Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 6/2016
- Page: 641
- First Published: 07 June 2016

Front Cover: A multilayer nanocoating composed of polyelectrolytes and carbon nanotubes is able to render polyurethane foam flame retardant. This cover image represents the potential to protect household furniture from fire using this simple water-based coating. Further details can be found in the article by Kevin M. Holder, Amanda A. Cain, Morgan G. Plummer, Bart E. Stevens, Patrick K. Odenborg, Alexander B. Morgan, and Jaime C. Grunlan* on page 665.
Back Cover
Macromol. Mater. Eng. 6/2016
- Page: 764
- First Published: 07 June 2016

Back Cover: A green polymer self-etching strategy for fabricating superhydrophobic surfaces exhibiting low and high adhesion is proposed by using hot-pressing and exfoliation on a pair of low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films. Hierarchical micro-/nanostructures are observed in the exfoliated LDPE surfaces and superhydrophobic vessels can be obtained. Further details can be found in the article by Zhong Xiong,* Chenglin Zheng, and Yanzhi Xia* on page 653.
Masthead
Contents
Contents: Macromol. Mater. Eng. 6/2016
- Pages: 643-647
- First Published: 07 June 2016
Communications
Nondestructive Molecular Characterization of Polycarbonate–Polyvinylamine Composites after Thermally Induced Aminolysis
- Pages: 648-652
- First Published: 21 April 2016
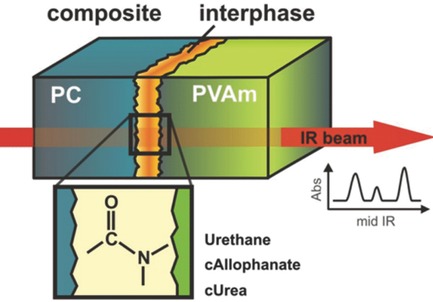
Solid-state reaction between polycarbonate and polyvinylamine is applied to form permanent composites. Reaction products formed at interface are explored by FT-IR spectroscopy. Assignment to different amidation products is performed by synthesized reference substances representing functional coupling structures between both polymers. Urethane, cyclic Allophanate, and cyclic Urea are identified as main reaction products of the interfacial complex mixture.
Polymer Self-Etching for Superhydrophobicity through a Green Hot-Pressing-Exfoliation Process: Low and High Adhesion
- Pages: 653-658
- First Published: 13 April 2016
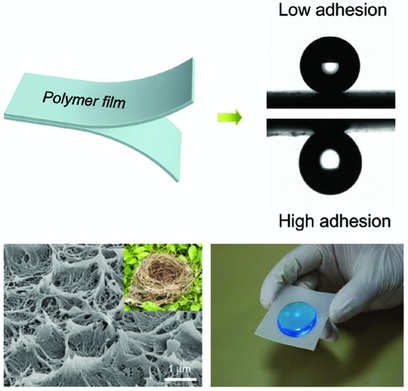
A polymer self-etching strategy is applied to fabricate superhydrophobic low-density polyethylene (LDPE) films with low adhesion (sliding angle <5°) and high adhesion through a simple and green hot-pressing-exfoliation process. Hierarchical micro- and nanostructures are observed in the exfoliated LDPE surfaces and superhydrophobic vessels can be obtained.
Synthesis of Hydrophobic Polymeric Cryogels with Supermacroporous Structure
- Pages: 659-664
- First Published: 01 March 2016
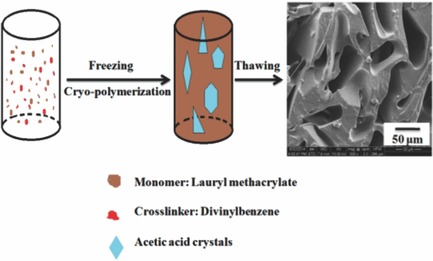
By virtue of acetic acid crystals as a porogen, a versatile and green route is proposed for the synthesis of hydrophobic cryogels with several-decade micrometer-sized supermacropores via cryo-polymerization. Owing to their supermacroporosity and distinctive hydrophobicity, the obtained poly(lauryl methacrylate-divinylbenzene) cryogels present superfast responsiveness to organic solvents.
