Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 05 September 2024

The cover image is based on the article Tetrahedral framework nucleic acid–based small-molecule inhibitor delivery for ecological prevention of biofilm by Yuhao Liu et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13678.
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
AAV-mediated gene therapy restores natural fertility and improves physical function in the Lhcgr-deficient mouse model of Leydig cell failure
- First Published: 30 May 2024
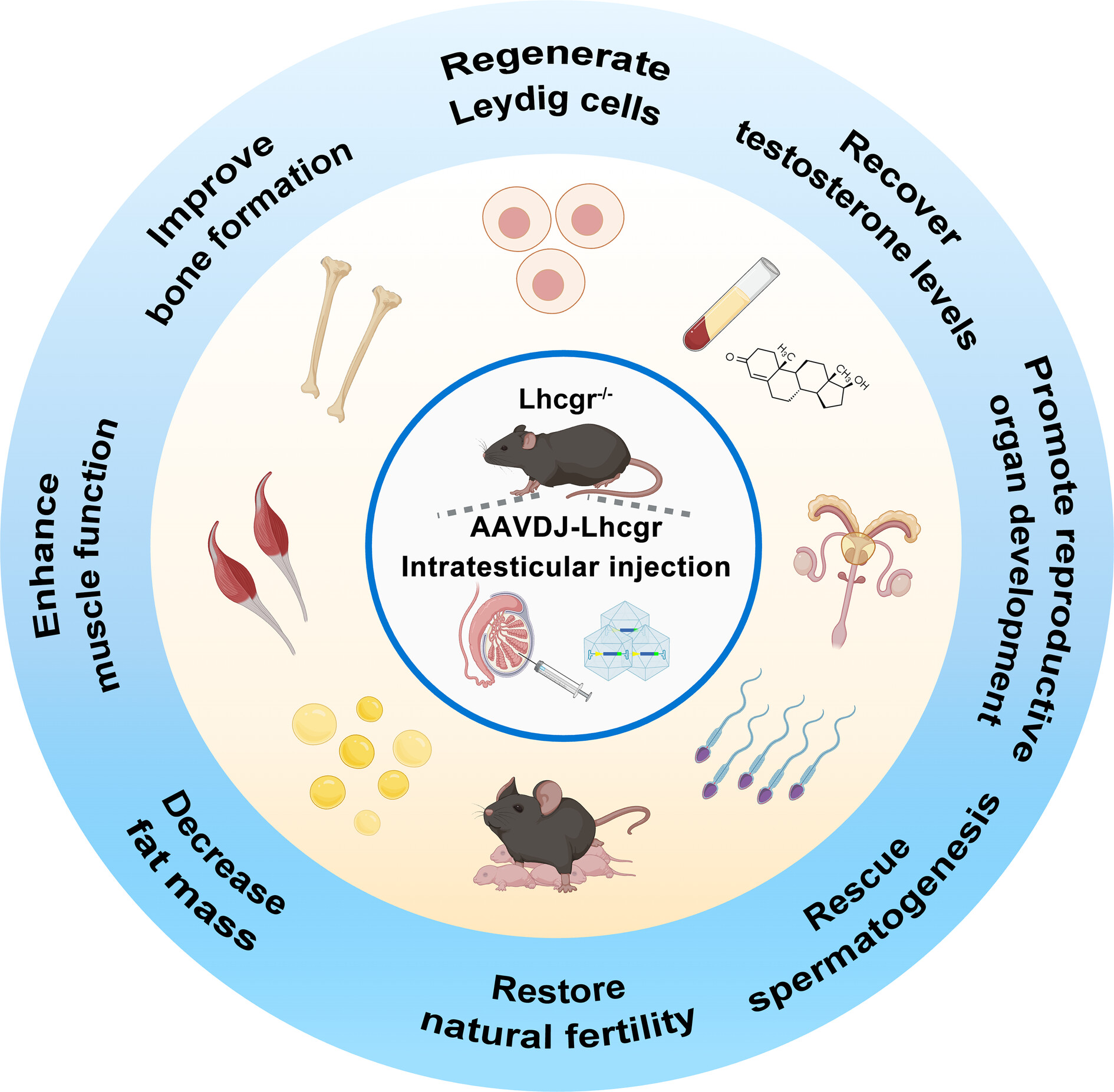
This study conducted AAV vectors scanning and pinpointed AAVDJ as highly efficient for targeting Leydig cell progenitors. Intratesticular injection of AAVDJ-Lhcgr in the Leydig cell failure mouse model (Lhcgr−/−) exhibited excellent tolerance, recovered testosterone production, resumed sexual development, rescued spermatogenesis, restored natural fertility, produced fertile offspring and improved physical function.
