Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Comparing safety of proton-pump inhibitors versus H2-receptor antagonists in kidney transplant recipients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 567-574
- First Published: 20 December 2021
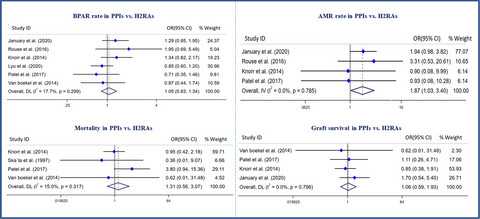
This systematic review and meta-analysis show that the risk of biopsy-proven acute rejection, patients mortality, graft loss, and infection-related outcomes do not differ between kidney transplant patients who use PPIs versus those who take H2RAs as acid suppressant agents. The higher rates of antibody mediated rejection and hypomagnesemia, and lower level of kidney function at one year after transplantation were seen in the PPIs group.
Risk of cardiovascular disease in breast cancer patients receiving aromatase inhibitors vs. tamoxifen: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 575-587
- First Published: 04 January 2022
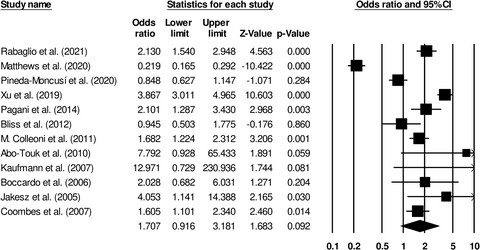
This study compared the cardiovascular adverse outcomes in patients with breast cancer receiving tamoxifen & aromatase inhibitors. The study reports an insignificant increase in the events of stroke, angina, myocardial infarction & heart failure in breast cancer patients treated with aromatase inhibitors as compared to tamoxifen.
Challenges for expansion of thoracic transplant clinical pharmacy in a developing country: comparison with U.S. accredited centres and call for action
- Pages: 588-591
- First Published: 28 November 2021
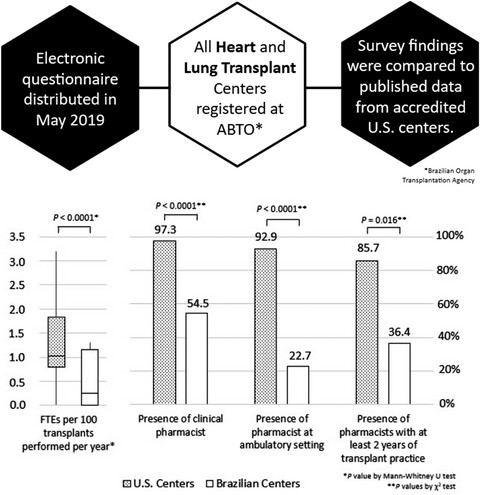
An electronic questionnaire was distributed to all 40 heart and lung transplant centres in Brazil to explore clinical pharmacy activities and compared them with accredited programs in the United States. From 22 centres respondents, ten (45.5%) declared not to have a pharmacist at any part of the transplantation process, which translated into 158 (37.6%) transplant recipients without any direct pharmaceutical care. When compared to U.S. centres, there was a significantly lower insertion of clinical pharmacist activities among Brazilian centres.
Evaluation of desensitization protocols to betalactam antibiotics
- Pages: 592-599
- First Published: 24 November 2021
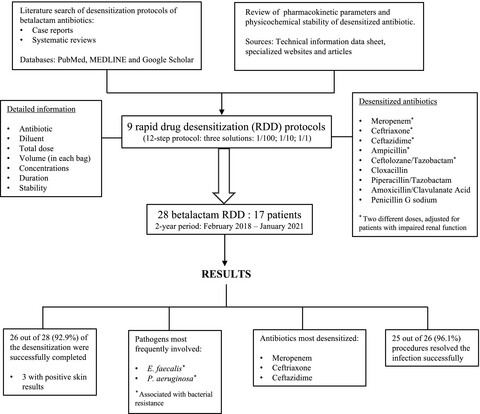
Betalactam antibiotic desensitization may be a key therapeutic option for treating multidrug-resistant infections in patients with confirmed allergy and in those strongly suspected to have Type I hypersensitivity. Detailed information about compounding, dilution and stability is crucial to ensure safe and successful desensitization processes.
