Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION - COVER AND EDITORIAL BOARD
ISSUE INFORMATION - TOC
IN THIS ISSUE: GRAPHICAL ABSTRACTS
EDITORIAL
Glycomics in tears: seeking for new biomarkers for ocular allergy diagnosis
- Pages: 2335-2336
- First Published: 07 April 2021
GUIDELINES
Efficacy and safety of treatment with biologicals for severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A systematic review for the EAACI guidelines
- Pages: 2337-2353
- First Published: 08 March 2021
EAACI POSITION PAPERS
Differentiation of COVID-19 signs and symptoms from allergic rhinitis and common cold: An ARIA-EAACI-GA2LEN consensus
- Pages: 2354-2366
- First Published: 17 March 2021
REVIEW ARTICLES
Allergens and their associated small molecule ligands—their dual role in sensitization
- Pages: 2367-2382
- First Published: 18 April 2021
Carbohydrate epitopes currently recognized as targets for IgE antibodies
- Pages: 2383-2394
- First Published: 02 March 2021
Will the asthma revolution fostered by biologics also benefit adult ICU patients?
- Pages: 2395-2406
- First Published: 07 December 2020
Multidisciplinary consensus on sputum induction biosafety during the COVID-19 pandemic
- Pages: 2407-2419
- First Published: 12 December 2020
Basophil activation test: Mechanisms and considerations for use in clinical trials and clinical practice
- Pages: 2420-2432
- First Published: 21 January 2021
The diagnosis and management of allergic reactions in patients sensitized to non-specific lipid transfer proteins
- Pages: 2433-2446
- First Published: 02 March 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Basic and Translational Allergy Immunology
Breastfeeding promotes early neonatal regulatory T-cell expansion and immune tolerance of non-inherited maternal antigens
- Pages: 2447-2460
- First Published: 12 January 2021
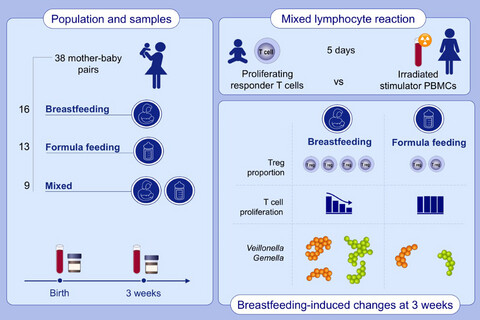
The proportion of Tregs is nearly twofold higher in exclusively breastfed neonates compared with those who received formula milk only. Breastfed neonates show a specific and Treg-dependent reduction in proliferative T-cell responses to non-inherited maternal antigens. Short chain fatty acid producing taxa (Veillonella and Gemella) are enriched in stool samples of exclusively breastfed neonates.
Allergen-specific immunotherapy induces the suppressive secretoglobin 1A1 in cells of the lower airways
- Pages: 2461-2474
- First Published: 02 February 2021
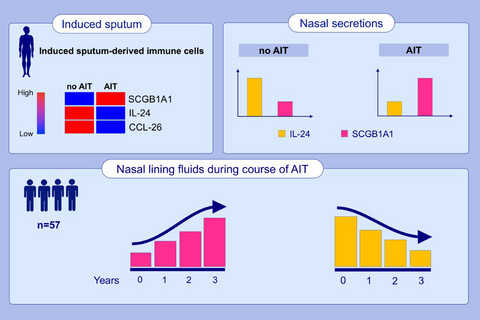
Allergen-specific immunotherapy inhibited pro-inflammatory CXCL8, IL24 and CCL26 mRNA expression in alveolar sputum cells. SCGB1A1 was induced in lower airway cells independently of the asthma status and allergen season. The epithelial type-2 (E2) cytokine IL-24 was reduced following 3 years of AIT-treatment, while SCGB1A1 was significantly increased and identified as a suppressor of epithelial gene expression.
Asthma and Lower Airway Disease
Epithelial expression and role of secreted STC1 on asthma airway hyperresponsiveness through calcium channel modulation
- Pages: 2475-2487
- First Published: 30 December 2020
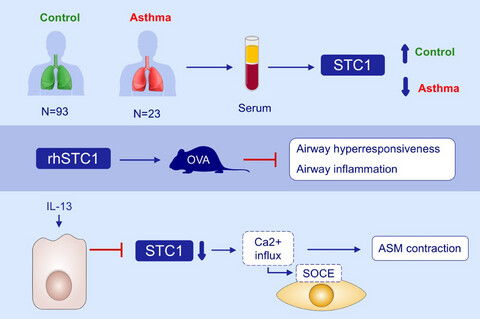
Serum levels of STC1 were decreased in asthma and correlated with asthma control and lung function. STC1 was mainly expressed in the bronchial epithelium and intranasal administration of rhSTC1 reduced AHR and inflammation in mice. IL-13 suppressed STC1 release from 16HBE cells, whereas rhSTC1 blocked SOCE by suppressing STIM1 and further inhibited ASM cell contractility.
