Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2/2017
- First Published: 13 February 2017

Front Cover: A new approach to prepare free-standing biodegradable nanopillar arrays on flexible substrates is developed by using plasma etching with block copolymer micelles encapsulating Au nanoparticles as an etching mask. This method can offer a feasible route to create vertically-aligned nanostructures of various materials with dimensional controllability. This is reported by Gyeong Won Lee, Seunghyun Lee, Jang Hwan Kim, Sang-Gu Yim, Jooyeon Ryu, Eunji Lee, Jaebeom Lee, Seong Il Yoo, and Seung Yun Yang in article number 1600361.
Masthead
Contents
Communications
Synthesis of Shape Memory Poly(glycerol sebacate)-Stearate Polymer
- First Published: 13 October 2016

A variable molar ratio of stearic acid is added into the synthesis of poly(glycerol sebacate) shape memory polymers. The use of a molar ratio of 0.5 leads to the obtaining of shape memory polymers able to keep their deformed shape (160%) at room temperature and to recover their initial shape by 86%.
Multi-Wavelength Light Drivable Oscillatory Actuator on Graphene-Based Bilayer Film
- First Published: 11 November 2016
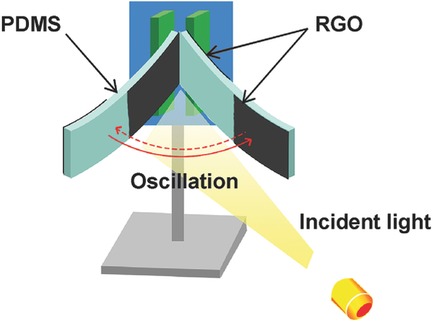
A wide-range wavelength light responsive bending/unbending bilayer film is fabricated by depositing one layer of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) onto flexible poly(dimethyl siloxane) (PDMS) film. RGO absorbs and converts the light into heat. Thus it results in the bilayer film expanding and bending towards the layer on the RGO side. Oscillatory motion is achieved by designing an offset sandwiched RGO/PDMS film, which provides a possibility for continuously transfering the light energy into mechanical work.
Highly Flexible, Tough, and Self-Healable Hydrogels Enabled by Dual Cross-Linking of Triblock Copolymer Micelles and Ionic Interactions
- First Published: 23 November 2016
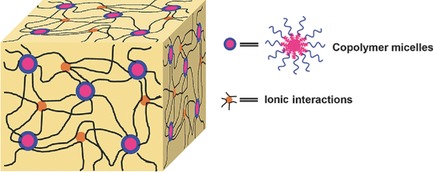
Highly flexible, tough, and self-healable hydrogels are synthesized by dually cross-linking of amphiphilic triblock copolymer micelles and ionic interactions. Due to the coexistence of these two cross-linking points, the resulting hydrogels can be flexibly stretched, bent, knotted, and twisted. Moreover, the hydrogels also show good self-healing and self-recovery abilities based-on these dynamic interactions.
Full Papers
Density-Controlled Freestanding Biodegradable Nanopillar Arrays Patterned via Block Copolymer Micelle Lithography
- First Published: 22 November 2016
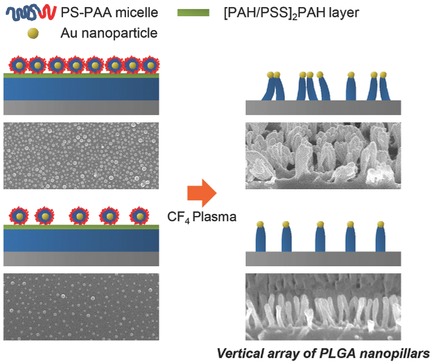
Dimensionally well-controlled biodegradable nanopillar arrays are successfully created by using density-controlled block copolymer nanomasks by pH and anisotropic plasma etching on different substrates including flexible sheets. This approach can offer a feasible route to create nanostructures on various soft materials with dimensional controllability.