Machine learning-based method for tacrolimus dose predictions in Chinese kidney transplant perioperative patients
- Pages: 600-608
- First Published: 21 November 2021
Correlation between CA12 and TFF3 and their prediction value of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in breast cancer
- Pages: 609-618
- First Published: 28 February 2022
Intervention fidelity and process outcomes of the IMMENSE study, a pharmacist-led interdisciplinary intervention to improve medication safety in older hospitalized patients
- Pages: 619-627
- First Published: 21 December 2021
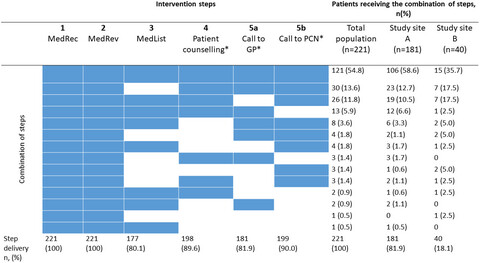
The IMMENSE study is a randomized controlled trial investigating the impact of a multi-step pharmacist-led interdisciplinary intervention on emergency medical visits. We found that 54.8% of patients received all intervention steps if appropriate. Many discrepancies and medication-related problems were identified and solved for the patients and may explain a potential effect of the IMMENSE study.
Comparison of antimicrobial dosing recommendations in patients receiving intermittent hemodialysis among drug information resources
- Pages: 628-635
- First Published: 05 December 2021
This study informs inconsistent antimicrobial dosing recommendations among four common drug information resources for patients receiving hemodialysis. Lack of clinical relevance was noted in many studies referenced in these resources to determine an optimal antimicrobial dosing for hemodialysis patients in contemporary practice.
Three new categories of hypoglycaemic agents and various cardiovascular diseases: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 636-642
- First Published: 23 December 2021
Clinical outcomes and safety of osimertinib plus anlotinib for patients with previously treated EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC: A retrospective study
- Pages: 643-651
- First Published: 12 January 2022
Clinical practice guidelines for management of dual antiplatelet therapy in patients with noncardiac surgery: A critical appraisal using the AGREE II instrument
- Pages: 652-661
- First Published: 23 December 2021
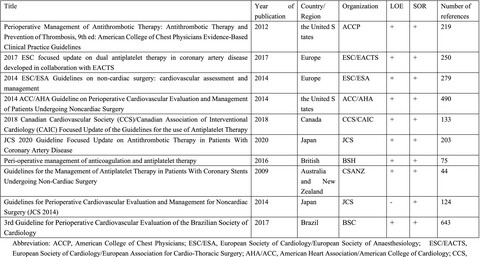
The ACCP, ESC/ESA and ACC/AHA CPGs were recommended. There is a need for high-quality prospective studies assessing different management strategies on this issue. Given the lack of consensus, the results of this study will help to guide perioperative dual antiplatelet management strategies for patients with coronary stents who are undergoing noncardiac surgery.
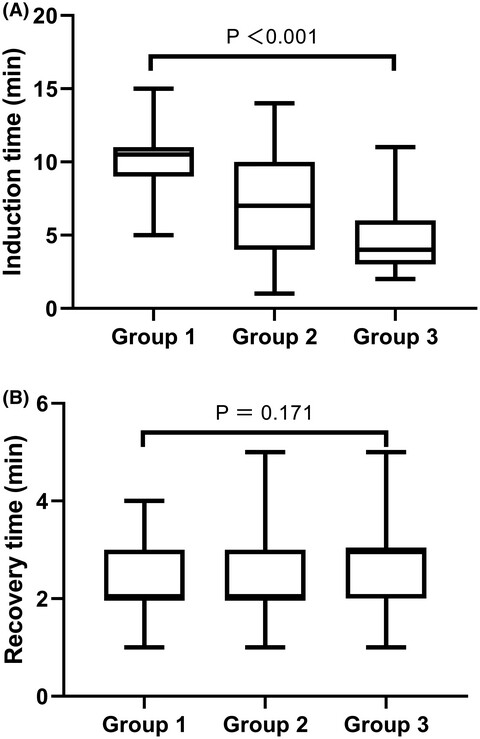
Body mass index and pharmacodynamics of target-controlled infusion of propofol: A prospective non-randomized controlled study
- Pages: 662-667
- First Published: 11 January 2022