RNA m6A modification regulates cell fate transition between pluripotent stem cells and 2-cell-like cells
- First Published: 01 July 2024
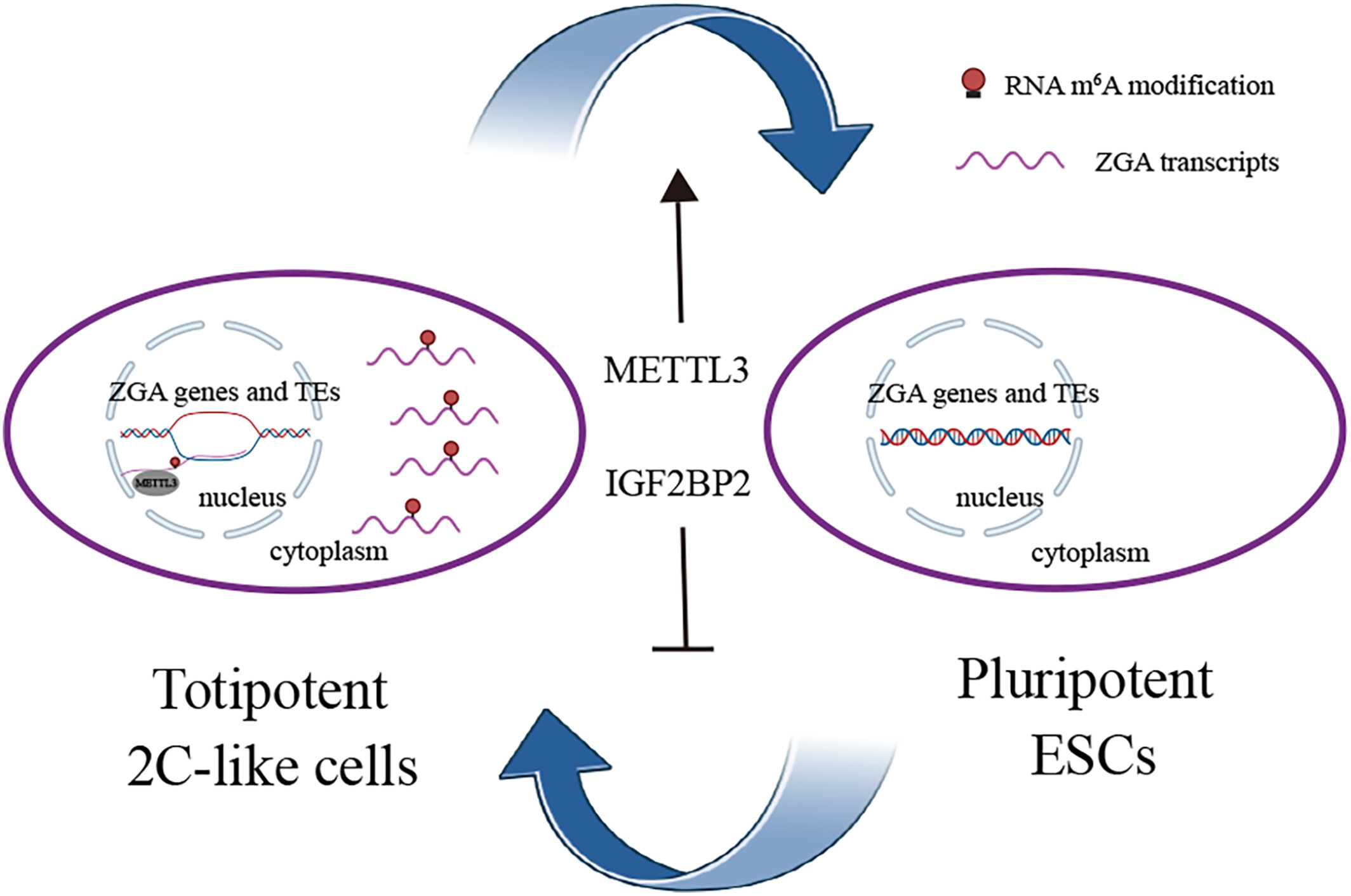
Su et al. show that RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modifications are preferentially enriched in zygotic genome activation (ZGA) transcripts and MERVL with high abundance in 2C-like cells and can facilitate the exit of the 2C-like state. Inhibition of m6A effectors can increase the stability of ZGA transcripts and expand the population of 2C-like cells.
REVIEW
Methylation modifications in tRNA and associated disorders: Current research and potential therapeutic targets
- First Published: 28 June 2024
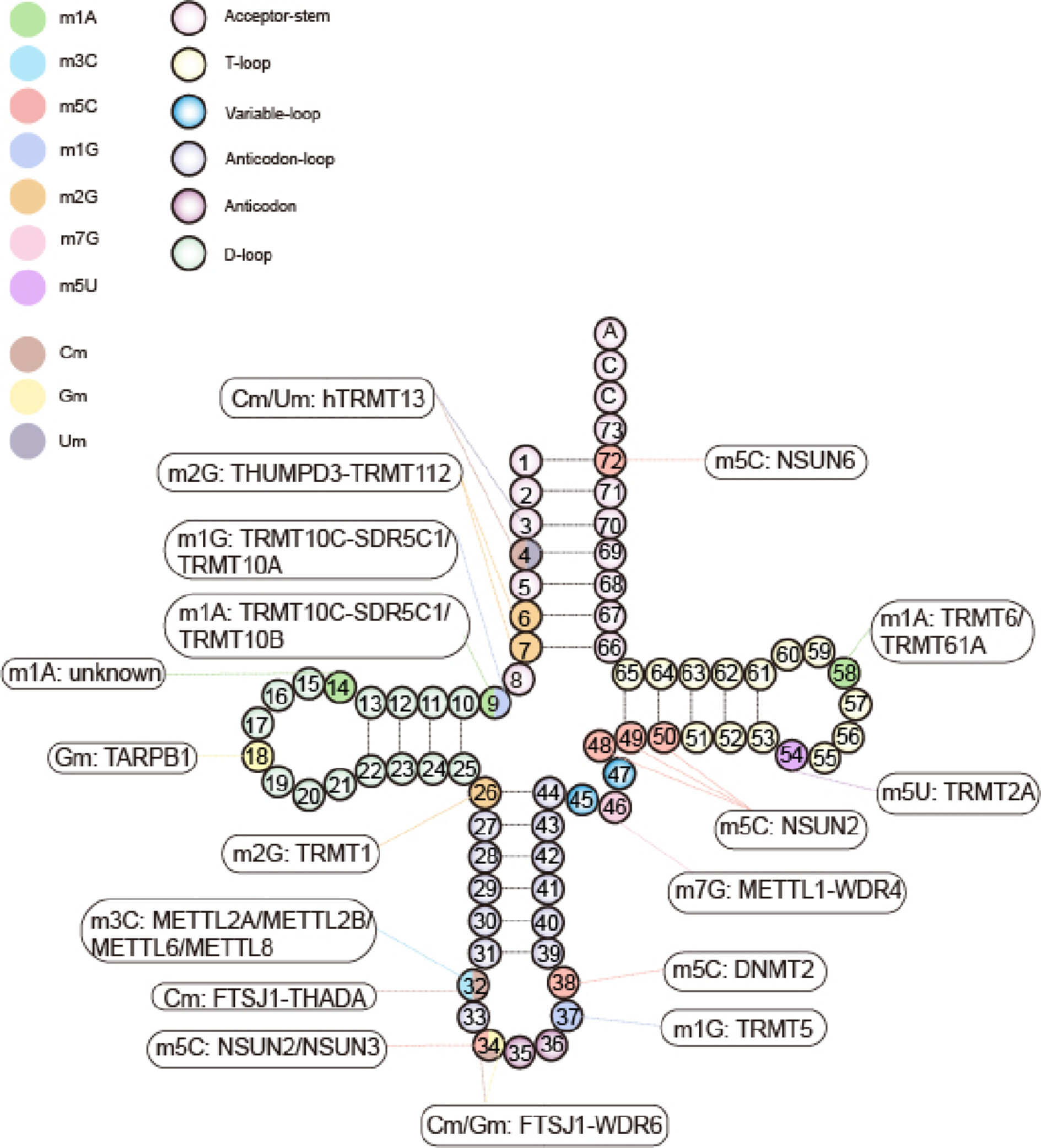
Dysregulation of tRNA methylation modifications and their associated enzymes has been implicated in a spectrum of diseases, including cancer and neurological disorders. Further exploration is warranted to fully elucidate the diagnostic and therapeutic potential of tRNA methylations in human diseases.
