Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
MINI REVIEW
REVIEWS
Chronic constipation in adults: Contemporary perspectives and clinical challenges. 2: Conservative, behavioural, medical and surgical treatment
- First Published: 01 February 2021
Translating the seminal findings of Carl Lüderitz: A description in English of his extraordinary studies of gastrointestinal motility accompanied by a historical view of peristalsis
- First Published: 11 October 2020

The painting from Elisabeth Lüderitz shows Dr. Carl Lüderitz standing to the right. Carl Lüderitz provided the first comprehensive description of peristalsis in 1889, 10 years before Bayliss and Starling described the peristaltic reflex. At that time, the peristaltic reflex was referred to as the Lüderitz–Bayliss–Starling reflex. This review provides a short biography of Dr. Carl Lüderitz, a translation of his 1889 paper, honors his contributions, and reviews the history of peristalsis.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
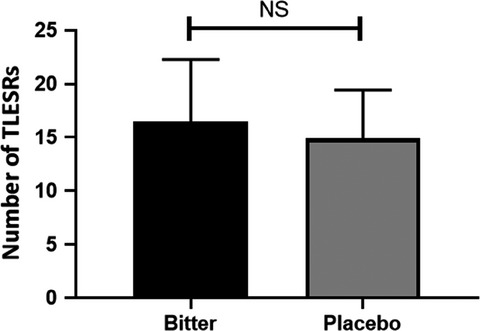
The bitter tastant denatonium benzoate has no influence on the number of transient lower esophageal sphincter relaxations in health
- First Published: 29 December 2020
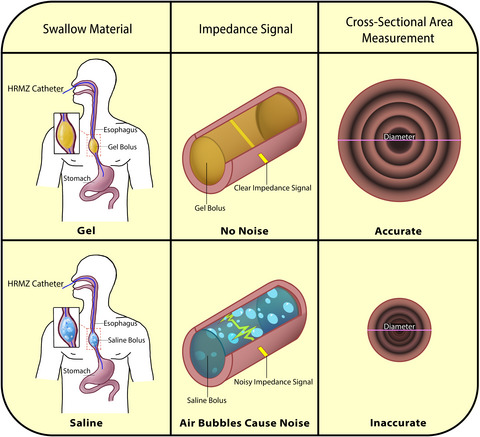
Novel gel bolus to improve impedance-based measurements of esophageal cross-sectional area during primary peristalsis
- First Published: 29 December 2020
Gastrointestinal medication burden among persons with the Ehlers-Danlos syndromes
- First Published: 03 January 2021
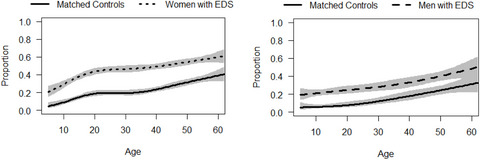
44% of women and 25.3% of men with EDS had prescription claims for at least one class of GI drugs compared with 19.2% and 9.6% of controls, respectively (P < .0001). Note the peripubertal increase in GI prescriptions among women with EDS, which adds to the evidence of worsening EDS disease burden among peripubertal females, as well as a critical time window for future research.
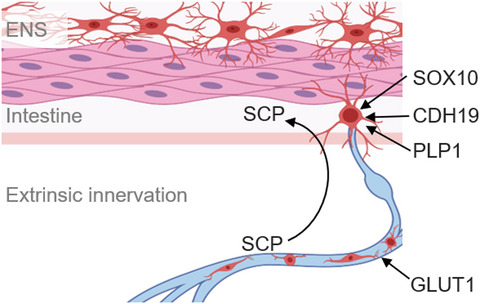
Neurons populating the rectal extrinsic nerves in humans express neuronal and Schwann cell markers
- First Published: 31 December 2020
Mental distress among adult patients with eosinophilic esophagitis
- First Published: 31 December 2020
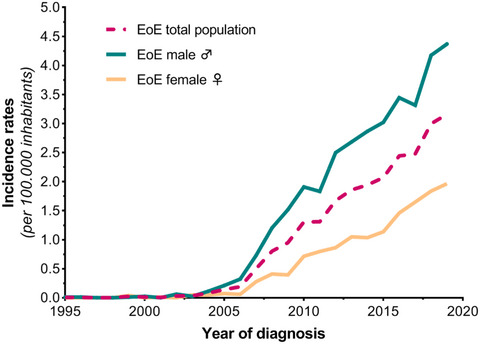
Emerging incidence trends of eosinophilic esophagitis over 25 years: Results of a nationwide register-based pathology cohort
- First Published: 10 January 2021
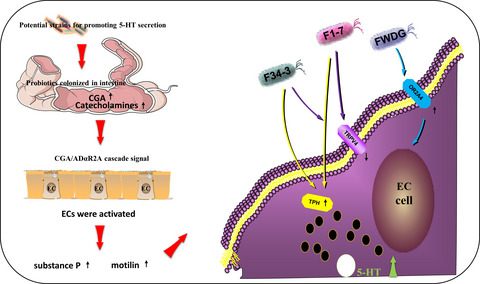