Assessment of Anti-Xa activity in patients receiving concomitant apixaban with strong p-glycoprotein inhibitors and statins
- Pages: 668-675
- First Published: 15 January 2022
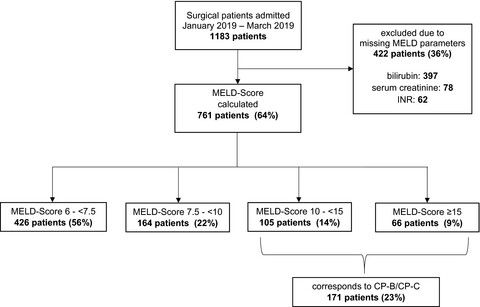
Feasibility of the MELD score as a screening tool for pharmacists to identify patients with impaired hepatic function at hospital admission
- Pages: 676-684
- First Published: 10 January 2022
The epidemiology of apnoea of prematurity
- Pages: 685-693
- First Published: 11 January 2022
Administering esomeprazole subcutaneously via a syringe driver in the palliative demographic: A case series
- Pages: 694-698
- First Published: 27 December 2021
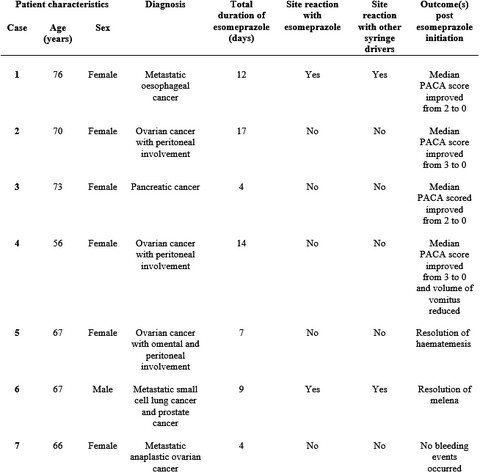
Esomeprazole when administered via a syringe driver over 24 hours appears well tolerated and effective for the prophylaxis of gastrointestinal bleeding, prevention of re-bleeding, and for the symptomatic management of both dyspepsia, and reflux. Overall, this series adds to the limited evidence base for using subcutaneous proton pump inhibitors in the palliative demographic.
Letermovir and maribavir for pan-resistant cytomegalovirus infection in a patient with haematologic malignancy: Consideration for combination therapy
- Pages: 699-702
- First Published: 12 January 2022
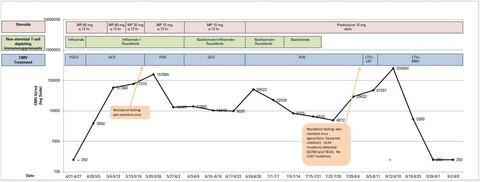
CMV viral load by date and medications. The black line represents the CMV viral load measured in IU/ml over time. The orange arrows indicate the timing and results of resistance testing. The blue block shows the antiviral treatment for CMV the patient was receiving on the corresponding dates. The green blocks demonstrate the patient's treatment for GVHD with non-steroidal T cell–depleting immunosuppressants (ruxolitinib, infliximab, basiliximab), and the pink blocks indicate the steroid dose our patient received for GVHD. Our patient's CMV PCR decreased dramatically upon initiation of maribavir and letermovir. Abbreviations: MP, methylprednisolone; VGCV, valganciclovir; GCV, ganciclovir; FOS, foscarnet; LTV, letermovir; LEF, leflunomide; MBV, maribavir.
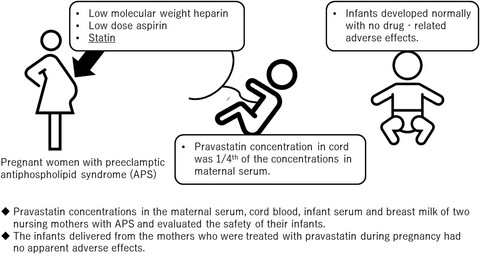
Pravastatin concentrations in maternal serum, umbilical cord serum, breast milk and neonatal serum during pregnancy and lactation: A case study
- Pages: 703-706
- First Published: 23 December 2021
Does COVID-19 increase tacrolimus levels in kidney transplant recipients?
- Pages: 707-708
- First Published: 23 December 2021
Comment on: ‘Detecting drug-drug interactions that increase the incidence of long QT syndrome using a spontaneous reporting system’ by Matsuo et al
- Pages: 709-710
- First Published: 28 December 2021
Retraction: Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide (CGRP) Antagonists: A comprehensive review of safety, efficacy and prescribing information
- Page: 711
- First Published: 13 December 2021