Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
FEATURED COVER
Featured Cover
- First Published: 03 July 2022

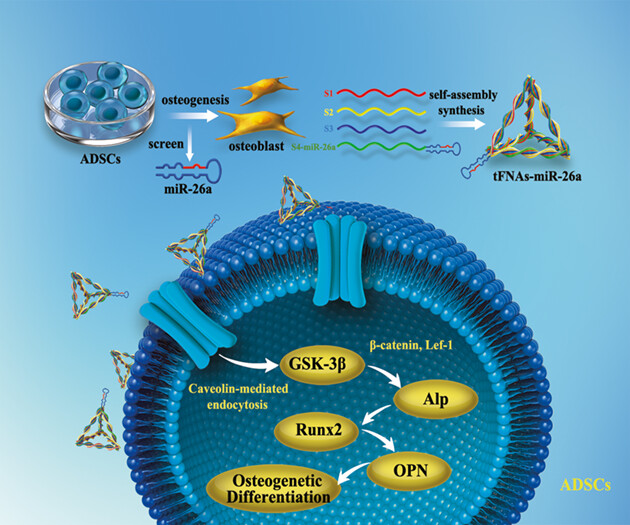
The cover image is based on the Original Article MiR-26a-tetrahedral framework nucleic acids mediated osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by Xiaoru Shao et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.13272.
ISSUE INFORMATION
BRIEF REPORT
Biobanking of human pluripotent stem cells in China
- First Published: 02 June 2022

The substantial number of pluripotent stem cell lines established in China now have the opportunity to be coordinatedin an initiative involving the Chinese Society for Stem Cell Research, that provides a central resource centre (NSCRC) to facilitate a range of clinical studies all formally recorded in international clinical trials registries.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Retinoic acid induced meiosis initiation in female germline stem cells by remodelling three-dimensional chromatin structure
- First Published: 28 May 2022
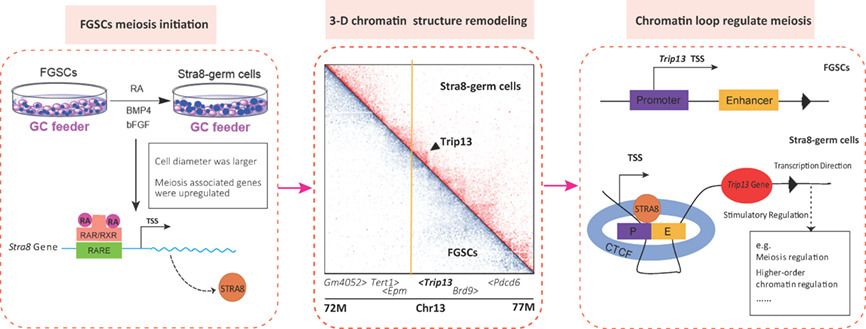
FGSCs were induced into meiosis initiation in differentiation medium (MEMα supplemented with FBS, BMP4, bFGF, RA). Meiosis-associated genes were upregulated in Stra8-germ cells. FGSCs underwent chromatin structure remodelling from undifferentiated stage to meiosis-initiation stage, which facilitated STRA8 binding to the promoter of Trip13 and promoting its expression.
Altered gut microbiota and metabolites profile are associated with reduced bone metabolism in ethanol-induced osteoporosis
- First Published: 10 June 2022
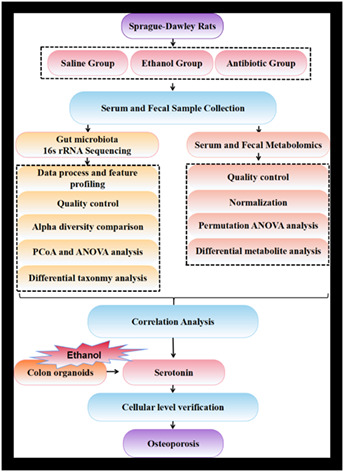
A rat ethanol-induced osteoporosis model was established by long-term ethanol intake. Taking the antibiotic application as the matched group of dysbacteriosis, an integrated 16S rRNA sequencing and liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry-based metabolomics in serum and faeces were applied to explore the association of differential metabolic phenotypes and screen out the candidate metabolites detrimental to ossification. The colon organoids were used to track the source of 5-HT and the effect of 5-HT on bone formation was examined in vitro.
