Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIALS
Surgical lung biopsies in elderly patients with interstitial lung disease: Weighing up the pros and cons
- Pages: 444-445
- First Published: 18 February 2018
Respiratory symptoms and small airway dysfunction in current and former smokers without spirometric COPD
- Pages: 446-447
- First Published: 09 January 2018
Secondary spontaneous pneumothorax in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: Grim news
- Pages: 448-449
- First Published: 09 January 2018
Empiric antibiotics for community-acquired pneumonia: A macrolide and a beta-lactam please!
- Pages: 450-451
- First Published: 26 December 2017
COMMENTARY
Green respiratory health care: Time for us all to act
- Pages: 452-454
- First Published: 06 March 2018
INVITED REVIEW SERIES
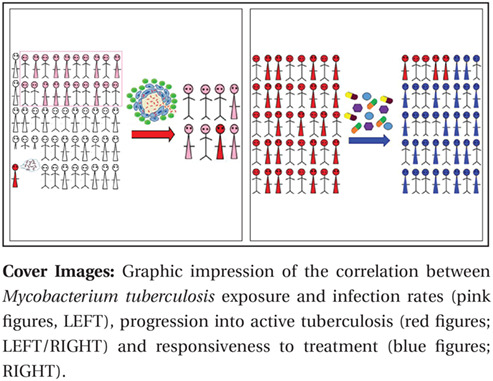
Tuberculosis Updates 2018
Update on tuberculosis biomarkers: From correlates of risk, to correlates of active disease and of cure from disease
- Pages: 455-466
- First Published: 18 February 2018
SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
Efficacy and safety of phosphodiesterase 4 inhibitors in patients with asthma: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 467-477
- First Published: 04 March 2018
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Asthma and Allergy
Comparison of respiratory system impedance in asthma and COPD: A prospective observational study
- Pages: 478-484
- First Published: 17 January 2018
Changes in a single assessment of within-breath variations of respiratory system reactance (Xrs) at 5 Hz (ΔX5) in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are significantly greater than in patients with asthma. ΔX5 may reflect the pathophysiological changes in COPD and can be useful for its long-term assessment.
COPD
The importance of symptoms in the longitudinal variability of clusters in COPD patients: A validation study
- Pages: 485-491
- First Published: 12 October 2017
This longitudinal analysis of a large chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) study explored the identification of clusters and their behaviour over 2 years. We validated previous data on the topic but in a multicentre study and with 2 years of follow-up (previously only 1 year). We also identified factors associated with cluster changes.
Critical Care
Models of care for non-invasive ventilation in the Acute COPD Comparison of three Tertiary hospitals (ACT3) study
- Pages: 492-497
- First Published: 10 December 2017
Although non-invasive ventilation (NIV) is an established treatment for acute hypercapnic COPD, the optimal model of care is not known. We undertook a comparison of NIV delivery in general, high dependency and intensive care wards and identified equal efficacy, with considerable financial savings using the general ward model.
Interstitial Lung Disease
Phenotypic characteristics associated with slow gait speed in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pages: 498-506
- First Published: 14 November 2017
We evaluated 4 m gait speed (4MGS), a simple functional performance test, in people with stable idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. We found 4MGS a reliable, valid and responsive measure that can detect a patient phenotype with worse dyspnoea, exercise performance, quality of life and prognostic risk.
Diagnostic utility of surgical lung biopsies in elderly patients with indeterminate interstitial lung disease
- Pages: 507-511
- First Published: 27 November 2017

This study addresses the utility and safety of surgical lung biopsies in diagnosing interstitial lung disease in patients older than 75 years. More than one-third of the patients with a computed tomography pattern incompatible with usual interstitial pneumonia had diagnoses other than idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. The mortality in our cohort was higher than that reported in the literature.
Lung Function
Peripheral airway dysfunction and relationship with symptoms in smokers with preserved spirometry
- Pages: 512-518
- First Published: 15 November 2017
Multiple breath nitrogen washout (MBNW) or impulse oscillometry system (IOS) abnormalities were highly prevalent in smokers without COPD but highly discordant between individuals. Cough was related to peripheral conductive airway function, while wheeze was related to IOS and spirometry. In smokers with normal spirometry, MBNW and IOS abnormalities may have different underlying structural bases and prognostic significance.
Pleural Disease
The prognostic significance of pneumothorax in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pages: 519-525
- First Published: 12 November 2017
We evaluated prognostic significance of pneumothorax and the risk factors for its onset in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We demonstrate that the onset of pneumothorax predicts a poor outcome in the patients with IPF. Lower BMI and the presence of extensive reticular abnormalities are associated with developing pneumothorax.
Respiratory Infections
Mortality in patients with community-onset pneumonia at low risk of drug-resistant pathogens: Impact of β-lactam plus macrolide combination therapy
- Pages: 526-534
- First Published: 14 December 2017
LETTER FROM ASIA-PACIFIC REGION
YEAR IN REVIEW
Year in review 2017: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma
- Pages: 538-545
- First Published: 04 March 2018
CORRESPONDENCE
Corticosteroids in acute exacerbations of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: Time to debate
- Page: 546
- First Published: 11 March 2018
See Reply
Corticosteroids in acute exacerbations of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: Time to debate – Reply
- Pages: 546-547
- First Published: 11 March 2018
See Letter











-1652674259.png)

