Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- Page: i
- First Published: 27 November 2021
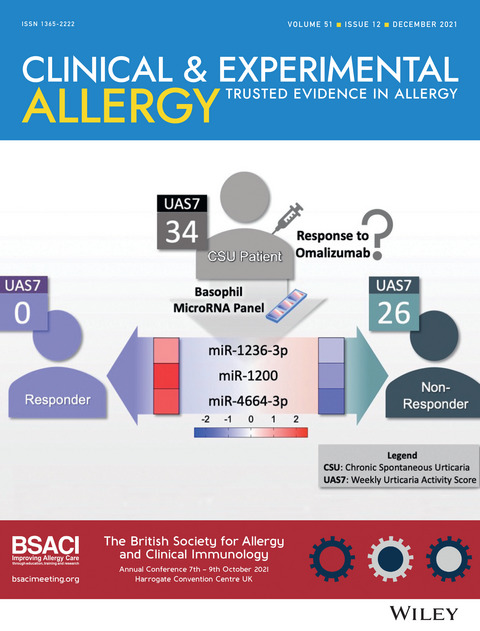
The cover image is based on the Research Letter Unique basophil microRNA signature in chronic spontaneous urtricaria patients who respond to omalizumab by William Reed Henderson et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.14014.
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIALS
Allergic diseases and novel targets in allergen immunotherapy
- Pages: 1526-1528
- First Published: 27 November 2021
Prize-winning abstracts from BSACI 2021 meeting
- Pages: 1529-1530
- First Published: 27 November 2021
REVIEW ARTICLES
Developments in the field of allergy in 2020 through the eyes of Clinical and Experimental Allergy
- Pages: 1531-1537
- First Published: 09 November 2021
Type 2 immunity-driven diseases: Towards a multidisciplinary approach
- Pages: 1538-1552
- First Published: 07 October 2021
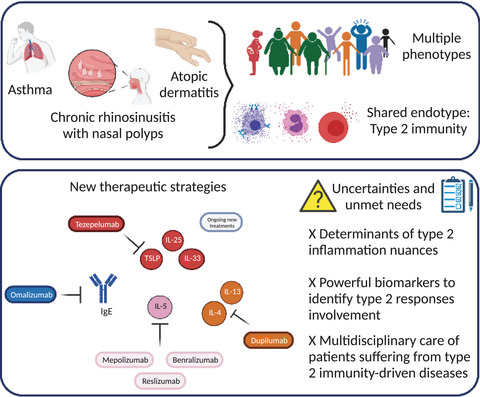
Heterogenic diseases as asthma, atopic dermatitis and chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis can be divided into multiple phenotypes. Such clinical presentations share common pathophysiological paths among with type 2 immunity play an important role. Better understanding of the mechanisms underlying type 2 responses allowed the successful development of specific therapeutic strategies. Indeed, biotherapies are now available to target key actors like the immunoglobulin E, the interleukin (IL) 5, the IL-4 and IL-13 pathway and more recently, the thymic stromal lymphopoietin. Even though those innovations improve the healthcare of type-2 mediated diseases, unmet needs remain to be resolved. Graphic abstract created with BioRender.com
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Asthma and Rhinitis
Role of autophagy in regulating interleukin-10 and the responses to corticosteroids and statins in asthma
- Pages: 1553-1565
- First Published: 10 January 2021
Increased epithelial galectin-13 expression associates with eosinophilic airway inflammation in asthma
- Pages: 1566-1576
- First Published: 02 June 2021
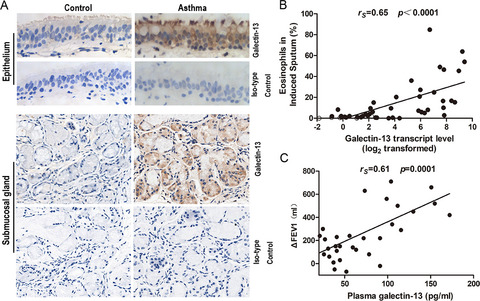
Galectin-13 is markedly increased in subjects with asthma and is mainly expressed in airway epithelial cells and submucosal gland cells. Increased galectin-13 expression associates with airway eosinophilic inflammation and may be a candidate signature gene for type 2 status in asthma. Plasma galectin-13 level may be useful for predicting responses to asthma therapy during treatment with inhaled corticosteroid.
Sputum microRNA-screening reveals Prostaglandin EP3 receptor as selective target in allergen-specific immunotherapy
- Pages: 1577-1591
- First Published: 12 September 2021
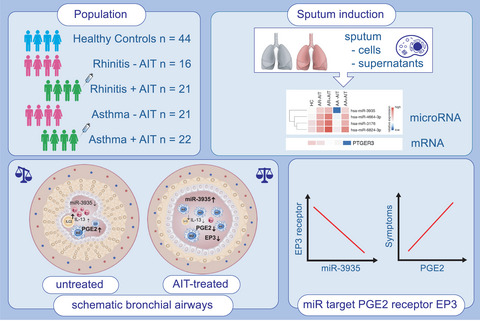
miR-3935 is upregulated in sputum cells of allergic asthma patients, who received allergen-specific immunotherapy treatement, while mRNA levels of its predicted target, the prostaglandin E2 receptor, is downregulated as its ligand PGE2 as well. PGE2 is strongly upregulated in sputum supernatants of untreated allergic patients and is reduced in patients, who received allergen-specific immunotherapy. PGE2 levels correlate with clinical parameters, like eosinophils and symptom score.
