Improvement of Mechanical Ductile Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) by Using Vegetable Oil Derivatives
Corresponding Author
Daniel Garcia-Garcia
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorOctavio Fenollar
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorVicent Fombuena
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorJuan Lopez-Martinez
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorRafael Balart
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Daniel Garcia-Garcia
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorOctavio Fenollar
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorVicent Fombuena
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorJuan Lopez-Martinez
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorRafael Balart
Instituto de Tecnología de Materiales (ITM), Universitat Politècnica de València (UPV), Plaza Ferrándiz y Carbonell s/n, 03801 Alcoy, Alicante, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorAbstract
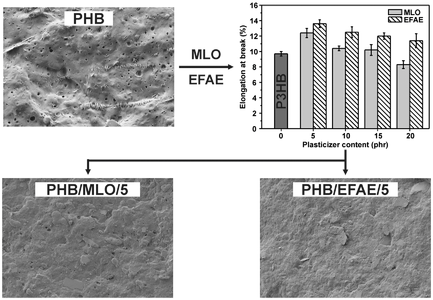
Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate), P3HB is a thermoplastic polyester synthesized from bacterial fermentation with potential uses in packaging due to its biodegradability. Nevertheless, P3HB is a fragile material and its processing temperature window is very narrow which restricts its use. This study explores the potential of vegetable oil-derived plasticizers, i.e., maleinized linseed oil (MLO) and an epoxidized fatty acid ester (EFAE) in the 5–20 phr range as environmentally friendly solutions for P3HB industrial formulations with improved toughness. The results show that optimum balance between ductile properties is achieved with low plasticizer content (5 phr) for both plasticizer types. Elongation at break and the impact resistance are increased by 28 and 71% respectively after addition of 5 phr MLO. With regard to EFAE, the elongation at break is improved by 40% and the impact resistance is increased to twice the value of P3HB. Another effect that both plasticizers provide is the thermal stabilization with a delay in the onset degradation temperature.
References
- 1M. Hassan, K. R. Reddy, E. Haque, A. I. Minett, V. G. Gomes, J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 410, 43.
- 2M. Hassan, K. R. Reddy, E. Haque, S. N. Faisal, S. Ghasemi, A. I. Minett, V. G. Gomes, Compos. Sci. Technol. 2014, 98, 1.
- 3S. H. Choi, D. H. Kim, A. V. Raghu, K. R. Reddy, H.-I. Lee, K. S. Yoon, H. M. Jeong, B. K. Kim, J. Macromol. Sci., Part B: Phys. 2012, 51, 197.
- 4K. R. Reddy, K.-P. Lee, A. I. Gopalan, J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2007, 7, 3117.
- 5Y. P. Zhang, S. H. Lee, K. R. Reddy, A. I. Gopalan, K. P. Lee, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 104, 2743.
- 6P. Bhagowati, S. Pradhan, H. R. Dash, S. Das, Biosci., Biotechnol., Biochem. 2015, 79, 1454.
- 7D. D'Amico, M. I. Montes, L. Manfredi, V. Cyras, Polym. Test. 2016, 49, 22.
- 8S. M. Lai, W. W. Sun, T. M. Don, Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 1321.
- 9V. Mittal, T. Akhtar, N. Matsko, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 423.
- 10P. Bordes, E. Pollet, L. Avérous, Prog. Polym. Sci. 2009, 34, 125.
- 11X. Fan, Q. Jiang, Z. Sun, G. Li, X. Ren, J. Liang, T. Huang, Fibers Polym. 2015, 16, 1751.
- 12D. Garcia-Garcia, J. M. Ferri, T. Boronat, J. Lopez-Martinez, R. Balart, Polym. Bull. 2016, 73, 3333.
- 13Z. Karahaliloglu, B. Ercan, E. N. Taylor, S. Chung, E. B. Denkbaş, T. J. Webster, J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2015, 11, 2253.
- 14A. I. Romero, J. M. Bermudez, M. Villegas, M. F. D. Ashur, M. L. Parentis, E. E. Gonzo, AAPS PharmSciTech 2015, 17, 898.
- 15D. Bucci, L. Tavares, I. Sell, Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 908.
- 16D. Bucci, L. Tavares, I. Sell, Polym. Test. 2005, 24, 564.
- 17A. Meszynska, E. Pollet, K. Odelius, M. Hakkarainen, L. Avérous, Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 661.
- 18C. Zhijiang, X. Yi, Y. Haizheng, J. Jia, Y. Liu, Mater. Sci. Eng., C 2016, 58, 757.
- 19S. Safari, T. G.van de Ven, J. Mater. Sci. 2015, 50, 3686.
- 20C. R. Arza, P. Jannasch, P. Johansson, P. Magnusson, A. Werker, F. H. Maurer, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41836.
- 21O. Sharhan, A. H. Yahaya, M. M. Nasef, Asian J. Chem. 2015, 27, 979.
- 22I. Janigova, I. Lacík, I. Chodak, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2002, 77, 35.
- 23Y. Ke, X. Zhang, S. Ramakrishna, L. He, G. Wu, eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2016, 10, 36.
- 24S.-G. Hong, T.-K. Gau, S.-C. Huang, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2011, 103, 967.
- 25X. Wen, X. Lu, Q. Peng, F. Zhu, N. Zheng, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2012, 109, 959.