Endothelial progenitor cells for fabrication of engineered vascular units and angiogenesis induction
- First Published: 25 July 2024
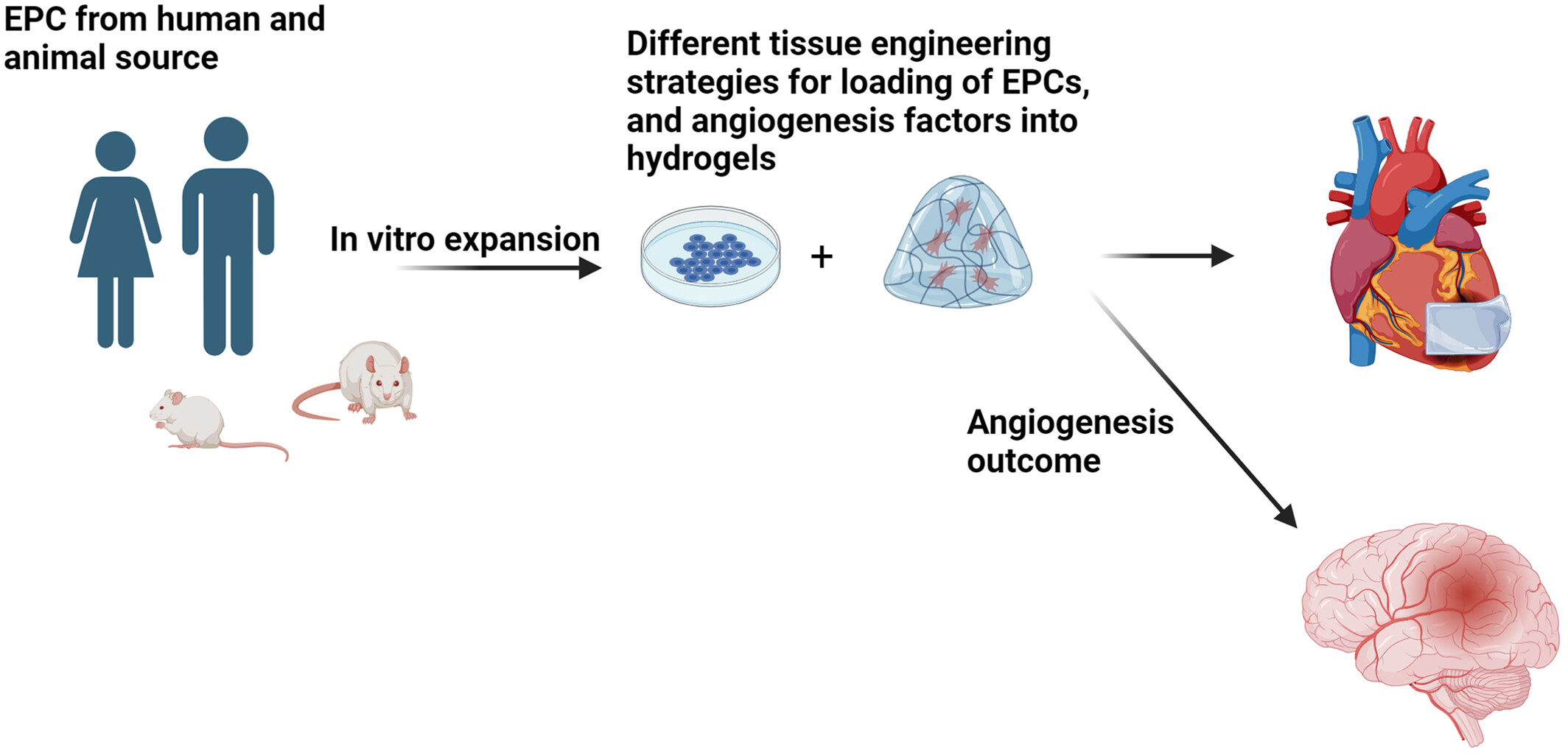
The current review article highlights the angiogenesis properties of endothelial progenitor cells as valid cell sources for the induction of angiogenesis using various tissue engineering modalities. The application of different substrates with several synthesis protocols was also discussed in detail.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
GATAD2B is required for pre-implantation embryonic development by regulating zygotic genome activation
- First Published: 12 April 2024
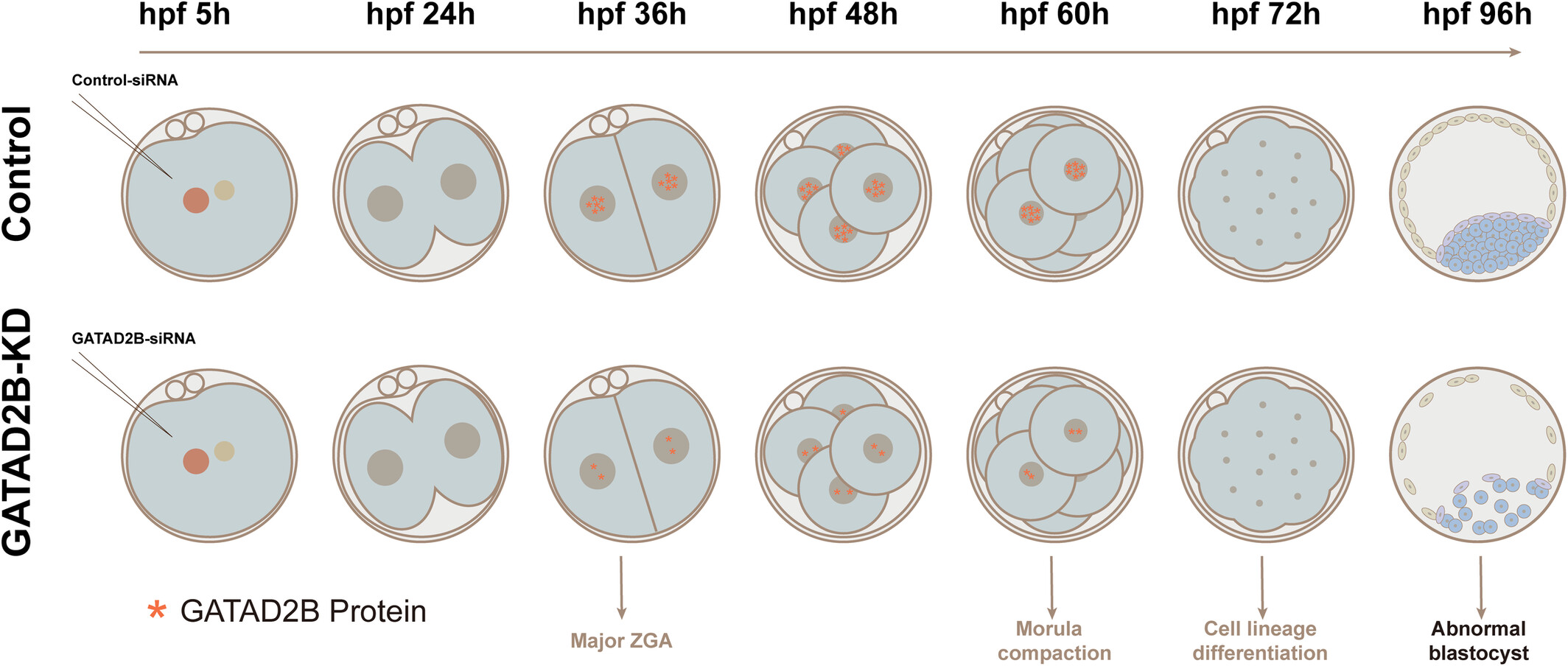
Major ZGA occurs at the late-2 cell stage and involves the activation of thousands of genes, supporting early embryonic development. GATAD2B is one of the core subunits of the nucleosome remodelling and histone deacetylation (NuRD) complex. Our results demonstrate that GATAD2B is essential for pre-implantation embryonic development, in part through facilitating ZGA.