Mechanisms underlying the promotion of 5-hydroxytryptamine secretion in enterochromaffin cells of constipation mice by Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus
- First Published: 15 January 2021
Esophageal pH increments associated with post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic waves show the occurrence and relevance of esophago-salivary reflex in clinical setting
- First Published: 20 January 2021
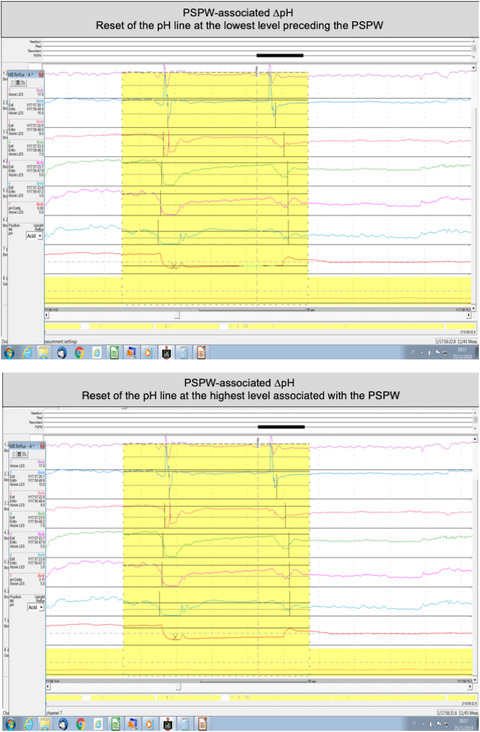
Remarkable increments of esophageal pH (∆pH) were found to be associated with post-reflux swallow-induced peristaltic waves (PSPWs), showing the occurrence of esophago-salivary reflex in clinical setting. PSPW-associated ∆pH was significantly lower in PPI-refractory than in PPI-responsive reflux-related heartburn, representing a predictor of PPI response.
Gastric accumulation of enteral nutrition reduces pressure changes induced by phasic contractility in an isovolumetric intragastric balloon
- First Published: 03 February 2021
Impact of joint hypermobility syndrome on gastric accommodation and nutrient tolerance in functional dyspepsia
- First Published: 02 February 2021
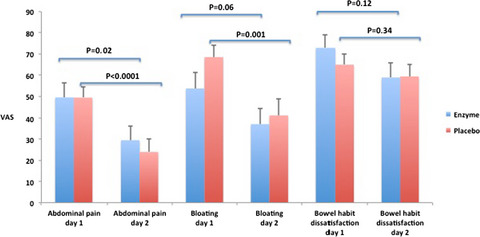
A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled crossover pilot study: Acute effects of the enzyme α-galactosidase on gastrointestinal symptoms in irritable bowel syndrome patients
- First Published: 22 February 2021
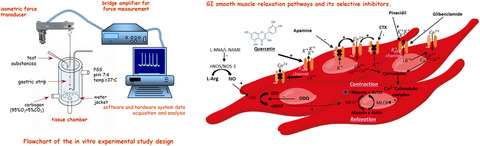
Quercetin relaxes human gastric smooth muscles directly through ATP-sensitive potassium channels and not depending on the nitric oxide pathway
- First Published: 02 February 2021
Motor patterns in the proximal and distal mouse colon which underlie formation and propulsion of feces
- First Published: 15 February 2021
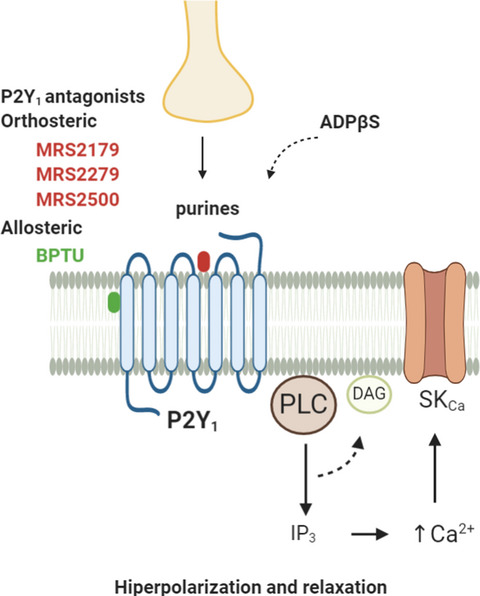
Different responses of the blockade of the P2Y1 receptor with BPTU in human and porcine intestinal tissues and in cell cultures
- First Published: 22 February 2021
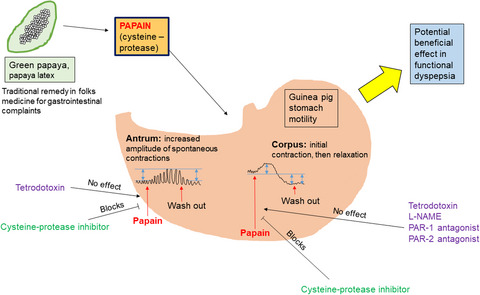
Region-specific effects of the cysteine protease papain on gastric motility
- First Published: 12 March 2021
TECHNICAL NOTE
Chicago Classification update (version 4.0): Technical review on diagnostic criteria for achalasia
- First Published: 30 June 2021
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Reply: The key to success: Targeting enzymes to their dietary counterpart
- First Published: 21 June 2021