Increased day-to-day fluctuations in exhaled breath profiles after a rhinovirus challenge in asthma
- Pages: 2488-2499
- First Published: 11 March 2021
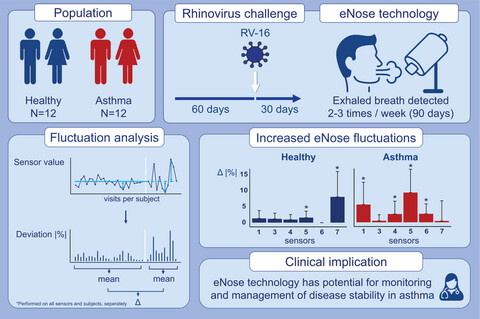
Electronic nose sensor fluctuations increased after a RV-16 challenge in asthmatic and healthy adults, more evidently in asthma. In asthma, the increase in eNose fluctuations occurred before the onset of cold-like symptoms. The magnitude of the change in eNose fluctuations was not correlated with FeNO and cold-like symptoms, but moderately correlated with pre- and post-challenge cytokine levels in asthma.
Rhinitis, Sinusitis, and Upper Airway Disease
Tear N-glycomics in vernal and atopic keratoconjunctivitis
- Pages: 2500-2509
- First Published: 14 February 2021
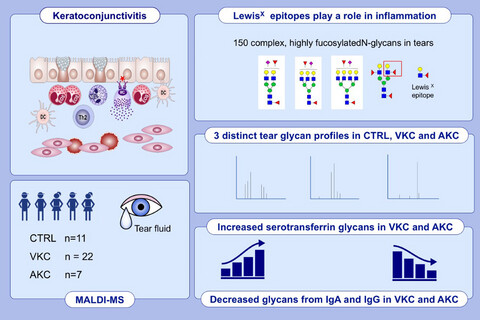
Using MALDI-TOF MS and MALDI-TOF MS/MS techniques, we identify more than 150 different N-glycans in the tear fluid, with LewisX epitopes playing a role in inflammation. There are distinct and unique N-glycome profiles in tear fluid from CTRL, VKC and AKC. Increased intensities of peaks refer to glycans from serotransferrin in VKC and AKC, and decreased intensity of peaks - to IgG and IgA in VKC and AKC compared to CTRLs.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Whole genome sequencing identifies novel genetic mutations in patients with eczema herpeticum
- Pages: 2510-2523
- First Published: 06 February 2021
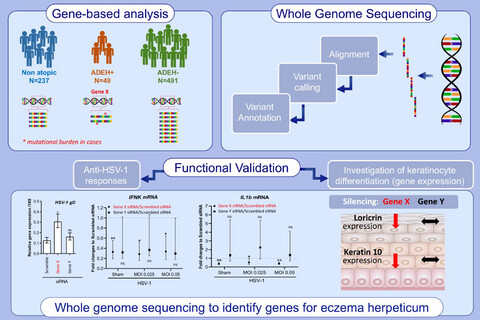
Whole genome sequencing was used to search genome-wide for deleterious genetic variants that are differentially enriched in ADEH+compared to ADEH−and non-atopic controls. A gene-based comparison between cases and controls was used prioritize genes enriched for such variants to be followed up for functional validation. Functional validation reveals two genes: SIDT2 and RBBP8NL are involved in keratinocyte differentiation and responses against HSV-1 infection.
Atopic Dermatitis,Urticaria and Skin Disease
Association between ambient air pollution and development and persistence of atopic and non-atopic eczema in a cohort of adults
- Pages: 2524-2534
- First Published: 18 February 2021
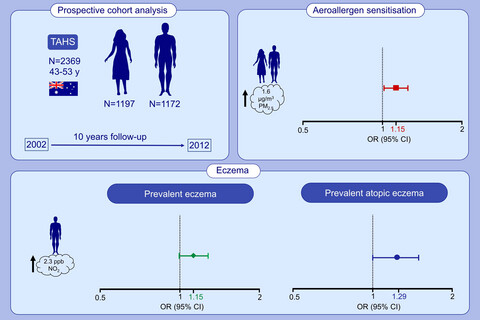
In this population-based prospective cohort study in Australia, we evaluate air pollution association with eczema and allergic sensitisation. After 10 years of follow-up, a 1.6 µg/m3 increase in PM2.5 exposure is associated with increased odds of aeroallergen sensitisation in both sexes. In males, a 2.3 ppb increase in NO2 is associated with increased odds of prevalent eczema and atopic eczema.
