Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
MINI REVIEW
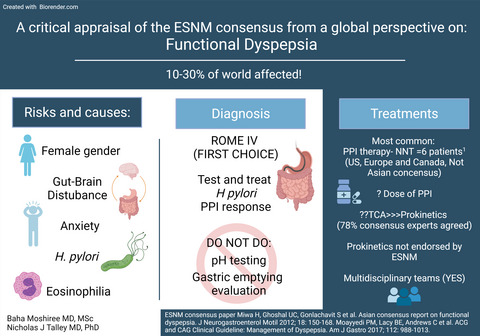
Functional dyspepsia: A critical appraisal of the European consensus from a global perspective
- First Published: 01 August 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
United European Gastroenterology (UEG) and European Society for Neurogastroenterology and Motility (ESNM) consensus on functional dyspepsia
- First Published: 29 September 2021
Current knowledge
-
Functional dyspepsia is one of the most common conditions encountered in clinical practice.
-
There is a lack of guidance for clinicians in guiding diagnosis and treatment of this prevalent condition.
-
No treatments are currently approved for the treatment of functional dyspepsia in Europe.
What is new here
-
A Delphi panel consisting of 41 experts from 22 European countries established the level of consensus on 87 statements regarding functional dyspepsia.
-
The statements reaching consensus serve to guide clinicians in recognizing, diagnosing and treating FD in clinical practice.
-
Endoscopy is mandatory for establishing a firm diagnosis of functional dyspepsia D, but in primary care patients without alarm symptoms or risk factors can be managed without endoscopy.
-
Helicobacter pylori status should be determined in every patient with dyspeptic symptoms and H. Pylori positive patients should receive eradication therapy.
-
Proton pump inhibitor-therapy is considered an effective therapy for FD, but no other treatment approach reached consensus support.
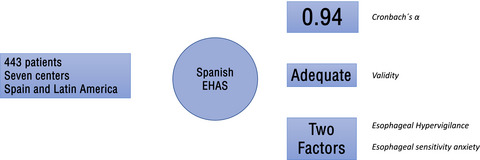
The Spanish version of the esophageal hypervigilance and anxiety score shows strong psychometric properties: Results of a large prospective multicenter study in Spain and Latin America
- First Published: 13 February 2021
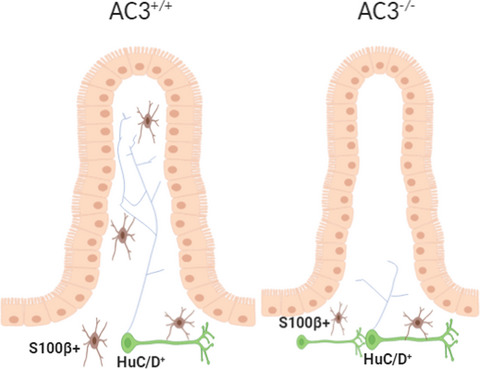
The type 3 adenylyl cyclase is crucial for intestinal mucosal neural network in the gut lamina propria
- First Published: 03 May 2021
Role of enteric dopaminergic neurons in regulating peristalsis of rat proximal colon
- First Published: 03 May 2021
Spatio-temporal mapping of rat colonic wall motion revealed that the D1-like receptor antagonist inhibits peristaltic waves with a colonic constriction, while exogenous dopamine inhibits the waves with a dilatation through the activation of D1-like receptors. Dopamine released from enteric neurons activates nitrergic neurons via D1-like receptors to suppress non-propagating contractions for the generation of coordinated peristalsis.
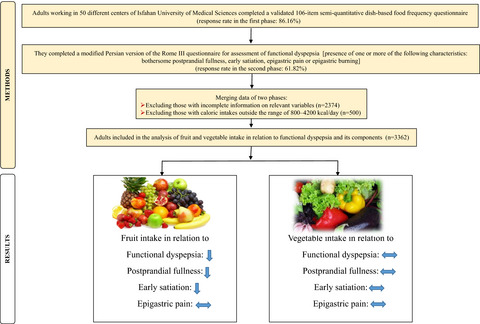
The relationship between fruit and vegetable intake with functional dyspepsia in adults
- First Published: 02 April 2021
Psychometric evaluation of an experience sampling method–based patient-reported outcome measure in functional dyspepsia
- First Published: 02 May 2021
Accurate recording of symptoms is the cornerstone of the clinical evaluation of functional gastrointestinal disorders, including FD. Due to important biases, conventional end-of-day and end-of-week assessment methods of gastrointestinal symptoms are considered suboptimal. Our novel ESM-based PROM is valid and reliable to asses symptoms in FD. The use of ESM-based PROMs in patients with FD has the potential to aid in the shift towards personalised healthcare.
