2025
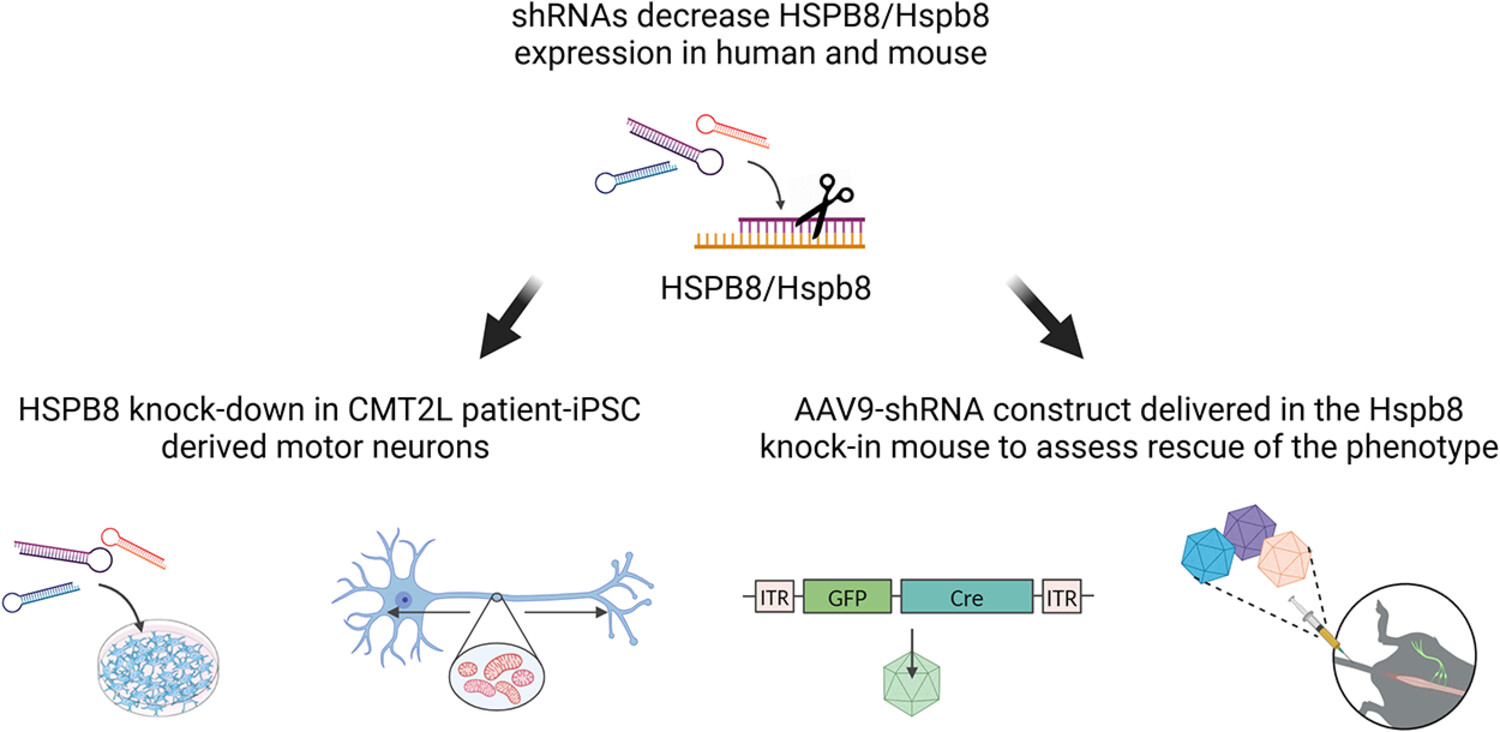
Mutations in HSPB8 cause distal hereditary motor neuropathy or axonal Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease. Mice expressing mutant Hspb8 mimic the disease, whereas mice lacking Hspb8 show no overt phenotype. We designed an RNAi treatment strategy to rescue mutant HSPB8 in patient-derived motor neurons and an Hspb8 knock-in mouse model of the disease. In patient-derived-induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated into motor neurons, reducing HSPB8 expression with a shRNA targeting its 3′UTR could improve mitochondrial morphology and fragmentation. However, adeno-associated virus-mediated treatment with the 3′UTR shRNA showed inconclusive results in terms of functional improvement in the knock-in mouse.