Melatonin promotes hair regeneration by modulating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway
- First Published: 21 May 2024
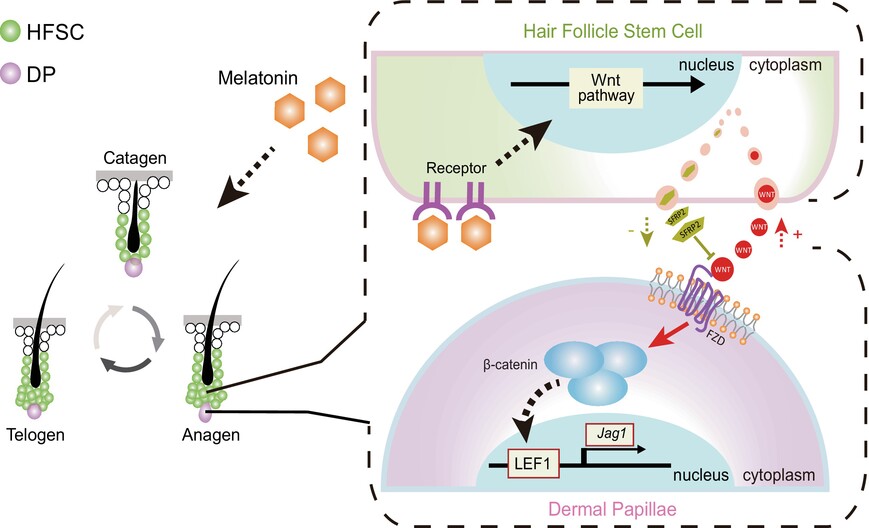
Melatonin up-regulates the release of Wnt3a and Wnt5a in HFSCs and down-regulates the expression of SFRP2, which promotes the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in DP. The addition of melatonin significantly activates the Wnt signalling pathway in DP, which ultimately affects hair regeneration.
Tetrahedral framework nucleic acid–based small-molecule inhibitor delivery for ecological prevention of biofilm
- First Published: 29 May 2024
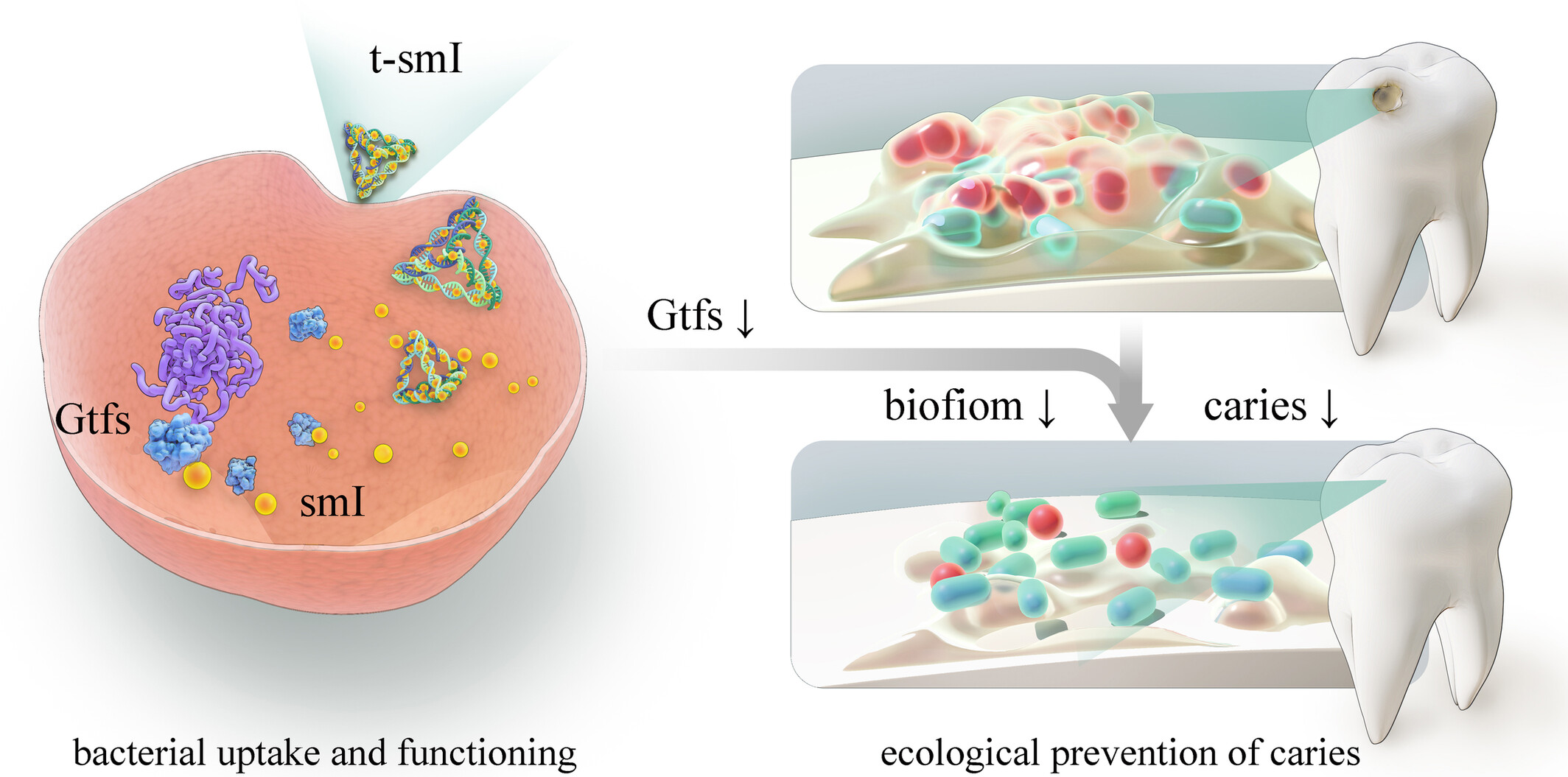
This study marks the first confirmation that tetrahedral framework nucleic acid efficiently loads the anti-biofilm small-molecule inhibitor, which inhibits biofilm formation in vitro and in vivo without bactericidal effects on pathogenic and symbiotic bacteria. The study introduces the innovative concept of ‘ecological prevention of biofilm’ for advancing the precise prevention of biofilm-related diseases.