Atopic Dermatitis, Urticaria and Skin Disease
Impact of anxiety, stress and depression related to COVID-19 pandemic on the course of hereditary angioedema with C1-inhibitor deficiency
- Pages: 2535-2543
- First Published: 01 March 2021
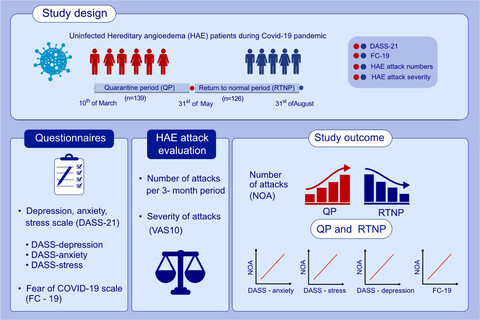
Uninfected HAE patients were assessed in QP and RTNP during COVID-19. A number of HAE attacks, in correlation with DASS-stress, DASS-anxiety, DASS-depression and FC-19 scores, were higher in QP than RTNP, whereas attack severity was not different. COVID-19 outbreak causes an increase in the number of HAE attacks in relation to anxiety, depression, stress and fear of COVID-19. Abbreviations: DASS, depression anxiety stress scale; FC-19, fear of Covid-19 scale; HAE, hereditary angioedema; NOA, number of attacks; QP, quarantine period; RTNP, return to normal period; VAS10, visual analogue scale.
Drug Allergy, Insect Sting Allergy, and Anaphylaxis
Single-dose prolonged drug provocation test, without previous skin testing, is safe for diagnosing children with mild non-immediate reactions to beta-lactams
- Pages: 2544-2554
- First Published: 01 March 2021
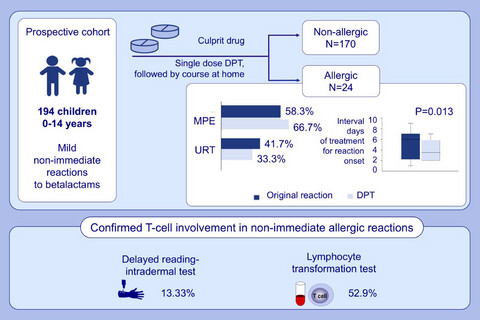
Allergy was confirmed in the 12.4% of children reporting non-immediate reactions to beta-lactams. A shorter interval of days of treatment for reaction onset was found in DPT when comparing with the original reaction, but no differences were found regarding the percentage of experienced symptoms. Delayed reading-intradermal and lymphocyte transformation tests were positive in 13.33% and 52.9% of allergic children, respectively.
Allergen-Specific Immunotherapy and Biologics
IgE-cross-blocking antibodies to Fagales following sublingual immunotherapy with recombinant Bet v 1
- Pages: 2555-2564
- First Published: 16 March 2021
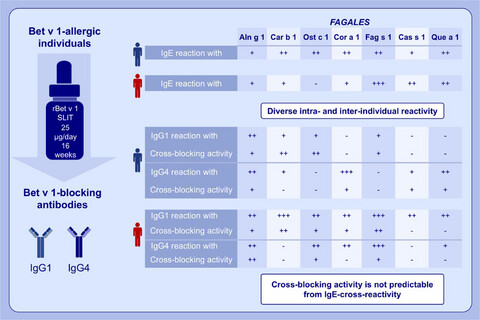
Bet v 1-allergic individuals show IgE cross-reactivity with allergens from Fagales. Sublingual immunotherapy with the reference allergen Bet v 1 induces individually diverse repertoires of cross-reactive IgG1 and IgG4 antibodies. The cross-blocking bioactivity of IgG1 and IgG4 antibodies is highly variable and not predictable from IgE-cross-reactivity.
Low-affinity but high-avidity interactions may offer an explanation for IgE-mediated allergen cross-reactivity
- Pages: 2565-2574
- First Published: 18 April 2021
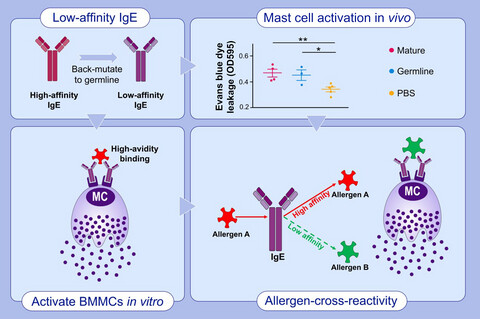
Germline IgE antibodies were of low affinity to allergen. Low-affinity IgE antibodies are able to activate mast cells in vitro and in vivo via high-avidity binding. Allergen A induces specific high-affinity IgE antibodies, but with low affinity to allergen B, which could activate mast cells by high-avidity binding to IgE antibodies. Abbreviations: OD595, optical density 595 nm; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.