Somatostatin signalling promotes the differentiation of rod photoreceptors in human pluripotent stem cell-derived retinal organoid
- First Published: 28 May 2022
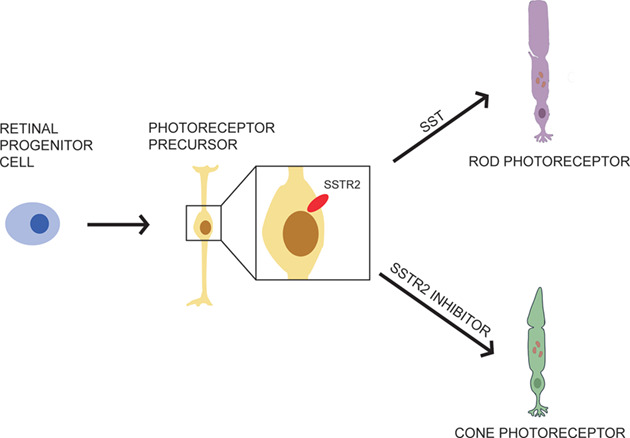
The somatostatin receptor 2 (SSTR2)-mediated signalling modulates the fate determination of photoreceptor precursors in hESC-derived retinal organoids. The activation of SSTR2 signalling is critical for rod photoreceptor differentiation. Specifically, somatostatin increases rod photoreceptor production, while SSTR2 antagonist promotes the fate bias of photoreceptor precursors towards the cone photoreceptors.
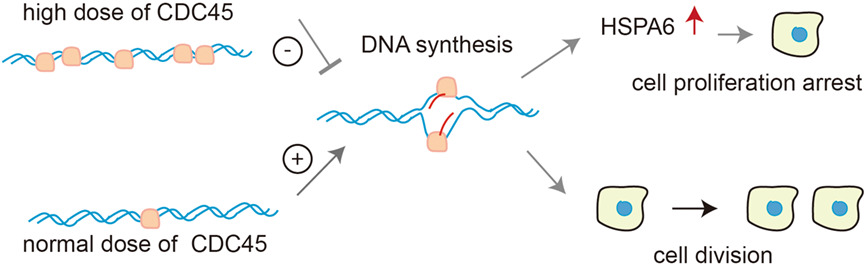
High abundance of CDC45 inhibits cell proliferation through elevation of HSPA6
- First Published: 01 June 2022
Downregulation of PLK4 expression induces apoptosis and G0/G1-phase cell cycle arrest in keloid fibroblasts
- First Published: 07 June 2022
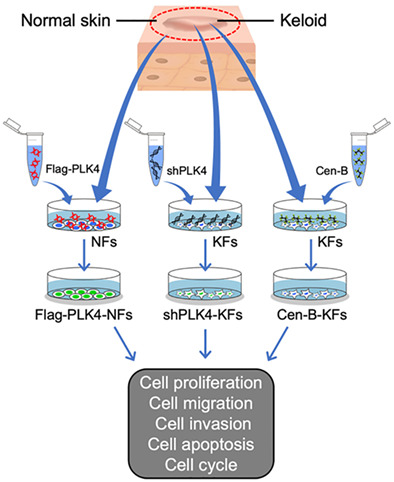
Keloids are benign fibroproliferative tumors that display many cancer-like characteristics, such as progressive uncontrolled growth, lack of spontaneous regression, and extremely high rates of recurrence. Polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) was recently identified as a master regulator of centriole replication, and its aberrant expression is closely associated with tumorigenesis. This study aimed to investigate the expression and biological role of PLK4 in the pathogenesis of keloids. Here, we discovered that PLK4 is a potential target for the treatment of keloids. PLK4 was overexpressed in keloid dermal samples and keloid fibroblasts (KFs) compared with adjacent normal skin samples and normal skin fibroblasts derived from the same patients. High PLK4 expression was positively associated with the proliferation, migration, and invasion of KFs. Furthermore, knockdown of PLK4 expression or inhibition of PLK4 activity by a highly selective inhibitor, centrinone B (Cen-B), suppressed KF growth, induced KF apoptosis via the caspase-9/3 pathway, and induced cell cycle arrest at the G0/G1 phase via the p53/p21/Cyclin D1 pathway in vitro. These findings demonstrate that PLK4 is a critical regulator of KF proliferation, migration, and invasion, and thus, Cen-B is a promising candidate drug for keloid treatment.