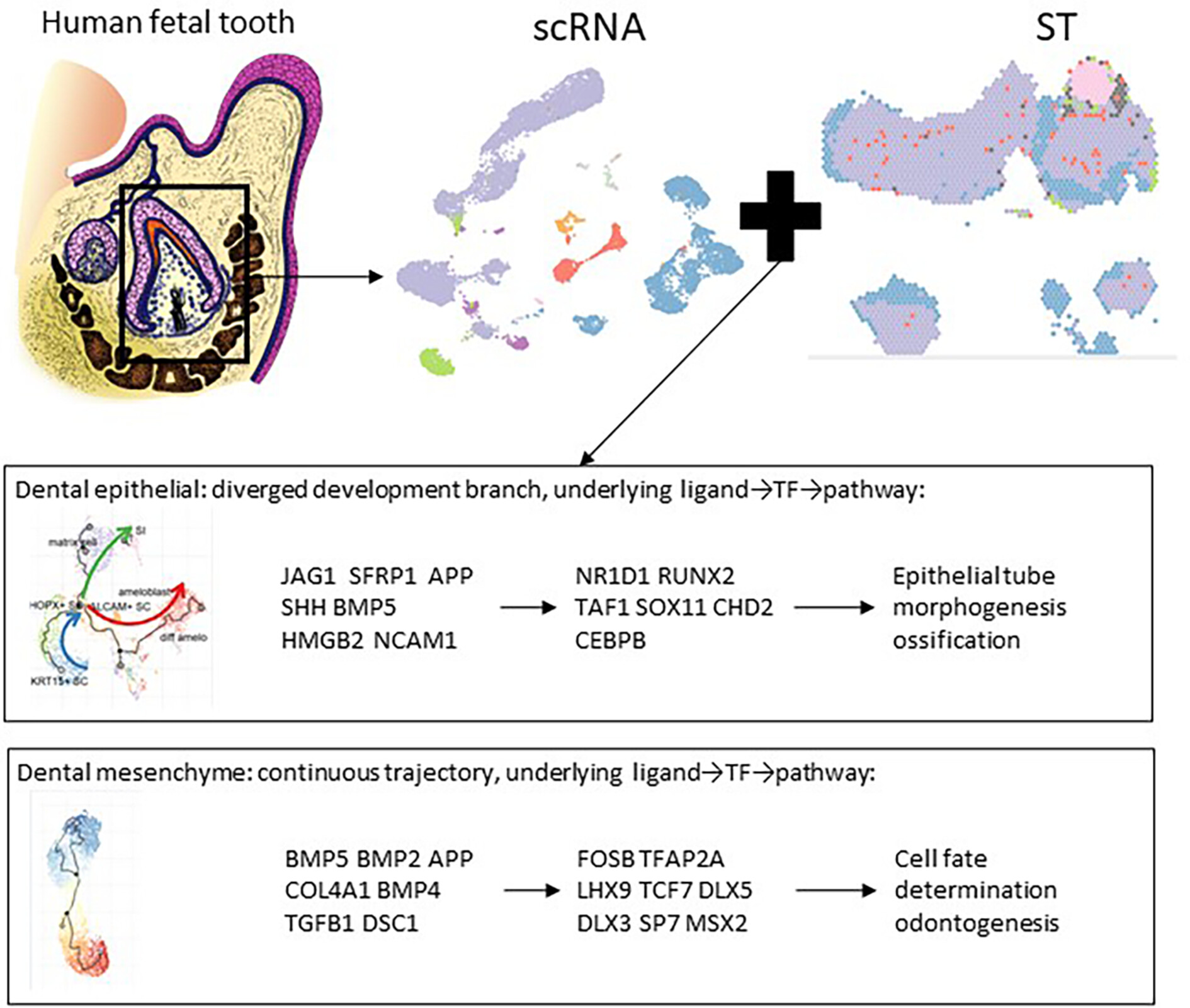
Spatiotemporal cell landscape of human embryonic tooth development
- First Published: 12 June 2024
Protein phosphatase SCP4 regulates cartilage development and endochondral osteogenesis via FoxO3a dephosphorylation
- First Published: 17 June 2024
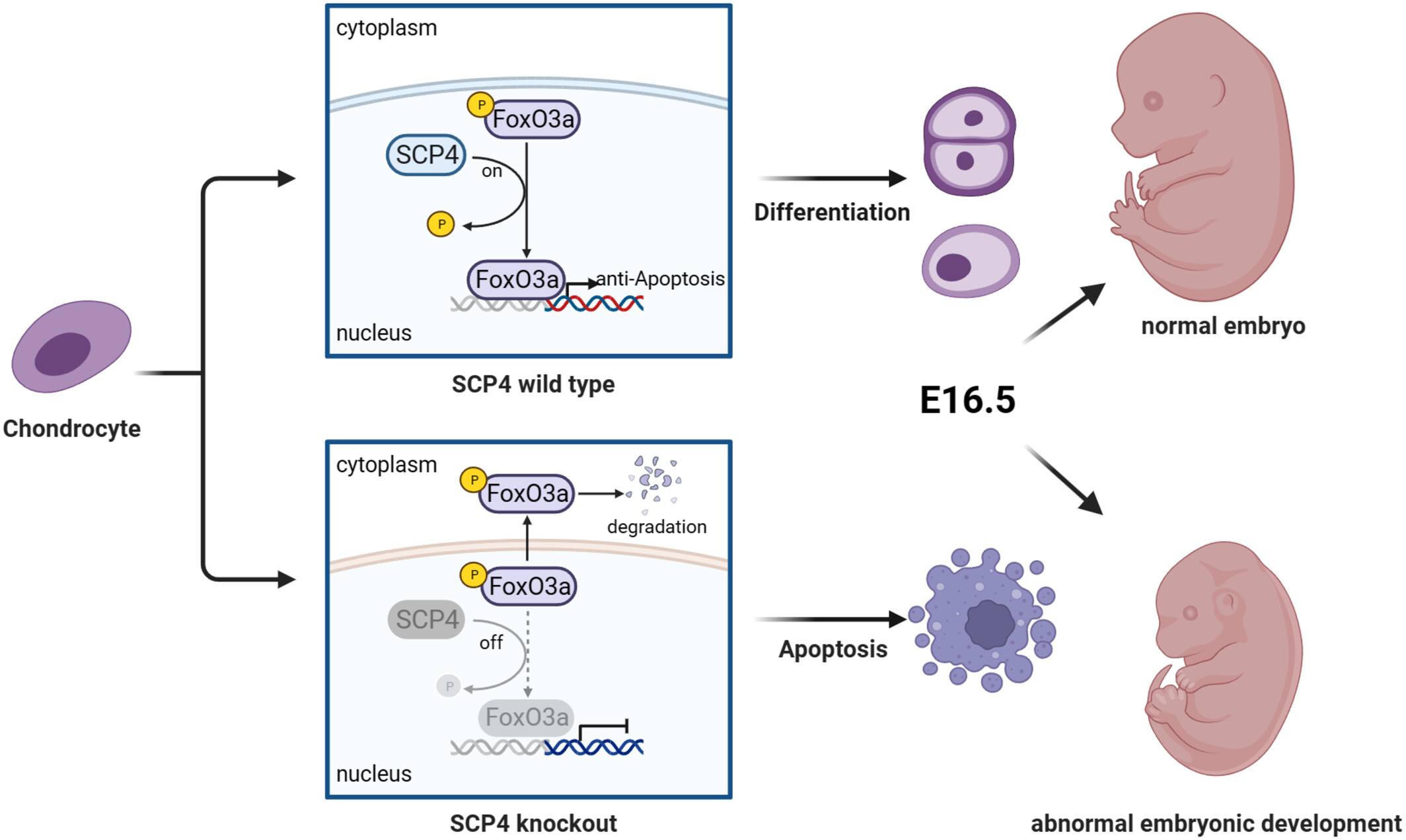
A noval protein phosphatase SCP4 regulates cartilage development and endochondral osteogenesis through the apoptotic pathway during embryonic development. SCP4 could direct interaction with pFoxO3a and dephosphorylated it. The deficiency of SCP4 resulted in the inactivation of FoxO3a, leading to growth plate chondrocytes apoptosis and abnormal embryonic development.