Bicarbonate ion transport by the electrogenic Na+/HCO3− cotransporter, NBCe1, is required for normal electrical slow-wave activity in mouse small intestine
- First Published: 10 April 2021
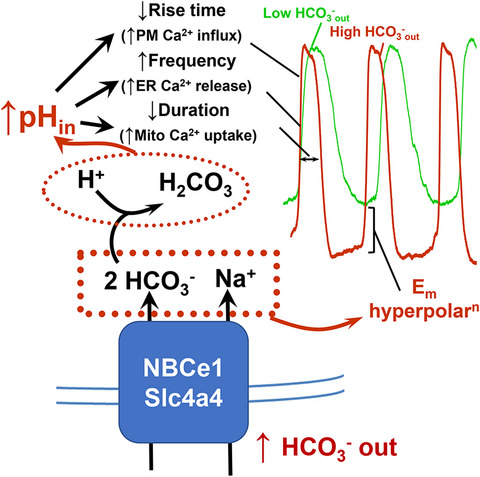
Model for the role of electrogenic Na+/HCO3− cotransport by NBCe1 in slow-wave generation by Interstitial Cells of Cajal (ICC). Transport of extracellular HCO3− results in membrane potential (Em) hyperpolarization, and faster, more frequent slow waves probably by increasing intracellular pH and altering Ca2+ handling in ICC.
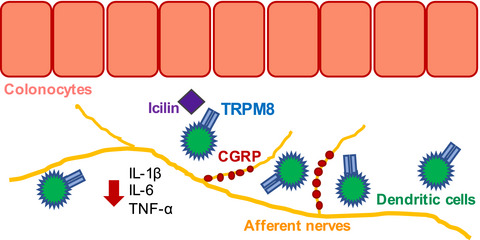
A putative anti-inflammatory role for TRPM8 in irritable bowel syndrome—An exploratory study
- First Published: 19 June 2021
Exploring parameters of gamma transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) and full-spectrum transcranial random noise stimulation (tRNS) on human pharyngeal cortical excitability
- First Published: 03 June 2021
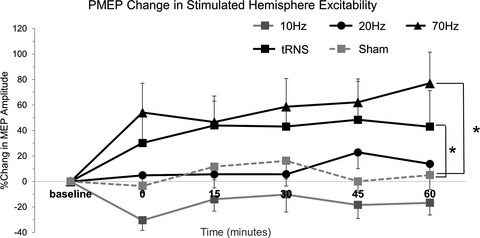
Compared with sham, across time, both 70 Hz transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS) and full-spectrum transcranial random noise stimulation at 1.5 mA for 10 min produced increases in cortical excitability for the pharynx in the conditioned (stimulated) hemisphere (F[1,14] = 9.065, *p = 0.005 and F[1,14] = 5.394, *p = 0.027, respectively), with increases in pharyngeal motor evoked amplitudes of up to +77 ± 24% and +59 ± 30%, respectively. By contrast, 10 Hz tACS appeared to slightly suppress pharyngeal cortical excitability, with a trend to decreased pharyngeal motor evoked amplitudes of −30 ± 7% whereas 20Hz tACS elicited no obvious changes in pharyngeal amplitudes.
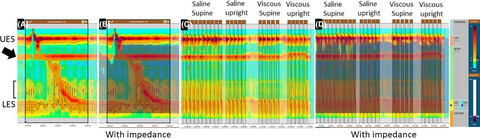
Dysphagia lusoria: utility of high-resolution impedance manometry to identify true disease
- First Published: 01 June 2021
Increased visceral sensitivity, elevated anxiety, and depression levels in patients with functional esophageal disorders and non-erosive reflux disease
- First Published: 14 June 2021
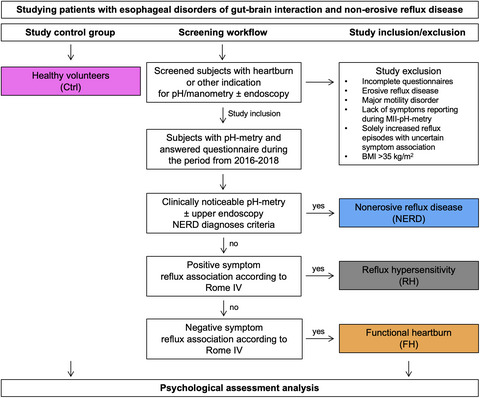
In this study, Losa/Manz et al. investigated whether visceral sensitivity, anxiety, and depression levels are altered in patients with non-erosive reflux disease as well as in patients with functional esophageal disorders, namely reflux hypersensitivity and functional heartburn, as compared to healthy volunteers. The findings presented here are in line with the disease concept of disorders of gut-brain interaction in which psychological comorbidities and visceral hypersensitivity play a major role.