Basic Mechanisms in Allergic Disease
Microbiome and mycobiome interaction in house dust mites and impact on airway cells
- Pages: 1592-1602
- First Published: 04 June 2021
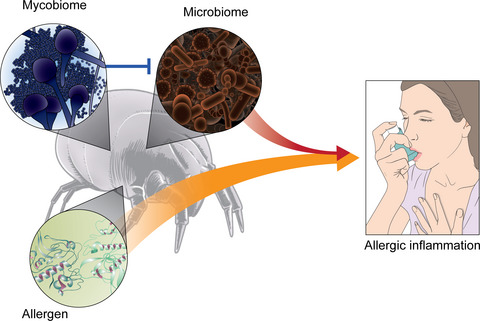
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of airway epithelial cells treated with extracts from Dermatophagoides farinae, D. pteronyssinus, and Tyrophagus putrescentiae reveal microbiome and mycobiome interaction in the mites and impact on allergic airway inflammation. D. farinae harbors a large amount of bacteria, which exerts a synergistic effect on allergic inflammation in vitro. D. pteronyssinus hosts a large amount of Aspergillus penicillioides, which suppresses bacterial microbiome growth in the mite.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A qualitative and quantitative comparison of IgE antibody profiles with two multiplex platforms for component-resolved diagnostics in allergic patients
- Pages: 1603-1612
- First Published: 14 September 2021
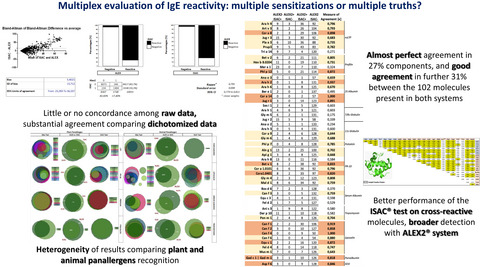
Little or no concordance among raw data, substantial agreement comparing dichotomized data (94,3% concordant results). Heterogeneity of results comparing plant and animal panallergens recognition of the two methods Almost perfect agreement in 27% components, and good in further 31% between the 102 molecules present in both systems Binding with carbohydrate determinants abolished in 60% of cases with ALEX system Better performance of the ISAC® test on cross-reactive molecules, wider patients identification with ALEX2® system.
Allergens
Molecular and immunochemical characterization of Pop n 2: A new allergen of Populus nigra pollen
- Pages: 1613-1623
- First Published: 19 November 2020
Clinical and immunological evaluation of cat-allergic asthmatics living with or without a cat
- Pages: 1624-1633
- First Published: 02 October 2021
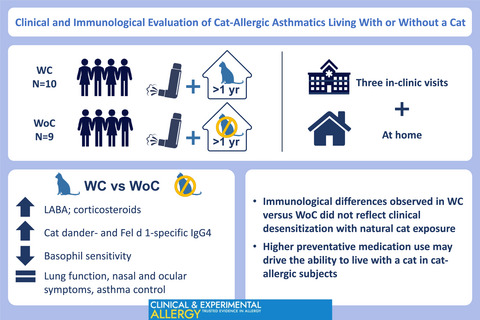
Exploratory study characterizing the impact of daily cat exposure in cat-allergic subjects living with/without cats (WC/WoC). Cat dander- and Fel d 1-specific IgG4 concentrations were higher in WC versus WoC subjects (p < .05); lower basophil sensitivity to cat dander extract/Fel d 1 in WC versus WoC subjects (p < .05) correlated with higher IgG4 concentrations (r = 0.63; p = .009). Immunological differences not reflected in clinical tolerance with cat exposure. Fel d 1, major cat allergen; Ig, immunoglobulin; WC, with cat; WoC, without cat.
RESEARCH LETTERS
House dust mite sensitization is associated with food sensitization in early-onset atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 1634-1636
- First Published: 26 May 2021
Non-asthmatic eosinophilic bronchitis is characterized by proximal airway eosinophilic inflammation as compared with classic asthma and cough variant asthma
- Pages: 1637-1640
- First Published: 26 July 2021
Clinical, serological and basophil response to a wasp sting in patients with European hornet sting anaphylaxis
- Pages: 1641-1644
- First Published: 05 August 2021
Environmental exposure of Der p 23 in household dust samples
- Pages: 1645-1647
- First Published: 24 August 2021
Unique basophil microRNA signature in chronic spontaneous urticaria patients who respond to omalizumab
- Pages: 1648-1652
- First Published: 14 September 2021
ABSTRACT
British Society for Allergy and Immunology (BSACI) Abstracts of the 2021 Annual Meeting
- Pages: 1653-1695
- First Published: 22 November 2021