MRE11 is essential for the long-term viability of undifferentiated spermatogonia
- First Published: 18 June 2024
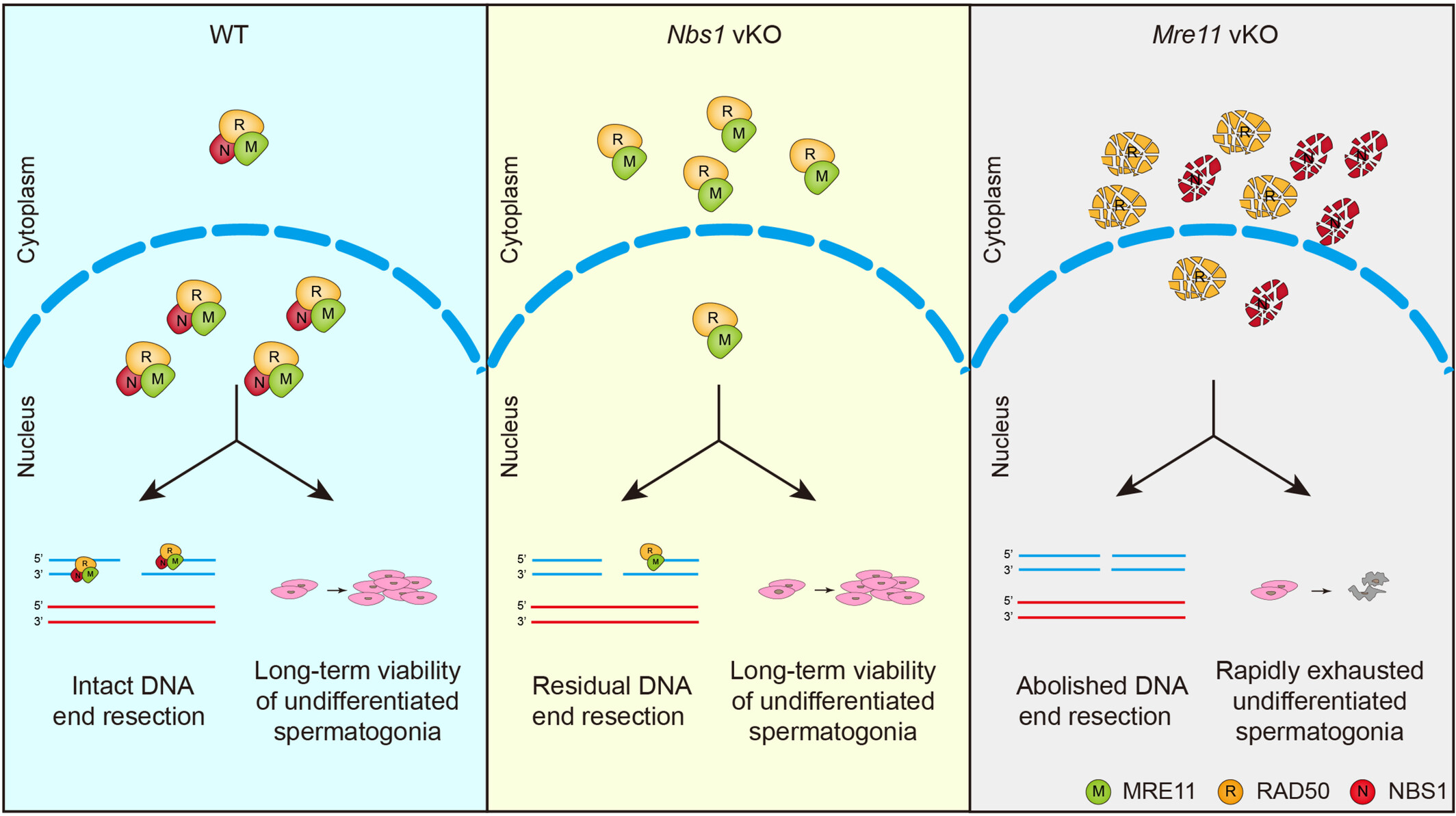
The MRE11-RAD50-NBS1 (MRN) complex in the nucleus initiates DNA end resection at double-strand break (DSB) sites and supports the long-term viability of undifferentiated spermatogonia in mice. In the absence of NBS1, a small amount of intact MRE11-RAD50 complex can still localise to the nucleus and can promote residual DNA end resection to keep the long-term viability of undifferentiated spermatogonia. However, in the absence of MRE11, DNA end resection is completely abolished and undifferentiated spermatogonia are rapid exhausted due to DSB accumulation and apoptosis.