- 26S.-G. Hong, H.-W. Hsu, M.-T. Ye, J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2013, 111, 1243.
- 27L. Wang, W. Zhu, X. Wang, X. Chen, G. Q. Chen, K. Xu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 107, 166.
- 28M. Auriemma, A. Piscitelli, R. Pasquino, P. Cerruti, M. Malinconico, N. Grizzuti, Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 63, 123.
- 29K. R. Reddy, H. Sato, I. Takahashi, Y. Ozaki, Polymer 2015, 75, 141.
- 30D. Puglia, E. Fortunati, D. D. Amico, V. Miri, G. Stoclet, L. Manfredi, V. Cyras, J. Kenny, J. Polym. Environ. 2015, 24, 12.
- 31J. S. Choi, W. H. Park, Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 455.
- 32R. C. Baltieri, I. Mei, H. Lucia, J. Bartoli, Macromol. Symp. 2003, 197, 33.
- 33E. Grillo Fernandes, M. Pietrini, E. Chiellini, Macromol. Symp. 2004, 218, 157.
10.1002/masy.200451416 Google Scholar
- 34M. Bocqué, C. Voirin, V. Lapinte, S. Caillol, J. J. Robin, J. Polym. Sci., Part A: Polym. Chem. 2016, 54, 11.
- 35B. W. Chieng, N. A. Ibrahim, Y. Y. Then, Y. Y. Loo, Molecules 2014, 19, 16024.
- 36V. Silverajah, N. A. Ibrahim, W. M. Z. W. Yunus, H. A. Hassan, C. B. Woei, Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 5878.
- 37M. Wadhi, R. Weliam, Res. Chem. Intermed. 2014, 40, 399.
- 38N. Prempeh, J. Li, D. Liu, K. Das, S. Maiti, Y. Zhang, Polym. Sci., Ser. A 2014, 56, 856.
- 39E. F. Santos, R. V. Oliveira, Q. B. Reiznautt, D. Samios, S. M. Nachtigall, Polym. Test. 2014, 39, 23.
- 40J. Ferri, D. Garcia-Garcia, L. Sánchez-Nacher, O. Fenollar, R. Balart, Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 147, 60.
- 41A. Ruellan, A. Guinault, C. Sollogoub, G. Chollet, A. Ait-Mada, V. Ducruet, S. Domenek, eXPRESS Polym. Lett. 2015, 9, 1087.
- 42O. Fenollar, D. Garcia-Sanoguera, L. Sánchez-Nácher, J. López, R. Balart, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 124, 2550.
- 43P. G. Nihul, S. T. Mhaske, V. V. Shertukde, Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 599.
- 44O. Fenollar, D. Garcia-Sanoguera, L. Sanchez-Nacher, J. Lopez, R. Balart, J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 4406.
- 45B. K. Sharma, A. Adhvaryu, Z. Liu, S. Z. Erhan, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2006, 83, 129.
- 46S. Tan, W. Chow, Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 2010, 49, 1581.
- 47A. Campanella, E. Rustoy, A. Baldessari, M. A. Baltanás, Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 245.
- 48C. Zhang, R. Ding, M. R. Kessler, Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2014, 35, 1068.
- 49A. Lee, Y. Deng, Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 63, 67.
- 50C. Zhang, H. Wu, M. R. Kessler, Polymer 2015, 69, 52.
- 51M. Domínguez-Díaz, A. Meneses-Acosta, A. Romo-Uribe, C. Peña, D. Segura, G. Espin, Eur. Polym. J. 2015, 63, 101.
- 52J. Ferri, M. Samper, D. García-Sanoguera, M. Reig, O. Fenollar, R. Balart, J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 5356.
- 53D. Garcia-Garcia, J. M. Ferri, N. Montanes, J. Lopez-Martinez, R. Balart, Polym. Int. 2016, 65, 1157.
- 54Y. Q. Xu, J. P. Qu, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2009, 112, 3185.
- 55Y. Zhao, J. Qu, Y. Feng, Z. Wu, F. Chen, H. Tang, Polym. Adv. Technol. 2012, 23, 632.
- 56M. P. Arrieta, M. D. Samper, J. López, A. Jiménez, J. Polym. Environ. 2014, 22, 460.
- 57P. Small, J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 1953, 3, 71.
- 58K. Prakalathan, S. Mohanty, S. K. Nayak, Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 999.
- 59V. S. G. Silverajah, N. A. Ibrahim, N. Zainuddin, W. M. Z. W. Yunus, H. Abu Hassan, Molecules 2012, 17, 11729.
- 60M. Erceg, T. Kovacˇić, I. Klarić, Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2005, 90, 313.
- 61M. Zhang, N. L. Thomas, Adv. Polym. Technol. 2011, 30, 67.
- 62T. Furukawa, H. Sato, R. Murakami, J. Zhang, Y.-X. Duan, I. Noda, S. Ochiai, Y. Ozaki, Macromolecules 2005, 38, 6445.
- 63P. S.de O Patrício, F. V. Pereira, M. C. dos Santos, P. P.de Souza, J. P. Roa, R. L. Orefice, J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2013, 127, 3613.
- 64M. Râpă, R. Darie-Niţă, E. Grosu, E. Tănase, A. Trifoi, T. PAPa, C. Vasile, J. Optoelectron. Adv. Mater. 2015, 17, 1778.