Epidemiology and Genetics
Associations between specific IgE sensitization to 26 respiratory allergen molecules and HLA class II alleles in the EGEA cohort
- Pages: 2575-2586
- First Published: 19 March 2021
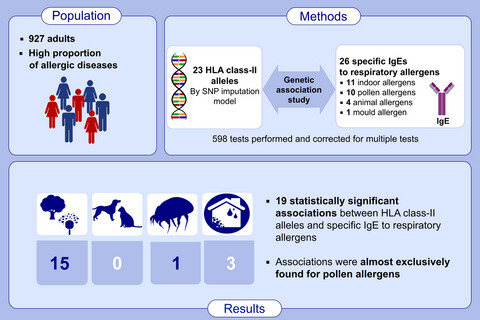
This association study between HLA class-II alleles and specific IgE sensitization to a large panel of aeroallergens reveals 19 statistically significant associations, almost exclusively with pollen allergens. The strongest associations are found for mugwort Art v1, with DQB1*05:01, DQA1*01:01 and DRB1*01:01 alleles. HLA class-II alleles might be specifically associated with sensitization to seasonal allergens. Abbreviations: IgE, immunoglobin E; HLA, human leukocyte antigen.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Are peas a safe food for lipid transfer protein allergic patients?
- Pages: 2587-2589
- First Published: 03 March 2021
Benralizumab restores gene and microRNA expression involved in steroid sensitivity in severe asthma
- Pages: 2589-2592
- First Published: 19 March 2021
Serum sphingosine-1-phosphate is elevated in atopic dermatitis and associated with severity
- Pages: 2592-2595
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Detection of SARS-CoV-2-specific memory B cells to delineate long-term COVID-19 immunity
- Pages: 2595-2599
- First Published: 25 March 2021
Higher risk of allergies at 4–6 years of age after systemic antibiotics in the first week of life
- Pages: 2599-2602
- First Published: 27 March 2021
Multi-omics analyses implicate EARS2 in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 2602-2604
- First Published: 31 March 2021
Skin tests in urticaria/angioedema and flushing to Pfizer-BioNTech SARS-CoV-2 vaccine: Limits of intradermal testing
- Pages: 2605-2607
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Ovomucoid-specific IgD increases in children who naturally outgrow egg allergy in a cross-sectional study
- Pages: 2607-2609
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Severe cold urticaria can point to an underlying clonal mast cell disorder
- Pages: 2609-2613
- First Published: 02 April 2021
GPR109A deficiency promotes IL-33 overproduction and type 2 immune response in food allergy in mice
- Pages: 2613-2616
- First Published: 08 April 2021
Role of salivary microbiome in IL-10 production and efficacy of sublingual immunotherapy
- Pages: 2617-2620
- First Published: 17 April 2021
Dupilumab efficacy in adolescents with uncontrolled, moderate-to-severe asthma: LIBERTY ASTHMA QUEST
- Pages: 2621-2624
- First Published: 27 April 2021
Anaphylaxis in the Emergency Department Unit: Before and during COVID-19
- Pages: 2624-2626
- First Published: 27 April 2021
Characterization of the major allergen, Que ac 1, from sawtooth oak pollen
- Pages: 2626-2629
- First Published: 25 April 2021
NEWS & VIEWS
One Health in allergology: A concept that connects humans, animals, plants, and the environment
- Pages: 2630-2633
- First Published: 04 March 2021
NEWS & VIEWS: LEGENDS OF ALLERGY AND IMMUNOLOGY
Legends of allergology and immunology: Per Brandtzaeg – Pillar of mucosal immunology
- Pages: 2634-2635
- First Published: 22 March 2021
NEWS & VIEWS: ALGORITHMS IN ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Medical algorithm: Diagnosis and treatment of hypersensitivity reactions to cancer chemotherapy
- Pages: 2636-2640
- First Published: 08 March 2021
NEWS & VIEWS: GROUNDBREAKING DISCOVERIES IN IMMUNOLOGY
Emollients for the prevention of atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 2641-2643
- First Published: 04 November 2020
NEWS &VIEWS : CONTROVERSIES IN ALLERGY, ASTHMA AND IMMUNOLOGY
Pros and cons for the role of air pollution on COVID-19 development
- Pages: 2647-2649
- First Published: 18 March 2021