Modelling bone metastasis in spheroids to study cancer progression and screen cisplatin efficacy
- First Published: 20 June 2024
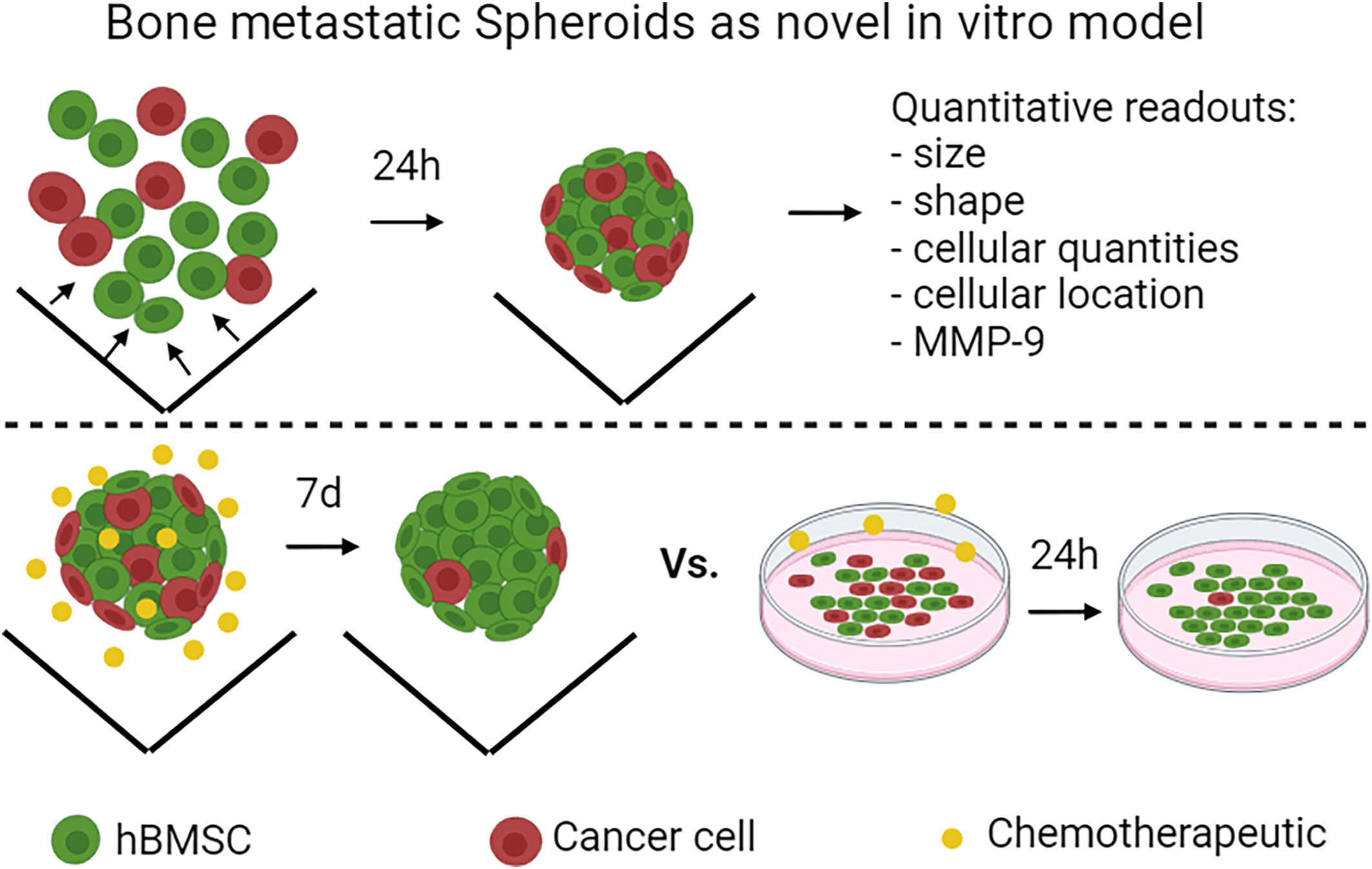
Bone metastatic spheroids were developed by co-culturing healthy and cancer cells directly in ultra-low attachment plates. Among other readouts, bone metastatic spheroids showed higher cancer cell proliferation and more relevant response to the chemotherapeutic cisplatin compared to 2D co-cultures with similar seeding ratios.
Impact of CD151 overexpression on prognosis and therapy in non-small cell lung cancer patients lacking EGFR mutations
- First Published: 09 July 2024
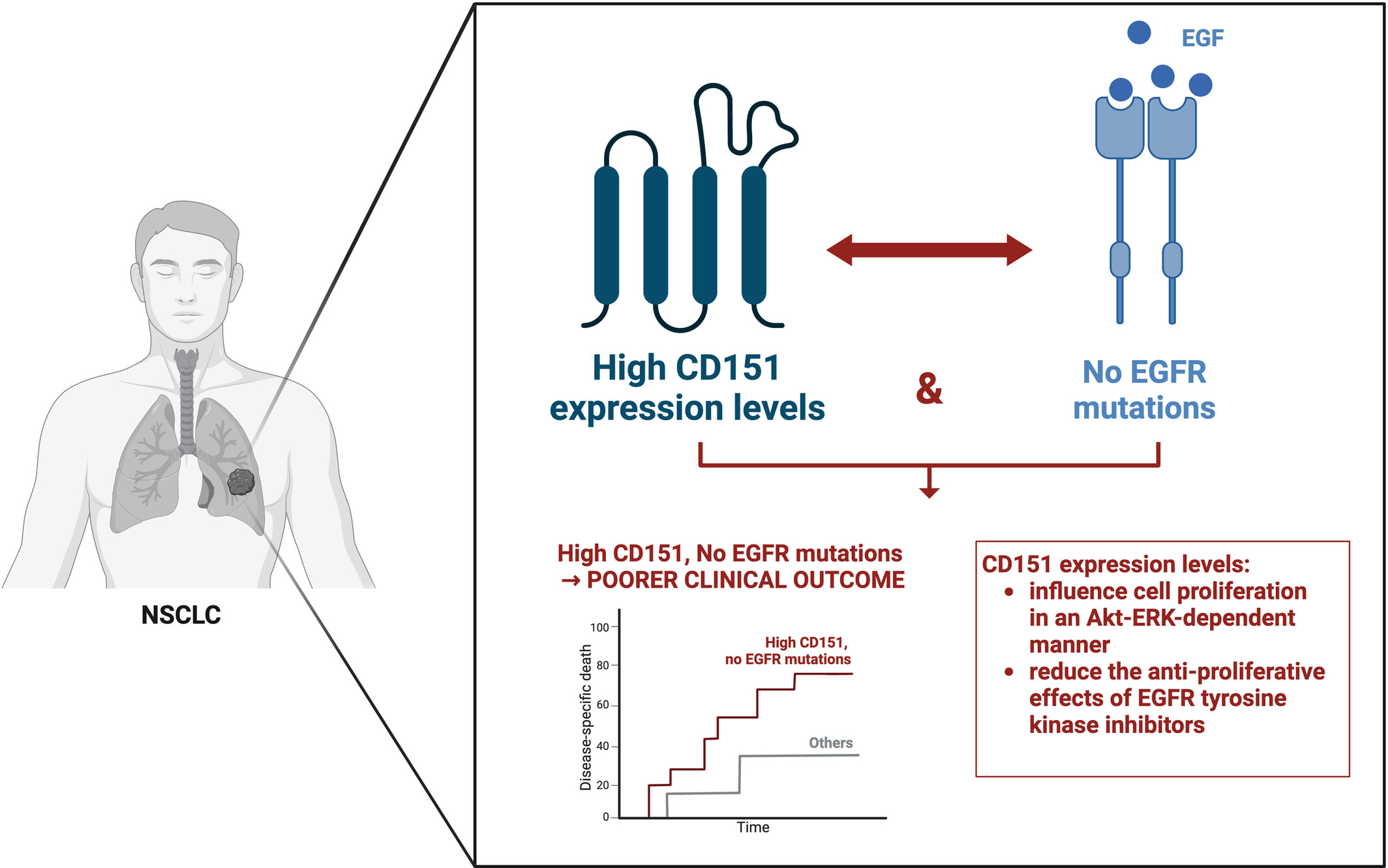
High CD151 expression levels in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients lacking epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are associated with poorer clinical outcomes. Mechanistically, CD151 