Fabrication of Silicone Rubber Foam with Tailored Porous Structures by Supercritical CO2
- First Published: 17 November 2016
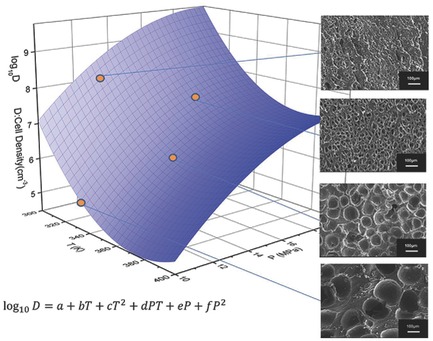
The effects of silica content and foaming process on the porous structure of high-temperature-vulcanized silicon rubber foams, which are prepared by supercritical CO2 as foaming agent, are evaluated. The relationship of cell density and saturation parameters is summarized by a fitted equation, which suggested the porous structures of silicone foams can be tailored by foaming process parameters facilely.
Development of Ethylene-Vinyl Acetate Composites Reinforced with Graphene Platelets
- First Published: 26 October 2016
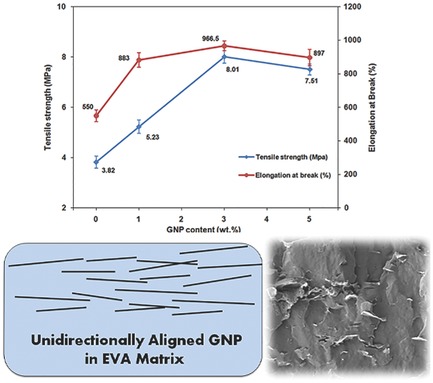
The tensile property of ethylene-vinyl acetate composites reinforced with graphene platelets is explored as a function of graphene platelets direction into the matrix. Unidirectional orientation of the graphene platelets in the matrix is observed which are parallel to the surface of composite films. The graphene platelets alignment within the matrix enhances the tensile strength as well as the composites extendibility dramatically.
Polyolefin Microfiber Based Antibacterial Fibrous Membrane by Forced Assembly Coextrusion
- First Published: 13 October 2016
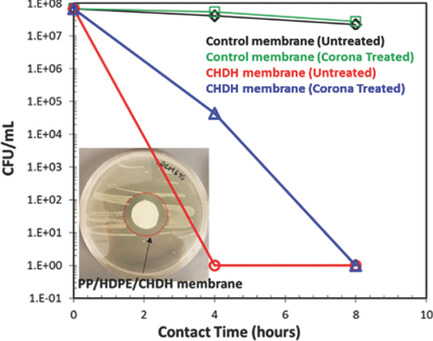
The use of a novel technique, forced assembly coextrusion, for the continuous production of polyolefin based fibers and fibrous membranes with an associated delamination technique is reported. In the same process, micro-/nanofibers and membranes having antibacterial characteristics can be produced. A complete set of systematic analysis shows that the biocomponent fibers with the inclusion of an antibacterial agent can effectively make fibrous membranes.
Periodic Surface Structures Induced by a Single Laser Beam Irradiation
- First Published: 10 November 2016
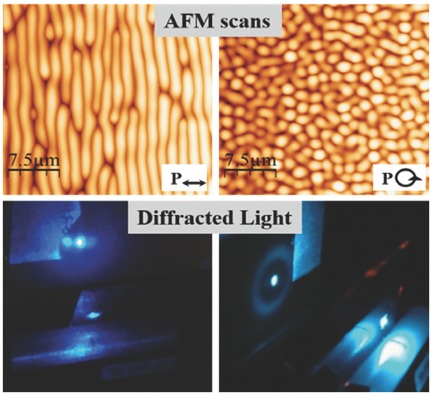
Periodic surface patterns or willow structures, obtained by irradiation of azopolymer films with a single linearly polarized laser beam, can be an alternative to the surface-relief grating formation under interference irradiation. It is demonstrated that the periodicity of the willow structures depends on parameters such as film thickness and inscription temperature.
Improvement of Mechanical Ductile Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by Using Vegetable Oil Derivatives
- First Published: 04 November 2016

The effect of maleinized linseed oil and an epoxidized fatty acid ester on mechanical and thermal properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) has been evaluated. The results show that a small addition of both plasticizers (5 phr) provides increased elongation at break values together with a remarkable increase in the impact resistance and, subsequently, toughness improvement.