Full Papers
Carbon Nanotube Multilayer Nanocoatings Prevent Flame Spread on Flexible Polyurethane Foam
- Pages: 665-673
- First Published: 21 December 2015
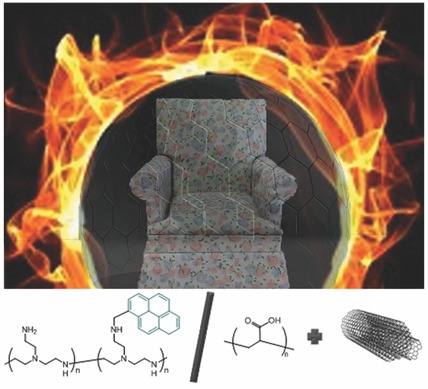
A layer-by-layer nanocoating combining polymers and multiwalled carbon nanotubes renders polyurethane foam flame retardant. Pyrene-modified polyethylenimine and poly(acrylic acid) are used to stabilize multiwalled carbon nanotubes in water-based solutions to create nanocomposite thin films on polyurethane foam. These thin films dramatically reduce the flammability of polyurethane foam during cone calorimetry and open flame tests.
Macroporous Polytetrafluoroethylene Film with a Reusable Matrix and Its Application as the Microreactors
- Pages: 674-681
- First Published: 15 February 2016
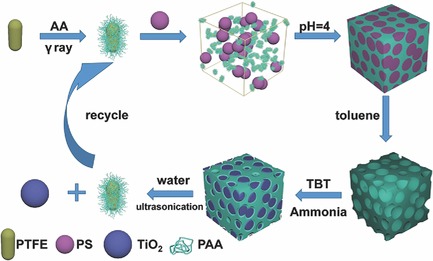
Inverse-opal-like macroporous polytetrafluoroethylene (IO-PTFE) film can be simply prepared by the simultaneous deposition of poly(acrylic acid) grafted PTFE (PTFE-g-PAA) particles and monodispersed polystyrene template microspheres in an acidic aqueous solution followed by a chemical etching process. The IO-PTFE film can be used as microreactors to prepare TiO2 microparticles, and disintegrated in water to recycle PTFE-g-PAA particles.
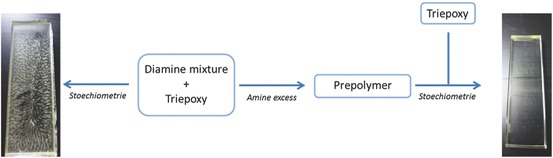
Synthesis of Aminotelechelic Prepolymers to Circumvent the Carbonation of Amines in Epoxy Coatings
- Pages: 682-693
- First Published: 03 May 2016
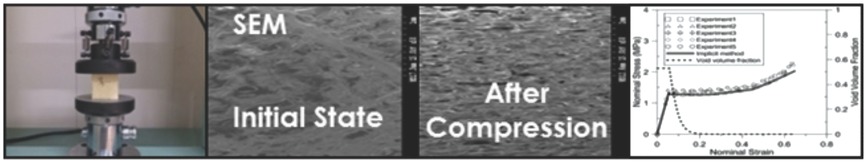
Application of Gurson Model for Evaluation of Density-Dependent Mechanical Behavior of Polyurethane Foam: Comparative Study on Explicit and Implicit Method
- Pages: 694-706
- First Published: 13 April 2016
Polypyrrole-Coated PDMS Fibrous Membrane: Flexible Strain Sensor with Distinctive Resistance Responses at Different Strain Ranges
- Pages: 707-713
- First Published: 07 March 2016
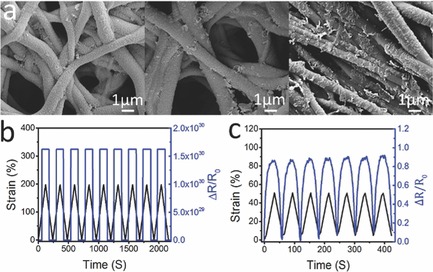
Electrospun poly(dimethylsiloxane) fibers after being coated with a thin layer of polypyrrole on the fiber surface show a normal monotonic resistance response to strain in the range of 0–50%, but the response becomes an “on-off switching” mode when the strain is between 100 and 200%. Such distinctive resistance response may be useful for monitoring the states where motions are allowed in a particular range such as joint rehabilitation.