FOXA3: A Novel Tumor Suppressor in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- First Published: 18 February 2025
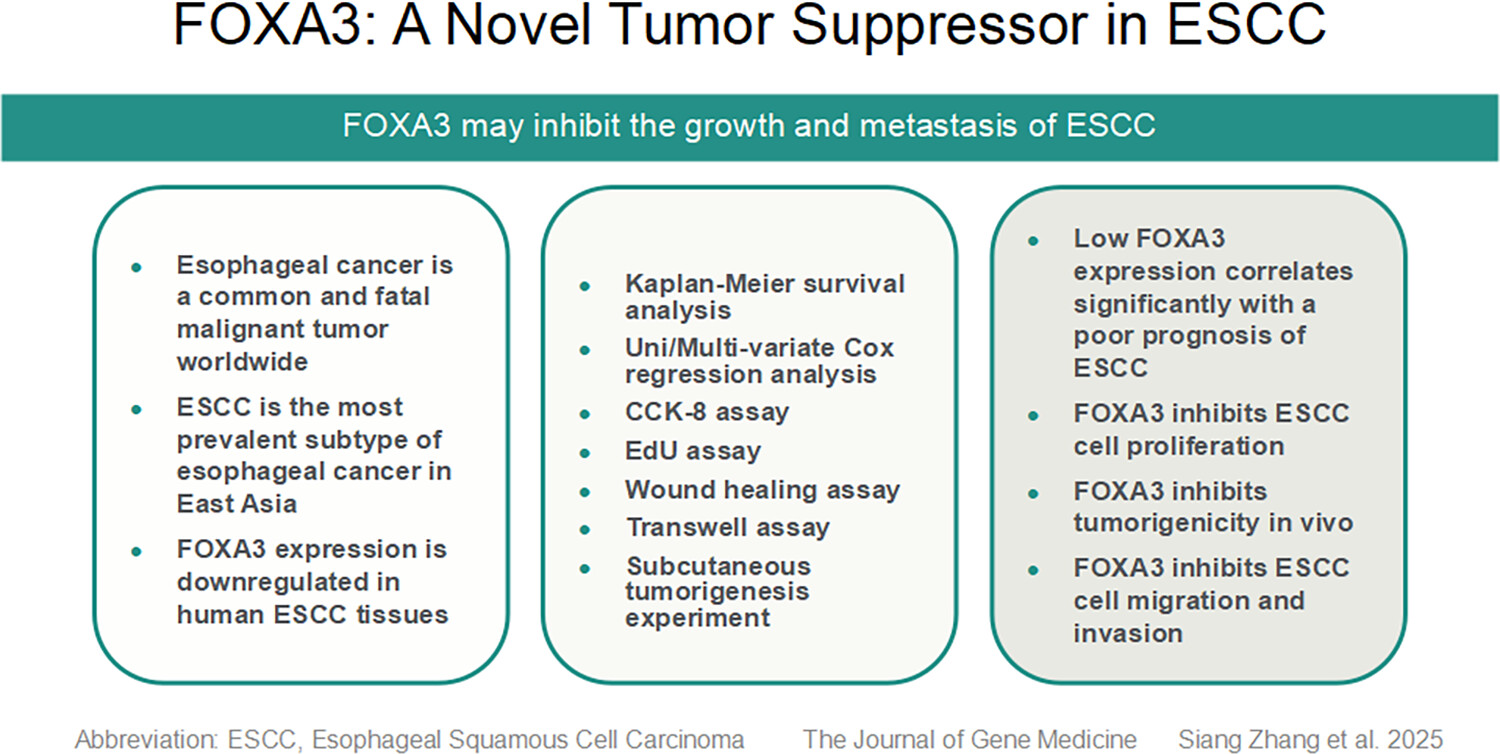
This study investigates the role of FOXA3 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). FOXA3 expression was significantly reduced in ESCC tissues and correlated with poor prognosis. Overexpression of FOXA3 inhibited ESCC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in vitro and tumor growth in vivo. These findings suggest that FOXA3 acts as a tumor suppressor in ESCC and may serve as a potential diagnostic and therapeutic target.