influences Akt-ERK-dependent cell growth and the effectiveness of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Our study proposes CD151 as a potential therapeutic target in NSCLC patients without EGFR mutations whose treatment options are currently limited.
Single-cell sequencing reveals the transcriptional alternations of 17β-estradiol suppressing primordial follicle formation in neonatal mouse ovaries
- First Published: 10 July 2024
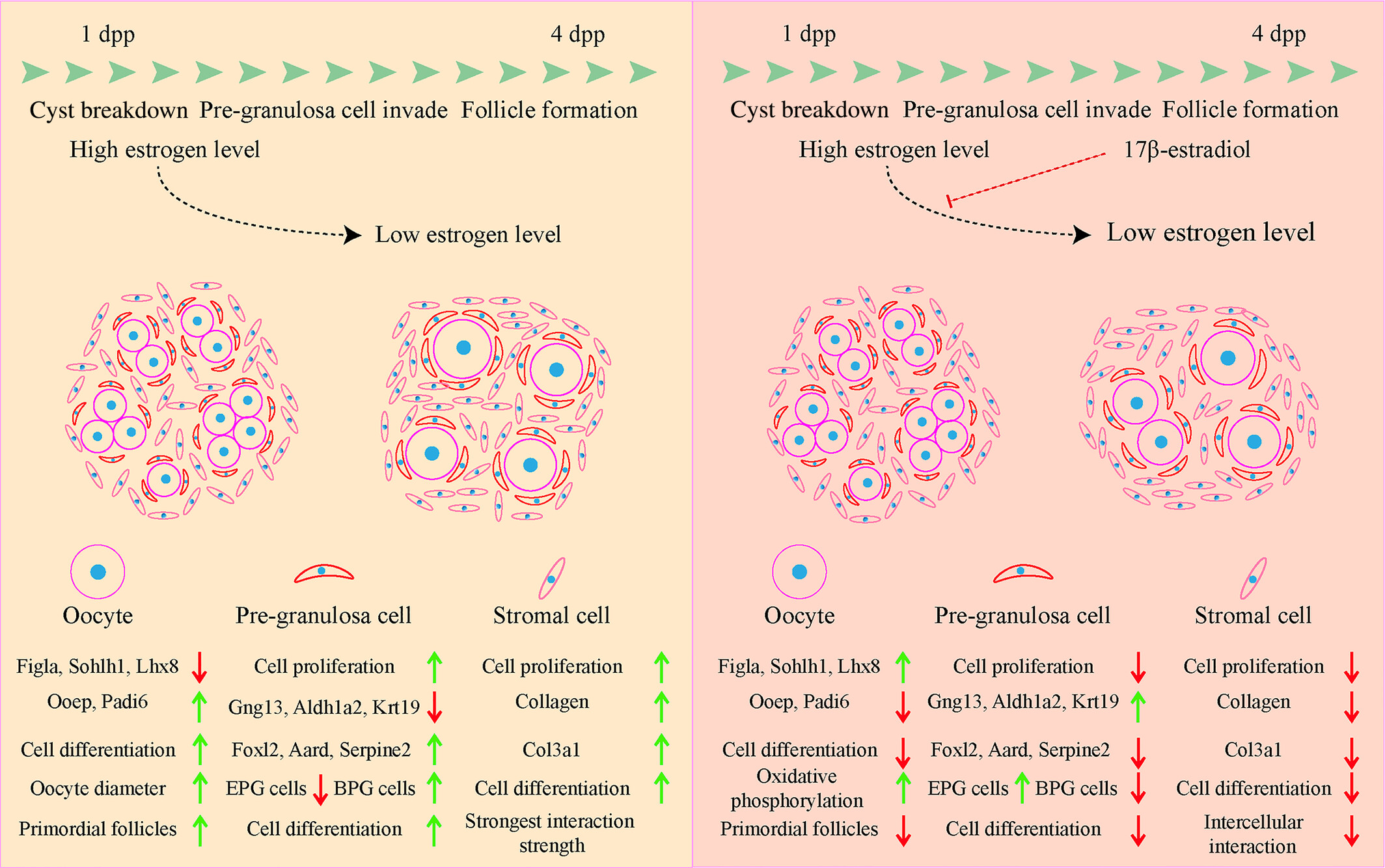
The work first presented the transcriptional programmes of primordial follicle (PF) formation regulated by 17β-estradiol in neonatal mouse ovaries, which not only revealed insights into the regulatory role of estrogen during PF formation, but also filled in knowledge of dramatic changes in perinatal hormones, which are critical for the physiological significance of understanding hormone changes and reproductive protection.