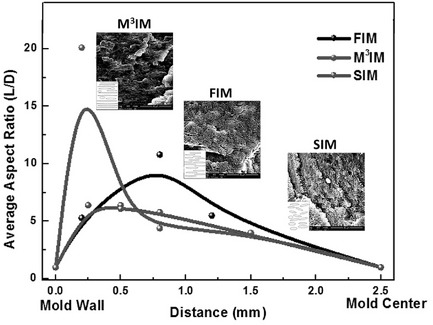
Morphological Evolution of Polystyrene/Polyethylene Blend Induced by Strong Second Melt Penetration
- Pages: 714-724
- First Published: 15 March 2016
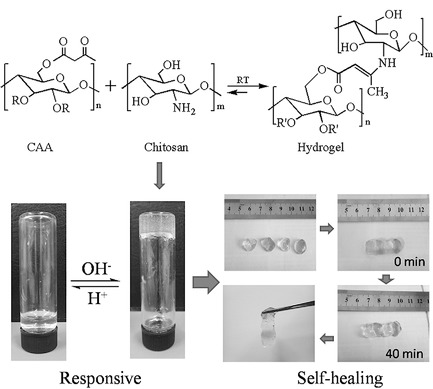
Self-Healing Polysaccharide Hydrogel Based on Dynamic Covalent Enamine Bonds
- Pages: 725-732
- First Published: 13 April 2016
New Radiopaque Bromine-Containing Monomers for Dental Restorative Materials
- Pages: 733-742
- First Published: 14 April 2016
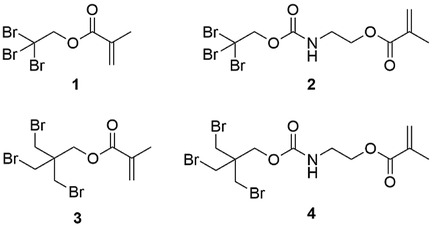
New bromine-containing monomers 1–4 are prepared. Free radical solution homopolymerizations are carried out and the photopolymerization behaviors of methacrylates 1–4 are investigated. The incorporation of monomers 1–4 to dental resins allows a significant increase of the radiopacity without impairing the mechanical properties.
Fabrication of Polymer Film with Extraordinary Conductive Anisotropy by Forming Parallel Conductive Vorticity-Aligned Stripes and Its Formation Mechanism
- Pages: 743-749
- First Published: 13 April 2016
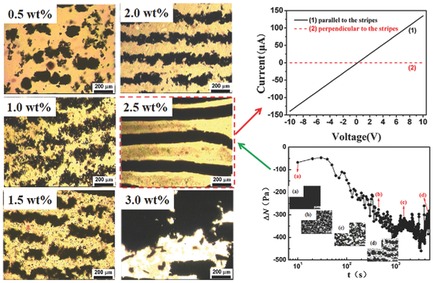
An appropriate carbon black (CB) content is needed for forming parallel vorticity-aligned stripes to fabricate polymer film with extraordinary conductivity anisotropy: the difference between the electrical resistivity in the direction parallel and perpendicular to the CB stripes is almost eight orders of magnitude. The rheological measurement and the study of morphological evolution are also performed to reveal the formation mechanism of the stripe.
New Diluents for Dental Composites
- Pages: 750-759
- First Published: 25 April 2016
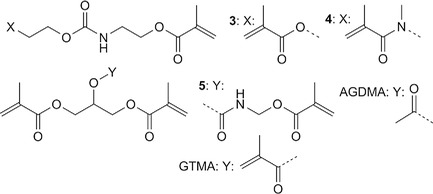
New urethane group containing monomers 3–5, GTMA and AGDMA are synthesized and evaluated in terms of radical photopolymerization reactivity, polymerization shrinkage, and toxicity. Three-point bending tests of Bis-GMA-based resins or composites show that 3–5, GTMA and AGDMA can be used as alternatives for the diluent.
Correction
Improvement in Mechanical Properties and Electromagnetic Interference Shielding Effectiveness of PVA-Based Composites: Synergistic Effect Between Graphene Nano-Sheets and Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes
- Page: 760
- First Published: 03 May 2016