Multiple Shape Memory, Self-Healable, and Supertough PAA-GO-Fe3+ Hydrogel
- First Published: 03 November 2016
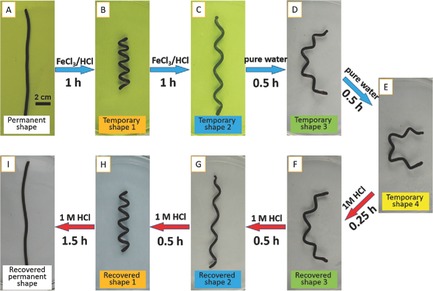
A multiple shape memory and self-healing poly(acrylic acid)-graphene oxide-Fe3+ (PAA-GO-Fe3+) hydrogel with supertough strength is synthesized containing dual physically cross-linked PAA network by GO and Fe3+. Based on the reversible cross-linking of Fe3+ to COO−, the gel exhibits multiple shape memory and self-healing effects, which can be achieved by immersing the gel in different solutions and for different times.
Hybrid Hydrogels Based on Poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA)/Agar/Poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) Prepared by High Energy Electron Beam Irradiation: Investigation of Physico-Mechanical and Rheological Properties
- First Published: 04 November 2016
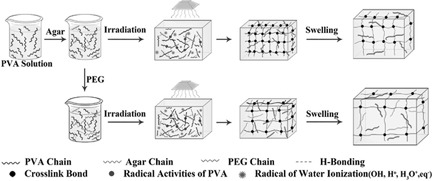
PVA/agar/PEG hybrid hydrogels for wound dressing applications are prepared by an EB irradiation method. The effects of agar and PEG on their physico-mechanical and rheological properties are systematically investigated. A theoretical analysis of swelling kinetics reveals that the swelling mechanism is under the influence of both agar and PEG contents. The rheological behavior of the hydrogels shows a strong dependency on PEG content.
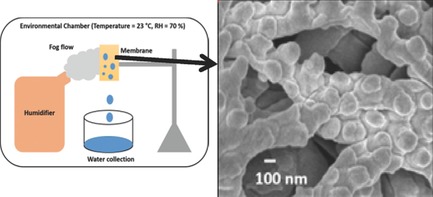
Hierarchical Structured Electrospun Nanofibers for Improved Fog Harvesting Applications
- First Published: 17 November 2016
Sterilization of Thiol-ene/Acrylate Based Shape Memory Polymers for Biomedical Applications
- First Published: 12 October 2016
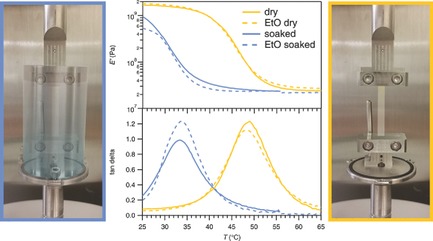
Sterilization of shape memory polymers for biomedical devices with self-softening capabilities is demonstrated. Ethylene oxide is shown to be an appropriate method to sterilize temperature sensitive thiol-ene/acrylate polymers. The thermomechanical properties and softening characteristics of the shape memory polymers are not affected as demonstrated by dynamic mechanical analysis on dry and in phosphate buffered saline immersed samples.
One-Pot Substitution Approach for the Syntheses of Nonfunctional and Functional Poly[(amino acid ester)phosphazene] Biomaterials
- First Published: 15 November 2016
![One-Pot Substitution Approach for the Syntheses of Nonfunctional and Functional Poly[(amino acid ester)phosphazene] Biomaterials](/cms/asset/3252fb67-7134-4330-a45d-7c74635dab67/mame201600318-gra-0001-m.jpg)
One-pot room temperature substitution approach is used to prepare functional poly[(amino acid ester)phosphazene] biomaterials. It is demonstrated that poly[(amino acid ester)phosphazene]s can be prepared in air without the need of specialized equipment via ring opening polymerization of hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene and subsequent macromolecular substitution with amino acid esters hydrochloride salts. By controlling the extent of the reaction and purification by precipitation, high molecular weight polymers with low polydispersity can be obtained reproducibly.