Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIALS
Obesity and the lungs: Not just a crush
- Pages: 502-503
- First Published: 21 March 2019
See related Article
How best to assess cough as an outcome measure
- Pages: 504-505
- First Published: 25 March 2019
See related Article
Azithromycin and ABBA in the chest clinic: ‘The winner takes it all...’
- Pages: 506-507
- First Published: 27 March 2019
See related Article
Treatment of interstitial lung disease: Do the ends justify the means?
- Pages: 508-509
- First Published: 19 March 2019
See related Article
Predicting which children have asthma: Are we any closer to finding the Holy Grail?
- Pages: 510-511
- First Published: 18 March 2019
See related Article
INVITED REVIEW SERIES
Non-invasive ventilation
Respiratory adjuncts to NIV in neuromuscular disease
- Pages: 512-520
- First Published: 08 November 2018
NIV in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: The ‘when’ and ‘how’ of the matter
- Pages: 521-530
- First Published: 25 March 2019
INVITED REVIEW
Endobronchial ultrasound-guided transbronchial needle aspiration in sarcoidosis: Beyond the diagnostic yield
- Pages: 531-542
- First Published: 25 March 2019
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Asthma and Allergy
BMI but not central obesity predisposes to airway closure during bronchoconstriction
- Pages: 543-550
- First Published: 29 January 2019
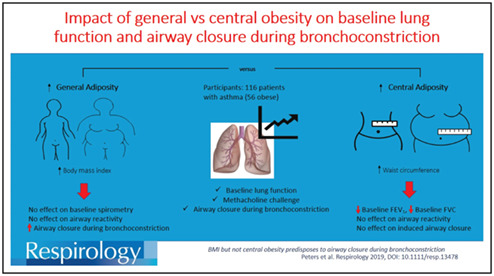
The effect of body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC) on spirometric lung function and airway closure during induced bronchoconstriction was assessed in patients with asthma. WC, but not BMI, was associated with restrictive effects on baseline spirometry. However, during bronchoconstriction, airway closure was associated with increased BMI, rather than WC.
See related Editorial
Development and validation of the COugh Assessment Test (COAT)
- Pages: 551-557
- First Published: 25 January 2019
The COugh Assessment Test (COAT) is a simple assessment that has good repeatability, reliability and validity, with clear discriminative properties. The COAT might serve as a useful parameter for the evaluation of chronic cough in clinic and research settings.
See related Editorial
Bronchiectasis
Idiopathic chronic productive cough and response to open-label macrolide therapy: An observational study
- Pages: 558-565
- First Published: 05 February 2019
A group of patients with chronic productive cough of unknown cause not adequately described by existing disease labels is described in terms of their physiological, radiological and pathological features. The majority of these patients demonstrated neutrophilic or paucigranulocytic airway inflammation and their symptoms responded well to azithromycin.
See related Editorial
Interstitial Lung Disease
Therapeutic burden in interstitial lung disease: Lessons to learn
- Pages: 566-571
- First Published: 20 February 2019

This is the first study providing insights into the significance of therapeutic complexity and polypharmacy in patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD). Patients receiving systemic corticosteroids are at high risk of drug–disease interactions. Additional studies are needed to evaluate the impacts of therapeutic burden on clinical outcomes in patients with ILD.
See related Editorial
Paediatric Lung Disease
Urine metabolic profiles in paediatric asthma
- Pages: 572-581
- First Published: 14 February 2019
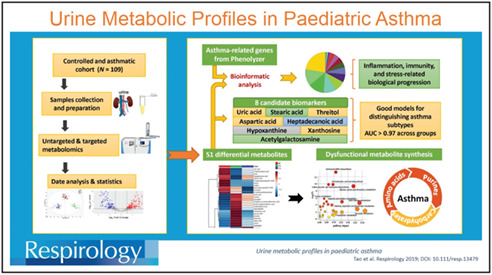
We investigated metabolic profiles of paediatric asthma patients to identify asthma-specific biomarkers in urine. A combination of eight metabolites showed excellent discrimination across groups. Enrichment analysis identified complex biological processes associated with immunity, inflammation, oxidative stress and DNA damage. These approaches enabled discrimination between asthma stages and elucidate its mechanisms.
See related Editorial
Sleep and Ventilation
Pharyngeal distensibility during expiration is an independent predictor of the severity of obstructive sleep apnoea
- Pages: 582-589
- First Published: 24 January 2019
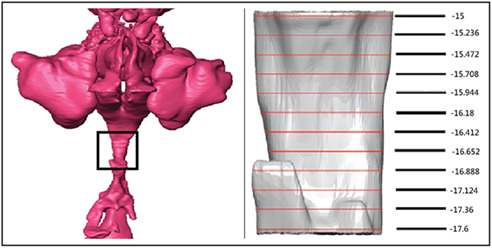
We have devised an image-based method that can rapidly assess obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) severity in awake patients. We have shown that, in awake patients, airway distensibility/collapsibility during expiration, but not inspiration, is related to the severity of OSA. Airway distensibility is an independent risk factor for OSA, but not related to anatomical changes in the tongue and soft palate.
POSITION STATEMENT
Emerging respiratory infections threatening public health in the Asia-Pacific region: A position paper of the Asian Pacific Society of Respirology
- Pages: 590-597
- First Published: 15 April 2019
CONTEMPORARY CONCISE REVIEW
Contemporary Concise Review 2018: Respiratory infections and tuberculosis
- Pages: 598-604
- First Published: 30 March 2019
LETTER FROM ASIA-PACIFIC AND BEYOND
CORRESPONDENCE
Airway distensibility: Bringing physiology to the bedside
- Page: 607
- First Published: 03 April 2019
See Reply
Airway distensibility: Bringing physiology to the bedside – Reply
- Pages: 607-608
- First Published: 03 April 2019
See Letter










-1652674259.png)