Betulinic Acid Inhibits Glioma Progression by Inducing Ferroptosis Through the PI3K/Akt and NRF2/HO-1 Pathways
- First Published: 18 February 2025
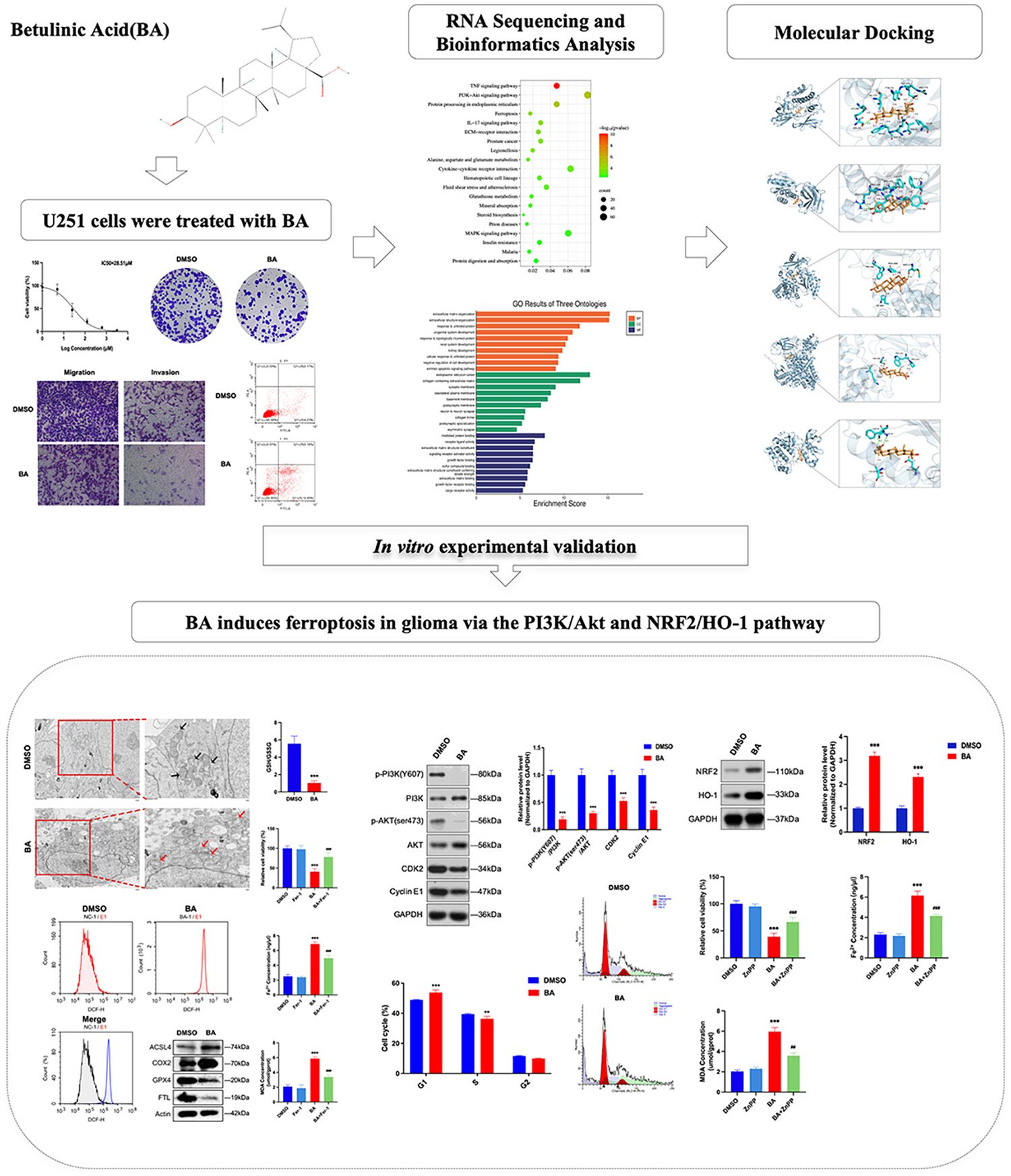
This study investigates the antitumor mechanisms of betulinic acid (BA) in gliomas. BA effectively inhibits the viability of U251 glioma cells. RNA sequencing showed that differentially expressed genes are enriched in the TNF, PI3K-Akt, and ferroptosis pathways. Molecular docking indicated that BA has a strong interaction with key molecules in the PI3K/AKT pathway. In vitro experiments confirmed that BA can induce ferroptosis in U251 cells, possibly by downregulating the phosphorylation levels of the PI3K/Akt pathway and increasing the expression levels of NRF2/HO-1. These findings suggest BA's potential as a novel therapeutic agent for gliomas by modulating multiple pathways.