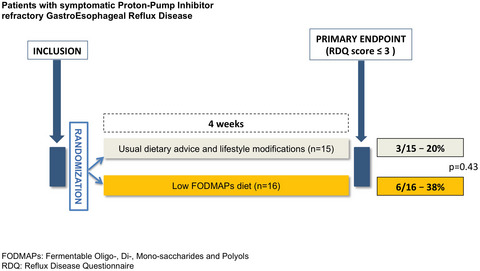
Low FODMAPs diet or usual dietary advice for the treatment of refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease: An open-labeled randomized trial
- First Published: 29 May 2021
Gastric electrical stimulation improves symptoms and need for supplemental nutrition in children with severe nausea and vomiting: A ten-year experience
- First Published: 15 June 2021
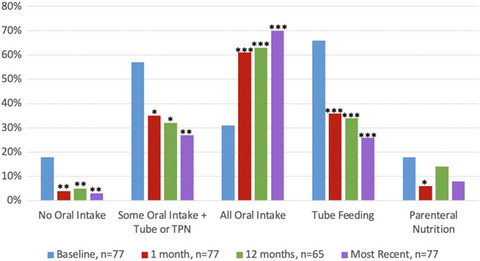
Children with severe nausea and vomiting treated with gastric electrical stimulation experienced significant improvement in their symptoms and ability to tolerate oral nutrition. The use of tube feeding and parenteral nutrition decreased from 73% at baseline to 30% at the most recent follow-up. *denotes p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 when compared to baseline.
Characterizing clinical features and location-specific gene expression profiles associated with pain burden in children with functional dyspepsia
- First Published: 13 June 2021
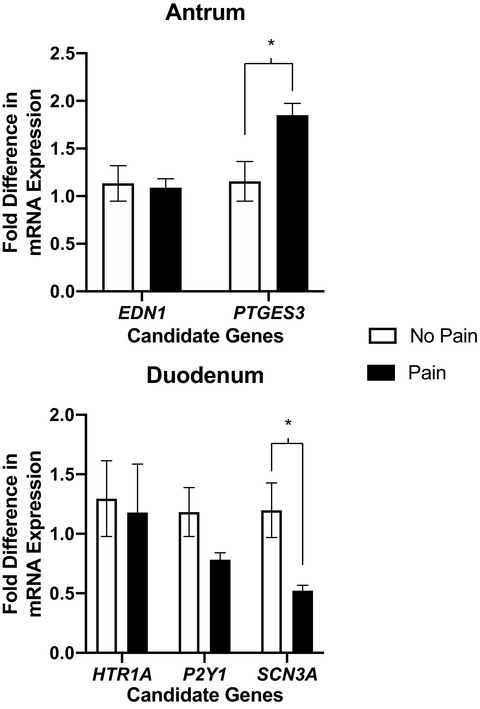
Mean fold differences in candidate gene mRNA expression in antrum (EDN1, PTGES3) and duodenum (HTR1A, P2Y1, SCN3A) biopsies from patients (collapsed across PDS, EPS, PDS+EPS, and EoE) with pain versus those reporting no pain at the time of diagnosis. Cq values of each gene of interest were normalized to the average Cq values of 3 housekeeping genes (GAPDH, ACTB, and B2M) resulting in a ΔCq for each sample. ΔΔCq calculated by normalizing ΔCq from each sample to the average ΔCq for healthy control subjects with EoE as the only pain-free clinical diagnosis. Fold differences in expression are presented as mean ± SEM. Significant differences between groups analyzed with independent samples t test (p < 0.01). * = p < 0.001.
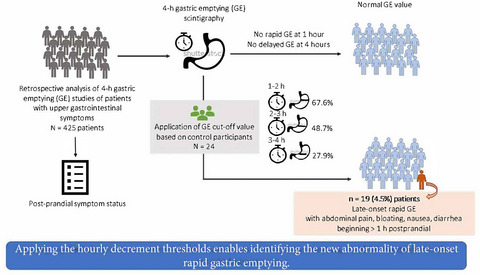
Late-onset rapid gastric emptying: Identification of a new abnormal finding in patients with otherwise normal results on gastric emptying scintigraphy
- First Published: 25 September 2021