MiR-26a-tetrahedral framework nucleic acids mediated osteogenesis of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- First Published: 05 June 2022
Mitochondrial genome mutations and neuronal dysfunction of induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 13 June 2022
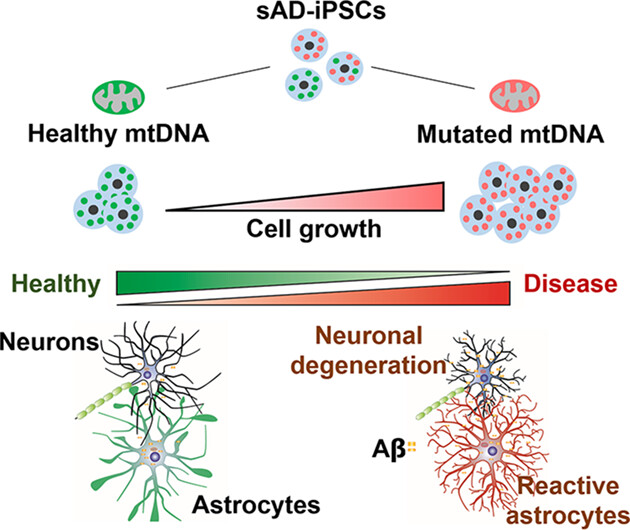
mtDNA mutations were found in induced pluripotent stem cells derived from patients with Alzheimer's disease. The mutations could induce growth advantage due to their high viability and proliferation. Differentiated neuronal cells with mtDNA mutations exhibited mitochondrial and neuronal dysfunction, as well as increased Aβ deposition.
BCL2-associated athanogene 6 exon24 contributes to testosterone synthesis and male fertility in mammals
- First Published: 10 June 2022
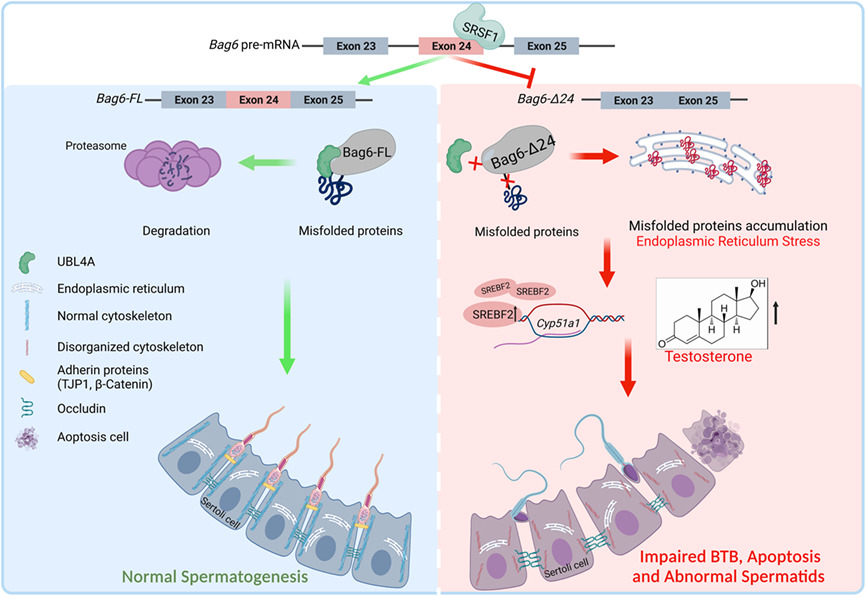
The schematic diagram displays the requirement for Bag6 exon24 in normal spermatogenesis. SRSF1 inhibits Bag6 exon24 exclusion. The full-length Bag6 transcript could encode the complete BAG domain, ensuring its ability to guide the degradation of the misfolded protein and maintain normal spermatogenesis. But the Bag6-Δ24 transcript encodes an incomplete BAG domain, therefore reducing the interaction with UBL4A protein, which leads to ER stress misfolded proteins accumulation in the ER and. ER stress induces testosterone production in Bag6exon24−/− mice, resulting in impaired BTB, cell apoptosis and abnormal spermatogenesis.